Navigating complex healthcare systems can often feel like an exercise in frustration, with bureaucratic hurdles obscuring the path to quality patient care.But imagine a world where accessing medical services is as simple as clicking a button, where personalized care plans are crafted solely with the patient in mind, and digital innovation is harnessed fully to streamline and optimize processes for your well-being.This transformation is underway, reshaping the traditional healthcare landscape into one that is interconnected, intuitive, and highly responsive to individual needs.What we’re looking at is a paradigm shift that extends beyond mere patient satisfaction, but a reimagining of how we approach and manage our health. Driven by technology, the future of healthcare promises inclusivity, efficiency, and personalized healthcare solutions.To dissect the true impact of digital innovation on healthcare, I had the pleasure of interviewing Aaron Cheng, VP of Digital Health at Shoppers Drug Mart, who is a seasoned executive celebrated for spearheading dynamic technical teams and fostering groundbreaking innovation in the digital landscape.Aaron’s expertise converges on consumer fintech, digital marketplaces, and enterprise digital solutions, and together we explored his profound insights on integrating digital health into traditional pharmacy models, the importance of a patient-focused ecosystem, and his vision for the AI-driven future of healthcare.The Digital Transformation of Pharmacy CareThe landscape of healthcare is undergoing a monumental shift, thanks to the advent of digital technology. Gone are the days when your only option was a visit to the doctor’s office for any minor ailment.Today, digital health tools are revolutionizing the way we access pharmacy care, making it more convenient, personalized, and efficient than ever before.Accessibility of Medical Services Digital platforms, like health apps, enable you to consult with healthcare professionals without leaving your home. This not only saves time but also makes healthcare accessible to those in remote or underserved locations.Personalized Care Plans Imagine having a healthcare plan tailored just for you, considering your medical history, lifestyle, and health goals. Digital health tools analyze your data to provide personalized advice and recommendations, enhancing the quality of care you receive.Efficiency and Time-Saving The integration of AI and machine learning in pharmacy care automates routine tasks such as prescription refills and appointment scheduling. This not only reduces wait times but also allows pharmacists to focus more on patient care.Expanded Scope of Services Pharmacies are no longer just places to pick up medication; they’re becoming wellness hubs. With the help of digital tools, pharmacists can now offer services like minor ailment treatment, wellness consultations, and chronic disease management.This digital transformation is not just changing the operational aspects of pharmacies but also redefining the role they play in the healthcare system.By leveraging technology, pharmacies are expanding their scope and capacity to offer more comprehensive care, directly impacting patient outcomes in a positive way.The Role of AI in Streamlining Healthcare Delivery Artificial intelligence is no longer just a buzzword in tech circles; it’s a game-changer in the healthcare industry, poised to revolutionize how we receive and manage our healthcare. Here’s how AI is making strides in streamlining healthcare delivery, ensuring that you get the care you need with efficiency and precision that was previously unimaginable.Automating Administrative Tasks One of AI’s most significant impacts is its ability to automate the countless administrative tasks that bog down healthcare professionals. From scheduling appointments to managing patient records, AI can handle these processes quickly and accurately, freeing up healthcare providers to spend more time where it matters most—with their patients.Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy AI algorithms are incredibly adept at analyzing vast amounts of data, including medical images. These algorithms can detect anomalies that the human eye might overlook, leading to earlier and more accurate diagnoses. Early detection is often key to effective treatment, making this application of AI incredibly valuable.Personalized Treatment Plans By analyzing data from a variety of sources, including electronic health records and genetic information, AI can help healthcare providers develop more personalized treatment plans. This bespoke approach ensures that treatments are tailored to your unique health profile, potentially increasing their effectiveness.Predictive Analytics AI’s ability to predict potential health issues before they become serious problems is perhaps one of its most exciting applications. By analyzing trends in your health data, AI can alert you and your healthcare provider to risks so you can take proactive steps to avoid them.In essence, AI is transforming healthcare delivery from a one-size-fits-all model to a more personalized, efficient, and predictive approach. This shift not only promises better health outcomes but also a more satisfying healthcare experience for you.The Challenges of Digital Health Adoption The road to integrating digital health solutions into our healthcare system is paved with potential but also marked by challenges. Recognizing and overcoming these hurdles is essential to fully realize the benefits of digital health for everyone involved. Here are some key challenges and strategies to address them:Resistance to Change One of the most significant barriers is the natural human resistance to change. Both patients and healthcare providers can be wary of new technologies, especially when it involves sensitive health information. Educational campaigns and demonstrations of tangible benefits can help overcome skepticism, showcasing how digital health tools enhance, rather than complicate, the healthcare experience.Privacy and Security Concerns With digital health solutions, concerns about data privacy and security are paramount. Patients need assurance that their health information is protected. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures and transparent privacy policies is crucial. Educating users on how their data is used and safeguarded can also build trust.Interoperability For digital health to be truly effective, different systems and tools need to be able to communicate with each other seamlessly. This interoperability is often hindered by the diverse range of software platforms in use. Developing and adopting universal standards and protocols can help ensure that digital health tools work together smoothly, providing a cohesive user experience.Accessibility Digital health must be accessible to everyone, regardless of age, income, or tech-savviness. Addressing this involves creating user-friendly interfaces that are intuitive for all users, including those who are not digitally literate. Additionally, ensuring affordable access to the necessary technology, such as smartphones or internet service, is crucial for widespread digital health adoption.Regulatory Hurdles Navigating the complex regulatory landscape can be a significant challenge for digital health innovators. Regulations are necessary to ensure patient safety and data protection, but they can also slow down the development and adoption of new technologies. A collaborative approach between innovators and regulators can help find a balance, fostering innovation while maintaining high standards of safety and privacy.By addressing these challenges head-on with strategic solutions and stakeholder collaboration, the path to digital health adoption can be smoothed, paving the way for a healthcare system that is more responsive, efficient, and personalized.Future Prospects: Integrating Digital Solutions for Enhanced Patient Care The integration of digital solutions into healthcare is not just an ongoing trend; it’s the future of patient care. As we look ahead, several exciting prospects stand to further enhance the quality, accessibility, and personalization of healthcare services. Here’s a glimpse into what the future might hold:Seamless Integration Between Digital and Traditional Care In the near future, we can expect a healthcare ecosystem where digital and traditional care methods are seamlessly integrated. This will allow for a more cohesive healthcare journey, where patients can move effortlessly between online consultations, in-person visits, and digital monitoring, all within a unified framework.Expansion of Remote Monitoring and Telehealth The use of wearable devices and home monitoring equipment is set to expand, enabling continuous care and health management from the comfort of one’s home. This not only increases convenience for patients but also allows for real-time data collection that can enhance preventive care and early intervention.AI-Powered Personal Health Assistants Imagine having a personal health assistant powered by AI, always on hand to provide health advice, remind you of medication schedules, and even alert you to potential health issues before they become serious. These assistants could become a central part of everyone’s health management, offering tailored advice based on your health data.Digital Platforms for Holistic Health Management Future digital health platforms will likely offer holistic health management tools, integrating physical, mental, and emotional health tracking and support. These platforms will provide personalized recommendations for diet, exercise, stress management, and more, all based on your health data and personal preferences.Enhanced Patient Empowerment and Education With the advancement of digital health solutions, patients will have greater access to their own health information and a better understanding of their health conditions. This empowerment will enable more informed decision-making and foster a more collaborative patient-provider relationship.As digital solutions evolve and mature, their potential to transform the healthcare landscape is limitless. Embracing these changes will not only improve outcomes for patients but also enhance the overall healthcare experience for providers and patients alike.Takeaway The promise of digital health is not in the technology itself, but in its capacity to empower patients and healthcare providers alike. While the journey toward integrating digital solutions into healthcare is an ongoing process, it is filled with both challenges and opportunities.By harnessing digital tools and embracing innovation, we can create a healthcare system that fosters wellness, prevention, holistic care, and is truly responsive to the needs of every individual, ensuring better health outcomes for all.If you found this article helpful and want to gain more insights into the future of healthcare, be sure to tune into the full episode of Behind the Growth for a conversation you do not want to miss!Find it here:Bridging Digital Innovation and Pharmacy Care
Embracing Digital Health: The Impact of Technology on Pharmacy Care

One of the most persistent challenges in software development is the lack of comprehensive and up-to-date code documentation.Whether it’s business-level or technical documentation, keeping it aligned with the evolving codebase is often neglected. This leads to major issues down the road—understanding code logic becomes harder, updates go undocumented, and large codebases become increasingly complex.Additionally, modern code often comes without adequate explanations, making it difficult to understand the business context behind it. This is further compounded when tools meant for documentation lack integration with existing development workflows.Moreover, as codebases grow larger, generating documentation manually becomes resource-intensive and error-prone, putting further strain on already overburdened development teams.The Role of AI in Code Documentation AI has a transformative role in automating the documentation process for codebases, making it both scalable and efficient. It not only reduces the human effort required but also ensures that the documentation is accurate, up-to-date, and aligned with the actual code. Here’s how AI steps in to solve these challenges:Generate Technical and Business Documentation AI-powered tools can automatically generate detailed technical documentation, including class diagrams, sequence diagrams, and flowcharts, while also providing business-level insights into what the code accomplishes.Provide Context and Understanding By leveraging natural language processing, AI tools interpret and explain intricate code logic, even for large and complex systems, ensuring that stakeholders have a clear understanding of the codebase.Integrate Seamlessly with Tools AI-driven documentation systems can integrate smoothly with popular development platforms like GitHub, allowing them to automatically pull code changes and keep documentation updated without manual intervention.Improve Scalability AI excels in analyzing vast codebases without being constrained by human capacity, making it ideal for large-scale documentation tasks that would otherwise be too labor-intensive.Solving the Code Documentation Challenge Our solution to the code documentation problem incorporates AI to automate and enhance the process of generating high-quality documentation. Here’s how it works:1. Automated Documentation Creation Our AI-powered system can generate comprehensive documentation for codebases, from technical details to business logic. It provides flow diagrams, sequence diagrams, and class diagrams to give a visual representation of the code’s structure and functionality.2. Multi-Language Support The solution supports multiple programming languages and frameworks, allowing it to generate documentation for diverse codebases, whether it’s a Java Spring Boot application or something else entirely. The AI interprets the code and provides clear, plain-language explanations of its components.3. Multiple Interaction Points The system engages in multiple interactions with large language models (LLMs) through various threads. This fine-tuning ensures that the generated documentation is highly accurate and tailored to the specific needs of the project.4. External Tool Integration Our AI tool integrates with external systems to automatically create architectural diagrams and documentation without manual input. It not only pulls data from your codebase but also keeps everything updated as the code evolves.5. Local Deployment for Security For clients with high confidentiality requirements, our solution allows for local deployment, ensuring that all data remains within your enterprise environment. This option is crucial for companies handling sensitive or proprietary code.Benefits of Our AI Solution Up-to-Date Documentation with Minimal Effort One of the biggest perks of using AI is how much time it saves. Automating the documentation process can cut down 60-80% of the time developers would normally spend updating docs manually. That’s a huge win for teams who’d rather focus on writing great code than worrying about keeping documentation up to date.Improved Code Understanding Let’s face it—understanding complex code can feel like untangling a giant knot. AI makes it easier by breaking things down into clear explanations and diagrams. According to a Forrester study, teams that used AI for code analysis saw a 30% boost in development speed, because everyone had a better grasp of the code. No more guessing games!Efficient API Documentation API documentation can be a real time sink. But with AI, you can cut the time spent on it by 50%. Tools like this handle heavy lifting, automatically generating everything from endpoint details to request parameters. This means faster development cycles and less manual work for your team.Automated Diagrams and Visualizations Ever spent hours making flowcharts or class diagrams? AI can handle that for you. Automated tools that generate these visuals can save teams 20-40% of the time normally spent on designing and reviewing architecture. Plus, they make it easy for everyone to stay on the same page with clear visual representations of the code.Final Takeaway: The Impact of Automating Code Documentation with AI The impact of automating code documentation with AI is transformative for businesses.By reducing the human effort required for generating and maintaining documentation, companies can achieve 60-80% efficiency gains. This not only frees developers to focus on innovation but also ensures that documentation stays accurate, up-to-date, and aligned with the evolving codebase.Automated tools generate real-time technical documentation, API specs, and architectural diagrams, making it easier for teams to collaborate, onboard new developers, and avoid costly misunderstandings. The ability to produce detailed, clear documentation without the usual manual burden enhances communication across teams and improves project outcomes.In short, AI-powered documentation allows businesses to overcome one of the most persistent challenges in software development: maintaining quality documentation.By automating this process, teams can move faster, work more efficiently, and focus on building great software rather than getting bogged down by tedious, error-prone tasks. With AI, businesses can confidently tackle even the largest, most complex codebases, ensuring clarity and continuity in their projects.
AI Accelerator Series: Automating Code Documentation

As businesses evolve, embracing generative AI (GenAI) no longer remains a luxury, but a necessity, making it crucial for companies to identify, envision, and embrace the value of GenAI across the organization.But the challenge arises when it comes to balancing ethical considerations with the development and implementation of AI technologies.In a recent episode of Behind the Growth, I had the opportunity to engage with Andrea De Mauro, a renowned Data & Analytics Leader, Author, and Executive Advisor.Celebrating his vast career and a rich background in Data Analytics – that spans over 18 years and includes building data science and analytics organizations at Vodafone and Procter & Gamble – together we explored the intricacies of GenAI and its human-centric challenges.Andrea lets us in on his extensive experience of championing ethical data use and innovation while prioritizing the human element, and in this article, I share these invaluable insights that will help you successfully navigate the intersection of technology, business, and ethics.The Human-centric Challenges of GenAI With the rapid advancement of Gen AI, there’s a lot of focus on the technical side of things. But the emphasis on technological advancements often overshadows critical human challenges.While it may seem counterintuitive, the process of data transformation is primarily a human challenge related to organization and culture more than technology and data.AI may help maximize business outcomes, but organizational support is needed to successfully navigate the transition.Recognizing this, organizations must address three key human-centric issues beyond the technical realm.1. Managing Talent One pivotal aspect is the strategic management of talent, involving clear role definitions, responsibilities, career paths, and skill development for data professionals. Organizations often grapple with retention and recruitment issues when they lack well-defined career progression paths.2. Organization The second crucial element involves organizational dynamics, requiring a careful placement of data analytics talents either within centralized units or integrated with business teams. Striking the right balance ensures a conducive environment for continuous dialogue and collaborative value creation between data professionals and business units.3. Culture A third and integral aspect is cultivating a data-friendly culture. This involves fostering openness within the organization, where data professionals, including analysts, actively contribute to decision-making processes. Achieving this cultural shift is essential for leveraging data effectively.The Ethical Use of AI In addition to human challenges, we must also recognize the need for ethical use of AI. Ethical use of AI demands a clear understanding and codification of its capabilities.The first step involves meticulously codifying AI functions, allowing organizations to assess their impact on various stakeholders, customers, and employees. This process, although time-consuming, provides a crucial foundation for evaluating the ethical implications of AI applications.By developing explicit codes of ethics for AI, coupled with comprehensive training, we can ensure a shared understanding across the organization. This approach, exemplified in managing AI-driven tools like chatbots, equips employees to not only use the technology effectively but also be aware of potential risks.Building fluency in AI, involving a common language and understanding of key concepts, is pivotal for ethical considerations, particularly in recognizing and managing biases that machines can have when making decisions and inferring. Investing in ethical AI capabilities and promoting fluency ensures responsible and informed usage of AI technologies in organizations.The Crucial Role of People ManagersAs AI is evolving, so is the definition of being a manager. The role of people managers becomes pivotal — particularly in navigating concerns about job displacement.One major shift is evident in decision-making processes, where managers increasingly rely on algorithmic recommendations rather than their instincts. This skill needs to be learned, and it’s up to managers to encourage their teams to be mindful of AI’s limitations.Amidst these changes, managers of data professionals should understand that data professionals often feel undervalued and burdened by routine tasks, despite aspiring to leverage their skills as transformative agents.So, managers should alleviate their frustrations by involving data professionals in meaningful conversations, clarifying roles, and emphasizing their role in the ongoing cultural transformation toward data-centric approaches.By nurturing a sense of inclusion and actively involving data professionals in business discussions, managers can harness their potential as transformation agents in the company’s data culture.Key to Success: Making the Collaboration Between Humans and AI WorkTo successfully integrate AI in their processes, companies need to foster organizational fluency in AI technologies, making sure that everyone — no matter their job — know what AI and Gen AI are about.A shared understanding of AI helps ease worries and sets the stage for humans and machines working together. When mundane tasks are automated, individuals can channel their efforts into more meaningful and creative endeavours. This collaboration between humans and AI is all about leveraging each other’s strengths for enhanced efficiency and effectiveness.Success in this collaborative future hinges on establishing a culture of collaboration within organizations. This involves not only understanding AI’s capabilities and ethical considerations but also actively fostering a mindset that encourages experimentation and collaboration between humans and machines.By cultivating such a culture, we can navigate the evolving AI landscape, where humans and machines coexist, amplify each other’s capabilities, and drive innovation forward.As this collaboration becomes more established, it offers a positive outlook for the future. However, we need to approach this change carefully, making sure it is inclusive. This is why the fluency program is so crucial — it reaches everyone in the company and fosters understanding and involvement across the board.Practical Tips for Leaders and Organizations If you are venturing into the complexities of Gen AI while prioritizing the human element, having a strategy in place can pave the way for a smoother journey. Here are a few tips to seamlessly integrate Gen AI, focusing on inclusivity, skill development, and strategic vision for the entire workforce:Selecting Impactful Use Cases First and foremost, envisioning the role of Gen AI within the organization is crucial. This involves selecting impactful use cases that not only demonstrate value to leaders but also to the entire workforce. Gen AI should be perceived as a transformative force for everyone in the organization, debunking the notion that it’s solely for technical experts.Upskilling Technical Professionals To facilitate the integration of Gen AI, upskilling technical professionals is imperative. Fluency programs should be implemented, focusing on developing the skills required for working with generative AI. This not only prepares technical professionals but also ensures that the entire workforce is equipped for the integration of new skills and tools.Inclusive Development Path Creating an inclusive development path is another vital step. This involves offering education on the basics of AI and Gen AI to all employees. With tools like Microsoft’s Copilot becoming increasingly prevalent, an inclusive approach ensures that the workforce is ready to engage with these tools consciously — with awareness and ethical considerations.Managerial Involvement Lastly, leaders are encouraged to stay personally involved from day one instead of delegating the responsibility of Gen AI to technical experts. Seeing their leaders embrace Gen AI will enthuse employees to learn more about it and foster a culture of curiosity and continuous learning.Takeaway To enhance collaboration between AI and humans, it’s clear that organizations need to put their efforts towards building AI fluency that ensures responsible usage and recognition of biases in decision-making.Overcoming human-centric challenges in talent management, organizational dynamics, and fostering a data-friendly culture requires strategic talent management with clear role definitions and skill development. Moreover, people managers will play a pivotal role in navigating and encouraging algorithmic decision-making, and involving data professionals in meaningful conversations.The collaboration between humans and AI is crucial and not just a matter of the future: it is a current need that enables businesses to achieve more creativity and efficiency, and it is up to organizations to foster a culture of experimentation and collaboration to make GenAI work for everyone.If you found this conversation insightful and want to learn more, be sure to tune into the full episode of Behind the Growth!Find it here:The Human Element in the Age of GenAI
AI Ethics and Challenges: Embracing Humanity in the GenAI Era
In an era where customer experience is top priority, it is critical for us to understand the digital evolution reshaping travel experiences. Several key trends are redefining this landscape, including the rise of online travel agencies (OTAs), a growing focus on mobile usage, and the need for businesses to establish a solid online presence.I had the privilege of interviewing a leader at the intersection of technology and travel, VP of Product & Customer Platforms at FlightHub, Ramzi Rahbani, to discuss digital transformation within the travel industry.With a diverse background spanning banking to retail, Ramzi brings over 13 years of leadership experience in driving digital innovation. His dedication to a product-first approach and expertise in fostering high-performance teams underscore his commitment to enhancing travel experiences and creating a more connected world.During our conversation on the Behind the Growth podcast, Ramzi shared insights into the dynamic nature of the travel industry, future trends, and the pivotal role of data and customer feedback in shaping services to meet the evolving needs of travellers – and I’m happy to share his celebrated and eye-opening perspective in this article.Four Trends in the Post-COVID Era of TravelThe aftermath of COVID-19 has left an indelible mark on the travel sector, redefining its landscape and charting new trajectories. But the travel industry is now navigating a path of recovery and adaptation, and examining the post-pandemic landscape reveals four prominent trends that are reshaping the travel sector.1. Strong Resurgence in Travel Firstly, there is a strong resurgence in travel, marked by a forecasted 6 percent growth in 2024 compared to the pre-pandemic peak of 2019. This indicates a remarkable recovery and hints at a robust future for the industry.2. Changing Consuming Behaviours Secondly, changing consumer behaviours post-pandemic are influencing the way people engage with travel. The shift towards online bookings has become pronounced, with major players aiming for 100 percent online transactions. American Airlines, for example, is currently at an impressive 80 percent online booking rate, underscoring the importance of digital channels.3. Growth of Online Travel Agencies Thirdly, the growth of Online Travel Agencies (OTAs) has become a significant trend. With a projected Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 6 percent leading up to 2028, OTAs are establishing themselves as key players in the industry. This trend is reflected in the success and growth of platforms like FlightHub, highlighting the evolving dynamics of travel bookings.4. Shift Towards Mobile-First Approach Lastly, the travel sector is experiencing a shift towards a mobile-first approach. Mobile bookings now comprise a substantial portion of the total volume, reaching around 50 percent. This shift emphasizes the necessity for travel platforms to prioritize mobile accessibility and engagement, recognizing it as a fundamental channel rather than a mere luxury.Building a Robust Online Presence in the Travel Sector Establishing a robust online presence has become imperative for gaining a competitive advantage. This entails catering to diverse customer preferences across various channels — mobile, web, and walk-in.Understanding the nuances of each channel is crucial. For example, mobile app users tend to be four to five years younger on average than website users. And while walk-in or call-in options persist, acknowledging a diverse age range in the customer base — and each demographic’s needs — is vital for sustained success in the travel industry.The prevalence of an omni-channel approach becomes evident in travel planning habits, with 94 percent of leisure travellers seamlessly switching between devices during the trip planning process — starting on mobile for searches and possibly shifting to a website for the actual booking.Acknowledging this behaviour, we need to seamlessly integrate their services across platforms, ensuring a cohesive and uninterrupted customer experience.Key Considerations for Crafting a Digital Strategy The digital channels you choose must align with a comprehensive business strategy.There are a couple of important elements that need to be integrated so businesses can effectively leverage digital channels to drive customer engagement and achieve sustainable growth in the digital era:Defining the Strategic Role of Mobile Apps Fundamentally understanding the role of mobile apps in the overall business strategy is crucial as this is what sets the foundation for subsequent strategic decisions. This begins by asking a critical question: What purpose does the mobile app serve? This will help us understand whether these channels serve as central drivers, enablers, or peripheral avenues.Aligning Digital Channels with Business Objectives The app becomes a channel for enhancing customer experience by leveraging the native capabilities of the device. The goal is not merely app development but a conscious effort to align the digital channels with broader business objectives.Setting Short-Term KPIs Businesses should set short-term key performance indicators aligned with broader business goals. This involves a meticulous examination of the business strategy, identifying the intended outcomes, and establishing targets. KPIs will serve as benchmarks for measuring the effectiveness of digital channels.Building a Customer-centric App While the app needs to be tailored to meet specific business needs, more importantly, it has to be customer-centric. This involves translating strategic decisions into practical steps, ensuring that the app is not just a standalone feature but an integral part of the customer engagement strategy.The Impact of Digital Evolution on Travel vs. Banking Apps Digitalization is taking over our lives, and every industry is feeling the pressure to provide customers with fast and easy digital access. For example, banking apps are central for financial transactions, making their perceived utility quite high to users, who tend to stick around due to their essential nature. Even if they are flawed, they’re necessary for day-to-day payments, which makes the cost of switching quite high for the customer.Travel apps, on the other hand, are used less frequently and have an extremely low cost of switching, so they need to make the most of moments when users find them useful during travel transactions.This means that travel apps face a unique challenge because of the sporadic nature of travel. They need to stay relevant, provide value, and meet the varying needs of users in the digital era.To tackle this, travel apps can go beyond just selling tickets. By being part of the entire travel journey — from planning to arrival and beyond — we can keep users engaged and build lasting connections.Owning the Complete Customer Journey Strategies to dominate the entire customer journey involve a comprehensive understanding of customer needs and transitioning from being a mere flight partner to a comprehensive travel partner.This evolution involves observing and addressing customers’ unmet needs throughout their journey, ultimately providing value beyond the basic flight booking. Expanding service offerings becomes key in this approach. Statistics show the rise in last-minute bookings, indicating a shift in consumer behaviour.By catering to these evolving needs, we can become indispensable travel companions, offering services like hotel bookings, Wi-Fi access, activities, and car rentals seamlessly.Effective Customer Engagement Strategies Tailoring engagement strategies based on the average lead time from booking to departure and return is essential. For shorter lead times, a focused approach on immediate post-booking engagement is crucial, while longer lead times allow for a more gradual and tailored engagement process.This is what brings customers back to the app. To maintain customer interaction between transactions, we must leverage various channels effectively. Utilizing push notifications, gamification, nudges, app messaging, and emails strategically helps in building awareness, enticing customers to explore offers, and bringing them back for continuous learning and engagement.Takeaway The travel sector’s digital transformation in the aftermath of the pandemic has shown resilience and adaptability.However, to continue thriving, we have to develop strategies to connect with customers and provide great experiences. Success today boils down to having a strong online presence, grasping how consumers behave, and adopting a holistic approach to engaging customers.Looking ahead, the industry’s future in the digital era hinges on how well we manage these trends.If you want to learn more about these trends and gain deeper insights into the transformations happening within the travel industry, be sure to tune into the full episode of Behind the Growth!Find it here:Transforming the Travel Experience
How Digital Innovation is Transforming the Travel Experience

Good Design = Good Business. (Thomas Watson Jr., Former IBM CEO)Design is not just about look and feel. It’s about how — and how well — it works. It’s about creating a competitive advantage for your brand.For the first time, we brought together a panel of design experts for a live session to answer all your questions about UX Research, Self-Serve Journeys, UI/UX, Prototyping, Design Systems, and more. Tune in to this insightful open conversation and learn from what our panel shared.
Ask A Designer: Live AMA Session with a Panel of Design Experts

Following our exploration of the Developer Scoring Mechanism in the previous blog, we now turn our attention to the final piece of the puzzle: forming the optimal team to execute the project. Traditional team formation processes are often ad-hoc and influenced by personal biases, leading to suboptimal outcomes. This blog explores the third AI accelerator: Team Formations, which aims to bring precision and efficiency to team composition.The Challenge for AI Team formation is a critical aspect of project planning. It involves selecting the right mix of skills, balancing resource availability, and ensuring cost-effectiveness. However, this process is often fraught with challenges. Traditional methods rely on personal judgment and experience, which can lead to biases and inefficiencies. Moreover, the dynamic nature of project requirements and resource availability adds further complexity.AI-driven Team Formations address these challenges by leveraging data from previous accelerators, HR systems, and costing tools. By analyzing this data and applying Machine Learning (ML) algorithms, the system suggests the optimal team configuration for a project.How it Works This accelerator uses data from the WBS and Developer Scoring Mechanism to suggest the best team composition for a project. It considers factors like skill sets, availability, and cost to propose the most effective team. The process involves several steps:Resource Availability: The system integrates with HR systems to check resource availability. This ensures that only available resources are considered for the project. Cost Analysis: Using data on resource costs, the system suggests budget-friendly teams. This involves analyzing hourly rates, project timelines, and overall budget constraints. Team Suggestion: The AI suggests the optimal team configuration based on project requirements. This involves balancing skills, experience, and availability to form the most effective team. Feature Breakdown: Under The Hood Data Integration: The system pulls data from HR, cost management, and performance scoring systems. This comprehensive data collection ensures that all relevant factors are considered. Algorithmic Analysis: ML algorithms evaluate potential team configurations based on various criteria, including skill sets, availability, and cost. Team Suggestions: The system proposes teams that balance skills, cost, and availability. This ensures that the project is executed by the most suitable team. Project Planning: The accelerator generates project plans and Gantt charts for the chosen team. This provides a clear roadmap for project execution, ensuring alignment and coordination among team members.Accelerator Benefits Deploying this accelerator ensures that project teams are not only well-balanced in terms of skills but also cost-effective. Industry statistics indicate that optimal team formations can lead to a 15-25% increase in project efficiency. Some of the key benefits include:Reduced Project Costs: By selecting budget-friendly teams, the accelerator helps in reducing overall project costs. This involves optimizing resource allocation and minimizing wastage. Improved Project Timelines: Well-balanced teams are more efficient, leading to improved project timelines. This ensures that projects are delivered on time, meeting client expectations. Enhanced Project Success Rates: AI-driven team formations lead to better alignment of skills and project requirements, resulting in higher project success rates. Business Impact The business impact of this accelerator is significant. By forming the best possible teams, companies can deliver projects more efficiently and effectively, leading to increased client satisfaction and better market competitiveness. According to a study by Harvard Business Review, companies that use AI for team formation report a 20% increase in project success rates and a 15% reduction in project costs.As an example, we helped a multinational corporation implementthe Team Formation Accelerator and reported a 30% improvement in project delivery times and a 25% increase in project success rates. These improvements were attributed to better team alignment, optimized resource allocation, and enhanced project planning.Ending Note In conclusion, the Team Formation Accelerator powered by AI represents a significant advancement in project management. By leveraging data from previous accelerators and applying sophisticated ML algorithms, it suggests the optimal team configuration for a project. This leads to reduced project costs, improved project timelines, and enhanced project success rates. As the industry continues to embrace AI, tools like this accelerator will become indispensable for project managers seeking to optimize team formation and drive project success.Looking Ahead This concludes our blog series on AI accelerators for project management. We hope this series has provided valuable insights into how AI can revolutionize the planning and execution of software development projects. Stay tuned for more in-depth explorations of emerging technologies and their applications in project management.
AI-based Accelerators Series: Forming Optimal Teams with AI

The impact of Artificial Intelligence is rapidly expanding, reshaping industries and redefining how we approach creativity. For designers, this evolution presents both exciting opportunities and complex challenges.As AI-driven tools become integral to the design process, designers face new challenges in their work.From design tools to ethical concerns, our design team was posed the following questions:Question 1What’s the first thing that comes to mind when talking about AI? Name: Véronique JanosyTitle: Lead Product DesignerAnswer: Frankly, I’m suffering from AI fatigue. It seems everyone is talking about where they can use AI, without really addressing whether we should be using it. I liken it to getting a new hammer and looking around desperately for nails to hammer but ignoring the fact that we might not actually need to hammer anything in at all.A hammer is innocent enough, though, and with AI we do have to contend with ethical questions that arise around its use, which relatively few people seem to be addressing.My fear is that once the novelty wears off (and I believe that much of its popularity right now is due to its novelty), we will have to grapple with the fallout of not having been cautious enough in the first place.Name: Adriano RenziTitle: UX ResearcherAnswer: AI and Machine Learning have been well adopted in recommendation systems since Amazon started to use hybrid recommendation system, reaching great achievements on the e-commerce industry, becoming the sparkle for experimentation with music categorization and patterns association (Pandora), leading to a complex new era of music (entertainment in general) recommendation.I would say that the state of the art in recommendation systems today has evolved to behavioral prediction systems, which certainly can be used (and has been used) to influence society on political decisions and makes us uneasy about the future.On the generative side, the natural programmed machine learning through patterns, have been appropriating graphic and textual material from real people to generate new products, which unfortunately is affecting the market and rising a new educational paradigm in a bad way – in the name of saving expenses.In many areas of expertise, it has shown to be a tool for the mediocre professional to improve their results.Name: Ram KumarTitle: UX ResearcherAnswer: Prompts.Love or hate it, AI is not a fad, and it is here to stay in some form. It is better to befriend it to empower us than to detest it as a force of evil.That said, prompts are how we communicate with AI tools. It would be good to grasp AI prompting techniques and try them out with tools to see what works and what does not.It is also an excellent way to learn how we and the AI models reason and respond. Think, ‘Her!’ I find these tips on effective prompting quite useful.Name: Carlos SalgueroTitle: Senior Product DesignerAnswer: Since ChatGPT went mainstream at the beginning of 2023, we have witnessed how rapidly “AI” has become a household term.When Artificial Intelligence is mentioned, I immediately think, “This is the new reality,” and I feel the urgency to embrace it to fully harness its benefits.Like any tool at our disposal, AI can be used for both good and bad purposes. I am also reminded of Hollywood movies like “Her” and “Ex-Machina,” which show that our fascination with AI is not new but a topic we have been contemplating for decades.Name: Osama NadeemTitle: Senior Product DesignerAnswer: The first thing that comes to mind and how I’ve used AI, is that of an Assistant.I’ve found AI to be helpful in solving even some design scenarios and edge cases, and it’s very interesting to see that AI is being ingested everywhere – from apps to operating systems and hardware systems.Question 2Have you explored or experimented with any AI tools? Name: Véronique JanosyTitle: Lead Product DesignerAnswer: I have only played for a few minutes with the GenAI built into Adobe Illustrator and Photoshop, to satisfy my own curiosity.In my professional work, however, the client I work for is very restrictive about the tools we use, so I have not used it there.Name: Carlos SalgueroTitle: Senior Product DesignerAnswer: Yes, I’ve experimented with several AI tools. Midjourney and DALL-E have been particularly fascinating for generating unique visual content and concept art, which can be a huge asset during the initial stages of design ideation or to complement a blog post. I’ve also explored Microsoft’s Copilot and Anthropic’s Claude for coding assistance.Furthermore, I’ve created a few GPTs for OpenAI’s ChatGPT store, tailored for specific design and productivity needs.I’m also looking forward to the release of Figma AI, anticipating its potential to further streamline and enhance the design process for UX, UI and Product designers.Name: Ram KumarTitle: UX ResearcherAnswer: Yes, I have been using Grammarly extensively to ensure my writing is on point and have experimented with Grammarly AI tools to change my tone and improve the impact of my writing.I got a ChatGPT subscription a couple of months ago and signed up for an AI boot camp to learn about building products using a combination of No-code tools and ChatGPT. It has been fascinating so far.However, it can be a bit of a rabbit hole, and it would be helpful to time-box your efforts if you plan to dip your toes in trying AI tools.Name: Adriano RenziTitle: UX researcherAnswer: Yes, I experimented with Mdjourney, Dall-E, ChatGPT and Grammarly on different occasions, mostly in an exploratory learning sense. But I haven’t pursued them on a regular basis usage.Name: Osama NadeemTitle: Senior Product DesignerAnswer: I’ve explored many tools – Midjourney, DALL-E, ChatGPT and other AI based plugins for Figma. I’m really looking forward to Figma AI though, I believe it would be very interesting to play around with AI meant for UX/UI design, in a tool that we love.It would eliminate all the third party plugins that are marketed as AI but they’re hardly there.Question 3If you have worked with or experimented with any AI tools, what have you found useful? Name: Véronique JanosyTitle: Lead Product DesignerAnswer: Honestly, I haven’t found anything to be useful. In my personal exploration with GenAI, I’ve found the results to be so poor that I would never use it for anything. Both in Illustrator for icon creation, and in Photoshop for generative fill (to complete a cropped image, for instance), results were strange, unnatural, and would have taken massive amounts of tweaking to achieve anything resembling what I’d need.With that much work, I would much rather browse the internet for inspiration and then use traditional Illustrator and Photoshop methods to achieve the results.The only use I can find for AI in my work might be for doing repetitive tasks, calculations, batch renaming etc., but scripts exist, so I would question why we would want to use AI instead.Name: Carlos SalgueroTitle: Senior Product DesignerAnswer: AI tools have really surprised me with what they can do. Midjourney and DALL-E, for example, can create incredible visuals from just a text prompt that can be used for quick ideation or as inspiration. ChatGPT has been great for bouncing ideas around and getting new perspectives, almost like having a brainstorming buddy available 24/7.I have also learned to appreciate how AI can help in the early stages of research and can help me come up with solutions or ideas that I might not have thought of on my own.As of late, using Adobe’s Firefly within Photoshop and Illustrator has proven quite helpful when modifying images that just need small but specific visual changes.Name: Ram KumarTitle: UX ResearcherAnswer: AI tools can be a good starting point to brainstorm ideas or learn about topics or tools one wants to become familiar with. AI responses can be wordy, so it is helpful to break down the questions into parts or even ask the AI tools to list the response it provides in steps and ask for explanations about each step.I found the step-by-step instructions provided by ChatGPT helpful in learning how to use no-code tools for a basic application or a landing page.Name: Adriano RenziTitle: UX researcherAnswer: The only AI tool I found useful for my needs was Grammarly to check errors on my papers, but with a very attentive review of making sure the meanings would not be distorted (which happened a few times).Nevertheless, I do see non-visual professionals using generative AI to create design and visual posts, instead of hiring a visual artist, corroborating my answer for #1: “it has shown to be a tool for the mediocre professional to improve their results”Name: Osama NadeemTitle: Senior Product DesignerAnswer: If I think about tools, it’s just ChatGPT which I’ve found usable. Other tools right now, especially the ones for images and illustrations are mostly useless for the purpose of UX/UI design.For art however, Midjourney and DALL-E are pretty fascinating.Question 4Has AI impacted your work? Name: Véronique JanosyTitle: Lead Product DesignerAnswer: Only insofar as I cannot escape talk of it, or announcements from apps including AI in their latest updates. AI will affect the industry in the near future, however, as designers will be required to learn certain AI wrangling skills or risk being passed up for employment opportunities.I also fear that as companies start using AI for a variety of tasks, designers’ roles will change to include “fixing” aberrations or mistakes made by AI.Name: Carlos SalgueroTitle: Senior Product DesignerAnswer: AI has definitely made my work faster and more efficient. Tasks that used to take days or weeks can now be done in a fraction of the time. This means I can take on more projects and push creative boundaries further than before.Tech advancements are also keeping everyone in the industry on their toes, constantly learning and adapting to new tools and methods. I have had to pick up new skills, like prompt engineering and using AI-driven insights for user research, which has been both challenging and rewarding.AI isn’t about replacing jobs; it is about enhancing what we can do. People who know how to use AI effectively are the ones who will really stand out in the job market.Overall, AI has been a huge growth opportunity for me, pushing me to innovate and stay ahead in a fast-paced field.Name: Ram KumarTitle: UX ResearcherAnswer: Not yet, at least not directly. However, this is likely to change in the coming months.There are valid concerns about the type of data AI tools can store and utilize.As a researcher, it’s crucial to consider these tools for tasks like extracting a quote from a specific participant in a usability test. It’s essential that we engage in discussions and implement safeguards to ensure the data and the individuals involved are treated with the utmost respect and privacy.Name: Adriano RenziTitle: UX ResearcherAnswer: As a researcher, no. The pattern mapping done by AI is very simple and high level. Similar results from a PO running a survey and presenting percentage results – it can be very misleading. But I think it can be useful to find specific parts of a transcript if needed, and obviously save a lot of time.As an artist, yes. Customers are looking more and more for the human-made real thing and interested in personal views of the world.Nevertheless, illustrators that work with realism painting are getting impacted negatively by AI, as industry sees AI to save moneyName: Osama NadeemTitle: Senior Product DesignerAnswer: AI has an impact but not a lot right now. I frequently visit ChatGPT for general assistance, brainstorm ideas or improve my writing/content.I’ve never used AI to create illustrations or icons because that seems like a lot of work, especially when you must tailor those assets – which cannot be accurately achieved by changing your prompt.
Ask A Designer Round 7: AI & Design

Following the discussion on the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) accelerator in our previous blog, which you can read here, we now turn our attention to the next crucial step in project planning: understanding and scoring the capabilities of the development team. Traditional performance management systems often rely heavily on subjective judgment and lack real-time, data-driven insights. This can lead to misalignment of resources, inefficiencies, and missed opportunities for optimization. This blog delves into the second AI accelerator: the Developer Scoring Mechanism, which aims to bring precision and objectivity to developer performance evaluation.The Need for AI Effective project execution hinges on the capabilities and performance of the development team. However, accurately assessing and scoring developer performance is a complex task. Traditional methods involve periodic performance reviews, often biased by personal judgment and limited by infrequent evaluation periods. These methods fail to provide a continuous, data-driven view of developer performance, making it challenging to make informed decisions about team composition and resource allocation.The AI-driven Developer Scoring Mechanism addresses these challenges by leveraging data from tools like Jira, GitHub, and SonarQube. By analyzing this data and applying sophisticated Machine Learning (ML) algorithms, the system provides an objective, real-time performance score for each developer.How it Works This accelerator utilizes data from project management and code repositories, combined with ML models, to generate accurate performance scores. The process involves several steps:Data Collection: Gather data from tools such as Jira, GitHub, and SonarQube. This data includes metrics like ticket resolution times, code quality, number of commits, and peer reviews. Data Processing: Use Large Language Models (LLMs) to fill in any missing data and standardize the information. Scoring Algorithm: Apply ML models to analyze the data and generate a performance score for each developer. This score reflects various performance metrics and provides a comprehensive view of the developer’s capabilities. Feature Breakdown: Under The Hood Data Integration: The system collects and integrates data from multiple sources, including Jira, GitHub, and SonarQube. This comprehensive data collection ensures that all relevant performance metrics are captured. Data Normalization: LLMs and ML models standardize the data, filling in gaps where necessary. This step ensures that the data is clean, complete, and ready for analysis. Performance Scoring: The AI generates a score based on various performance metrics, such as code quality, bug resolution time, and task completion rate. This score provides an objective measure of a developer’s performance. Dashboard: Scores are displayed on a user-friendly dashboard, providing insights into individual and team performance. This dashboard allows project managers to quickly identify high-performing developers and make informed decisions about team composition.Accelerator Benefits Implementing this accelerator allows project managers to make informed decisions about team composition and identify high-performing developers. Industry statistics indicate that accurate performance assessment can improve team productivity by 20-30%. Some of the key benefits include:Objective Performance Evaluation: The system provides an objective measure of developer performance, reducing the potential for bias. This leads to fairer and more accurate assessments. Real-Time Insights: The AI-driven approach provides real-time insights into developer capabilities, allowing for timely interventions and adjustments. Enhanced Team Formation: By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of individual developers, project managers can form more balanced and effective teams. This leads to improved project outcomes and higher team morale. Business Impact The business impact of this accelerator is profound. By providing accurate and objective performance scores, it enables better resource management and project execution. According to a study by McKinsey, companies that use data-driven performance management practices are 23% more likely to outperform their competitors in terms of project success. Additionally, a survey by Deloitte found that organizations using AI for performance management reported a 45% increase in employee satisfaction.In our experience, the implementation of the Developer Scoring Mechanism at a large telco client led to a 25% improvement in project delivery times and a 30% reduction in project costs. These improvements were attributed to better team formation, optimized resource allocation, and enhanced project monitoring.Ending Note In conclusion, the Developer Scoring Mechanism powered by AI represents a significant advancement in performance management. By leveraging data from various sources and applying sophisticated ML algorithms, it provides an objective, real-time view of developer performance. This leads to better team formation, improved project outcomes, and enhanced resource management. As the industry continues to embrace AI, tools like this accelerator will become essential for project managers seeking to optimize performance and drive project success.Up Next In the next blog, we will explore the third AI accelerator: Team Formations. This tool leverages AI to suggest the optimal team configuration for a project, considering factors such as skill sets, availability, and cost. By doing so, it ensures that project teams are well-balanced and efficient, leading to improved project outcomes.
AI-Based Accelerators Series: AI for Precision Developer Scoring

Introduction The Canadian banking sector is at a crossroads. On one hand, it boasts a global reputation for stability and security. On the other, it faces pressure to embrace rapid digital innovation and keep pace with evolving customer expectations.To learn more about the shift, I interviewed Nelson De Jesus, SVP and CIO of Personal and Business Banking & Direct Financial at CIBC. With over two decades in the financial sector, Nelson brings a unique perspective on how Canadian banks can balance their traditional strengths with the quickly changing needs of a digital-first world.Here’s Nelson’s perspective on the four key areas trending in the Canadian banking sector:Trend 1: The Rise of Experiential Banking The more in tune we get with client preferences, the more we can interface with our clients... those relationships don't have to be human. They can be digital. I think the better the products will be able to offer, the better we will tailor our digital experience to client expectations.Customers are no longer satisfied with simply completing transactions at their bank. They expect their financial institutions to understand their individual needs, anticipate their financial goals, and offer personalized solutions that seamlessly integrate with their lives. This is driving the shift toward what Nelson calls “experiential banking,” a trend that reimagines the entire banking journey.“It’s a process,” Nelson explained. “And you know, I think like everything else, you begin with ‘let’s go 100% digital.’ That’s not the right answer.” He believes that the key to experiential banking lies in striking the right balance between digital convenience and human connection. This means offering a hybrid approach that combines the efficiency of digital tools with the personalized guidance of human advisors, allowing customers to choose the level of interaction that best suits their needs.For example, CIBC’s mobile app now goes far beyond basic account management. It provides personalized financial advice based on individual spending patterns and goals, offers insightful nudges to help customers save more effectively, and even allows you to deposit cheques.This approach reflects a deeper understanding of how different customers interact with their finances, acknowledging that a one-size-fits-all digital solution simply won’t cut it.Nelson emphasized the need to understand customer preferences at a granular level, moving beyond broad demographics to create truly personalized experiences. “If you can offer a better experience, people will take it,” he said. Experiential banking is about providing that better experience — one that not only meets customers’ functional needs but also anticipates their desires, reduces friction, and fosters a sense of trust and engagement.Trend 2: Open Banking’s Slow but Steady Progress While Open Banking has been making headlines globally, its implementation in Canada has been a more gradual process. Nelson acknowledges the potential of Open Banking to create a more competitive and innovative financial landscape, but he also expresses a degree of caution.“I’m very positive [about Open Banking], but I’m also very skeptical as to the timeframe,” he admitted. The regulatory landscape in Canada is still evolving, and Nelson pointed to the relatively low adoption rates in other jurisdictions as a potential challenge. “In the UK, client buy-in is sub-20%, meaning 80% of people have not registered to take part in it,” he shared.Despite the uncertainties, Nelson believes that the industry is moving in the right direction. “To the extent that [Open Banking regulation] obligates us to run a better bank, I think it’s good. I think it’s good for everybody,” Nelson stated.Open Banking holds the promise of empowering customers by giving them more control over their financial data and enabling them to access a wider range of financial products and services. However, its success in Canada will depend on a coordinated effort between regulators, financial institutions, and technology providers to build a secure, transparent, and user-friendly ecosystem.Trend 3: Generative AI’s Potential and Challenges Generative AI is one of the most talked-about technologies, and its potential to revolutionize industries — including banking — is undeniable. Nelson is particularly excited about the possibilities of generative AI, seeing it as a far more transformative force than blockchain or cryptocurrencies.“With AI, there’s a general familiarity with modeling. So, people understand … what it does. It looks for big patterns of data … and you’re basically testing that hypothesis,” he explained. Generative AI takes this a step further by using those data patterns to create new content, predictions, and insights. Nelson believes that generative AI can fundamentally change how banks interact with their customers.However, he acknowledges the ethical considerations and potential risks, especially when it comes to “hallucinations” — instances where AI generates outputs that are nonsensical or even harmful. “How do we now prevent those fatalistic scenarios from playing out like once you get to the point where, you know, it is that powerful? Have you crossed the line that makes it too powerful?”Despite these challenges, Nelson is optimistic about the future of generative AI in banking. He believes that with careful planning, robust governance structures, and a focus on responsible implementation, this technology can enhance customer experiences, improve decision-making, and create new value across the financial ecosystem.Trend 4: The Evolution of Mega Platforms The rise of mega platforms like Google, Amazon, and Microsoft is reshaping industries across the board, and banking is no exception. Nelson sees these partnerships as both a significant opportunity and a potential challenge for traditional financial institutions.He highlights the ability of mega platforms to innovate rapidly and adapt to changing market demands. He pointed to the evolution of Microsoft Teams as a prime example, noting how the company quickly pivoted from the aging Skype platform to create a solution that met the surging demand for video conferencing during the pandemic.Nelson also emphasized the strategic importance of partnerships, particularly in the field of AI. “Now they’ve signed up with OpenAI; I think it’s been a very fruitful partnership for them,” he observed. By collaborating with specialized AI companies like OpenAI, mega platforms can accelerate their development of new products and services, gaining access to cutting-edge technologies and expertise.However, these partnerships also present challenges. Nelson questioned whether mega platforms can consistently deliver “commercial-grade” solutions that meet the stringent requirements of the financial industry. “If I’m going to buy this service, then I want to be sure that they’re not going to turn it off tomorrow,” he cautioned.The evolution of mega platforms will undoubtedly continue to shape the banking landscape. Financial institutions will need to carefully evaluate the benefits and risks of these collaborations, ensuring that they maintain control over critical data and processes while leveraging the innovation and scale that mega platforms can provide.Takeaway The future of Canadian banking belongs to those who can strike the right balance between embracing innovation and preserving the trust that customers have come to expect. It’s a delicate act, but one that holds immense potential to create a more dynamic, customer-centric, and ultimately valuable financial ecosystem.If you found these trends insightful, be sure to tune into the full episode of Behind the Growth for a conversation you don’t want to miss! You’ll hear even more from Nelson De Jesus as he shares his deep expertise and perspectives on the future of Canadian banking.Find it here:Leadership and Innovation in the Banking Sector
Mega Platforms, Gen-AI, Open and Experiential Banking in Canada

Introduction Okay, let’s be honest. How many times have you fumbled with those tiny SIM cards, trying to pry them out of your phone with a paperclip? Or worse, completely lost one right when you needed it most? We’ve all been there, frustrated by those fiddly physical SIMs in a world that demands constant connectivity.But what if I told you there’s a better way? A way to switch carriers, activate new devices, and even travel internationally without ever having to touch a physical SIM card again?That’s where eSIMs come in. And trust me, once you understand how they work, you’ll wonder how we ever lived without them.I recently had the pleasure of interviewing Larry Baziw, a seasoned telecom expert, to celebrate his incredible journey in the industry. Larry’s been at the forefront of mobile technology for decades, and he walked me through the exciting world of eSIMs, explaining how they’re poised to revolutionize the way we connect.In this blog, I’ll share everything I learned from Larry, breaking down the complexities of eSIMs in simple terms so you can understand how they work and why they matter.What Is an eSIM? Now that you know eSIMs offer a more convenient way to connect, let’s dive deeper into what they actually are. As Larry explained it, an eSIM, or Embedded Subscriber Identity Module, is essentially “a tiny chip embedded directly into your device, replacing the traditional, removable SIM card.” It’s a small, rewritable chip that stores your network information digitally, eliminating the need for those cumbersome physical SIM cards.The magic of eSIMs lies in their software-based nature. Larry pointed out the key distinctions between eSIMs and their physical counterparts:eSIM vs. Physical SIM: The Software Advantage Software-Based: eSIMs operate entirely in the digital realm, storing your carrier information as software profiles. Imagine downloading a carrier “app” directly onto your phone — that’s essentially what an eSIM does. Remote Provisioning: No more trekking to the carrier store for a new SIM card. With eSIMs, you can download and activate a carrier profile directly from your device settings — no physical swapping required. How eSIMs Work: Multiple Profiles and Over-the-Air Magic To understand how this all works in practice, let’s break down two key features of eSIM technology:Multiple Profiles: eSIMs can store multiple carrier profiles simultaneously, giving you the flexibility to switch between them seamlessly. Larry compared this to “switching between apps on your phone”. Imagine having profiles for your work line, personal line, and even international carriers, all ready to go at a moment’s notice. Over-the-Air (OTA) Activation: Activating a new carrier profile is as simple as selecting it from your device settings and letting it download over the air. No special equipment or technical knowledge required — it’s all handled seamlessly through software updates. Benefits of eSIMs? What it comes down to is one fundamental security issue: something you know (your carrier subscription) and something you have (the physical SIM card). As long as we keep that going, we can keep customers' identities secure.Okay, so eSIMs sound pretty cool, right? But how do they actually make your life easier and more connected? Larry had a lot to say about the benefits of eSIMs.Convenience: Say Goodbye to SIM Card Struggles Seamless Switching: One of the most obvious advantages of eSIMs is the ease with which you can switch carriers. No more fiddling with SIM card trays or waiting for a new card to arrive in the mail. Larry shared, “And you can start to understand how easy it was to just sit at home and activate your new subscription service and not have to wait for something physical to be mailed to you or to have to drive somewhere to pick up a physical card.” Effortless Device Setup: With eSIMs, setting up a new phone or tablet becomes a breeze. You can activate your service and start using your device almost instantly. Remote Management: Imagine being able to manage your entire mobile subscription from the comfort of your couch. With eSIMs, you can. Change plans, update your information, and even troubleshoot issues remotely, without ever having to step foot in a carrier store. Flexibility: Your Connectivity, Your Way Multiple Lines, One Device: Juggling multiple phones for work and personal use? eSIMs let you consolidate. Store both profiles on a single device and switch between them seamlessly, depending on which number you need to use. Global Connectivity: Traveling internationally has never been easier. Instead of scrambling to find a local SIM card at the airport (or paying exorbitant roaming charges), you can activate an international data plan directly on your eSIM, often at a fraction of the cost. Larry even shared his own experience with this, saying, “Yeah, traveling, getting an eSIM for — I wanted a roaming package for data, and I’ve never met the operator. Obviously, it was all digital. I bought it online. It was an eSIM experience. There’s just so much to the whole experience that it absolutely makes sense. Why would we not have it?” Device Design & Security: A Win-Win Sleeker Devices: eSIMs free up valuable space inside your devices, allowing manufacturers to create thinner, lighter, and more stylish phones, tablets, and wearables. Enhanced Security: Believe it or not, eSIMs can actually be more secure than traditional SIM cards. Because they’re embedded and not physically removable, they’re much harder to steal or tamper with. eSIMs in Action: Beyond Smartphones You might be thinking, “Okay, eSIMs sound great for my phone, but what else can they do?” Well, get ready to be amazed, because Larry discussed a whole world of eSIM applications that extend far beyond our smartphones.The IoT Revolution: Connecting Everything eSIMs are a driving force behind the rapidly expanding Internet of Things (IoT), enabling seamless connectivity for a vast array of devices across industries.Industrial Automation: Imagine factories where machines can communicate with each other, self-diagnose problems, and even order replacement parts automatically. That’s the power of eSIMs in industrial automation. They allow for remote monitoring and control of equipment, optimizing efficiency and reducing downtime. Connected Cars: Your next car might be equipped with an eSIM, providing access to navigation, entertainment, emergency services, and real-time diagnostics. eSIMs are making cars smarter, safer, and more connected than ever before. Smart Cities: eSIMs are playing a critical role in building smarter, more efficient cities. They’re connecting infrastructure like traffic lights, parking meters, and public transportation systems, allowing for better management, resource optimization, and improved citizen services. Wearables and Beyond: A World of Possibilities eSIMs aren’t just transforming industries; they’re also changing the way we interact with our personal devices.Seamless Integration: Larry pointed out that eSIMs were actually adopted in machine-to-machine (M2M) and IoT devices long before they became common in smartphones. He said, “When I look back from the Canadian perspective, eSIMs were introduced into sort of machine-to-machine and IoT services long before they came into consumer hands.” This early adoption in wearables has led to a seamless integration of eSIM technology in devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers, giving them standalone connectivity. Emerging Applications: The potential applications for eSIMs are seemingly endless. Think about it: Larry even posed this question: “Could you imagine a day when you buy a TV for your home and it comes with a SIM slot? What does that mean?” He believes that eSIMs could revolutionize everything from payment systems and digital IDs to home appliances and entertainment systems. The Future Is Connected The future of eSIMs is truly exciting. Here’s why:A Growing Ecosystem: Embracing the eSIM Revolution The adoption of eSIM technology is accelerating at an incredible pace. More and more device manufacturers, from smartphone giants to wearable innovators, are integrating eSIMs into their latest products. And network operators around the world are rapidly expanding their eSIM support, recognizing the convenience and flexibility it offers their customers.Universal Profiles: The Dream of Seamless Connectivity Universal eSIM profiles allow for truly seamless connectivity across devices and networks. Imagine a world where you can activate any device on any compatible network with a single eSIM profile. No more carrier restrictions, no more regional limitations — just instant, global connectivity at your fingertips. While we’re not quite there yet, the industry is moving in that direction, and the possibilities are endless.Takeaway The future of connectivity is here, and it’s embedded. eSIMs are transforming the way we connect, making our lives easier, more flexible, and more connected than ever before.Want to dive deeper into the world of eSIMs and hear more from telecom expert Larry Baziw? Be sure to check out our full conversation on the Behind the Growth podcast. You won’t want to miss Larry’s insights on the future of this game-changing technology!Find it here:The Rise of eSIMs in the Tech Ecosystem
Exploring eSIMs and Its Multi-Industry Use Cases

The integration of AI, especially NLP, in Back-End Development is a growing trend because of its advanced solutions compared to traditional methods. Learning and implementing NLP models can significantly improve the efficiency and accuracy of text processing tasks.This webinar on Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Back-end Development will help you stay current with cutting-edge practices and learn how to implement NLP in Back-End Systems.Expertly tailored for BE Developers, Tech Leads, Solution Architects, Data Scientists, and AI Enthusiasts, this webinar is a must-watch if you want to gainUse Cases: Specific use cases where NLP can be applied in Back-End development to replace traditional methods. Best Practices: How to integrate NLP models into existing Back-End systems, including best practices and common pitfalls. Tools & Libraries: An overview of key tools and libraries for NLP integration in Back-End development. Real Examples: Case studies and examples of how NLP has been successfully used in backend development to solve real-world problems. Future Trends: Insights into future trends in AI and backend development, and how NLP is expected to evolve and impact the field. Don’t let outdated methods hold you back. Watch now to learn more!
Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Back-End Development

The planning phase of the software development lifecycle (SDLC) is often riddled with challenges and uncertainties. It’s a phase where meticulous attention to detail and precise estimations are crucial. Yet, it’s also the phase most susceptible to human error and misjudgment. In many cases, these errors lead to project delays, cost overruns, and resource misallocation. For instance, consider a CRM application project initially estimated to take one year but ultimately stretched to three years due to unforeseen complexities and a lack of proper documentation and team alignment.These common issues in project planning have driven the need for more advanced, reliable solutions. Enter AI-based accelerators, specifically designed to streamline and enhance the planning process. This blog is the first of a three-part series and will focus on the first of these accelerators: creating Work Breakdown Structures (WBS) for business requirements using AI. The upcoming parts of this blog series will focus on Developer Scoring Mechanism and Team Formations.The Role of AI Artificial Intelligence (AI) has the potential to revolutionize the way we approach WBS creation. Traditionally, WBS creation involves breaking down a project into smaller, manageable tasks, estimating the effort required for each task, and ensuring that these tasks align with the overall project goals. This process is often manual, time-consuming, and heavily reliant on the experience and judgment of project managers.By leveraging AI, particularly Large Language Models (LLMs) and Machine Learning (ML), we can automate and enhance this process. AI can process unstructured data from Business Requirement Documents (BRD), analyze historical data, and generate detailed WBS with precise effort estimations. This not only reduces the time and effort required but also improves the accuracy and reliability of the estimations.How it Works Input BRD: The process begins with the user providing the BRD. This document outlines the project requirements in detail. WBS Task Creation: The AI system, powered by LLMs, processes the BRD and breaks it down into smaller, specific tasks. This involves understanding the requirements and translating them into actionable items in the form of Epics and Stories. Effort Estimation: Each task is then assigned an effort estimation based on ML models trained on historical project data. This step involves vectorizing the tasks and matching them with similar tasks from past projects to determine the likely effort required. Feature Breakdown: Under the Hood Natural Language Processing: The AI system reads the BRD and identifies key components. Using Natural Language Processing (NLP), it extracts relevant information and structures it into a format suitable for further processing. Leveraging LLMs: The system breaks down the requirements into specific, manageable tasks. This step ensures that all aspects of the project are covered, and nothing is overlooked. ML Models: These models come into play to estimate the time and resources needed for each task. These models use historical data to provide accurate and realistic estimations. Integration: The system integrates with project management tools like Jira, allowing seamless transition from planning to execution. This integration ensures that tasks are not only well-defined but also easily manageable within existing project management frameworks.Accelerator Benefits Deploying this accelerator in a project management setting can bring about significant improvements in efficiency and accuracy. According to industry statistics, project delays and budget overruns are primarily due to inaccurate initial estimates. By using AI to generate WBS and effort estimations, businesses can:Reduce Planning Time: The time required to create a WBS and estimate efforts can be reduced by up to 50%. This acceleration in the planning phase allows projects to commence more quickly. Increase Estimation Accuracy: AI-driven estimations are more accurate and reliable, reducing the likelihood of project delays by up to 30%. This accuracy helps in setting realistic timelines and budgets. Enhance Resource Allocation: With detailed and accurate WBS, resource allocation becomes more efficient. This ensures that the right resources are assigned to the right tasks, improving overall project execution. Business Impact The business impact of deploying this accelerator is substantial. It not only saves time and reduces costs but also ensures that project teams are better prepared and more accurately aligned with project goals. This leads to higher project success rates and increased client satisfaction.For example, a study by the Project Management Institute (PMI) found that poor project planning is a leading cause of project failure, affecting 39% of projects. By integrating AI-driven WBS creation, companies can mitigate this risk, leading to more successful project outcomes. Additionally, Gartner predicts that by 2025, AI will play a role in the management of at least 50% of all projects, highlighting the growing importance and relevance of AI in project management.Summing It Up In conclusion, the WBS accelerator powered by AI represents a significant advancement in project management. By automating and enhancing the WBS creation and effort estimation process, it addresses many of the common challenges and uncertainties faced during the planning phase. This leads to more accurate planning, better resource allocation, and ultimately, more successful project outcomes. As the industry continues to embrace AI, tools like this accelerator will become indispensable for project managers seeking to improve efficiency and accuracy in their projects.Up Next In the next blog, we will dive into the second AI accelerator: the Developer Scoring Mechanism. We will explore how this tool leverages AI to provide precise, real-time performance evaluations of developers, helping project managers to make informed decisions about team composition and resource allocation.
AI-Based Accelerators Series: AI for Effortless Work Breakdown Structures (WBS)

Introduction Is your business feeling the heat when it comes to sustainability? You’re not alone. From evolving consumer expectations to stricter regulations, companies are under pressure to adopt more sustainable practices. But the path forward isn’t always clear.That’s where the power of AI comes in.I had the pleasure of interviewing Dr. Sedef Akinli Kocak, Director of Professional Development at the Vector Institute, to explore this topic. Dr. Kocak is a leading voice in the world of AI and its potential to address some of the world’s most pressing challenges — what she refers to as “wicked problems.”In this article, we’ll delve into Dr. Kocak’s insights on how AI is transforming sustainability, from optimizing energy use in data centers to mitigating climate risks using cutting-edge technologies. Get ready to discover how AI can help your business navigate the complexities of sustainability and pave the way for a brighter, more sustainable future.AI: A Catalyst for Sustainable Transformation Artificial intelligence, at its core, is about leveraging data to solve problems. AI systems excel at analyzing vast datasets, identifying patterns we might miss, and using those insights to make intelligent predictions. But how does this translate to real-world sustainability action?Think of it this way: almost every aspect of a business, from manufacturing processes to supply chains, relies on energy and resources. AI can help us understand these systems in ways we haven’t been able to before, optimizing them for efficiency and minimizing their environmental impact.Here are just a few ways AI is already making a difference:Energy Efficiency: Imagine a future where buildings automatically adjust their energy usage based on occupancy and weather patterns. Or where traffic flows smoothly, reducing congestion and emissions. AI is making these scenarios a reality. Resource Management: From smart grids that balance energy supply and demand to AI-powered recycling systems that sort materials with incredible accuracy, AI is helping us conserve precious resources and transition towards a circular economy. Climate Modeling & Prediction: AI is enabling scientists to build more accurate climate models, predict extreme weather events with greater precision, and develop strategies to mitigate risks and build resilience. Case Study: AI-Powered Data Center Optimization In today’s digital world, data is king. But this comes at a cost. Data centers, those massive hubs that power our online activity, consume enormous amounts of energy, making them a significant contributor to global carbon emissions.Dr. Kocak highlighted one solution during our conversation — a collaborative project between The Vector Institute and TELUS, a leading Canadian telecommunications company. Their goal? To leverage AI to reduce energy consumption in TELUS’s data centers. The project was inspired by DeepMind and Google System Energy Reduction using reinforcement learning.This type of AI, known as model-based reinforcement learning, essentially allows a system to learn and adapt in real time. It’s like teaching a computer to play a game, where it receives rewards for good decisions (energy savings) and penalties for bad ones (energy waste). Over time, the system becomes incredibly adept at optimizing energy usage based on factors like temperature, humidity, and even server load.And the results speak for themselves. “TELUS piloted this project,” says Kocak, “and the pilot results show that [there was] around 12% in reduced annual energy consumption in a small data center.”Imagine the impact of scaling this solution across more data centers and even other industries grappling with energy efficiency challenges. That’s the power of AI in action.Case Study: Satellite Imagery for Climate Risk Mitigation Climate change is no longer a distant threat; its impacts are being felt globally with increasing intensity. From severe storms to prolonged droughts, extreme weather events pose significant risks to communities, infrastructure, and businesses.AI is emerging as a powerful tool in our efforts to understand and mitigate these risks. One promising application involves the analysis of high-resolution satellite imagery.Dr. Kocak explains, “We work with companies using computer vision technique on satellite high-resolution images to co-develop a solution towards identifying and mitigating climate change risk.”Imagine AI systems capable of scanning vast geographical areas, identifying subtle changes in land cover, water levels, or vegetation health. This data can then be used to:Identify Vulnerable Areas: Pinpoint regions most susceptible to flooding, wildfires, or other climate-related hazards. Predict and Mitigate Risks: Develop early warning systems that alert communities and businesses to impending threats, allowing for timely preparation and response. Support Climate Resilience: Inform long-term infrastructure planning and resource allocation decisions, creating more resilient communities and businesses in the face of a changing climate. Navigating the Challenges of AI for Sustainability AI should benefit humans and the planet. AI systems must reflect the privacy and security interest of the individual.While the potential of AI to drive positive change in the realm of sustainability is undeniable, we must also acknowledge the potential pitfalls. Dr. Kocak emphasizes the importance of a thoughtful, ethical approach to AI development and implementation.One key area of concern is ensuring that AI systems are built on principles of trust and safety. As AI becomes more integrated into decision-making processes that impact our environment and society, transparency and accountability are paramount.“We at Vector, we recently released our trust and safety principles to help our ecosystem,” shares Kocak. These principles highlight the need for AI systems that:Benefit Humanity and the Planet: AI should be a force for good, addressing challenges in a way that aligns with our values and goals for a sustainable future. Reflect Democratic Values: AI development and deployment should be guided by principles of fairness, equity, and inclusivity, avoiding biases that could perpetuate existing inequalities. Prioritize Privacy and Security: As AI systems often rely on vast amounts of data, robust measures must be in place to protect individual privacy and prevent misuse of sensitive information. Navigating these complex issues requires a collaborative effort. Technologists, policymakers, ethicists, and domain experts must work together to ensure that AI is developed and deployed responsibly, maximizing its potential for good while mitigating potential harms.Takeaway The business case for sustainability is clear, and AI is rapidly emerging as a powerful tool in this critical journey. From optimizing energy use to mitigating climate risks, AI empowers companies to make smarter decisions for a healthier planet. By partnering with AI experts and embracing innovative solutions, businesses can unlock a more sustainable future, today.If you found this information insightful, tune into the full episode of Behind the Growth for a conversation you do not want to miss!Find it here:The Transformative Power of AI in Sustainability
How AI is Driving a More Sustainable Future for Businesses

[Toronto, Ontario] – mobileLIVE proudly announces its successful achievement of two significant certifications: ISO 27001 for Information Security Management and ISO 9001 for Quality Management Systems. These prestigious certifications reflect the company’s commitment to quality management and information security, reinforcing its dedication to providing exceptional products and services to its customers.ISO 27001 is an internationally recognized standard for information security management, signifying mobileLIVE’s commitment to protecting sensitive company and client information through rigorous policies and controls. This certification assures clients of mobileLIVE’s capability to manage information securely, thereby enhancing trust and confidence.Simultaneously, ISO 9001 certification underscores mobileLIVE’s dedication to efficiency and organizational excellence in delivering products and services. It validates our adherence to stringent quality standards, ensuring consistent customer satisfaction and continual improvement across all operations.“This dual certification is a testament to our unwavering dedication to excellence and security,” said Mohammad Siddiqui, Vice President Operations, PMO & Delivery. “It highlights our team’s hard work and commitment to maintaining the highest standards in everything we do.”mobileLIVE remains committed to innovation and customer satisfaction, leveraging these certifications to further enhance service delivery and operational efficiency.
mobileLIVE Achieves ISO 27001 and ISO 9001 Certifications, Demonstrating Commitment to Excellence

Introduction The financial services industry is on the cusp of a dramatic transformation, driven by the rapid advancements and growing influence of Artificial Intelligence (AI). Understanding and harnessing the power of AI is no longer a luxury but a necessity for banks seeking to remain competitive, deliver exceptional customer experiences, and thrive in an increasingly digital world.To shed light on what this future holds, I sat down with Yannick Lallement, Chief AI Officer at Scotiabank, one of North America’s largest financial institutions. With a PhD in Artificial Intelligence and a career spanning academia and the private sector, Lallement brings a unique perspective to the intersection of AI and banking.In this guide, we’ll draw upon Lallement’s insights to explore the potential impact of AI on the future of banking. We’ll examine key trends, explore emerging use cases, and provide practical considerations for financial leaders seeking to navigate this exciting and transformative period.The Evolving Landscape of AI in BankingWhile AI has already made inroads in automating back-office tasks and improving operational efficiency in banking, its future impact will extend far beyond these early applications.One of the most significant developments driving this evolution is the rise of Large Language Models (LLMs). These AI models, trained on massive datasets of text and code, possess an impressive ability to comprehend and generate human-like language. This capability makes LLMs particularly well-suited for tasks that were once considered the exclusive domain of humans, such as customer service, document analysis, and even strategic decision-making.As Yannick Lallement highlights, “What the LLMs can do is evolving pretty much, literally, every day.” This rapid evolution means that banks must continually adapt and embrace new possibilities to stay ahead of the curve.Lallement points out that the key to leveraging the power of LLMs lies in having “good source data.” As AI becomes more sophisticated and integrated into core banking functions, the ability to collect, manage, and analyze data becomes a strategic imperative. Banks that can effectively utilize their data will be best positioned to unlock the full potential of LLMs and gain a competitive advantage in the future of finance.Transforming the Customer Experience The future of banking is undeniably customer-centric. Banks that prioritize delivering exceptional, personalized customer experiences will be the ones that attract and retain customers in a competitive market. And AI, especially LLMs, has the potential to revolutionize how banks interact with and serve their customers.Imagine a banking experience where every interaction feels personalized, relevant, and tailored to your specific needs. AI is making this vision a reality. By analyzing vast amounts of customer data—transaction history, financial goals, risk tolerance, and even communication preferences—AI can help banks understand their customers on a deeper level than ever before. This knowledge empowers banks to move beyond generic financial products and services, offering hyper-personalized solutions that resonate with individual needs and aspirations.The rise of AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants is already transforming customer service in banking. These intelligent systems can handle routine inquiries, answer questions, provide financial guidance, and even resolve issues 24/7. As these technologies become more sophisticated, they will become increasingly adept at understanding complex requests, offering personalized recommendations, and providing a seamless, intuitive customer experience across all channels.AI also allows banks to move beyond reactive customer service to a more proactive and predictive approach. By analyzing customer data, AI can anticipate needs, identify potential risks, and recommend relevant products or services before the customer even realizes they need them. This proactive approach not only enhances customer satisfaction but also strengthens relationships and builds trust.Revolutionizing Bank Operations The LLM is not going to replace a person. The question is always: how can you use an LLM to augment an existing employee?Beyond enhancing the customer experience, AI is poised to revolutionize how banks operate behind the scenes. From streamlining processes to uncovering hidden insights and empowering employees, AI offers the potential for greater efficiency, reduced costs, and improved decision-making across all areas of a bank’s operations.One of the most immediate impacts of AI in banking is the continued automation of repetitive, rule-based tasks. Processes such as loan applications, fraud detection, KYC (Know Your Customer) checks, compliance reporting, and risk assessment can be significantly streamlined with AI-powered solutions. This automation not only frees up valuable employee time for more strategic activities but also reduces errors, speeds up processing times, and ultimately lowers operational costs.The sheer volume of data generated in banking presents both a challenge and an opportunity. AI excels at analyzing these vast datasets, uncovering hidden patterns and trends that would be impossible for humans to detect. These data-driven insights can inform a wide range of decisions, from developing new products and services to optimizing marketing strategies and managing risk more effectively.AI isn’t about replacing human judgment; it’s about augmenting it. By providing bank employees with AI-powered tools that offer data-driven insights, predictive analytics, and real-time risk assessments, AI can empower them to make faster, more informed decisions.This means loan officers can assess creditworthiness more accurately, financial advisors can offer personalized investment recommendations, and risk managers can identify and mitigate potential threats more proactively.Navigating the Future of AI in BankingThe transformative potential of AI in banking is undeniable, but harnessing that potential requires more than simply implementing the latest technologies. Banks must adopt a strategic, forward-thinking approach that embraces innovation, invests in talent, and addresses the ethical considerations surrounding AI deployment.First and foremost, banks must cultivate a culture that embraces innovation and continuous learning. This means fostering an environment where employees are encouraged to explore new technologies, experiment with AI solutions, and view change as an opportunity for growth. Leadership must champion AI initiatives, providing the necessary resources and support to drive adoption across the organization.As AI becomes increasingly integrated into banking, the skills needed to thrive in this new landscape will evolve. Banks must invest in their workforce, providing training and upskilling opportunities to equip employees with the knowledge and expertise to work effectively alongside AI. Attracting top talent with backgrounds in AI, data science, and related fields will also be crucial to driving innovation and staying ahead of the curve.The increasing reliance on AI in banking raises important ethical considerations. Banks must ensure that AI systems are developed and deployed responsibly, addressing concerns surrounding bias in algorithms, protecting the privacy and security of customer data, and operating with transparency in how AI is being used to make decisions that impact people’s financial lives.Takeaway The future of banking belongs to those who embrace AI not as a replacement for human ingenuity, but as a powerful tool to enhance it. By fostering a culture of innovation, investing in their workforce, and prioritizing ethical AI development, banks can navigate this transformative era and create a future where technology empowers both institutions and the customers they serve.If you found these trends insightful, be sure to tune into the full episode of Behind the Growth for a conversation you do not want to miss!Find it here:Complexities of AI Implementation in Banking
The Potential Impact of AI on the Future of Banking

Keeping up with innovation and the fast pace of technological advancements is challenging. It requires Product Managers to continuously update their knowledge and skills and stay current with emerging technologies, tools, and trends.This webinar on Next Gen Product Management (NGPM) shares frameworks for skill advancement, the impact of ProductOps on lifecycle management, and the transformative role of AI in enhancing traditional Product Management roles.You will gain: NGPM Skill Maturity Matrix A detailed framework for advancing product management skills, including AI integration, ethical product design, and strategic foresight.Revolutionizing ProductOps A revolutionary approach to product lifecycle management by enhancing cross-functional collaboration and accelerating decision-making.Artificial Intelligence for PMs AI First approach to transform traditional PM tasks, such as, user story automation, dynamic road mapping, and data-driven user testing.Watch now to gain insights into skill advancement, lifecycle management, and AI integration in product management.
Next-Gen Product Management: Innovation, Skills, and Artificial Intelligence

Introduction Is your business ready to weather the storm of the climate crisis? The financial risks, the operational disruptions, the reputational hits — they’re no longer hypothetical. They’re the cost of doing business in a world where climate change is the new normal.I sat down with Vince Gasparro, a veteran of both government and finance, who’s dedicated his career to climate action, most recently as Managing Director and Head of Sustainable Finance at Roynat Capital, Scotiabank. Vince doesn’t sugarcoat the challenges ahead, but he firmly believes we have the tools to turn the tide.In this blog, you’ll get a glimpse into his no-nonsense take on why addressing climate change is no longer optional for businesses and how collaboration is key to creating lasting solutions. Get ready for a dose of clear-eyed optimism and practical insights to help your business navigate the complexities of a changing world.Vince Gasparro on the Urgency of Climate Action To grasp the urgency Vince brings to the table, you have to hear about his trip to British Columbia in 2021. Imagine driving through what should be pristine landscapes, only to encounter the worst air quality on the planet.That’s what Vince and his wife faced. Wildfires, fueled by a warming climate, had choked the region with smoke, turning a leisurely trip into a stark reminder of climate change’s immediate impact. “That’s just one anecdotal sort of point,” Vince remarks, “but when climate change hits, it hits hard.”A Burning Planet, A Bruised Bottom LineAnd it’s hitting businesses hard, too. We’re not talking about distant, abstract threats. From extreme weather events disrupting supply chains to the rising cost of resources and energy, the consequences of a destabilized climate are already being felt on balance sheets worldwide.What’s more, the way we power our businesses is in question. Vince points out that carbon emissions and methane, largely tied to our dependence on fossil fuels, are the primary culprits behind a warming planet.But he’s quick to emphasize that this isn’t about pointing fingers. “This isn’t an attack on those who work in the oil and gas industry,” he clarifies, acknowledging the need for empathy and understanding as we navigate this complex transition.The Power of Collective Action So, what’s the solution? It’s not a quick fix, and it’s not something any one entity can tackle alone. “No one group can do it on its own,” Vince emphasizes. He’s a staunch advocate for collaboration — a coordinated effort between governments enacting smart policies, businesses investing in innovative solutions, and individuals demanding change.He points to the inspiring example of Mark Carney, who rallied 450 of the world’s largest financial institutions, controlling $130 trillion in assets, to commit to net-zero emissions — a powerful testament to the impact of collective action.Vince’s message is clear: The time to act is now. Delaying action will only make the inevitable transition more disruptive and costly.Stakeholders in the Solution Vince is adamant that tackling the climate crisis isn’t a spectator sport. It’s a team effort, and everyone has a role to play.The Policy Pendulum: A Cautionary Tale Governments, with their ability to shape policy and incentivize action, are critical players. However, Vince uses the example of recent policy shifts in Ontario to illustrate the dangers of inconsistency, highlighting how short-sighted decisions can stall progress and even lead to increased reliance on fossil fuels.The lesson? We need consistent, long-term planning from policymakers to provide businesses with the certainty they need to invest in a greener future.Business Leadership: Beyond Compliance A lot of the problems we face move more quickly now than ever before. And one government can't do it on its own.But government action alone isn’t enough. Vince sees businesses as engines of innovation, capable of driving change at scale. It’s not just about complying with regulations; it’s about recognizing the competitive advantage of being a sustainability leader.Those who embrace sustainable practices, invest in green technologies, and embed environmental considerations into their operations will be better positioned to thrive in a carbon-constrained world.The Voice of the Consumer And then there’s the consumer. Never underestimate the power of their choices. Individual action and consumer demand are forces that can shift markets, Vince reminds us. When they choose eco-friendly products, support businesses with strong sustainability track records, and demand transparency, they send a clear message to the market: Sustainability matters.The key takeaway? Solving the climate crisis is a shared responsibility. Each stakeholder group — governments, businesses, and individuals — must play their part to drive meaningful and lasting change.Solutions and OpportunitiesWhile the scale of the climate crisis can feel daunting, Vince is a firm believer that we already have many of the solutions needed to build a more sustainable future. The key, he says, is embracing innovation and collaboration on multiple fronts.Investing in Renewable Energy: The Only Path Forward First and foremost, we need to accelerate the transition away from fossil fuels and towards cleaner sources of energy. “Ask them [investment bankers] how easy it is to raise equity or capital for a solar, wind…project—it’s become much easier,” Vince observes. This shift towards renewables, he argues, is already well underway, driven by a combination of market forces, technological advancements, and growing investor demand for sustainable options.Climate Tech: Innovation for a Sustainable Future Beyond renewable energy, Vince sees tremendous potential in the burgeoning field of climate tech. “Climate tech will play a significant role,” he states, highlighting innovations like carbon capture and storage, battery storage, and ever-increasing efficiencies in solar panel technology. These advancements, he believes, will be essential in decarbonizing industries that are difficult to electrify directly, such as heavy industry and transportation.Operational Efficiency: Doing More with Less But innovation isn’t just about high-tech solutions, Vince reminds us. Sometimes, the most impactful changes are surprisingly practical. He points to the often-overlooked area of operational efficiency. “Start with the low-hanging fruit,” he advises businesses. Building retrofits, for example, can lead to significant cost savings and emissions reductions. By optimizing energy use, minimizing waste, and embracing circular economy principles, businesses can shrink their environmental footprint while boosting their bottom line.For Vince, the path forward is clear. By embracing a combination of renewable energy, innovative technologies, and smart operational practices, businesses can position themselves not just to weather the climate crisis, but also to thrive in a more sustainable future.Takeaway The climate crisis demands action, not complacency. By embracing renewable energy, climate tech, and operational efficiency, businesses can drive meaningful change while securing their place in a sustainable future. The time for collaborative action is now – are you ready to lead the charge?If you enjoyed this blog, check out the full episode on the Behind the Growth podcast!Find it here:Taking Collective Action to Combat Climate Change
A Collective Action to Combat Climate Change

mobileLIVE is proud to celebrate another milestone this year–being recognized as one of the 2024 Best Workplaces in Technology. mobileLIVE received this honor after a thorough and independent analysis conducted by Great Place to Work®.The list is based on direct feedback from employees of the hundreds of organizations that were surveyed by Great Place to Work®. To be eligible for this list, organizations must be Great Place to Work-Certified™ and have exceptionally high scores from employees on the Trust Index survey.The recognition is a true honor, for the Best Workplaces in Technology list includes approximately 40 top companies in tech, including giants like NVIDIA and Cisco. Great Place to Work® has a set of themes and metrics that not only reveal whether employees feel their workplace is great, but also predict retention, agility, and overall business success. Using their proprietary Trust Index™ survey, they look at the core of what they know creates great workplaces — key behaviors that drive trust in management, connection with colleagues, and loyalty to the company.mobileLIVE is proud to have scored high on the Trust Index, roving that our approach is in the right direction: empowering employees, valuing diversity, and nurturing innovation throughout our workforce. At mobileLIVE, our people are the real drivers behind success, and this is a win for each of our valued employee.About Great Place to Work® Great Place to Work® is the global authority on high-trust, high-performance workplace cultures. A global research and consulting firm, Great Place to Work® provides the benchmarks and expertise needed to create, sustain, and recognize outstanding workplace cultures. In Canada, Great Place to Work® produces both industry and demographic-specific Best Workplace™ lists and represents the voices of 500,000 employees across industries. This is part of the world’s largest annual workplace study, recognizing the world’s Best Workplaces in a series of national lists including those published by The Globe and Mail (Canada) and Fortune Magazine (USA). Visit us at www.greatplacetowork.ca
mobileLIVE Recognized on the 2024 Best Workplaces in Technology List!

Introduction Have you ever stopped to count how many women are in the room? It’s not something most people do regularly, but for Lisa Sutherland, Senior Director of Emerging Markets at Rogers Communications, it’s a question her daughters have innocently asked her throughout her career: Why do you count the women in the room?Because even in 2024, women are still underrepresented in the tech industry, particularly in leadership positions.While progress is being made, deeply ingrained myths continue to discourage talented women from pursuing and advancing in tech careers. To help clear the path for the next generation, I had the pleasure of interviewing Lisa for the “Behind the Growth” podcast to get her insights on debunking these harmful misconceptions.With over three decades of experience witnessing the evolution of the tech landscape firsthand, Lisa offers invaluable wisdom on how we can create a more inclusive and equitable industry. Let’s dive into four persistent myths that she’s encountered and why they simply don’t hold up.Myth #1 – Tech is a “Boys’ Club”Picture a typical tech startup: a dimly lit room buzzing with the sound of fingers flying across keyboards. Empty energy drink cans litter the tables alongside scattered takeout containers. And huddled over glowing screens are… well, you know the image. It’s likely a group of young men, sporting hoodies and headphones, intensely focused on their code.This pervasive stereotype of tech being a “boys’ club” is one of the biggest hurdles women face. But according to Lisa, it’s a narrative rooted more in Hollywood than in historical reality. “Leading out of the Second World War, and even into the 1950s, computer programmers were mostly women,” she points out.The image of meticulous code written out on paper and fed into massive machines might not be as flashy as today’s sleek tech offices, but it underscores a crucial point: women have always been pioneers in tech, even if their contributions have been overshadowed.This historical erasure is precisely what makes movies like “Hidden Figures” so important, as Lisa highlights. The film sheds light on the brilliant African American women whose mathematical prowess was instrumental to NASA’s success, even as they faced segregation and discrimination. These stories challenge the narrow lens through which we often view tech achievements.Lisa further underscores this point by recalling her own experience attending tech events: “If you imagine a hackathon […] what’s that picture that you see?” It’s often the same stereotypical image—a homogeneous group lacking diversity. By acknowledging these ingrained biases, we can start to break them down and create a more welcoming and inclusive tech culture.Myth #2 – Women Aren’t “Naturally” Suited for Tech The notion that women somehow lack the inherent aptitude for tech is a damaging and persistent myth. It often rears its head in subtle ways, such as assumptions that women are less logical, less comfortable with numbers, or less drawn to technical fields. But as Lisa points out, these stereotypes are a relatively recent phenomenon.“Think about computer programming when you had to draw [it] on a piece of paper and insert it into a machine,” she suggests. “Those were computer programmers, and it was vastly women.” This historical context is crucial.In the early days of computing, programming was often viewed as detail-oriented and even secretarial — tasks often relegated to women. As technology evolved and became more lucrative and prestigious, the perception shifted, and it became increasingly masculinized.This evolution reveals a fundamental truth: success in tech isn’t about innate ability determined by gender; it’s about skills, dedication, and, importantly, opportunity.The fields of software development, data science, AI, and countless others require diverse talents, including problem-solving, creativity, and communication – none of which are exclusive to any gender.By letting go of the limiting belief that women aren’t “cut out” for tech, we open doors for countless individuals to discover their potential and contribute to a more innovative future.Myth #3 – Women Need to “Work Harder” to be Noticed Be present, lean in, and take on those challenges because you can make a difference with your beautiful talent, your creativity, your innovation.For many women in tech, especially those from older generations, the prevailing advice often boiled down to: put your head down, work hard, and wait to be recognized. It’s a well-intentioned sentiment, but as Lisa aptly points out, “Men were advocating for themselves and saying they could do the job, and women were waiting to be noticed.”This disparity in self-promotion is a key factor contributing to the gender gap in leadership roles and compensation. While hard work is undoubtedly essential, it’s often not enough in a competitive industry where men are often socialized to be more assertive in promoting their accomplishments and vying for opportunities.Lisa has observed a heartening shift in recent years, particularly among younger generations of women entering the tech workforce. “They are really learning to advocate for themselves, understand what they’re good at, and lean into those strengths,” she notes.This proactive approach is essential. Women in tech must feel empowered to own their accomplishments, articulate their value, and negotiate for the recognition and opportunities they deserve. This includes seeking out mentors and allies who can amplify their voices and champion their growth.Myth #4 – The Opportunities for Women in Tech Are LimitedIt’s a stark reality: women remain significantly underrepresented in tech leadership roles, and the gender pay gap persists. The numbers can feel discouraging, leading many to believe that the opportunities for women in tech are inherently limited.Lisa acknowledges this challenge, recalling a time when “there seemed to be this perception there was only enough room for one or two women around the table.” But she also emphasizes that this perception is changing, and companies are recognizing the value of building more diverse and inclusive teams.Her example of the Apple Health app initially overlooking women’s health needs is a powerful illustration. This oversight not only alienated a significant portion of potential users but also demonstrated the crucial need for diverse perspectives in product development. When women have a seat at the table, the products and solutions created are better, more innovative, and more relevant to a wider range of people.Lisa’s optimism shines through in her compelling analogy: “It’s a little bit like love,” she says. “There’s always enough love to go around for everybody if you make enough room in your heart.” By embracing this philosophy of abundance and actively “making room” for women in tech, companies can unlock a wealth of untapped talent, drive innovation, and create a more equitable and fulfilling industry for everyone.Takeaway It’s time to rewrite the narrative about women in tech. By debunking these persistent myths and fostering a more inclusive environment, we can unlock a wealth of untapped talent and create a future where everyone has the opportunity to contribute to a thriving tech industry.Want to hear more from Lisa on this important topic? Tune into the full episode of Behind the Growth for a conversation you don’t want to miss!Find it here:Advocating for Women in Tech
Debunking Four Myths About Women in Tech

Introduction Starting a business can feel like an insurmountable challenge, fraught with uncertainty and endless obstacles. How do you turn your entrepreneurial dreams into reality?I had the pleasure of interviewing Jahan Ali, a serial entrepreneur and the CEO of mobileLIVE, to celebrate his remarkable journey and gain insights from his experiences.Jahan is not just the founder of mobileLIVE but also the visionary behind HachiAI and XapCard. His journey from a new immigrant to a successful entrepreneur offers a wealth of knowledge and inspiration.In this blog, you’ll discover Jahan’s practical advice on overcoming early challenges, building a business from the ground up, embracing innovation, and the core values essential for entrepreneurial success. His insights will provide you with the tools and motivation to navigate your own entrepreneurial path.The Beginnings of an Entrepreneur We did not know anyone in Canada at that time, we did not have any funds, all the funds that we had, we paid our international tuition fees and, and then we are just here in a new country.Jahan’s entrepreneurial journey began with a leap of faith when he moved to Canada in 1998. As international students, he and his wife faced significant financial challenges in a new and unfamiliar country.They managed their finances meticulously, living in a one-bedroom basement apartment and sharing Happy Meals. Jahan secured a teaching assistantship, which paid $700 a month, while his wife worked at Yellow Pages.Despite the intense financial strain, Jahan’s determination and resilience set the foundation for his future success.The Power of Persistence and Support The support from his wife was crucial. Together, they navigated these tough times, proving that community and familial support are invaluable in the early stages of entrepreneurship.Jahan’s early experiences show that success often requires starting from the bottom, embracing a positive mindset, and persistently working towards your goals, no matter how daunting the circumstances.Building a Business from the Ground UpThe idea for mobileLIVE was sparked by Jahan’s realization of a gap in the market for high-quality, onshore digital transformation and IT consulting services.This insight came while he was working at Motorola, where he noticed inefficiencies and communication issues with offshore solutions. Jahan’s ability to identify a market need and his willingness to take risks were crucial in turning his vision into reality.Securing the First Client One of the key strategies Jahan employed to get mobileLIVE off the ground was offering free pilot projects to potential clients. This approach is a powerful lesson in building trust and showcasing value.By removing the initial financial risk for his clients, Jahan demonstrated the high standards and effectiveness of mobileLIVE’s solutions. This strategy not only secured his first clients but also established a foundation of trust and long-term relationships, highlighting the importance of innovation and bold moves in business.Key Growth Milestones mobileLIVE’s strategic thinking and willingness to innovate contributed to their growth. Winning a Request for Proposal (RFP) as the alternate vendor for device testing was a pivotal milestone moment. This achievement, which led to the creation of the first-ever 3G lab in Canada, underscores the importance of seizing opportunities and investing in unique capabilities to stand out in the market.Jahan’s experience with mobileLIVE teaches the importance of identifying market gaps, taking calculated risks, and continuously striving for excellence. By focusing on quality, building trust through innovative approaches, and capitalizing on growth opportunities, entrepreneurs can navigate the challenges of building a successful business from the ground up.Embracing Innovation and Adaptability Things are changing at lighting speed. So have a learn-it-all attitude. The moment you have a know-it all-attitude, the decline will start. So always keep learning.For Jahan, innovation and adaptability are essential to success. He believes that continuous learning and the ability to adapt to changing market conditions are crucial for any entrepreneur. His ventures, such as HachiAI and XapCard, are prime examples of how embracing innovation can lead to significant market impact.The Role of Innovation in Success Jahan views innovation as a driving force behind business success. He emphasizes the necessity of staying ahead of industry trends and continuously seeking new ways to solve problems.For instance, HachiAI was born out of a need to improve user acceptance testing across various platforms. By developing a product that could pre-code human gestures and automate processes, Jahan created a solution that filled a significant gap in the market.From HachiAI & XapCard: Pioneering New Solutions Jahan stresses the importance of encouraging innovation within the company.He shares how the ideas for HachiAI and XapCard emerged from mobileLIVE’s internal incubation program, demonstrating how fostering a culture of innovation within a company can lead to groundbreaking products.Jahan’s approach teaches the importance of being adaptable and open to new ideas. By continuously learning and embracing change, businesses can stay competitive and responsive to market needs. Innovation is not a one-time effort but a continuous journey that requires persistence and a proactive mindset.The Recipe for Entrepreneurial SuccessJahan’s journey offers a blueprint for entrepreneurial success, grounded in core values and practical wisdom. His experiences highlight the importance of hard work, persistence, emotional intelligence, and maintaining a positive attitude.Core Values for Success Jahan attributes his success to a set of core values that have guided him throughout his journey. First and foremost is hard work. Jahan believes that there is no substitute for dedication and effort.Persistence is another critical value. The entrepreneurial journey is filled with ups and downs, but Jahan’s story shows that those who remain persistent and refuse to give up are more likely to achieve their goals. This persistence is closely linked with maintaining a positive attitude, even in the face of adversity.Emotional intelligence, or EQ, is also essential. Jahan emphasizes the importance of understanding and managing one’s emotions, as well as empathizing with others. High EQ helps in building strong relationships, both within a team and with clients, which is crucial for long-term success.Final Words of Wisdom Jahan’s advice is clear: surround yourself with positive, supportive people, stay focused on your goals, and continuously strive to learn and adapt. He believes that luck favors those who are prepared and persistent. Success is not about being the smartest person in the room but about being the most resilient and adaptable.Jahan also stresses the importance of giving back. Whether it’s supporting your team, helping other entrepreneurs, or contributing to your community, being a giver creates a positive cycle of growth and success. After all, entrepreneurial success is not just about personal achievement but also about uplifting others and creating a lasting impact.Takeaway Jahan’s journey highlights the power of persistence, innovation, and community support in achieving entrepreneurial success. His insights provide a roadmap for aspiring entrepreneurs to navigate their own challenges and create lasting impact.If you found Jahan’s story inspiring, be sure to tune into the full episode of Behind the Growth for more valuable insights and advice!Find it here:Successfully Navigating the Entrepreneurial Journey
The Entrepreneurial Journey: Insights for Aspiring Business Owners

Toronto, ON–June 19 , 2024— mobileLIVE, a Toronto-based technology services and consulting company, is excited to announce the successful delivery of a highly anticipated masterclass on “7 AI-Xcelerators” at the Collision Conference. The event attracted overwhelming interest, with three times the number of registrants than the venue could accommodate, and only 100 attendees managed to secure their spots.The masterclass showcased seven practical and proven AI-Xcelerators that addressing Project Planning, Code Modernization, and Operational Automation:Code Transformation: This tool comprehends and analyzes legacy code, transforming it into modern languages and architectures, enhancing efficiency and compatibility.Code to Documentation: This accelerator generates code from various documents, including business logic, flow diagrams, sequence diagrams, and class diagrams, streamlining the documentation process.Knowledge Management: By processing input documents or data against existing repository documents, this tool performs analysis, comparison, and suggestion tasks, improving document management and utilization.Effort Estimations: Utilizing AI and machine learning models, this accelerator analyzes business requirements and generates a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) to provide accurate time and cost estimates.Team Scoring: This tool collects metrics on code quality, task completion times, and peer reviews to generate a comprehensive performance score for each developer, fostering a data-driven approach to team management.Team Formations: Analyzing project requirements, developer scores, and historical project data, this accelerator suggests optimal team configurations, ensuring project success through strategic team alignment.Intelligent Digital Workers: Pre-trained to follow your processes and operate on various applications without requiring integration, these digital workers function around the clock without errors, significantly boosting productivity.The masterclass received rave reviews from attendees, underscoring the industry’s growing interest in AI-driven solutions.For more information about our AI-Xcelerators and to stay updated on upcoming events, subscribe to mobileLIVEs content.
mobileLIVE Hosts a Masterclass on “7 AI-Xcelerators” at the Collision Conference, 2024

Translating business requirements into technical deliverables, accurately estimating effort, and allocating the right talent is complicated. This often leads to cost estimation errors, talent misallocation, and project failure.Here’s how our AI-Powered approach has addressed these challenges:Effort Estimation We leverage AI to transform a Business Requirements Document (BRD) into a detailed Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) with time and cost estimates, reducing the time and human error involved in project planning.Team Scoring We use data from tools like Jira, GitHub, and SonarQube to calculate a comprehensive score for developers based on their performance, experience, and code quality, facilitating informed team selection and performance monitoring.Team Formation Our approach recommends optimal project teams by analysing historical performance data and matching it with project requirements, ensuring the best fit in terms of skill, cost, and delivery time.Watch this webinar for a demonstration highlighting AI-powered approach to Effort Estimation, Team Scoring, and Formation.
AI-Powered Project Planning, Effort Estimation, and Team Formation

The secret to a company’s success often lies in how a business treats its two most important assets: its customers and its employees.This approach is vital because fostering a positive employee environment translates into exceptional customer service, thereby creating a cycle that drives sustainable growth and profitability.In this episode of ‘Behind the Growth’, I had the honour of interviewing Hussain Qureshi, the President of mobileLIVE, to celebrate his journey and explore his perspectives on the topic.With a career spanning several decades in the tech and telecommunications industries, Hussain has a wealth of knowledge on what it takes to drive a company to success. From his early days as an electronics engineer to leading mobileLIVE as its President, his insights provide a valuable roadmap for any business aiming to prioritize both customer and employee satisfaction.In this blog, you’ll learn Hussain’s strategies for driving business growth while fostering a thriving workplace culture and a satisfied customer base.Identifying and Addressing Customer Needs At the core of any successful business lies a profound understanding of customer needs. Hussain emphasizes that mobileLIVE’s sustained growth is largely attributed to its ability to identify and effectively address these needs. This approach has kept it competitive and fostered strong, enduring relationships with its clients.Engaging Directly to Fine-Tune Solutions At mobileLIVE, the engagement process is designed to ensure that customer interactions are meaningful and productive.Hussain highlights importance of using detailed feedback mechanisms, which help capture essential insights into customer needs and preferences. This process involves regular surveys, customer interviews, and the use of customer service analytics to gauge satisfaction and pinpoint areas for improvement.Moreover, he employs a proactive approach by involving customers early in the development process. This allows for iterative feedback, refining products and services in response to direct customer input before final release.This hands-on engagement strategy ensures that solutions are not only effectively addressing the identified issues but are also evolving with the customer’s changing needs, thereby enhancing overall satisfaction and loyalty.Tailoring Solutions for Enhanced Customer Satisfaction Such a customer-centric approach ensures that every solution provided is tailored to meet specific needs, thus enhancing satisfaction and loyalty. This method of operation doesn’t just solve immediate issues but builds a foundation for long-term success and customer retention by consistently delivering value that customers truly need and appreciate. This proactive stance on customer experience is the cornerstone of a successful business, driving growth through customer satisfaction and loyalty.Fostering Employee Satisfaction and Engagement At mobileLIVE, the emphasis on employee satisfaction is as strong as the focus on customer needs. Hussain believes that a motivated and satisfied workforce is essential to the company’s success. By creating an environment where employees feel valued and part of the company’s mission, you can ensure that your team is productive and deeply engaged with their work.Strategies for Enhancing Employee Engagement mobileLIVE employs several strategies to keep its employees engaged and committed. This includes a robust internal communication strategy that ensures all team members are informed and their voices heard. Regular town halls, feedback sessions, and open forums are part of the company’s culture, fostering a sense of inclusion and transparency.Moreover, Hussain highlights the importance of investing in employees’ professional growth. Through continuous training and development opportunities, employees at all levels should be encouraged to acquire new skills and advance their careers within the company. This focus on personal and professional growth helps maintain high engagement and job satisfaction levels, contributing directly to employee retention and overall company success.Cultivating a Culture of Recognition Recognizing and rewarding employees’ efforts and achievements is another pillar of mobileLIVE’s strategy. Regular celebratory events, performance bonuses, and public acknowledgments contribute to a positive work environment. Such practices boost morale and reinforce the company’s values of hard work and excellence.By prioritizing employee satisfaction and engagement, you can create a motivated workforce that is well-prepared to meet the challenges of the market while driving the company forward.Integrating Employee Goals with Customer Outcomes At mobileLIVE, the alignment of employee goals with customer outcomes is a strategic imperative that drives mutual success. This integration ensures that as employees achieve their professional goals, they concurrently advance the company’s mission to enhance customer satisfaction. It’s a synergistic approach where employee success and customer success are seen as interconnected objectives that fuel the company’s overall growth.Feedback Loops and Communication Key to this integration is the robust feedback loops and open lines of communication between different levels of the organization. By fostering a culture where feedback is both given and received across all hierarchies, mobileLIVE ensures that employee initiatives are in harmony with customer needs. This ongoing dialogue helps in fine-tuning processes and services in real-time, enhancing the ability to meet customer expectations more efficiently and effectively.Empowering Employees to Deliver Excellence Employees at mobileLIVE are empowered to take ownership of projects that directly impact customer experiences. This empowerment is facilitated through access to the necessary tools, authority, and confidence to make decisions that benefit the customer. As a result, employees feel more vested in the outcomes of their work, driving them to excel and innovate in ways that significantly enhance customer satisfaction.Through these strategies, you can foster a positive and proactive workplace and ensures that the company’s objectives of delivering exceptional customer service are met. This alignment of employee and customer goals creates a dynamic where both the company and its clients thrive together.Lessons Learned and Future Directions Capitalizing on Past Experiences Over the years, mobileLIVE has learned valuable lessons that have shaped its strategies and approaches to business. One of the key insights is the importance of staying adaptable and responsive to both market changes and internal feedback. Hussain stresses that this adaptability allows companies to continuously refine their services and internal practices to better meet the evolving needs of customers and the aspirations of their employees.Anticipating the Future Looking ahead, Hussain suggests focusing on leveraging your past experiences to anticipate future challenges and opportunities. mobileLive plans to integrate technology and innovative practices further to streamline operations and enhance the customer and employee experience. This includes adopting more advanced data analytics for deeper customer insights and further automating processes to free up employee time for more strategic tasks.Continued Commitment to Core Values As it moves forward, mobileLIVE remains committed to its core values as they guide the company’s decisions and strategies, ensuring that as they grow, they continue to provide value to their customers while maintaining a supportive and engaging work environment for their employees.Through thoughtful reflection on past lessons and a clear vision for the future, you will be well-positioned to continue your trajectory of growth and success.Takeaway As we’ve delved into mobileLIVE’s successful strategies with Hussain Qureshi, it’s evident that the key to thriving in today’s dynamic market lies in simultaneously enhancing customer experiences and nurturing employee engagement.This exploration offers a guide for businesses to understand the importance of balancing these critical areas effectively. Organizations adopting similar approaches can foster a more engaged workforce and a more satisfied customer base, propelling themselves toward sustained growth and success.If you found these insights valuable, be sure to tune into the full episode of “Behind the Growth” for a conversation you won’t want to miss!Find it here:Prioritizing Customer and Employee Experience
Prioritizing Customer and Employee Experience to Drive Business Growth

User personas are one of the many tools a designer can use to guide the design process.The intention of these semi-fictional representations of your audience is to aid in humanizing your approach and understanding who you’re designing for.Thinking about the motivations, goals, challenges and preferences of your target can help in designing in a more user centric and thoughtful way – but are these useful?In this round of “Ask a Designer,” we asked members of our design team about their experience with navigating user personas and how they remain mindful of empathy in design.Question 1How often do you create user personas? Name: Irum TariqTitle: Lead Product DesignerAnswer: Creating personas is typically common when working on a new project or a large-scale initiative. Several factors contribute to this practice, such as budget availability, time constraints, and the need for personas given existing data. Ideally, personas should be created frequently and updated after significant market research activities, like surveys, interviews, or usability testing, as these activities reveal new user information. However, due to various constraints, personas are usually created only when embarking on new projects.Name: Ram KumarasubramanianTitle: Senior UX ResearcherAnswer: In my 8 years of experience, I have created personas from scratch only on a few occasions. I have assisted in developing personas to support the establishment of a research team and utilized them to illustrate the typical day of our target users, providing valuable insights for the design process.Additionally, I curated personas and developed broad archetypes (a higher-level abstraction of a collection of personas) to facilitate internal consensus on the user base for a platform I was helping build. These archetypes aided in aligning internal stakeholders and provided clarity on the objectives and obstacles faced by the end users of our platform.Name: Sheyla AmaralTitle: Lead Product DesignerAnswer: It’s not very common. When working on existing products, it’s typical for user personas to have been established at the start of the project. In my experience, I’ve encountered situations where the target users for these personas changed slightly, requiring a reassessment. For new products, the process is different, and the method for defining personas can vary based on the product’s goals, and I have worked defining some of them, which is an interesting and deep process.Question 2What methods do you use to ensure relevance when creating user personas? Name: Irum TariqTitle: Lead Product DesignerAnswer: My process for creating user personas is straightforward. I begin by setting the objective and scope to determine why we need personas and how they will be used. Next, I conduct research using qualitative and quantitative methods. I recruit participants from targeted age groups for interviews and distribute questionnaires. Once the data is collected, I organize it according to different segments such as demographic and behavioral. I then create persona profiles, adding details and summarizing key insights from the data. Before utilizing the personas in my design, I validate and refine them by sharing with key stakeholders to ensure accuracy and relevance.Name: Ram KumarasubramanianTitle: Senior UX ResearcherAnswer: It is essential to know why personas are needed, the context behind creating one, and how the team plans to use them. It is also helpful to align with the key partners and requestors to flesh out any existing assumptions and curate available resources to build a baseline understanding of the organizational needs before creating the plan for building a persona.Personas are ideally created by conducting research with the target segments and analyzing the patterns and trends that emerge from the insights. The team working on building personas can leverage analytics and support data, such as call and chat transcripts, to identify the target segments and recruit appropriately for conducting persona research.Name: Sheyla AmaralTitle: Lead Product DesignerAnswer: To create user personas, I start by identifying and segmenting our in-house customer data. Once that’s done, I conduct a quantitative survey to gather additional information and confirm the in-house data. Depending on the project, interviews and focus groups are essential for obtaining more detailed analysis of behaviors, goals, and pain points. One particularly interesting project I worked on involved conducting a diary study with kids aged 8 to 12. It’s crucial to choose the method that aligns with your target audience so they can actively participate.Question 3Have you encountered any challenges in using user personas? If so, how have you addressed them? Name: Ram KumarasubramanianTitle: Senior UX ResearcherAnswer: One of the challenges I have encountered in using personas is that there is great enthusiasm for building one or more personas at the start of the exercise, but the energy and commitment dwindle once these personas are created. The personas also tend to become stale over time, and often, there is a lack of real application in day-to-day work. An alternative might be maintaining a list of Jobs-to-be-done by each persona that gets refreshed periodically in the context of the problems being solved.Name: Sheyla AmaralTitle: Lead Product DesignerAnswer: One of the challenges I faced before was regarding the huge number of personas. Sometimes, businesses want products to range from 18 to 99 years old, and it makes it hard to prioritize design decisions when we have so many different user needs. While having a clear problem statement helps, it’s still too broad.Another major challenge is keeping the personas updated. As user goals change over time, so do their needs. Continuously validating and analyzing data is costly and time-consuming, so often we end up not doing it.Name: Irum TariqTitle: Lead Product DesignerAnswer: Creating and using user personas can present several challenges. One of the biggest challenges I face is the lack of accurate data. Personas are only as reliable as the data they’re based on, and inaccurate or insufficient data can result in personas that do not accurately represent the target audience. To address this, I validate my data by conducting follow-up interviews and surveys. Additionally, working closely with the analytics team and gathering as much information as possible helps me validate my research and ensure the personas are accurate.Question 4Are there specific scenarios where user personas prove more valuable than segmentation models, and vice versa? Name: Irum TariqTitle: Lead Product DesignerAnswer: There are specific scenarios where user personas and segmentation models can each be more valuable. Understanding the contexts in which each tool is most effective can help make informed decisions about when to use them.For example, when designing a new product interface or improving an existing one, user personas provide a detailed, narrative-driven understanding of users’ goals, behaviors, and pain points, helping designers create more intuitive and user-friendly interfaces.On the other hand, when conducting market analysis and defining market entry strategies, segmentation models offer a broad overview of different market segments based on demographics, behaviors, and other quantifiable criteria, enabling businesses to identify and target high-potential market segments.By recognizing the specific contexts and scenarios where each tool excels, you can effectively combine user personas and segmentation models to enhance decision-making and user-centered design processes.Name: Ram KumarasubramanianTitle: Senior UX ResearcherAnswer: Personas often provide the most value when kickstarting product development from scratch. During this time, the team needs clarity to identify where to invest its time and resources to maximize value creation and minimize the risk of failure.Personas can also be an excellent tool for onboarding new team members and orienting them to the nuances of the problem space.Segments are more pertinent to targeting users for large-scale quantitative exercises such as surveys and growth-oriented activities such as ad-targeting.Name: Sheyla AmaralTitle: Lead Product DesignerAnswer: When building a product from scratch, starting with personas can help the team visualize the target users. It also assists in defining the tone and language for marketing efforts to reach those users. Product iterations and features are typically based on user needs, which can be validated using personas.However, before using personas, it’s important to develop segmentation models. These models can help us understand promising markets and trends.Takeaway The insights provided by our design team members underscore the significance of empathy in design, particularly through the utilization of user personas.User personas offer a means to humanize the design process, facilitating a deeper understanding of the target audience’s motivations and preferences. However, the frequency of creating user personas varies, often occurring at the onset of new projects due to constraints like time and resources.Ensuring the relevance of user personas involves a meticulous process of research and validation, utilizing both qualitative and quantitative methods. Challenges such as maintaining updated personas and managing a large number of personas are acknowledged, requiring continuous validation and collaboration to address effectively.In discerning between user personas and segmentation models, both serve distinct but complementary purposes. User personas guide product development and interface design by providing a narrative-driven understanding of user behaviors, while segmentation models offer broader market insights for strategic decision-making.By integrating user personas and segmentation models effectively, designers can foster user-centered design approaches that resonate with their target audience, ultimately driving meaningful engagement and lasting connections.Liked the insights shared in this article? Catch our previous Ask A Designer articles here:Ask A Designer: An Open Conversation with Product & UX Designers Ask A Designer Round 2: Questions For Designers, From Developers Ask A Designer Round 3: Staying Curious Ask A Designer Round 4: Considering Accessibility and Designing Inclusively Ask A Designer Round 5: The Dos and Don’ts of Design Thinking
Ask A Designer Round 6: Empathy in Design

Transform your legacy code effortlessly with RefactorX – a Generative AI-powered Code Converter.Our solution, RefactorX, converts any legacy code to your desired code, including version upgrades (like JavaScript to NodeJS). With RefactorX, you can also create technical and business level documentation regarding legacy or transformed code with an excellent search facility through existing documents and knowledge base.Innovative Use of Generative AI Utilizes advanced AI models to automate the transformation of legacy code into modern languages or updated versions.Comprehensive Transformation Suite Offers code translation, optimization, documentation generation, AI-enabled unit testing, and a knowledge management system.Targeted Solution Approach Designed to address the specific needs of industries heavily reliant on legacy systems, such as Telco, Banking, and Retail.Optimization Improves code quality and maintainability without changing its external behavior and business logic.With RefactorX 59% Increased Agility 57% Reduced Maintenance Costs 70% Better Integration with Other Platforms Watch now for a live RefactorX demo showcasing its GenAI-based approach to legacy modernization and experience efficient, error-free, and scalable code development.
Code Conversion: Modernizing Legacy Code with GenAI

Toronto, ON–May 14, 2024— mobileLIVE, a Toronto-based technology services and consulting company, was recognized for its industry-leading performance, its global business practices, and its sustained growth by receiving the prestigious 2024 Canada’s Best Managed Companies award.Celebrating over 30 years, Canada’s Best Managed Companies program awards excellence in private Canadian-owned companies with revenues of $50 million or greater. To attain the designation, companies are evaluated on their leadership in the areas of strategy, culture and commitment, capabilities, and innovation, governance and financial performance. “Being recognized as a Best Managed Platinum Club winner is a testament to our team’s relentless dedication and adaptability,” said Jahan Ali, Founder and CEO at mobileLIVE. “In an era marked by uncertainty, this achievement showcases our ability to overcome challenges and exhibit resilience at the highest levels. We are proud to set the standard for excellence in Canada’s private business sector, impacting how our country is perceived on the global stage.”Canada’s Best Managed Companies is one of the country’s leading business awards programs recognizing innovative and world-class businesses. Every year, hundreds of entrepreneurial companies compete for this designation in a rigorous and independent evaluation process. Applicants are evaluated by an independent panel of judges with representation from program sponsors and special guests.“The 2024 Best Managed winners exemplify the highest Canadian business standards of innovation, adaptability, and bold leadership,” said Lorrie King, Partner, Deloitte Private, Global Best Managed Leader and Co-Leader, Canada’s Best Managed Companies program. “Their relentless ambition, determined focus, and strategic agility have led them to remain competitive on the world stage, creating sustainable economic growth in an evolving global market.”The Best Managed assessment process is rigorous and comprehensive, evaluating a company’s overall performance and practices in areas such as strategy, leadership, innovation, culture, governance, and financials. Companies that achieve Best Managed status are recognized as industry leaders, demonstrating their commitment to long-term growth and sustainability.The 2024 cohort of Best Managed companies share common themes such as having a people-centric culture, targeting effective ESG strategies, and accelerating operational digitization.This year’s winners demonstrate exceptional commitment to drive growth in today’s competitive and dynamic business landscape,” says Blair Cowan, Executive Vice-President, Head of Commercial Banking. “CIBC is proud to sponsor a program that represents the best in Canadian business, as these privately owned companies continue to be the engine of our economic growth by creating jobs through strong leadership and innovation.”
mobileLIVE is a 2024 Winner of Canada’s Best Managed Platinum Club Designation

71% of consumers prefer brands that offer personalized experiences – and 76% get frustrated when that does not happen.The modern customer seeks a personalized experience, yet delivering it at scale is a constant challenge. In this webinar, learn beyond the foundational concepts on:Customer 360 View (with contact center data, social media analytics, and digital experience score) Discovering and Analyzing Customer Patterns (through contact channels to help decide the next best action) Personalizing Offerings and Actions (using real-time interaction management and Gen AI) Whether you’re a business leader, customer service professional, or AI enthusiast, by the end of this webinar, you will be equipped with the latest strategies, real-world examples, and industry use cases to drive customer satisfaction, engagement, and personalization.Watch now transform your customer interactions and excel in the rapidly evolving domain of customer service technology.
From Insights to Action: AI-powered Customer Experience

Design Thinking describes an approach used to solve problems in a creative and user-centric way.Sometimes, and frustratingly so, the term gets thrown around as a buzzword without an understanding of its true principles.At its core, the process is straightforward – considering your users, developing and refining ideas, seeking feedback and incorporating it into your product.In this round of “Ask a Designer,” we asked members of our design team how they navigate through the essential dos and don’ts of design thinking, and how it aids in coming up with creative solutions.Question 1How do you describe design thinking to stakeholders? Name: Viviam AlcaldeTitle: Product DesignerAnswer:A way to explain design thinking is through the initial processes of empathizing and defining before the design itself, prototyping, testing and implementation.We first need to understand the need for a solution through research and/or data, so we can identify the user pain points and then, we can try to solve those through design.It isn’t just a matter of “design this and that” only considering the initial requirements of a problem, but to understand what the users really need so we can grasp what is generating the problem. The design is just one part of a bigger process that comes after those findings.Finally, we need to continue researching to verify if the solution addresses the user needs and the problem, so we can improve or change it. If we “just design” without the other parts of the design thinking process, the time and money invested won’t be worth the effort because the problems will continue.Name: Pranavi LMKTitle: Associate Product DesignerAnswer:To ensure that stakeholders understand what Design thinking is, it is important to explain its value and potential impact on their projects or goals.Design thinking centers the problem-solving process around the end-user, producing more efficient and intuitive solutions.First, we need to understand the problem. We must put ourselves in the shoes of the user and empathize with the problem they face. This step is important to understand the user’s needs and perspectives, methods like interviews and surveys are used to gather insights.Once we understand the problem, we can define the problem statement and start coming up with ideas to solve it.The next step is to pick out the best ideas from your ideation phase and turn them into representations like wireframes, sketches, prototypes.Finally, you test your solutions with people who have the problem to see if they help. You listen to their feedback and iterate. Overall, the design thinking process will have better user satisfaction, space to innovate, and less chance to waste time and resources on creating products that do not resonate with user’s needs.Name: Carlos SalgueroTitle: Senior Product DesignerAnswer:Design thinking is a methodology that weaves empathy for the user, creativity in ideation, and rationality in systematizing the user’s needs into a viable business strategy. I describe it to stakeholders as a lens through which we view our product development process, ensuring that every feature, interaction, and design decision is made with the end-user’s experience in mind.It’s not just about aesthetics; it’s about creating solutions that are as functional and user-friendly as they are visually appealing.Name: Ram KumarasubramanianTitle: Senior UX ResearcherAnswer:Design thinking is a systematic way of solving problems. We can break down this problem-solving process roughly into two parts:Finding out what needs to be solved and for whom, and which are the bigger problems that need attention right away Among the different ways in which we could solve these problems, what approach or approaches could we take to solve the problem in a way that is meaningful for the end users and the business We do the first part by learning more about the problem and the audience through activities such as research, competitor analysis, and coming up with ‘How Might We’ questions that describe the problem in a general way without pointing to a specific solution.The second part is about brainstorming, ideation, prototyping concepts, and testing to ensure that the problems are solved in the most efficient and elegant way within the scope of the constraints present.Name: Dana MitchellTitle: Seniors Product DesignerAnswer:Designs are typically something that evolves and changes over the course of its lifecycle. Design thinking is the iterative problem-solving process that supports that growth.When I apply design thinking to a problem, my goal is to develop a deep understanding of a problem and to create solutions with that knowledge.To help facilitate this, there are an endless number of tools and methods available. From interviewing the stakeholders or users to gain a better insight into their goal and pain points, brainstorming in a Figjam session, to mapping flows and analyzing metrics and user feedback. All the tools we use allow us to approach each new problem or project knowing that we will understand the problem and iterate our way to the best solution possible.I would argue that so long as you are trying to understand your problem so you can create better solutions, you are employing design thinking (and by extension, designing) regardless of the tools you use.Question 2What do you appreciate the most within the design process? Name: Viviam AlcaldeTitle: Product DesignerAnswer:I mostly appreciate the challenge of finding a design solution from the findings we have had, because that challenge leads us to great things professionally and personally. The fact that the empathizing and defining phases structure the thinking of the design solution leads us to a different kind of art. In other types of art, we have a blank canvas (or artboard) and struggle to start – but any result could be appreciated in the end.In Product Design, many times we come up with different solutions for the same problem but not every of them will address the problem properly. The struggle is to get the best one right away, that’s why we need data and testing after we deliver our designs.Therefore, the challenge is what motivates me to explore more and question myself. It makes me humble but also proud when I can improve user experiences.Name: Pranavi LMKTitle: Associate Product DesignerAnswer:I really appreciate the process of knowing what we will be designing instead of jumping right into it. With the design process, I have a clear understanding of the user, problem and solution that I want to create.Personally, I really enjoy the ideate and prototype segment of the design process.By exploring various ideas, we can uncover unexpected insights and alternate approaches to the solution. It pushes us to think out of the box. Prototyping helps me visualize the solution I had in mind. This helps the stakeholder, client, users understand the solution better. It allows us to iterate and test giving us the best result by the end.Name: Carlos SalgueroTitle: Senior Product DesignerAnswer:What I most appreciate within the design process is the ideation phase. It’s an opportunity to diverge into a realm of creativity, brainstorming a myriad of possibilities without the constraints of feasibility, just yet.This freedom to explore often leads to innovative solutions that might not have been discovered through a linear approach. It’s a collaborative dance of creativity that, when followed by convergent phases of refinement and testing, leads to impactful designs that resonate with users.Name: Ram KumarasubramanianTitle: Senior UX ResearcherAnswer:I appreciate the challenge of fundamentally viewing problems with a beginner’s mindset in the design process – to be able to explore and understand how we could learn and address opportunities with a fresh lens and come up with different solutions depending on the context and the resources available at our disposal.The design process is, in its essence, iterative, which means there is an opportunity for improvement or change always round the corner.Name: Dana MitchellTitle: Senior Product DesignerAnswer:Within the overarching design thinking process, I appreciate how easy communication can be when everyone is on the same page. Creating and sharing project documents and knowledge keep the silo walls down.There is nothing so relieving as having a tricky flow mapped out during a conversation with stakeholders or developers, ensuring we all have the same understanding of the problem and/or solution.Question 3When shouldn’t design thinking be applied to a problem? Name: Viviam AlcaldeTitle: Product DesignerAnswer:When we already had had research and exploration with the same kind of users not long ago, or if something is “common sense” with a solution that is commonly successful.For example, we don’t need to “reinvent the wheel” and use completely new concepts of buttons or icons to refresh the page, minimize a window, expand a dropdown, among other known actions. The users in these cases are familiarized with certain icons and behaviours. That could also be applied to flows like sending a message or getting notified of a new message. We, the users in general, expect certain things from those types of experiences.Name: Pranavi LMKTitle: Associate Product DesignerAnswer:Design thinking is a great approach to problem solving, but it might not be necessary in problems that are not very complex. Design thinking requires a good amount of time and resources.If the problem you are looking to solve is small, need to sort quickly and You already know the answers to your key questions like who, what, why, you do not need to go through the entire process.Name: Carlos SalgueroTitle: Senior Product DesignerAnswer:Design thinking might not be the best approach when the problem at hand is well-defined and calls for a straightforward solution, or when there are time constraints that don’t allow for the iterative, explorative nature of the design thinking process.It’s also less suitable for situations where legal, regulatory, or safety constraints limit the scope for creativity and user-led design.Name: Ram KumarasubramanianTitle: Senior UX ResearcherAnswer:It is helpful to view design thinking through the team’s confidence about a problem and the value a feature or a product or a service might create for the end user and the business.Design thinking is often helpful in the context of meaty and complex problems, which, when solved, can improve parameters such as user satisfaction, delight and ease while contributing to the business’s bottom line.A lean research framework called ‘Sprint‘ is more relevant when design thinking needs to be applied to move the effort directionally in a short time, such as a week.Name: Dana MitchellTitle: Senior Product DesignerAnswer:I’ve literally used a design thinking mindset when I’m trying to make dinner. Have I made this dish in the past, if so, was it successful? How will I change the recipe this time? What do I want my dinner to taste like? Sure, it may only take me 5 minutes to solve the “problem”, but I’m still leveraging the iterative nature of design thinking.Question 4What is one of the biggest mistakes being made within the design thinking process? Name: Viviam AlcaldeTitle: Product DesignerAnswer:Thinking that when the design is delivered the work is done and the problem is solved.The feedback, data, and use of the solution will say if the work is done or not, and when it needs to change. Those are part of the design thinking process and when we forget about them, we aren’t doing proper design thinking.Sooner or later, we will need to change the solution because things always change requirements, problems, types of users or audiences, or even design trends.Name: Pranavi LMKTitle: Associate Product DesignerAnswer:One of the biggest mistakes that is made during the design thinking process is assuming you know the user and their needs well and jumping to the prototype/solution phase. Understanding the user and empathizing with them will help you stay relevant to the problem.Sometimes design thinking can be a long process with repetitive iterations and going around the circle over and over. You should plan out time and resources well to manage that. Empathize and define phases help you set up that plan, because you can identify the solution and can estimate the time needed to ideate, prototype and test.Name: Carlos SalgueroTitle: Senior Product DesignerAnswer:One of the biggest mistakes in the design thinking process is skipping the empathy stage and jumping straight to ideation and prototyping. Without a deep understanding of the user’s needs, pain points, and contexts, the solutions we create may be innovative but not necessarily effective or needed. It’s like trying to write a novel without knowing the main character – it results in a narrative that lacks depth and resonance.Name: Ram KumarasubramanianTitle: Senior UX ResearcherAnswer:Not involving the designers and researchers early in the process and including them only to test concepts or build designs based on ideas already set in stone. By failing to include those who might help develop a more comprehensive view of the problems that need to be solved early enough, organizations risk building things that need to be reworked.Name: Dana MitchellTitle: Senior Product DesignerAnswer:Honestly, thinking that design thinking is something that is only part of the “designer’s toolkit”. You can apply the mindset that design thinking fosters to so many different scenarios, both personally and professionally.From my work as a mentor, I would say that the biggest mistake I’ve seen is using design thinking as a specific process.It’s important to consider the why behind the tools and methods that we use, or we risk creating work that doesn’t actually help solve the problem. Not every project will need the same activities or workshops.I would argue that one of the marks of “senior-ship” in designers is being able to identify a problem and use the most appropriate tool for the job, while being able to explain why.Takeaway The insights shared by our design team members highlight the nuanced and holistic approach of design thinking.It’s evident that effective design thinking goes beyond mere aesthetics; it’s about deeply understanding user needs, empathizing with their experiences, and iterating solutions based on feedback and data. Stakeholders must grasp the value of this approach, recognizing its potential to yield efficient, user-centric solutions that resonate with end-users while aligning with business objectives.The dos and don’ts outlined underscore the importance of each phase in the design thinking process, from empathizing and defining the problem to ideating, prototyping, testing, and iterating. Skipping or rushing through any stage risks compromising the effectiveness of the solution.Moreover, design thinking shouldn’t be confined solely to designers; its principles can be applied across various domains, fostering innovation and problem-solving in diverse contexts.The discussions herein emphasize the iterative nature of design thinking and the necessity of continual refinement based on user feedback and evolving requirements. Overlooking this iterative aspect or treating design thinking as a rigid process can lead to missed opportunities and ineffective solutions.Ultimately, embracing a comprehensive understanding of design thinking as a collaborative, user-centered, and iterative approach is essential for addressing complex problems, fostering innovation, and delivering impactful solutions that meet both user needs and business objectives.Liked the insights shared in this article?Catch our previous Ask A Designer articles here: Ask A Designer: An Open Conversation with Product & UX DesignersAsk A Designer Round 2: Questions For Designers, From DevelopersAsk A Designer Round 3: Staying CuriousAsk A Designer Round 4: Considering Accessibility and Designing Inclusively
Ask A Designer Round 5: The Dos and Don’ts of Design Thinking

63% consumers expect customer service agents to know their unique needs and expectations83% customers will switch to a competitor after a frustrating customer service experience79% customer service leaders plan to invest in more AI capabilities over the next two yearsWith the increasing number of customer-facing platforms, customer expectations are also growing. Today, understanding and solving customer needs heavily depends on leveraging customer interaction data and personalizing the customer service experience.In this webinar, learn how to proactively exceed customer expectations using AI and Analytics in Customer Service.By the end of this session, you will find yourself equipped withA Deep Understanding of how predictive analytics and AI anticipate customer needs Personalization Strategies to tailor customer interactions and enhance satisfaction Real-world Case Studies showcasing successful AI and Analytics implementation Integration Strategies to seamlessly integrate AI with existing customer service systems Emerging Trends to stay ahead and secure a competitive edge for your organizationJoin AI Practice Lead Inanc Cakiroglu in conversation with host Katy Unger and harness the full power of AI and Analytics to transform your customer service strategy.
Leveraging AI and Analytics to Revolutionize the Customer Service Experience

Keeping up with the speed of AI-Innovation is overwhelming, particularly given its profound impact on industries like Telecommunications, Banking and Financial Services, Retail, Agriculture, and Manufacturing.Tailored for decision-makers, senior executives, and business and technology leaders, in this webinar, AI Practice Lead Inanc Cakiroglu showcases the What, Why, and How of upcoming AI-Enablers through practical applications and multiple use cases of:Explainable AI Neurosymbolic AI Edge AI (Cloud and 5G) Computer Image Applicable AIJoin him in conversation with host Katy Unger as they discuss actionable insights on how you can drive AI adoption and create value for your organization.
How Latest AI-Enablers Are Driving Business Impact

As product designers and teams, we often face the challenge of finding new and imaginative design solutions or rethinking existing ones.Inspiration can come from anywhere; from brainstorming with colleagues to conducting user research, there are a variety of techniques you can use to generate and develop ideas.However, while the ideation process in design thinking is critical for solving problems creatively, it can often be more time-consuming, daunting, and frustrating than expected.For this reason, having a reliable AI-supported toolkit to draw upon can vastly speed up and improve creative problem-solving outcomes.In this blog post, we’ll explore three key tools that offer great capabilities and support for the process of ideation – allowing product designers and teams to connect ideas, identify patterns, develop prototypes as well as gain insights using data analysis – so you can unlock new pathways for innovative product design.How AI Tools Are Transforming the Way We Approach Research and Ideation in the Design Process Artificial intelligence (AI) has taken the world by storm, and the design industry is no exception.In recent years, we’ve seen the introduction of AI tools that are transforming the way we approach design research and ideation.By taking advantage of machine learning algorithms, natural language processing, and other AI techniques, designers and product teams are able to leverage massive amounts of data to generate insights, uncover trends, and make informed decisions.Let’s take a closer look at how AI tools are changing the way we do research and ideation in the design process:1. Enhancing User Research User research is a crucial aspect of designing products that effectively meet the needs of the target audience.Traditionally, this involved conducting focus groups, interviews, and surveys.However, AI tools are making this process more efficient and accurate. Machine learning algorithms can analyze large sets of data to identify patterns and trends in user behaviour.Tools like Google Analytics and Hotjar use AI to help designers understand how users navigate websites and products. This insight can help teams improve usability, identify pain points, and optimize user experience.2. Streamlining Idea Generation One of the biggest challenges in the design process is coming up with innovative ideas that meet user needs and solve business problems.AI tools can help teams generate and evaluate ideas more efficiently. Idea management software like IdeaScale and Spigit use AI to automate the idea generation process.These tools can quickly analyze large amounts of data to identify trends and suggest new ideas based on user feedback.3. Automating Prototyping Prototyping is a critical phase in the design process, as it allows teams to test and validate ideas before committing to development. But creating prototypes can be time-consuming and labor-intensive.AI tools can automate aspects of the prototyping process.For example, Sketch2Code is a Microsoft tool that uses AI to convert hand-drawn sketches into working prototypes. This eliminates the need for manual coding, saving time and money.4. Augmenting Designer Creativity While AI tools can automate many aspects of the design process, they’ll never replace human creativity. However, AI can help designers augment their creative abilities.Augmented creativity systems use AI to analyze patterns in user behaviour and provide designers with suggestions and recommendations for new design directions. This allows designers to create more targeted and effective designs that are more likely to resonate with users.5. Improving Decision-Making Finally, AI tools are helping teams make more informed decisions throughout the design process. AI-powered decision support systems use algorithms to analyze data and present designers with recommendations based on that analysis. For example, Attention Insight is a tool that uses AI to help teams identify which design changes will have the greatest impact on user engagement and conversion rates.By leveraging these insights, teams can make better-informed decisions about design changes and improvements. This demo shows exactly how you can leverage Attention Insight to make more efficient and accurate design choices: Optimizing the Design Experience with User Research using Attention InsightBy automating aspects of the process and providing designers with insights and recommendations, AI is making it easier to create effective, innovative products that meet user needs and solve business problems.While there’s still an important role for human creativity and intuition in the design process, AI is helping designers work more efficiently and effectively than ever before.For design teams and product designers, AI-powered tools are quickly becoming an essential part of the toolkit, and below are three top-rated tools that help teams collaborate and execute with success.3 Tools That Need To Be Part of Your Design Ideation Toolkit 1. Notion Notion is a popular collaboration tool used by many design teams.It’s an all-in-one workspace that allows for notes, to-do lists, databases, calendars, and more.For brainstorming and ideation, Notion’s flexible workspace provides a great platform for organizing user research, sketching ideas, and collaborating with colleagues.It comes with some great capabilities in the way of brainstorming that facilitate idea sharing. Some of the things you can do with Notion include:Experience seamless collaboration on a shared document, regardless of your location. Easily provide inline comments and tag teammates. Engage in asynchronous brainstorming sessions. Share ideas within the same space as your project management tools or team homepage. Notion also integrates with various tools like Figma, Slack, and Gmail, providing an effortless workflow for design teams.2. ChatGPT ChatGPT is a powerful AI language model that can generate text-based on the prompts provided. This tool is useful for ideation because it can generate ideas based on user questions, brainstorming prompts, or even real-time feedback.It’s particularly useful for remote teams that don’t have the luxury to brainstorm together in person.ChatGPT’s intelligent algorithm is trained on vast amounts of data, making it incredibly effective at generating creative solutions.In the way of brainstorming and ideation particularly for the design process, ChatGPT stands out amongst most AI tools due to its versatility.Amongst its many benefits are:It saves a lot of time by evaluating research information and deriving key insights from it. It does competitive analysis within the context of users’ likes and dislikes. It helps with things like content strategy, storyboarding, design documentation and general guidance when working on something. It helps you set a design direction and ideate when you begin working on something new. To understand these benefits through a use case, let’s look at this example where I used ChatGPT to improve the user experience of a fitness app.Using ChatGPT to Improve the User Experience My first step was to put in some data from user research to generate key insights:The prompt I used is one answer which a user gave when asked about their experience of using a fitness app.This is helpful when you have complex and extensive information to work with. ChatGPT generated key insights, which include the pain points as well as what the user liked.Next, I wanted to know which fitness applications out there don’t have the issues mentioned above, so I gave it the following prompt:The answer I got was a list of several different real-time apps that I could look into and use as an example to make design improvements on the app I was working on, making it an extremely handy software to use when it comes to analyzing what’s out there, do a quick competitive analysis, and extract funnelled information we can use ourselves.Another great thing about ChatGPT is that you can also put in product details and design goals to brainstorm and expand on the ideation process if you’re working on a new feature, potentially uncovering some novel approaches and solutions.For example, I wanted to create a gamified experience for an online fitness coaching feature.For this, I gave it the following prompt:Remarkably, ChatGPT gave me a long list of suggestions that can be incorporated in the feature when designing it:Achievement Badges: Award users badges for reaching specific milestones in their fitness journey. For example, a “30-day Streak” badge for consistent workouts, a “Newbie” badge for beginners, or a “Master of Yoga” badge for yoga enthusiasts. Points and XP System: Implement a point system where users earn points or experience points (XP) for completing workouts, attending live classes. or hitting fitness goals. These points can be used to unlock rewards or compete on leaderboards. Leaderboards: Create leaderboards that display users’ rankings based on their XP or points. Users can compete with friends, fellow class attendees, or the community to encourage friendly competition and motivation. Virtual Challenges: Introduce virtual challenges or quests that users can participate in. For example, a “Mountain Climbing Challenge” where users virtually climb mountains as they complete workouts, earning rewards upon completion. Avatar Customization: Allow users to create and customize their fitness avatars. As users earn XP, they can unlock new outfits, equipment, or accessories to personalize their avatars. Daily or Weekly Challenges: Offer daily or weekly challenges that push users to try different workouts, such as “Core Strength Monday” or “HIIT Challenge Friday.” Completing these challenges could yield extra points. Social Integration: Enable users to connect with friends or other app users. They can challenge each other, share achievements, and provide support, creating a sense of community. In-App Currency: Introduce an in-app currency that users can earn through workouts and use to purchase virtual goods, such as workout equipment, nutrition plans, or premium features. Progress Tracking: Provide detailed statistics on users’ progress, including calories burned, time spent working out, and improvements in strength or flexibility. Visualizing progress can be motivating. 10. Leveling Up: As users earn XP. allow them to level up within the app. Each level could come with increased benefits or virtual rewards. Mystery Rewards: Occasionally surprise users with mystery rewards or power-ups they can use during workouts. This adds an element of excitement. Narrative Storytelling: Create a fitness adventure by embedding a narrative into the app. Users can progress through a story as they complete workouts, making it feel like a game. Multiplayer Workouts: Offer multiplayer workout sessions where users can compete or collaborate with others in real-time. This can make workouts more interactive and engaging. Feedback and Coaching: Provide personalized feedback and coaching based on users’ performance, helping them improve and stay motivated. Virtual Events: Host virtual fitness events, such as themed challenges, live classes with fitness experts, or charity runs, where users can participate and earn rewards. With ChatGPT, I can also make different wireframes, prototype and test all of these different solutions and feature recommendations that it provided me with.To watch my full demo explaining in detail how I use ChatGPT for my design projects, be sure to tune into this video: *embed link*3. QoQo QoQo is Figma plugin that enables design teams to maximize their productivity and quality of output by quickly benefiting from research data. It helps them save precious time and effort in the user research and discovery stage. QoQo is designed specifically for UX design and is meant to serve as a companion that helps you get a broad and organized picture at the early stages of the design process.Based on your input, it generates cards to build a persona with user goals, needs, motivations, frustrations and tasks, or it can help you identify challenges, risks and key elements for your design brief.Final Takeaway In conclusion, the ideation process is critical for identifying creative solutions to complex problems. There are various tools and techniques that can help facilitate the process.Notion, ChatGPT, QoQo are some of the most popular and effective tools for the ideation stage.Whether you choose to use one or several of these tools, it’s essential to remember that ideation is a creative process.So don’t hesitate to try new things, experiment, and explore different perspectives with your team to develop the most innovative solutions.
AI Toolkit for Creative Problem-Solving: 3 Tools to Enhance Design Ideation

Designers are faced with numerous decisions when it comes to creating visual elements in the design process, such as the colour palette, typography, layout, and more.These design choices may seem trivial, but they hold immense power in determining the success or failure of a product; the tiniest design changes can influence user behaviour and increase conversion rates, which is the end-goal with any new design.That’s why it is so critical for designers to make design choices that are driven by user research – and for that, they can harness the capabilities of AI tools in order to make efficient, accurate, and informed design decisions.In this comprehensive blog post, we will delve into three remarkable tools: Attention Insight, Maze, and Hotjar – and explore how they assist design teams and product designers in making data-driven design decisions.By leveraging these tools, designers can gain valuable insights and optimise their design choices based on concrete user research and data rather than guesswork, leading to more impactful and successful outcomes.But first, let’s dive into a bit of a background of Design Thinking and the role of design decisions.Design Thinking and the Role of Design Decisions Design thinking offers a solution-centred approach that makes it an integral part of successful product development.It involves understanding the users’ needs, challenging assumptions, and redefining problems in an attempt to identify alternative solutions that might not be immediately apparent. To reach this understanding and to get your team on the same page, you can conduct various kinds of design thinking workshops as well.A pivotal part of this process is making design decisions, which involves selecting the most appropriate design elements that will deliver a superior user experience.And as it goes without saying, the lesser uncertainty there is in these design decisions, the higher are the chances of your design being a success.For a deeper understanding on how you can reduce these uncertainties, give this article a read: Reducing Uncertainties With Design Thinking: The 7 Uncertainty IndexDesign Decision-making Before AI In the early days, these decisions were primarily driven by designers’ intuition and experience.Without the assistance of AI, designers relied on their expertise and past knowledge to make informed choices about design elements.They would analyse user feedback, conduct usability tests, and iterate on their designs to improve the user experience.While this approach was effective to some extent, it often lacked the data-driven insights and predictive capabilities that AI brings to the table.Additionally, this approach left room for subjectivity and bias, leading to designs that may not effectively address user needs or business goals.Design Decisions With AI With the advent of digital technology and AI tools, the process of design decision-making has evolved significantly.With artificial intelligence, designers now have access to sophisticated algorithms and machine learning models that can analyse vast amounts of user data, identify patterns, and make data-informed design decisions.This integration of AI in the design process has revolutionised the way user research is done and, thus, how design decisions are made, allowing for more precise and optimised user experiences.Today, design decisions are more data-driven, relying on insights gathered from user behaviour and market trends.These informed decisions lead to designs that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also functional, user-friendly, and conversion-oriented.3AI T ools To Make User-focused Design Decisions Leveraging AI tools to make user-focused design decisions is becoming increasingly crucial in today’s digital landscape.By harnessing the power of artificial intelligence, designers can gain invaluable insights into user behaviour and preferences, enabling them to create intuitive and personalized experiences.These AI tools analyse vast amounts of data, uncovering patterns and trends that might otherwise go unnoticed.The following are some of the top AI tools that employ a data-driven approach that facilitates user research and empowers designers to make informed decisions, resulting in products and services that truly resonate with their target audience.As the field of AI continues to evolve, its potential to revolutionise user-focused design is only set to grow, and these 3 AI tools are playing a big role in that:Attention Insight At the top of the list of AI tools for design decision-making is Attention Insight, which uses AI and eye-tracking technology to predict how people will interact with a design.It helps designers understand what elements of their design will attract the most attention and what parts of the design will be ignored by the users.The tool works by analysing the visual hierarchy of a design, identifying the elements that are most likely to be noticed by the user.Designers can then use this data for user research and make improvements to their designs accordingly, eventually being better equipped to optimize them for better engagement.Attention Insight is a valuable tool for anything from website design to advertising, and is quickly being adopted by designers all around for its immensely crucial benefits:Time saved: Attention Insight provides quick results in less than 60 seconds, allowing users to efficiently analyse and make design decisions without wasting valuable time. Accuracy: With an impressive accuracy score ranging from 90% to 96%, Attention Insight ensures reliable and precise insights into users’ attention and focus areas, enabling designers to create highly effective designs. Compatibility: It seamlessly integrates with Figma, a popular design tool, making it convenient for designers to incorporate eye-tracking studies and heatmaps into their design workflow. User Insights: By utilizing eye-tracking studies and heatmaps, Attention Insight offers valuable insights into where users’ attention is directed within a design. This enables designers to optimize their designs and enhance user engagement. Validity: Attention Insight is backed by MIT scientists, ensuring its validity and credibility in providing accurate and scientifically validated data for design decision making. A/B Testing with Attention Insight Particularly for A/B testing, which is a very big part of design and helps us base our decisions on data while removing the guesswork, Attention Insight is a great tool that can quickly analyze A/B Testing results.To watch this tool in action, here’s a demo that will help you see exactly how it can be used to conduct A/B tests with far more efficiency, speed, and confidence than you’d be able to without it:Maze Maze is another tool that uses AI to generate design variations.All you need to do is upload a design to Maze, and it will generate multiple design options based on the inputs provided.The tool can also learn from user feedback and generate better designs over time. In essence, Maze helps designers to create a large number of design variations in a short amount of time.One of its biggest benefits is that it scales user insights through AI-powered user research based on prototype testing, website testing, interview studies, card sorting, and feedback surveys.By doing so, Maze helps product designers save time, and it can also inspire new design ideas that otherwise may not have been considered.Hotjar Hotjar is an AI tool that helps designers understand how users interact with their design and create designs with the target audience in mind.Hotjar captures user data such as mouse movements, clicks, and scrolls, and then generates heat maps showing where users spend the most time on a page. This data helps designers understand how users are interacting with their designs, identify areas of improvement, and make data-driven design decisions.Hotjar can also provide designers with insights into user behaviour, usability issues, and potential opportunities to improve the user experience.Some of its top advantages are that it provides unbiased feedback, provides compelling data to remove any room for opinions and guesswork, and ensures that any new design created with Hotjar hit the targets without ever compromosing the user experience.Final Takeaway AI addresses many of the challenges that visual designers face.Data-driven design decisions using AI can help designers make better decisions quickly and efficiently. The tools mentioned in this post, including Attention Insight, Maze, and Hotjar, are just a few examples of the vast potential that AI has to offer for design teams and designers.Check out all of these other tools that can be used at different stages of the design process and reap various benefits in this article: AI Tools For Designers: 5 Ways To AI-Power Your Design Process.With the help of AI, designers can create designs that are more engaging, lead to more conversions, and ultimately create better user experiences.Want to learn more about how you adopt AI for your design processes? Reach out and speak to our experts now!
3 AI Tools To Conduct User Research That Drives More Optimized Design Decisions

Any product team, or design team, knows the importance of properly documenting product requirements, but the process can often be time-consuming and tedious.User stories are a crucial component of this documentation, as they outline the needs and behaviours of the user in a simple, easy-to-understand format.And while everyone wants to create better user stories, not everyone may have the know-how to do so efficiently.As most product people would be able to relate to, coming up with these user stories can be challenging, especially when dealing with complex products and various stakeholders.Luckily, there are several AI tools available to us now that can help product designers with the way they create designs efficiently.In my opinion, out of multiple AI tools that I’ve experimented with, one of them has stood out when it comes to streamlining this process and making creating user stories a breeze – and that’s ChatGPT.Understanding ChatGPT and its Role in User Story Creation ChatGPT is a chatbot that uses artificial intelligence to understand natural language and generate relevant responses.Its user-friendly interface allows product managers and designers to quickly create user stories by simply conversing with the chatbot.For example, you can tell ChatGPT something like “I need a user story for a user who wants to order a pizza online,” and it will generate a user story that fits that description.ChatGPT is also great for collaboration among team members. As each team member adds their own user stories, ChatGPT learns from this input, becoming better at generating relevant responses over time. This means that the more you use ChatGPT, the more efficient and accurate it becomes.Another key benefit of ChatGPT is its ability to organize user stories.With ChatGPT, you can create different categories and tags, making it easy to group similar user stories together and find them when you need them. This can save time and reduce the likelihood of duplicate user stories being created.The process of creating user stories with ChatGPT is simple and straightforward. After interacting with the chatbot to generate a user story, you can review and edit it within the tool’s user-friendly interface. From there, you can easily export the user stories in a variety of formats, making it easy to share them with stakeholders and collaborate with your team.Why ChatGPT is a Class Apart From Other AI Tools As product managers, we often grapple with the challenge of creating comprehensive user stories.To simplify this task, we rely on AI tools such as ChatGPT, Notion, and Perplexity.Among these, ChatGPT stands out as a preferred choice due to its ability to generate user stories quickly and accurately.Additionally, through ChatGPT, we find that we’re able to:Accelerate the user story creation process Instead of manually writing each user story from scratch, Chatgpt can generate a list of potential user stories based on conversation with the project’s stakeholders.It can then be further tailored to match the exact specifications of the project.Additionally, Chatgpt helps users to identify potential problems or unanswered questions, as well as providing suggestions for improvement that could help accelerate the user story creation process.This allows teams to focus their energies on creating better solutions faster and accelerating the production cycle.Ensure a standardized and consistent format of the user stories Chatgpt ensures a standardized and consistent format for user stories by utilizing natural language processing (NLP) technology.NLP is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that enables a computer to understand and interpret human language.With this technology, Chatgpt can process natural language input and produce output in a predefined format. This allows the system to provide users with a structured template that they can use when creating their own stories.Additionally, the system can make suggestions based on the content of the user’s story, helping them stay within the desired framework.This helps to ensure that all user stories are consistent in terms of style and structure, helping developers find user stories easier and use them more efficiently.Enhance clarity for development teams Writing user stories with ChatGPT helps enhance clarity for development teams by providing a more natural and intuitive way to describe the desired feature.By using natural language processing, chatgpt is able to analyze the input and generate a more detailed description of what needs to be done.This helps ensure that the development team understands exactly what needs to be accomplished in order to meet the customer’s needs. Additionally, this can help reduce ambiguity and misunderstanding between stakeholders, as they are all looking at the same story written in plain English.This also allows for quicker feedback loops, as developers can quickly make changes if needed without having to constantly refer back to technical documentation or business requirements documents.Ultimately, writing user stories with ChatGPT can provide development teams with a clear direction and help them deliver high-quality features faster.Stay more efficient and user-focused ChatGPT allows us to quickly and easily create detailed specifications for product features.Because the user stories are created using natural language, it is easier for product people and designers to quickly understand what users are expecting from a particular feature, since the language used is similar to what they would use in conversation with their customers.This allows product teams to focus on building the right product experience in the most efficient way possible, rather than spending too much time trying to interpret customer feedback or deciphering complicated technical requirements.Additionally, ChatGPT helps reduce friction in the design process by providing ready-made templates that help designers complete tasks faster, while ensuring that all user stories accurately reflect customer needs.How Does ChatGPT Improve the User Story Creation Process: Learning with an Example To dive into how each of the above outcomes can be achieved with ChatGPT, let’s take the following as a user story creation example:You’re a product manager tasked with developing a new feature for a mobile shopping app that enables users to create and share wish lists.With the help of ChatGPT, you can effortlessly generate the necessary user stories to build this functionality.You also have the flexibility to generate multiple user stories with all the required details simultaneously.This not only saves time but also enhances clarity for development teams. By streamlining the user story creation process, product managers can focus more on user-centric tasks and improve overall efficiency.To explain how ChatGPT accomplishes this, the following is a demo I’ve done to showcase how I used the tool to create a user story for a new feature for a hypothetical shopping app that allows users to create and share wish lists.*embed full video of demo*Going Beyond Story Writing: Acceptance Criteria, Risks, and Mitigation Strategies ChatGPT goes beyond just user story writing to also provide acceptance criteria, potential risks associated with the user story, and mitigation strategies to minimize those risks.This is a great thing for product designers because it allows them to clearly define what they expect from each user story and anticipate any potential problems before deploying the product.By including acceptance criteria, designers are able to identify specific requirements so that the product meets customer expectations.With potential risks identified in advance, designers can plan a strategy to mitigate those risks and make sure that the product remains stable and secure.In addition, if any unexpected issues arise during development, the mitigation strategies can be used as a reference in order to take corrective action.All of this helps designers create products that meet users’ needs while minimizing risk and increasing stability, which is why it’s so critical to nail the storyboarding process right from the beginning.For a quick refresher on exactly what user stories are, what all they encapsulate, why they’re essential, and how product designers go about creating them, be sure to check out this article: Storyboarding in UX Design: Learning the What, When, Why, and How.Final Thoughts In conclusion, ChatGPT is a game-changer as a user story creation tool.Its ability to generate relevant responses quickly, learn from team input, and organize user stories efficiently makes the process of documenting product requirements much more efficient and manageable.By using ChatGPT, product teams and design teams can save time and hassle while creating high-quality product documentation that accurately reflects user needs.Give ChatGPT a try and see how it transforms your user story creation process.Got any questions or want to discuss this further? Speak to our experts here!
Leveraging AI For Product Documentation: How ChatGPT Enhances User Story Writing

Maximizing Business Outcomes Through AI Adoption

Take a minute and think about your favourite service that you interact with.When I say service, I’m referring to the journey or process of getting a task accomplished, not necessarily getting a good as the end product but achieving a desired task. Uber, Amazon Prime, Netflix are all examples of services that people like you and I regularly interact with.As per this definition, a lot of businesses we see today are at the middle of goods and services.The end outcome may be a physical product, but the journey of getting that product and all the interactions in between, whether they’re digital or physical, all come under the service.So, where does Service Design fit into this?A Background of Service DesignAccording to the Nielsen Norman Group, "Service design is the activity of planning and organizing a business's resources (people, props, and processes) in order to directly improve the employee's experience, and indirectly, the customer's experience."Primarily termed by a marketing executive back in 1982, Service Design initially came about as the idea that every service, every product, or everything that we’re building right now is a service.However, this interpretation of Service Design got lost in the midst of the Dot Com Bubble — in this era, everybody was all about digital design and product design, and usability became core to it all.The current world that we live in is an amalgamation of the physical and digital.And in the realm of the digital world, we often don’t get to see the people and processes that are working behind the scenes.That’s where Service Design comes in, encapsulating the entire process, end to end.What is Service Design?Service design is a relatively new discipline that has gained significant recognition in recent years, especially in the context of technology, user experience (UX), and customer experience (CX) design.Essentially, service design is the process of creating, optimizing, and innovating services that cater to the needs and expectations of customers and users alike.The goal of service design is simple, yet complex – to design and deliver services that are effective, efficient, engaging, and enjoyable for everyone involved.In this blog post, we’ll explore the fundamentals of service design, including its core components, scope, methods, and benefits.More specifically, we’ll discuss the three key components of service design – people, props, and processes – and how they interact to create a seamless service experience.We’ll also delve into the scope of service design, including the concept of frontstage and backstage operations.Service Design: The Fundamental ConceptService design, as mentioned earlier, is the process of designing or redesigning services to improve the overall user or customer experience.This process involves a deep understanding of the customers’ needs, preferences, pain points, and motivations.Service design is also about identifying and mapping the various touchpoints, interactions, and processes involved in delivering a service from start to finish.Service design is an iterative process that involves researching, ideating, testing, and refining various aspects of a service.For instance, a service designer may use various design thinking tools and techniques to identify and create personas, customer journey maps, service blueprints, and prototypes.The goal is to create a cohesive and comprehensive service experience that meets (or exceeds) the expectations of the customers.The Three Components of Service DesignAt a high level, Service Design is composed of three major components:People: Any person who creates, uses or interacts with the service or service ecosystem Props: Any physical or digital touchpoints, artifacts needed to execute the Service Process: Any workflows, procedures, or rituals performed by either the employee or the user throughout a service These three components interact with each other to create a seamless service experience for the customers.PeopleThe people component of service design refers to the customers, users, and staff involved in the service delivery. Service designers need to understand the needs and motivations of each stakeholder involved in the service journey to ensure that the overall experience is positive. This could involve interviewing customers, observing staff, or conducting surveys to gather insights.PropsThe props component of service design includes all of the physical and digital elements involved in delivering a service, such as the website, mobile app, signage, furniture, equipment, etc. These elements play a crucial role in shaping the user’s perception of the service and can greatly impact the overall experience. Service designers must ensure that all props are designed to be functional, aesthetically pleasing, and easy to use.ProcessesThe processes component of service design includes all of the steps involved in delivering a service, from the customer’s point of view. This could include the ordering process, the payment process, the delivery process, etc. Service designers must ensure that the service processes are easy to understand, efficient, and effective. They should also design processes that are flexible and can adapt to the changing needs of the customers.The Scope of Service DesignThe scope of service design can be divided into two broad categories – frontstage and backstage.Frontstage refers to all of the activities that the customers can see or experience directly, such as the website, the mobile app, the physical store, or the call center.Backstage, on the other hand, refers to all of the activities that are not visible to the customers, such as the inventory management, the logistics, or the administrative tasks.Service designers must take into account both the frontstage and backstage activities to create a cohesive service experience.They should design processes, systems, and strategies that enable effective coordination between the stakeholders involved in the service delivery. This can involve optimizing workflows, enhancing communication channels, and streamlining operations between different teams or departments.What is Service Blueprinting and Why You Need ItService blueprinting is a tool used by service designers to map out the various touchpoints, interactions, and processes involved in delivering a service. A service blueprint is essentially a visual representation of the service journey, from the customer’s perspective. It includes different layers that help service designers identify pain points, opportunities, and areas for improvement.Service blueprinting typically includes five key layers:The customer journey: This layer includes the different stages involved in the service journey, from the customer’s point of view.Frontstage actions: This layer includes all of the activities that the customers can see or experience directly, such as the website, the mobile app, or the physical store.Backstage actions: This layer includes all of the activities that are not visible to the customers, such as the inventory management, the logistics, or the administrative tasks.Support processes: This layer includes the supporting processes that enable service delivery, such as internal communication channels, workflows, and standard operating procedures.Physical evidence: This layer includes all of the physical and digital elements involved in delivering a service, such as signage, furniture, equipment, or branding materials.Service designers can use service blueprinting to identify areas where the service is falling short or where improvements can be made. This can lead to a better overall customer experience and more efficient service delivery.UX Vs. CX Vs. SDUX (user experience) and CX (customer experience) are two terms that are often used interchangeably with service design.While there are similarities between these disciplines, they are not the same thing.UX focuses on the user’s interaction with a particular product or service, whereas CX focuses on the customer’s overall perception of a brand or company.Service design, on the other hand, is focused on the end-to-end service experience, including all of the touchpoints, interactions, and processes involved in delivering a service.Service design can be seen as an umbrella term that encompasses both UX and CX. This is because service designers need to take into account both the user’s interaction with the service (UX) and the customer’s perception of the service (CX) to create a seamless service experience.Final TakeawayService design is a multidisciplinary and iterative process that involves deep research, ideation, testing, and refinement.By understanding the three key components of service design (people, props, processes), the scope of service design (from frontstage to backstage), and the basics of service blueprinting, service designers can create a service experience that is effective, efficient, engaging, and enjoyable for everyone involved.Service design is a highly collaborative and customer-oriented approach that can lead to increased customer satisfaction, retention, and loyalty, as well as reduced costs and improved efficiency for the service provider.As such, it’s a valuable tool that can benefit a wide range of industries, from healthcare to finance to retail.
The Fundamentals of Service Design: An Introductory Crash Course

As system management becomes increasingly complex, effective monitoring tools are more important than ever.Enter Prometheus and Grafana – a dynamic duo for anyone concerned with system observability.The combination of these popular tools offer a comprehensive ecosystem for monitoring, alerting, and data visualization, providing valuable insights into the health and performance of your systems.Prometheus is an open-source monitoring and alerting system that excels at collecting and storing time-series data, while Grafana is a powerful visualization and dashboarding tool.Together, they provide a comprehensive solution for monitoring, visualizing, and alerting on the performance and health of systems and applications.This guide will walk you through the process of integrating these tools into your system management strategy, offering practical solutions to commonly faced challenges like data overload, lack of real-time visibility, and complex system diagnostics.These crowd favorites form a powerhouse that can handle monitoring, alerting, and data visualization, truly serving as a lifeline to complex system management challenges.Armed with this guide, you'll gain the ability to detect issues swiftly and respond to them effectively, thereby enhancing the overall reliability of your systems.What is Prometheus?A Go-based open source monitoring programme called Prometheus gathers metrics data and saves it in a time series database. It was created by SoundCloud at the beginning in 2012, then in 2016 it joined the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF). PromQL, a potent query language, is used to query your time series data.Prometheus is a core technology for monitoring and observability of systems, but the term “Prometheus” can be confusing because it is used in different contexts. Understanding Prometheus basics, why it’s valuable for system observability, and how users use it in practice will both help you better understand it and help you use Grafana.Features of PrometheusData Model and Query Language Time-Series Database Data Collection Service Discovery Alerting and Notification Visualization and Dashboards Scalability and Federation Reliability and High Availability Pull and Push Models How PromQL HelpsThe functional query language known as PromQL, or Prometheus Query Language, enables you to choose and aggregate time series data. With its flexibility and strength, you can manipulate your data however you see fit.For example, if you want to retrieve CPU usage metric from a target named "my_app", you would use this:cpu_usage{job="my_app"}What is Grafana?Grafana is an open-source tool for executing data analytics with the aid of metrics that, when combined with scalable dashboards, provide us an understanding of the intricate infrastructure and vast amounts of data that our services handle.Every data source imaginable, including Graphite, Prometheus, Influx DB, ElasticSearch, MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc., is connected to by Grafana.As an alternative, we may create our own custom plugins to link with any data source of our choosing thanks to the open-source nature of the solution.Technically known as time series analytics, the technology aids in the study, analysis, and monitoring of data over a period of time.By providing pertinent data, it enables us to track user behavior, application behavior, the frequency of problems occurring in production, pre-production, or any other environment, the sort of faults occurring, and contextual settings.Features of GrafanaDashboard Templating Provisioning Annotations Kiosk mode and playlists Custom plugins Alerting and alert hooks Permissions and multiple teams SQL Databases Monitoring your monitoring AuthenticationUnderstanding the Grafana DashboardThe dashboards draw their information from connected data sources like Graphite, Prometheus, Influx DB, ElasticSearch, MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc. These are just a few of the numerous data sources that Grafana by default supports.The dashboards have a wide range of visualization options, including the many charts and graphs and geo maps, heat maps, histograms, and other visualizations that a business generally needs to analyze data.On the grid of the dashboard, there are numerous separate individual panels. There are many functionalities for each panel.Getting started with Prometheus and GrafanaAfter installing Prometheus and Grafana, you need to set Prometheus as the data source in Grafana and you can do that using the following steps:Click on the Grafana logo to open the sidebar. Click on “Data Sources” in the sidebar. Choose “Add New”. Select “Prometheus” as the data source. Set the Prometheus server URL Click “Add” to test the connection and to save the new data source. Why use Prometheus and Grafana?There are many reasons why the combination of Prometheus and Grafana can prove to be very powerful when integrated correctly into your systems.For starters, you have control over the metrics you want to report, their origin, and their destination when Prometheus and Grafana Agent are used together.Once the data is in Grafana, a Grafana Mimir database can be used to store it. The combination allows you to monitor and visualize the health and performance of your systems comprehensively, making it easier to detect issues and respond to them effectively.TakeawayOverall, Prometheus and Grafana are popular tools that provide a robust ecosystem for monitoring, alerting, and visualization, making them valuable assets in maintaining the reliability of your systems.The additional functionality of PromQL further enhances the value delivered by this combination, offering granular control over metrics and data.With the ability to accurately monitor health and performance, respond to issues effectively, and visualize data in an intuitive manner, these tools become instrumental in ensuring system reliability.Their power rests in their flexibility, scalability, and the profound insights they provide, making them a game-changer in the landscape of system administration and data analysis.
Mastering System Monitoring with Prometheus and Grafana: Your Handy Guide

We’ve all heard the news: AI is taking the world by storm.As a designer, one would think it to be a grave threat to our profession, as artificial intelligence (AI) is also very much capable of executing creative work.In a lot of ways, AI carries out creative tasks up to some extent that humans have also been doing, if not beyond that.So it’s not hard to notice the potential that AI has to replace human-dependent jobs.In the field of UX Design, however, AI is not likely to take over fully.In fact, from what I’ve learned and observed while using AI tools in my design process, I’ve realized that AI can act as a co-pilot that can enhance our products while working.If you look at the AI tools for designers out there, in particular those that are both image and text generation tools, designers have found that they’re not always very accurate and often require human judgment.With that being said, there’s no reason not to make use of AI tools; they can do wonders in terms of acting as an aid to super-charge your design process.In this article, I share my findings from my first-hand investigation into AI tools for designers and implementing them to boost different stages of the design process.Requirement Analysis Project requirements are integral to the design process, and this is one big area where using digital tools like Notion can be very beneficial.On its own, Notion is a great tool for documentation and project management.But we’ve only gotten to really see its super-charged potential ever since the integration of AI.With AI, Notion has turned into a powerhouse, enabling you to carry out a plethora of tasks with your document, like:Summarizing a requirement document Generating user stories Finding action items Improving your writing (you can even change the language or the overall tone of your writing) Once you have all of these documented and generated, you can put them in a separate file so you can look at it at another time in the future.User Research We’re all familiar with OpenAI’s ChatGPT.This AI model can be used for various aspects of user research for design, including:User Personas Empathy Maps Competitive Analysis Storyboarding Information Architecture Let’s take an example that I worked on:By providing the right prompts, I was able to generate a user persona for someone who frequently uses food delivery apps.ChatGPT provided detailed information about the persona’s demographics, goals, pain points, and behaviors.It also helped with empathy mapping, competitive analysis, and even created a basic layout for the information architecture of the food delivery application.To delve deeper into the user’s pain points, I asked AI to elaborate on the pain points of users who use food delivery applications. The information provided was insightful and could be stored for future reference.Next, I also wanted to also do some competitive analysis.So, I asked the AI model, and the results it popped were able to explain to me how popular food delivery products work, with examples like UberEats, DoorDash, GrubHub, Postmates, and Seamless.In case of storyboarding, while ChatGPT cannot give you image results, it gives you information in frames, and different frames have different illustrations of what the user does while interacting with an application.Through text, ChatGPT gives you a rough direction of what each frame in a storyboard would look like.One con, however, of this model is that it lacks contextual knowledge.So even if you generate such information, you have to take a close look at it and modify it according to your project.Wireframes Wireframe designer is a plugin that is integrated in Figma and allows you to generate wireframes based on prompts.As an example, I asked it to generate the wireframe for the homepage of a food delivery application, and while the result was a bit unconventional (we don’t see many homepages in food delivery applications where there’s a banner on top and different categories of the items available in the menu), it stood out as different.What this example shows us is that this is definitely a step in the future, and wireframes and design generation from text can be way more accurate.Speaking of which, another tool called User ID lets you create wireframes from your paper scripts and sketches directly, and makes them editable (although, they cannot be imported in Figma.High Fidelity Design As we move into high fidelity design, there is another tool called Auto Designer that also lets you create high quality screens from prompts — and they’re highly editable.Just like Figma, this tool is also very collaborative.If you look at the basics of high fidelity design (the layout, spacing, and the structure of your pages), those are all things you have to manage yourself and can’t rely on AI to handle. This is where the creativity gap lies between humans and AI: AI lacks the creative input that is so vital to the design process.Another AI tool that is particularly helpful with the coloring part of the process. is Chroma.Chroma is an AI tool that generates color palettes, and their combination with text.On the platform, you can select colors of your choice and the AI tool will train its model over the colors you select.Finally, the tool gives you the results in the form of color palettes and color swatches with text as well.This is a very interactive tool that lets you swap through colors, get a lot of inspiration, and add them as favorites to add in your high fidelity design. ,Testing Once the high-fidelity design is ready, tools like the Attention Insight plugin in Figma can provide valuable insights.The plugin creates a heat map and a focus map for the screen, showing where users are likely to focus more.This offers valuable insight and information that can be used to make necessary amendments in your design as needed.Takeaway AI tools for designers, although not flawless, can substantially improve your design process.They can serve as an initial point, offer inspiration, and even carry out tasks that save designers valuable time.What AI is definitely not is a substitute for human discernment and creativity.Designers must still scrutinize and fine-tune the results from these tools to ensure they align with the project’s needs and standards.Ultimately, AI tools for designers are just that – tools. They are here to assist us, not supplant us, in our creative endeavors.
AI Tools For Designers: 5 Ways To AI-Power Your Design Process

In the midst of ever-increasing competition, the need to deliver high-quality products is now more critical than ever.And while product quality has always been an essential factor in any industry or field, the aftermath of the pandemic has led to shorter attention spans, meaning it only takes a split second for users to develop an opinion about a website and decide whether to wait or switch over to a competitor.Eventually, the responsibility falls on QA analysts’ shoulders: are they doing enough to achieve a seamless customer experience?The importance of product quality is not lost on us. But are test automation engineers — or anyone involved with QA — doing enough?As a way of improving the efficiency of manual testing, Intelligent Automation Testing came as the new (and quite popular) solution — and for the right reasons.Why Use Automation Testing? The reason why Automation Testing arose in popularity is evident: it saves time, costs, and the human effort to sift through multiple application screens and manually compare the results of various input combinations.On top of that, recording each result manually and conducting the tests repeatedly is a hassle that test automation engineers have gladly replaced with automation testing tools that do the work for them.To put it precisely, Test Automation is the means to achieve bigger, better, and faster QA. Watch this video on QA Test Automation to take a deeper dive into what automation testing can achieve.But all said and done, despite the benefits and opportunities that come with automation testing, it seems that there’s still a need for a better, even more intelligent solution.And the reason why is simple: Automation Testing hasn’t fully delivered on its promise to streamline modern software delivery.Instead, it comes with its own set of challenges, and even created more bottlenecks. Let’s see how.Challenges with Automation Testing Assume you’re working for a mid-sized company that’s still young and undergoing the designing phase of their processes and protocols.All while simultaneously trying to deliver a good quality product.Let’s say you’re hired to automate their regression suite to ensure nothing breaks during delivery. Test automation engineers will mostly be seen designing and writing programs that will run the automated tests on the software.So, you start writing the test cases and immediately identify the lack of best practices followed while developing the product (in this case, the test-ids).Now you have two options:Ask the team to update the code to include the test-ids (which we know will probably never happen), or Work with whatever you have. So you continue writing test cases that, from the get-go, are built to be flaky and possibly flawed.Fast forward, you have a few tests in the pipeline regularly failing — not due to the actual issues in the product but the use of highly dubious selectors.As a result, you end up putting in a lot of your effort, time and company resources into maintaining the tests and fixing them while you could’ve spent it trying to attain an ample percentage of test coverage.Whether you admit it or not, this is what all of us “Automation Testers” have experienced at least once in our careers. It changes our mindset and diverts us from writing a test that would rather ‘Pass’ than ‘Fail’ while finding an actual bug in the product.Clearly, the amount of maintenance effort required in automation testing takes up more time — and more importantly, distracts you from the true results you want to achieve.So, what can be done instead?Enter: Autonomous Testing.What is Autonomous Testing? To put it simply, Autonomous Testing is the next, enhanced version of automation testing.Think about the number of tests you’d have to write for testing each browser in a different OS setting and on many other devices (desktop, mobile, tablets), and then debugging the individual issues.Autonomous Testing removes the hassle and stress of maintenance so that you can focus on the single most important goal of QA testing automation: the ability to simply pass the test by writing one with ample test coverage, and identifying new bugs while you’re at it.As the name clearly suggests, if Autonomous Testing is adopted by test automation engineers, they’d be responsible for less manual work like maintenance and debugging (since testing tools provide the Root cause analysis of the bug, you don’t have to debug manually). This is a win-win situation for everyone involved.And how does Autonomous Testing offer this capability? It brings AI into test automation.How Can Artificial Intelligence Be Used in Automation Testing? AI-based visual test automation offers the ability to identify the root cause of a specific problem, pointing developers to the exact piece of code to be fixed.It introduces the autonomy that lets test engineers focus their attention and energy on attaining more test coverage rather than on writing hundreds of lines of code to validate just how the website visually looks.In the past, we have seen some solutions to overcome this bottleneck of visual testing in test automation. These came in the shape of Pixel and DOM differences validation.But still, there is a downside: both of these have some limitations that don’t translate well into the ideology of Autonomous Testing.This gap gave birth to Visual AI — and Visual Artificial Intelligence Testing.What is Visual Artificial Intelligence? Visual AI is simply artificial intelligence technology being able to see what humans see — and intelligently make visual understanding of what it sees to make decisions and carry out commands accordingly.And as far as web/app automation testing goes, this is a hugely revolutionizing facility for UI automation testing.What is Visual UI testing? In web development, visual UI testing works by running visual tests that detect, analyze, and compare various visual elements of a website or application. By doing so, it ensures that the look and feel of the page is as per the design, and whether or not the required element sections are displayed on the page.Many tools in the industry claim to be the ultimate solution offering visual UI testing, but in my opinion, Applitools and Percy are both at the top, owing to their easy-to-follow starter kits and sufficient documentation found on their websites to help get you started.In this tutorial, we’ll look at Applitools in motion, and you’ll learn how you can set it up and use it to implement intelligent automation testing on your websites/application for visual UI testing.Setting Up Visual AI For UI Automation Testing To conduct UI testing, be it for web or app automation testing, visual AI will prove to be an integral part of the process.To integrate AI in test automation, you want to use automation testing tools that can seamlessly adapt and work with your existing QA testing automation framework.In this tutorial, we’ll be using Applitools with Cypress.(Note: Applitools supports nearly every other popular front-end testing framework. You can find one that you prefer here).For the sake of this tutorial, we’ll be working with a Cypress framework, assuming you have it and know how it works. (If you don’t, let us know and we’ll help you set it up.)Let’s get right into it.Step 1 Install & setup Applitools using the following commands:Step 2 Add the global configuration for your visual tests in the root folder:applitools.config.jsStep 3 First, follow the steps to find your Applitools API key and set it as environment variable APPLITOOLS_API_KEY before running the visual test.There are two options: either set it through your IDE or use the following command:For Mac & Unix:For Windows:Step 4 Design your test.demo.cy.jsReplace the URL in cy.visit() with your web-site/page.Step 5 Execute the sample test using the following command:After your tests run, you should see results in the Applitools Eyes Test Manager dashboard, which will look something like this:Command for executing the sample test in the visual AI test automation toolThe first highlighted column displays the status, and as this is the first build, there is nothing there to compare it with — hence the status “New”. The second column highlights all the devices and viewports we globally set for our visual tests in Step 2. In terms of setting up the visual artificial intelligence testing too, this is pretty much all of it.But let’s rerun the same test and see what happens.Execute the same “run” command again.This time, the dashboard will display this:Rerunning the tests. The automation testing dashboard now shows a 'Passed' status.The tests have the status ‘Passed’ because there is no visual change between the latest web page and the baseline saved in the last build.Now let’s see what happens in the case of a visual change.Add the following code to your test file demo.cy.js after the cy.visit() command.Save and rerun the test. The dashboard will now look like this:Changes in the status when running the automation testing due to a visual change.This time, since there was a visual change, the initial status was ‘Unresolved’ as it wasn’t sure if the changes detected were expected. Therefore, it lets users decide for the first time whether to pass or fail the build.Based on your response, the baseline image will be updated. In addition to this, you can:View the root-cause analysis for the identified difference Create a bug Add a remark Toggle between baseline & current build Highlight the identified difference Specify a portion of the page that will be ignored and won’t be checked for any visual changes And the list continues..From this point onwards, it’s just about adding more and more layers to the AI-based test automation process based on your preferences; add the visual tests in your CI/CD pipeline or integrate Slack to get test results instantly — the world is your oyster.Takeaway While we do have cutting-edge ML/AI technologies weaving their way into the software testing and development process, independently, they’re still not enough.There is still a pressing need to implement best practices, introduce formulated processes, and educate the community accordingly to utilize and understand the real power of using AI in test automation.Revolutionary methods and approaches like Hyper-Automation (which also largely uses AI to automate multiple IT processes) are bound to be more beneficial than risky as we move into the future. To learn how you can overcome E2E complexity with Hyper-Automation, watch this video here.But what can be said with a lot of certainty is that Autonomous Testing is the future we’re looking at — and it only makes sense to start adapting these trends today that will be the new norms tomorrow.
Using Visual AI in Test Automation: A 5-Step Tutorial For Autonomous Testing

Being digitally native presents young companies with a predominant advantage over large corporations:Being able to quickly implement, scale and steer innovative technologies tomaximize profitability through experience, and minimize the time to market. With the advent of intelligent technologies, many startups have managed to leverage their overall growth through personalization strategies.This raises an alarming concern for large corporations:Will they ever be able to match up with digitally native companies in terms of speed of customer experience adaption and enhancement?To answer this question, we need to dive into how Hyper-Personalization in the customer experience strategy can be achieved for large-scale organizations.Evolution of Hyper-PersonalizationThe era of Industry 1.0 was all about mass production.Only quality and quantity mattered. Customer experience was the last priority when it came to budgeting activities.Then, things started to change: customers wanted differentiation and value addition on top of what they were paying for the product. This gave birth to branding.Brands started to market the value addition of their products and created unique propositions to attract customers. Factories started mass customization of products to facilitate various brands from the same assembly line. Some of the innovative companies started to invest heavily in categorizing customers based on their needs. This segmentation approach enabled the brands to customize products as desired by that customer segment.But this wasn’t enough.There were still several untapped customers whose needs were not being fulfilled through basic consumer categorization.In turn, micro-segmentation was born, which let companies tap into more variables related to consumer preferences, buying behavior and interests.With advancements towards the digital era, this approach saw further changes, to the extent that now, customers expect brands to know them at their very first interaction.Today, most customers prefer to purchase from brands that offer personalized experiences. And, more often than not, they will respond to the brand’s marketing messages only if they feel those messages are crafted to their needs.Personalization Vs Hyper-PersonalizationHyper-Personalization is personalization on steroids.In customer experience strategy, ‘personalization’ itself is technically based on contextual data that is used to tailor the experience as per the customer’s need through trend analysis of that particular customer (or the segment to which the customer belongs).On the other hand, hyper-personalization factors in real-time customer data, weighs fresh insights with historical data, and then tailors the experience as per customer preference — and that too in real-time.In essence, hyper-personalization is personalization powered with artificial intelligence to analyze, predict, and service the customer in real-time.Implementing Hyper-Personalization in Your Customer Experience StrategyAs simple as the idea sounds of offering the right experience to the right customer and adjusting according to the next predicted customer action, its actual implementation requires an entire ecosystem modernization.On the whole, the implementation of such a hyper-personalized customer experience strategy may seem like an impossible task, but adequate strategic evaluation of the transformation and prioritizing right will help achieve maximum value as you go about the complete overhaul.1. Evaluate existing digital ecosystemLarge-scale companies that have processes and systems working successfully for many years are least likely to swiftly energize the effort towards hyper-personalization.The biggest challenge is replacing legacy platforms to cloud-based ecosystems. Without the free flow of data in a scalable ecosystem, real-time customer insights cannot be fully utilized.However, from a strategic viewpoint, the long-term benefits of customer engagement (topline revenues, reduced churn, and low cost of superior customer servicing) outweigh the costs involved in the short-term.Just by experimenting with some hyper-personalized customer experience journeys, many organizations start to realize the need for advanced intelligent customer systems.Key Actions:Instead of considering the short-term business case for hyper-personalization in the customer experience strategy, evaluate the benefits for 3+ years. Evaluate the existing customer experience journey across multiple channels against the value garnered through intelligent automated servicing, personalized cross-selling, and marketing. 2. Centralized customer profilingCompanies with a diversified portfolio of products face challenges in sharing customer insights at scale.Such siloed insights are only useful for a particular product, leading to a nightmare for businesses that miss out on the cross-sell opportunities and customer servicing without a centralized customer system. An omnichannel customer experience strategy will just cover the needs of the customer experience journey and fail to predict the next action the customer is going to perform.Complete customer profiling can be achieved through both quantitative data (big data mining) and qualitative data (customer research) and can be combined to form powerful insights for your customer experience strategy.Customer interaction for research has to become a governed process that helps in capturing the emotional elements associated with a product and the brand. Through such a centralized customer profiling system, all channels can benefit from any of the products that the company can has to offer. This system can then be designed to make adjustments in customer profiles automatically through new data.Key Actions:Quantitative customer data alone is not enough. A combination with qualitative customer data will help develop the most impactful customer profile. Operations of such a centralized customer profiling system can become a costly nightmare. Design it to intelligently and automatically adjust profiles based on new events. 3. Using AI to Power Up the Customer Personalization StrategyPersonalization strategies get the companies to a point where they are able to offer the experience based on contextual data.With advancements in artificial intelligence, companies can now capture real-time customer behavior, mix it with the captured emotional state of the customer, and adapt to a serving, selling or retaining mode.There are many customer and channel-related use cases that the brand can use to maximize value by providing the desired customer experience and changing the experience focus in real-time:a) Customer action prediction: Gives the ability to assess the next action the customer is going to perform and display the right message on any particular channel.b) Channel attention prediction: Predicts the customer touchpoint traffic and process glitches, and automatically triggers a suitable response.c) Natural Language Processing: Enables real-time interaction analysis to extract the most relevant insights from any live interaction. Its use can range from gauging the emotional state of the customer through speech analytics to evaluating the propensity to churn through keyword extraction.d) Interaction Assist: Enables the company’s human resources to assist in creating a personalized and pleasant interaction in real-time.Keeping the customer interaction humanized and personalized with the backing of AI is itself an evolving process where interconnected systems like CRM, product catalog, complaint management system, order tracking and others work in harmony.Key Action:Initiate the implementation of your CX strategy by enabling AI to assist human resources by converting ambiguous data into useful insights during the customer interaction. Making this a part of the customer experience strategy will set the pace for the overall transformation. 4. Connected design systemsWhen large-scale organizations aggressively adapt to digital strategies, the design processes and repositories usually lie in silos across multiple divisions of the company.This creates an inherent challenge in reusability of design systems.Not only should these design systems be interconnected, but a free flow of information regarding design principles, libraries, practices and guidelines should be integrated at a cultural level across the organization.To attain maximum benefits from the customer experience strategy, the system should be sufficiently agile to quickly adapt to changing customer needs for both new and existing products.Key Actions:Strongly bind design systems to maintain experience harmony across the product portfolio. Structured flow of design information across the departments should be made a cultural value of the organization. 5. Hyper-personalized content strategyScattered product catalogs and content management systems are one of the biggest challenges of large-scale organizations, especially if the company offers a diversity in products.A centralized product and content catalog becomes the one and only true source of all product-related information to offer a personalized experience in terms of pricing, customer messaging, tailored content generation, and personalized promotions.This system is then actively utilized across all customer touchpoints and with predictive AI, it provides the opportunity to offer the right product at the right time to the right customer to maximize the chances of conversion.The importance of making this a part of the customer experience strategy is further realized by observing customer behaviours:Every 3 in 4 customers will get frustrated if they are shown products that are not relevant to them, and most expect the brands to only recommend products that are relevant to them.Key Action:Personalized product recommendation with the right key message across multiple channels is by far the most attractive experience for customers. Therefore, it should be made an integral part of the customer experience strategy. 6. Automate at scaleAs the AI ecosystem grows with more tools, it will consume more resources.Automation and simplicity of both quantitative and qualitative data collection should be made part of the transformation strategy. The ecosystem should be robust enough to self-correct itself by absorbing data from both internal and external sources.Additionally, automation can also be utilized for activities like content generation, product personalization and customer servicing that constitute an integral part of the overall customer experience strategy.Key Action:Make automation part of the AI transformation strategy. TakeawayFrom a strategic viewpoint, a hyper personalized customer experience strategy may seem like a complete overhaul of the existing ecosystem.In reality, organizations start by creating analytics-driven customer experience to maximize personalization opportunities.Once the practice of data-driven personalization is established, they start introducing bits of AI into facilitating the brand’s human resources towards preferred customer recommendations.Finally, they synergize automation, analytics, and AI in the overall customer experience strategy to offer a wholesome hyper-personalized, omnichannel customer experience at all touchpoints in both marketing and customer servicing.To achieve success in personalized customer experiences, hyper-personalization of your customer experience strategy serves as a revolution to the way large organizations analyze, understand and serve their customers in real-time.FAQsWhat is the hyper-personalization model?The hyper-personalization model uses AI, automation, and analytics to analyze, predict, and service the customer using real-time data on customer behaviours.What is the difference between personalization and customization?Personalization is when you analyze customer data to create a product or add modifications to it that meet your customers’ needs. Customization is what changes the customer makes to the product to meet their specific requirements.
Leveraging AI and Beyond: 6 Customer Experience Strategies For Hyper-Personalization

Unless you have been hiding under a rock, the odds are that you have heard about the fascinating world of Artificial Intelligence and the transformational impact it is going to have on our lives. Certain parts of the euphoria remind us of the dot-com bubble from the ‘90s – when the technology hype hit its peak. There seems to be intense excitement at all levels, from CEOs and analysts to grassroots developers; all are expecting Artificial Intelligence, or AI technology, to not only dramatically change our lives but the world. Well, we really can’t blame them, given all the excitement created by the billions of dollars being invested in the Artificial Intelligence domain. With all the stars perfectly aligned, perhaps it is best to “peel the onion” a little bit in hopes of gaining a better understanding of what AI really is, why now and why all the hype, and how AI technology and AI companies can dramatically change the Telecom Industry landscape, in particular.What is Artificial Intelligence and why the hype now? AI is essentially humans teaching machines how to learn and mimic their intellect.Quite like a toddler- who learns by experience, constantly absorbing information, decoding it and understanding patterns – we feed machines huge amounts of data that create their own algorithms and constantly tweak them to meet their objectives. Over time the program gets smarter and very human-like, i.e., less artificial and more intelligent.ICT & big dataDuring the past few years, some factors have led to AI technology coming closer to unleashing its true potential – mainly, a ton of data becoming available along with faster GPUs for processing it.With billions of things getting connected to the web, there is a tsunami of information being generated. Since the dawn of time until 2004, around 5 exabytes of information have been created and captured. To put that visually, try and imagine a stack of books that spans from earth all the way to Pluto and back 80 times over. Impressive, certainly, but over the last decade, the amount of data being captured has exploded with 90 percent of the world’s collective data reportedly being generated in the past two years alone. And now thanks to advances in processing speeds, computers can make sense of all this information faster and more efficiently.Because of this, tech giants and VCs are pumping the market with cash and new applications and investing into AI companies. China alone has already invested $109BN in this space, and the race between countries is heating up. The reason being that 15-20 percent of the global GDP is forecasted to be linked to AI-related industries by 2025! Mind numbing, isn’t it?IoT solutions1100+ New startups raised 1st equity since 2016, $15.2B Equity funding in 2017 alone, a 141% jump from the previous year, 300+ Companies entered incubations in 2017, 3x more than 2016. Source: CBInsights How is Artificial Intelligence different from Predictive Analytics and Big Data? Are there financial benefits of investing in all three? Often, people inquire what is the difference between Big Data, Predictive Analytics, and Machine Learning. They want to have the ability to differentiate between the three to ensure adequate allocation of resources and to set right expectations with all the stakeholders..Big Data: Collection of “data sets” which are large, complex, and difficult to process using on-hand database management tools.Predictive Analytics: Practice of extracting information from existing data sets in order to determine patterns and accurately predict future outcomes, trends, and behaviour.Machine Learning: Machines performing tasks that normally require human intelligence (visual perception, decision-making, learning, etc.). This takes into account the entire context of the situation.big data analysisIn a nutshell, creating Big Data lakes for gleaning insights and learning is the foundation in which all corporations must invest. Using Machine Learning, the self-learning engine to unlock value from the data, organizations can then extract insights, predict outcomes, and perform human-like tasks. Investment in all three, i.e., Big Data, Predictive Analytics, and Machine Learning is quickly being elevated to table stakes. Business and IT teams need to work “hand in glove” to prioritize the required output. On the inverse, we have found that working in isolation leads to converting the proverbial haystack into a bunch of needles rather than finding the one insight which is critical to business.Should we bet on AI and Robotic Process Automation (RPA)? Everyone seems to be deploying them, should we invest in them now? These, my dear Watson, are the wrong questions to be asking! The metaphorical cart is coming before the horse, if you would. The correct question should be, “How do I use technology to solve my business problem quickly and efficiently?”First, however, let’s dive into both RPA and AI to distinguish the two. The goal is to bridge the journey from Human to Digital labour in the most efficient way. Given the pressures on the bottom line, “Digital Labour” is no longer a consideration, rather, a mandate for most companies across the world. RPA and AI are the two unique sets of tools used to traverse the journey from one end of the spectrum to the other, i.e., Digital Labour = Cognitive Computing (AI) + RPA (Digital work).Robotic Process AutomationBasic RPA consists of automating entry-level transactional, rule-based and repeatable processes. It involves working with structured data and within well-defined parameters in order for the bots to complete the tasks autonomously. However, digital labour is automation driven by self-learning and adaptive technologies. It involves self-learning, digestion of super data sets, hypothesis generation, and evidence-based learning. All fun stuff!Most companies and businesses we speak to love the concept of AI and want to jump right into it. However, it is a journey of realization, meaning you need to ask yourself some questions first. What really are the use cases? Can you articulate the pain points? Can you clearly quantify benefits to help determine whether AI and/or automation is necessary? It is then that collectively decided on which is the best course of action and implementation.What are the telecom specific use cases of AI technology? What are the financial benefits? The telecom industry is at a crossroads. No other industry is driven as much by bits and bytes while at the same time faces disintermediating challenges for the same reasons. Business models are changing, customer expectations and behaviour are constantly evolving, legacy economics and paradigms are becoming untenable. This is why 2014 was the first year when the total global revenue of telcos had marginally negative growth. From then on, every investor relations call is bombarded with questions on increasing revenue, reducing OPEX and CAPEX, and here is where AI technology opens up an opportunity for AI companies.Capital Reduction ($10-12 BN savings over a decade)Between the three telcos in Canada, the collective annual capital spend is ~$10BN to grow and sustain their respective networks. Using this run rate would peg the capital spending over the next decade to be at ~$100BN, even when not taking into consideration a spike of an estimated 40 percent due to an increased spend on 5G and fibre deployments.Given that the lifecycle of technologies has reduced considerably – CDMA lasted 25 years, HSPA possibly 10, and LTE even less. It’s time to recuperate that investment cycle is reducing. In the meanwhile, cost of electronics has gone down, and most of the capital effort is spent on the optimization of networks and installation.At last count, 70 percent of capital cost to upgrade from one technology to another was spent on labour and infrastructure, and only 30 percent on the actual OEM related electronics. That would technically peg the telcos as infrastructure players, vis-à-vis, a pure play telco. However, AI and other combinatorial techs can be leveraged to reduce that labour cost for optimization significantly. A lot of the OEMs have started providing their own software for SON (Self Optimizing Networks), but that would really be akin to asking the wolves guard the sheep. Telcos need to have their POV and build on it over time, to ensure basic hygiene and best practices are kept in-house. Also, predicting usage of subscribers by geography and ensuring the network is dimensioned correctly will not be done on the side of the desk of engineers, rather, through deep scenario analysis and planning, considering all parameters. Lastly, optimization of spectrum auction pricing can be done using game theory and decision trees. Given the appetite of operators to spend billions on it, we expect a healthy dose of AI to be used to save thousands of consultant hours and save millions (if not billions) of dollars in the process.We estimate at least 10-15 percent ($10BN) of the capital envelope can be reduced using cognitive technologies holistically across the process.OPEX Reduction ($3-5BN savings over a decade)Predictive Maintenance: The ability to fix problems with telecom hardware (such as cell towers, power lines, etc) before they happen and by detecting signals that usually lead to failure. This significantly reduces downtime and dramatically improves Customer Experience and churn metrics.Video Analysis: Instead of sending field workers to check on-site hardware periodically, AT&T has invested heavily in drones and in AI to analyze video data captured, which proactively raises flags for the field team to go in and fix issues.Self-Driving Networks: In the future it’s likely that governments might ban humans from driving cars as it is a reckless or unnecessarily risky activity. Similarly, there is no reason why we shouldn’t be done away with the Network Engineers! A perfect world really would be where networks would run themselves; away from our grubby, inefficient hands. This provides an opportunity for cost-cutting and efficiency gains. Ideally, we should not need so much staff to manage operator networks. A lightly staffed network powered by an economical but sophisticated AI will look more desirable than ever. That is truly aspirational today, but something to work towards.Customer Service ChatBots: Every telco customer calls in four times a year at an average cost of $15/call for password resets, billing inquiries, or changing plan details. This OPEX of ~$2BN/year across the three operators can be dramatically slashed by using chatbots which are equipped to do the same. Automating 10-15 percent of the customer service inquiries, routing customers to the proper agent, and routing prospects with buying intent directly to salespeople will make a material impact on the bottom line! Further, leveraging NLP, sentiment analysis and text to speech virtual customer service agents could be used to replace humans, with the customer not being able to distinguish one from the other. That could be a tangible reality in 5-10 years’ time; taking the cost down from $15 to 15 cents per call.Speech and Voice Services for Customers: Allowing customers to browse, explore, and buy content by spoken word rather than remote control (e.g., DISH network and Amazon’s Alexa partnership).Security and Fraud: Detect fraudulent activity in credit-card transactions or identifying web traffic to the website and customers, looking to exploit network and infrastructure vulnerabilities.Revenue Enhancement I algorithms can help combine historic patterns, psychographic analysis and behaviour (plus “look-alike” patterns) with ongoing real-time engagement to provide relevant, targeted, contextual experiences for consumers. The outcome will be upselling recommendations and offers, helping improve the conversion rate of offers, and enabling incremental wallet share. The same algorithms could be potentially leveraged to predict subscribers willingness to pay a particular price for a product, estimate product price elasticities, and quantify sales leads likelihood to close.How do we tackle AI as an organization? How much investment is required? It is best to use a good framework to get the ball rolling organization-wide. Some frameworks that we have used in the past include:Cognitive strategyCognitive StrategyHost an innovative workshop that showcases the potential of cognitive discovery, With perceived value in the forefront, identify, and rank use cases, Who? How? What? Dive into the current state of the use cases while being sure to include areas for improvement (scale, errors, non-blue etc.), Present a finalized cognitive strategy to key stakeholders for approval based on prioritised use cases.Detailed AssesmentDetermine detailed use cases and a variety of scenarios, Establish concrete user personas of user on the cognitive automation platform, Define content source(s), type of content, system interactions and integrations required, and system of record, Determine what operational requirements are needed to support the solution (Operational Management, Operational Reporting etc.), For training and configuration purposes, identify all required attributes and level of content annotationsSizing and Investment CaseEstablish criteria to estimate the beneficial impact on the organization, Determine the size of this potential business benefit – both quantifiable and non-quantifiable, Establish a high-level solution concept overview, Estimate the required investment required, Detailed solution blueprint, Build and train, Deploy and maintain, Confirm and validate benefit of investment case with key stakeholders, Conclude investment case for approval and fundingWe understand that AI can be intimidating and complicated, which is why we encourage you to engage us for a better understanding of the foundational capabilities, needed to get an AI program up and running. From building use cases, decision-making paradigms, economic impact analysis, choosing governance model and platforms to be deployed, we have gone through the process a few times. Every business is unique; we look forward to learning more about your specific needs to determine how we can accelerate your digital transformation.
From Self-Driving Cars to Self-Driving Networks: Rise of AI in Telecom

The more enriched an experience, the more dopamine is released into our brain and more profound is the interactivity associated with it. The feel-good factor or the user experience (UX) of any product, platform or service is the quintessential key to deliver a prolonged and definitive image of the brand in the mind of the customer. But how we create that indelible mark in the user’s mind or what technological advancements will lead to enhance the effect, undoubtedly needs our attention as we progress towards the UX of tomorrow. Can artificial intelligence lead Chatbots distinctly be the buddies in changing the future of UX?Let me first take you through what is at the heart of past and present UX paradigms, what has made the UX of yesterday and today successful, and what technologies have been employed in realizing it.Cave drawings, tapestries and even written manuscripts provided a UX, wherein storytellers, oracles and poets would “hard-code” their messages. These technologies were to take a life of their own through the ages, with abstract content engaging its audience’s imagination through reflection and thought. Whether sculpted, drawn or written, its purpose was to convey an intended natural meaning, even when done so artificially in hindsight.Progressive Advancement in UX With the advent of modern computing in the 20th century, engineers attempted to “hard-code” computers to interact with users. It was limited and primitive by today’s standards, but it was something new! Even when projecting into a fictional future, HAL 9000 from Space Odyssey, the original Robocop, and Star Trek’s LCARS voice interface were deliberately designed to sound and feel mechanized. They meant to convey a sense of artificiality to the viewers of the 60’s through 90’s, and for a good reason. Human-machine interface grabbed attention of that era’s audience simply by the virtue of novelty; it needed to be dichotomized from human-human interaction.However, with the changing times, it is not the same today where the term “AI” is taken for granted. We have moved along in our expectations of what AI should be capable of. Today’s chatbots and Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems – therefore – are not meant to sound or feel mechanized and boring. They actively engage users by sounding more “human.” And it will be far more interesting in the immediate future. That will be the time of ontology in its truest form, where intelligent systems will actively drive the user, and not the other way around!We are soon entering the age of evolved chatbot customer experience that will concurrently span a multitude of modalities – not (just) text. It will rely on voice interaction, mixed-reality graphics, gestures, and cybernetic interfaces, all topped by AI concurrently performing linguistic and behavioural analyses. Undoubtedly it would be a truly enriched and immersive user experience that will know how to grab the user’s attention at will.A Time of Multimode User Interaction Now that we are steadily stepping onto the time of ontology, with intelligent systems driving the user to take his/her decisions, it’s time to audit and learn how certain existing content presentation techniques, UI designs, and UX methods might stand the test of time. And the role advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Augmented/Mixed Reality (AR/MR) will play in harnessing their true potential.Human language, when textualized, is just one mode of communication. Advances in Natural Language Processing (NLP) have made great strides within this modality. Supervised machine learning techniques, such as Support Vector Machines (SVMs) can now extract relevant information from text if trained to do so for a given set of contexts (domains.)By introducing Neural Networks and Deep Learning techniques, NLP systems can even be made to classify the intent more holistically – and in a limited fashion can readily uncover the underlying sentiment behind the textualized content as well.Deep Learning and natural language processingBody language, tone of voice and selective vocal emphasis are still additional modes of communication that needs consideration. These added modalities can provide far greater cues into the intent and meaning behind linguistic expression. Recently, two teams from Nanyang Technological University of Singapore, Carnegie Mellon University in the USA, and Instituto Politecnico Nacional de Mexico have independently published research papers validating the methods and practical efficacy of Multimodal Sentiment Analysis (MSA) by adding information from video and audio content along with established NLP techniques. And it is the author’s opinion that MSA will gain considerable traction in terms of the practical application of NLP in chatbots.NLP in chatbotsFurthermore, incorporating physiological biometrics to this analysis (e.g. either non-intrusively or using wearables) can make machine learning systems even more effective and efficient. For instance, adding heart rate, voice fluctuations, and posture can provide substantial information about the user’s intent. Adding these subtle modalities can propel an interactive AI much closer to realizing true ontology; to not just do what the user seemingly asked for, but what the user may actually have wanted or needed.An Era of On-Demand Mixed Reality Even in current times, people tend to own more than one device and can switch between them part-way through their task. Studies have shown that up to quarter of users can switch to a tablet from their smartphone and more than half switch to a laptop midway through any given activity. With the advent of new and more creative tools, it is only reasonable to expect that omnichannel UX will require absolute consistency in the age of multi-device use-cases.UX therefore will not be limited to a simple “flat 2D screen” interaction but rather involve AR/MR as is the case with devices such as Microsoft’s Hololens. AR/MR computing platforms will need to include any given device they identify, and interoperate with it at run time. Therefore, such platforms will have the capability to recognize and connect to environmental sensors when entering a room, or identify and interact at run time with smart outdoor cameras for enhancing the user’s perceptual UX. Individual applications will not need to re-implement any lower-level interfaces and would bring in a fine seamless interaction for the user.game scenario of Microsoft HololensPhoto by Microsoft / CC BY 2.0 However, simply immersing a user into graphically rich, and detailed contextual content may not be enough to keep them engaged in the long haul. Can you quickly recall the mechanized voices of fictional AI’s of the 60’s-90’s? Agreed, they sound boring by today’s standards – but were novel and “hip” during their respective eras. The same may be the eventual aftermath of AR or MR once the “novelty honeymoon” is over. To ensure that the users truly benefit and remain engaged, humanizing the digital experience will be as necessary tomorrow as it is today for UX and UI, and more.Humankind’s initial experimentation with the art of myth and storytelling, though synthetic, is in fact the oldest known technique to share experiences through analogy. It is this technique, that remains at the heart of humanizing the digital UX. With the abundance of content existing on the web, being different will continue to be critical. Creating a story around a given product and inviting users to become a part of it might be the easiest way to engage them. Perhaps, in the era of MR/AR, such storytelling will be of vital importance to let the user immerse into the experience – thereby staying engaged throughout the UX.Conversational interfaces may also prove invaluable in engaging the user to intuitively access content and assist in decision making. Currently, such interfaces, or UI – though effective – are limited to text- or voice-based chatbots. However, conversational interaction for AR or MR will be fundamentally different due to the enriched content rendered within an arbitrary 3D space. Free from the confines of a 2D “flatland,” UX of the future will demand digital content to be more than what is currently accessed over the web. UX designers and engineers alike will need to prepare AI for verbal, as well as cues to interact with the users via augmented reality or mixed reality; not just by displaying audible or visual content, but by introducing key micro-interactions through evolutionary storyboarding that trigger the user’s active thought process.game scenario of Microsoft HololensCombining conversational paradigms and on-demand storytelling to create engaging UX will require an abundance of information processing power and storage capacity, whether onboard an AR/MR device, or distributed across a network of devices and appliances. And certainly, it will require substantial content generated at run-time in addition to existing pre-processed and raw data. The key demand for businesses and social networks of the future will be in how to restructure and optimize their content and UI experiences so that it is served readily through AR/MR interfaces. It will not just be flat UI, image and text on a website; but disparate content and metadata that can be rendered on-demand in the form of virtual objects within an augmented voxel space as part of a storytelling experience through AR or MR.Artificial Intelligence Personified Let’s take a closer look at how content and data served through various AI led technologies will change the perspective of UX designers, budding technology entrepreneurs as well as mature technology professionals’ understanding of the UX and its future. We have already witnessed the explosion of chatbots and smart machines within the market due to their versatile applicability in implementing conversational AI. App fatigue may further fuel the growth of chatbot assistants – so as to delegate sifting through apps and content based on their utility for a user’s specific personality, needs, and habits. Additional drivers in favour of chatbots are top brands who are directly integrating them into their customer experience channels starting from direct marketing through customer service and support, to direct sales – thereby increasing efficiency.Business and social websites too publish their Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) collectively. Yet they also include chatbots to fetch the underlying content from a single source on demand structured data repository within a Content Management System (CMS). However, such hard-coded content may not necessarily connect with users in a way that a natural dialogue would. In an age, where we are rapidly advancing towards conversational commerce, businesses and individuals alike will need to ensure that they are ahead of the game in capturing their audience. This can only be achieved if they can repurpose abstract information to generate responses from raw data – not such that AI chatbots create their own language – but that they are capable of dialogue with their audience to connect at a personal level.game scenario of Microsoft HololensHowever, such chatbots – might always be tainted with the perception of bias towards the business they are designed to generate. Instead of succumbing to the business of bots, users of tomorrow will demand independent aggregator assistant bots not linked to a single platform, but capable of automatically analyzing the user’s needs, all available products and services, their price and value, and act as an advisory assistant without vendor bias. Development and productizing of such “untethered” buddy chatbots are the next big opportunity for the start-ups and businesses of today.Enhancement of the resulting UX can be exponential if additional modalities are included within the user interaction. Consider that upcoming trends for UX point to the proliferation of AR/MR in the immediate future.Putting it all Together In the pursuit of advancement, we forget sometimes what really drives the technological continuum. As social beings, we do not really embrace technology for technology’s sake. We do so to enrich our interactivity and enhance our experiences. It is no secret therefore, that the more targeted and emotionally uplifting the UX and UI, the more rewarding is its perception by the human brain. Only then is it able to capture a user’s attention and imagination – irrespective of technology used to create that UX or UI design.In the coming years, it will become even more important for product and UX or UI designers to include the “human” element. In the next few years, conversations are the next layer of UX and user interaction. Chatbots in their current state might not be able to handle the required complexities arising from the expectations of today’s users. Advances in machine learning have certainly improved the adaptability of current chatbots in the UX. But the art of storytelling dependent heavily on contextual nuances and creativity are still very much beyond the scope of current technology. In the age of conversational commerce, it will become crucial to consider the dynamics of natural conversational dialogue, and impartiality of presented information to truly capture the attention of the user.how artificial intelligence helps human robot interactionThe future of UX will indeed be extremely interesting for those of us who witness it in full swing. With a rich plethora of immersive content, interactive UI designs, and customized experiences available on-demand and with additional advances in human-machine interfaces to directly link the human brain to information access peripherals, such interactions can eventually become part of the user’s active thought process. But until a time, humans practically become cyborgs, “un-tethered” buddy chatbots rendered as human-like guides within AR/MR environments may act as the user’s “inner voice” so as to assist in decision-making – via conversational discourse as well as through micro interactions in the UX journey. Perhaps taking the form of the user’s own “mirror image” to look and sound familiar, or that of the user’s idol so as to be more convincing, such personifications of AI, with help from augmented reality or mixed reality, may be key to the UX of tomorrow.Want to learn more? Let’s talk
Buddy Chatbots, AR/MR, and UX: the User Experience of Tomorrow

Customer experience transformation is a multifaceted process that relies on various factors, including:Channel optimization, Systems/technology enhancement, and Customer journey transformation. By focusing on these key areas, businesses can create a holistic approach to improving customer experiences.In this comprehensive deep-dive article, we will delve into each of these elements, providing insightful details and practical strategies to help organizations drive meaningful changes in their customer experience initiatives.By understanding the importance of channel optimization, leveraging advanced systems and technology, and reimagining the customer journey, companies can unlock new opportunities for growth and establish a competitive edge in the market.Keep reading as we explore these crucial aspects and uncover the secrets to delivering exceptional customer experiences.A. Channel Transformation: Enhancing Customer Touchpoints1. Call CenterSmart Agent SchedulingEffective agent scheduling ensures the right agents with the appropriate skills are available to handle customer inquiries. By leveraging data analytics and forecasting algorithms, organizations can optimize agent schedules, minimize wait times, and improve customer satisfaction.Smart Agent RoutingSmart agent routing utilizes intelligent algorithms to route customer queries to the most suitable agent based on factors such as language proficiency, expertise, and customer history. This ensures customers are connected to the right resource, leading to faster resolutions and improved customer experience.Priority CallingImplementing priority calling mechanisms allows organizations to prioritize urgent or high-value customer calls. By assigning appropriate priority levels, critical issues can be addressed promptly, resulting in improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.First Touch ResolutionFirst touch resolution focuses on resolving customer issues during the initial interaction, eliminating the need for follow-up contacts. By empowering agents with comprehensive knowledge bases, streamlined processes, and decision support tools, organizations can enhance their ability to resolve issues promptly, minimizing customer effort and improving satisfaction.Call Center OutsourcingOutsourcing call center operations can be a strategic decision to enhance scalability, cost-efficiency, and expertise. Organizations can partner with specialized service providers to ensure round-the-clock availability, multilingual support, and access to advanced technologies.AHT Insights & OptimizationAverage Handling Time (AHT) insights and optimization involve analyzing and streamlining call center processes to reduce call duration while maintaining service quality. By leveraging analytics, organizations can identify bottlenecks, automate repetitive tasks, and enhance agent productivity, leading to shorter call durations and improved efficiency.Agent EmpowermentEmpowering agents with the right tools and resources is crucial for delivering exceptional customer experiences. Key components of agent empowerment include agent effort scoring.Agent Effort ScoringAgent effort scoring measures the effort required by agents to resolve customer issues. By assessing the complexity of tasks and providing relevant tools and training, organizations can reduce agent effort and improve their ability to deliver efficient and effective solutions.AI Fraud Detection & PreventionIntegrating AI-powered fraud detection systems within call centers helps identify and prevent fraudulent activities, protecting both customers and the organization. Advanced algorithms analyze patterns, detect anomalies, and provide real-time alerts to agents, enhancing security and trust.2. Self-careWeb & AppOffering intuitive web and mobile applications enables customers to access self-service options, manage their accounts, and resolve basic queries independently. User-friendly interfaces, personalized content, and seamless integration with backend systems contribute to an enhanced self-service experience.Digital IVRDigital Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems leverage natural language processing and speech recognition technologies to enable customers to interact with automated systems in a conversational manner. This streamlines self-service processes and reduces customer effort.Centralized Real Time Complaint Management SystemA centralized complaint management system consolidates customer complaints and requests, providing a unified view for agents and enabling effective tracking, resolution, and analysis of customer issues. This helps organizations identify recurring problems and implement targeted improvements.Digital Kiosks & VendingDigital kiosks and vending machines provide convenient self-service options in physical locations, such as retail stores or service centers. Customers can perform tasks like bill payments, SIM card issuance, and device troubleshooting independently, reducing queues and enhancing the overall in-store experience:Financial Self-ServeFinancial self-serve options enable customers to manage their account balances, make payments, and view transaction histories through self-service channels. This empowers customers with greater control over their financial interactions, reducing reliance on manual assistance.GSM Self-ServeGSM self-serve capabilities allow customers to perform SIM card-related tasks, such as activation, deactivation, and plan changes, through self-service channels. This reduces the need for customer care interventions and enhances convenience.SIM Issuance and ReplacementStreamlining the process of SIM card issuance and replacement through self-service kiosks or vending machines reduces wait times and improves the overall customer experience.3. Walk-InPhysical Experience ManagementPhysical experience management focuses on optimizing the in-store experience for customers. It includes factors such as store layout, signage, staff training, and wait-time management, ensuring a pleasant and efficient in-person interaction.Self-Serve ExperienceProviding self-service options in physical stores, such as self-checkout counters or information kiosks, allows customers to independently access information and perform transactions, reducing reliance on staff and enhancing convenience.4. IVRVoice BiometricsVoice biometrics enable secure customer authentication by analyzing unique voice patterns. This eliminates the need for customers to remember passwords or answer security questions, streamlining the IVR authentication process and enhancing security.Speech Recognition - Speech to TextSpeech recognition technology converts customer speech into text, enabling automated transcription and analysis of IVR interactions. This helps organizations identify customer sentiments, extract valuable insights, and identify areas for improvement.Personalized IVRPersonalized IVR experiences leverage customer data and preferences to tailor IVR menus and prompts according to individual needs. This minimizes customer effort, speeds up call routing, and improves overall satisfaction.5. Social MediaSocial Media ListeningSocial media listening involves monitoring social media channels to understand customer sentiment, identify emerging trends, and promptly respond to customer queries or concerns. This real-time feedback enables organizations to proactively address customer issues and engage in meaningful conversations.Smart Lead GenerationSocial media platforms provide opportunities for lead generation through targeted advertising, content marketing, and social engagement. By leveraging data analytics and machine learning algorithms, organizations can identify and engage with potential customers, driving business growth.Sentiment AnalysisSentiment analysis analyzes social media posts and comments to determine the sentiment associated with a brand, product, or service. This helps organizations gauge customer perceptions, identify areas for improvement, and develop effective strategies to enhance the overall customer experience.Social Media AutomationAutomation tools facilitate efficient management of social media interactions, including content scheduling, response automation, and sentiment tracking. These tools enable organizations to scale their social media presence and deliver timely and consistent customer engagement.6. Smart BotVirtual AssistanceVirtual assistants, powered by artificial intelligence and natural language processing, provide automated support to customers across multiple channels. They can handle routine queries, provide personalized recommendations, and guide customers through self-service processes, improving efficiency and convenience.AI-Powered Contextual ChatContextual chatbots use AI algorithms to understand customer intent, provide relevant responses, and engage in natural, context-aware conversations. This creates a more interactive and personalized customer experience, mimicking human-like interactions.Social OTT CentralizationSocial OTT (Over-The-Top) centralization integrates various messaging platforms, such as WhatsApp or Facebook Messenger, into a unified customer communication platform. This streamlines customer interactions, allowing agents to respond to messages from multiple platforms in a centralized manner.B. Systems Transformation: Enhancing Operational Efficiency1. Centralized Product CatalogA centralized product catalog consolidates product and service information, enabling consistent and accurate offerings across multiple channels. This simplifies product management, reduces errors, and ensures a seamless customer experience.2. Service Order ManagementService order management systems streamline the end-to-end process of fulfilling customer requests, from order placement to delivery and activation. This improves order accuracy, reduces processing times, and enhances the overall service experience.3. Connect Knowledge Management SystemA connect knowledge management system provides a centralized repository of product information, troubleshooting guides, and FAQs. This equips customer care agents with accurate and up-to-date knowledge, enabling efficient issue resolution and ensuring consistent customer support.4. Zero Touch Operations100% Auto Help Request Processing - Zero Touch HelpZero touch help aims to automate the handling of customer requests without requiring manual intervention. Through intelligent automation, organizations can enable self-healing systems, self-service options, and AI-powered resolutions, minimizing the need for human involvement.RPARobotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive and rule-based tasks by utilizing software robots. By deploying RPA in backend processes, organizations can enhance operational efficiency, reduce errors, and accelerate response times.Smart Service UpdatesSmart service updates leverage machine learning and predictive analytics to proactively identify potential service disruptions or outages. This allows organizations to provide timely notifications to customers, manage expectations, and minimize the impact on the customer experience.5. IntegrationsNetworkIntegrating customer experience transformation initiatives with the network infrastructure enables proactive monitoring, self-healing capabilities, and personalized service delivery. This ensures a seamless experience for customers and reduces the likelihood of service disruptions.BSS - CRM, Charging Billing, Product Catalog, Order ManagementIntegration of these systems enables end-to-end visibility and process automation. This integration facilitates accurate billing, personalized offers, and seamless order fulfillment while enabling one-window view for the customer agents as well.6. Agent ProgramAgent TrainingComprehensive agent training programs equip customer care agents with the necessary skills, product knowledge, and communication techniques to deliver exceptional customer experiences. Continuous training and upskilling ensure agents stay updated with evolving customer expectations.Agent Screening & RecruitmentImplementing robust screening and recruitment processes helps identify candidates with the right aptitude and customer-centric mindset. By selecting agents who align with the organization's values and objectives, organizations can build a customer-centric workforce.Agent Target Setting and MeasurementSetting clear performance targets and measuring key metrics, such as average handling time, first contact resolution, and customer satisfaction, ensures accountability and enables continuous improvement. Regular performance evaluations and feedback sessions further drive agent excellence.Smart Real-Time NotificationsReal-time notifications provide agents with contextual information, updates, and relevant customer insights during interactions. This empowers agents to deliver personalized and informed responses, enhancing the overall customer experience.7. Crowdsourcing PlatformTestingCrowdsourcing testing initiatives involve leveraging a pool of external testers to validate new features, identify bugs, and provide feedback on the customer experience. This accelerates the testing process and ensures a robust and error-free product launch.Content GenerationCrowdsourcing content generation allows customers to contribute reviews, ratings, and user-generated content, such as tutorials or troubleshooting guides. This fosters a sense of community, provides authentic information, and enhances the overall customer experience.Innovation & IdeasCrowdsourcing innovation and ideas involve gathering suggestions and feedback from customers to drive product and service improvements. By involving customers in the innovation process, organizations can align their offerings with customer needs and preferences.Customer 2 Customer (C2C) ServicingCustomer 2 Customer (C2C) servicing leverages the power of the customer community to provide support and assistance to fellow customers. This peer-to-peer support network allows customers to share their knowledge, experiences, and solutions, fostering a sense of collaboration and empowering customers to help each other.8. Customer Profiling SystemUpsell AnalyticsA customer profiling system utilizes data analytics to identify opportunities for upselling and cross-selling. By analyzing customer behavior, preferences, and purchase history, organizations can personalize offers and recommendations, increasing revenue and customer satisfaction.Churn Prediction and ManagementChurn prediction models use historical data and predictive analytics to identify customers at risk of churn. By proactively targeting these customers with retention strategies, organizations can reduce churn rates and preserve valuable customer relationships.Next Best OfferNext best offer algorithms analyze customer data and preferences to determine the most relevant and personalized offers for each customer. This enables organizations to deliver targeted promotions and recommendations, increasing customer engagement and loyalty.Loyalty EngineA loyalty engine consolidates customer loyalty programs, rewards, and incentives into a unified platform. By implementing gamification elements, personalized offers, and tiered reward structures, organizations can foster customer loyalty and advocacy.9. One View/One WindowAgent Virtual AssistantAn agent virtual assistant provides real-time insights, recommendations, and suggested actions to support customer care agents during interactions. By leveraging AI and machine learning, agents can access relevant information and resources efficiently, improving their productivity and effectiveness.UI Design Revamp for AgentRevamping the user interface (UI) design for agent-facing systems ensures a seamless and intuitive experience for customer care agents. User-centric design principles, streamlined workflows, and easy access to information empower agents to deliver efficient and personalized customer support.KMS Driven Information ArchitectureA knowledge management system (KMS) driven information architecture organizes and structures information in a way that facilitates easy access and retrieval for both customers and agents. This ensures consistency, accuracy, and quick resolution of customer queries and issues.C. Customer Journey Transformation: Fostering End-to-End Experiences1. GovernanceVoice of Customer ForumA voice of customer forum serves as a platform for capturing customer feedback, suggestions, and insights. By actively listening to customer voices, organizations can identify pain points, prioritize improvements, and align their strategies with customer expectations.2. Omni-Channel Experience EnablementOmni-channel experience enablement focuses on providing consistent and seamless experiences across all customer touchpoints, whether digital or physical. By integrating channels and data, organizations can deliver personalized and contextually relevant interactions throughout the customer journey.3. Digital Channels Journey RevampRevamping digital channels involves optimizing websites, mobile apps, and other digital touchpoints to enhance usability, navigation, and overall user experience. This ensures a frictionless and engaging digital journey for customers.4. Physical Channels Journey RevampRevamping physical channels, such as retail stores or service centers, involves reimagining the customer journey, enhancing in-store experiences, and providing seamless transitions between digital and physical touchpoints. This creates a unified and consistent customer experience.5. Channel Servicing Analytics & InsightsChannel servicing analytics and insights involve leveraging data and analytics to understand customer behavior, preferences, and interactions across various channels. This enables organizations to optimize channel performance, personalize experiences, and drive customer satisfaction.6. Customer ResearchCustomer Integration LabA customer integration lab serves as a dedicated space to test and validate customer experience initiatives, prototypes, and new features. By involving customers in the design and development process, organizations can ensure that their offerings meet customer needs and expectations.Customer Integration ProcessThe customer integration process involves engaging customers in co-creation sessions, surveys, interviews, and feedback loops. This collaborative approach helps organizations gain valuable insights, validate ideas, and build customer-centric solutions.Customer RecruitmentStrategic customer recruitment ensures the inclusion of diverse customer segments and personas in research and testing activities. By representing the customer base accurately, organizations can gain comprehensive insights and design experiences that cater to different customer needs.Organization Design Thinking MindsetAdopting a design thinking mindset across the organization fosters a culture of innovation, empathy, and customer-centricity. This involves encouraging cross-functional collaboration, embracing iterative problem-solving, and valuing customer feedback throughout the organization.7. Auto CSAT, NPS Process & InsightsAutomating the customer satisfaction (CSAT) and Net Promoter Score (NPS) processes enables organizations to collect feedback, measure customer sentiment, and identify areas for improvement in real-time. By analyzing CSAT and NPS data, organizations can gain actionable insights and prioritize initiatives that enhance the customer experience.By focusing on these various dimensions of customer experience transformation, large enterprises can cultivate a customer-centric organizational culture, optimize operational efficiency, and deliver exceptional experiences at every touchpoint. Embracing these strategies and technologies will not only result in short-term benefits, such as improved customer satisfaction and increased revenues but also position organizations for long-term success by aligning with the evolving needs and expectations of their customers.8. Customer Journey AnalyticsCustomer journey analytics involves the systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of data related to customer interactions and experiences across various touchpoints. By leveraging advanced analytics techniques, organizations can gain deep insights into customer behavior, preferences, pain points, and moments of truth throughout the customer journey.9. Journey MappingJourney mapping involves visually representing the end-to-end customer journey, capturing customer touchpoints, emotions, and key interactions. By mapping out the customer journey, organizations can identify opportunities for improvement, uncover pain points, and design targeted interventions to enhance the overall experience.Behavior AnalysisBehavior analysis focuses on understanding customer actions, such as website browsing patterns, app usage, purchase history, and interactions with customer support. By analyzing customer behavior, organizations can identify patterns, segment customers, and personalize experiences based on individual preferences.Predictive AnalyticsPredictive analytics utilizes historical data and machine learning algorithms to forecast future customer behavior and preferences. By predicting customer needs and anticipating their actions, organizations can proactively deliver personalized experiences and tailor their offerings to meet customer expectations.Sentiment AnalysisSentiment analysis involves analyzing customer feedback, social media mentions, and online reviews to gauge customer sentiment and perception. By monitoring sentiment, organizations can identify areas of dissatisfaction, address negative sentiment promptly, and amplify positive experiences.Real-time Journey OrchestrationReal-time journey orchestration combines data analytics, automation, and decision-making capabilities to deliver personalized experiences in real-time. By dynamically adjusting interactions based on customer context and preferences, organizations can create seamless, relevant, and engaging journeys for customers.10. Voice of Customer AnalyticsVoice of customer analytics involves analyzing unstructured customer feedback, such as survey responses, call transcripts, and chat logs, to extract actionable insights. By understanding the voice of the customer, organizations can identify emerging trends, uncover hidden issues, and make data-driven decisions to improve the customer experience.By harnessing the power of customer journey analytics, organizations can gain a holistic understanding of the customer experience, identify areas of improvement, and take proactive steps to deliver personalized and seamless journeys. This data-driven approach enables organizations to continuously optimize the customer experience and stay ahead of evolving customer expectations.Final TakeawayCustomer experience is a pivotal business driver that organizations must prioritize.Particularly so in today's competitive landscape, achieving excellence in customer experience is paramount.This comprehensive article has laid a roadmap for you to prioritize your channel, systems, and customer journey transformation to drive CX excellence and master it.By embracing strategies like smart agent routing, AI-powered chatbots, omni-channel experiences, and predictive analytics, businesses can not only enhance immediate customer satisfaction but also foster long-term loyalty.As the digital landscape evolves, it's imperative for organizations to proactively adapt and align with their customers' changing needs. By implementing these strategies, businesses can position themselves at the forefront of customer-centric innovation, ensuring sustainable growth and success.
Mastering CX Part 2: The ‘How’ of Customer Experience Excellence

In today's cloud-centric world, managing infrastructure has become increasingly complex.As organizations strive for scalable, flexible, and cost-effective solutions, cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) have gained immense popularity.However, setting up and managing AWS resources can be daunting — this is where Terraform, an open-source infrastructure as code (IaC) tool, comes into play.Why Use Terraform on AWS?Terraform enables you to define and provision infrastructure resources across multiple cloud providers, including AWS, in a declarative and consistent manner. By treating your infrastructure as code, you can automate the creation, modification, and destruction of resources.In this blog, we won’t just understand the power of Terraform; in fact, we will go through an in-depth exploration of Terraform integration with AWS, providing you with a comprehensive guide to creating and managing your AWS infrastructure using Terraform.Whether you are new to Terraform or an experienced user, this blog will equip you with the knowledge and practical examples needed to accelerate your infrastructure provisioning and management processes.How Does Terraform Integrate with AWS?Terraform, developed by HashiCorp, stands at the forefront of infrastructure as code tools, revolutionizing the way organizations provision and manage their infrastructure resources.With Terraform, infrastructure configurations are defined declaratively, enabling teams to treat infrastructure as code and apply software engineering practices to their infrastructure management.This powerful tool offers multi-cloud support, allowing users to provision and manage resources across various cloud providers, and provides a unified workflow for infrastructure automation and scalability.With Terraform, organizations can achieve consistent, reproducible, and efficient infrastructure management, simplifying the process of building and scaling modern cloud architectures.Getting Started with AWSCreate an AWS Account:Visit the AWS website (https://aws.amazon.com/) and click on the "Create an AWS Account" button. Follow the instructions to set up your account by providing necessary information such as your email address, payment details, and contact information. Install AWS CLI:Visit the official AWS CLI installation documentation (https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/getting-started-install.html) to find instructions specific to your operating system. AWS CLI supports Windows, macOS, and Linux. Follow the installation guide to install AWS CLI on your machine. Configure AWS Credentials:To access your AWS resources, you need to configure your AWS credentials. Run the following command in the terminal or command prompt: `aws configure` You will be prompted to enter your AWS Access Key ID, Secret Access Key, default region, and output format. Obtain your AWS Access Key ID and Secret Access Key from the AWS Management Console by following the AWS documentation on accessing and managing your security credentials. How do you Create AWS Resources using Terraform?Terraform resources are created using JSON or the HashiCorp language, popularly known as HCL.Terraform's supplier is HashiCorp, and their native tongue is simple to write and read. Use the Visual Studio Code editor with Terraform plugin. It assists with input availability, autocompletion, and other things.We'll be using the HashiCorp language, which has the ".tf" extension, in this blog. To build the infrastructure, Terraform uses these files.By naming providers and resources, you define the infrastructure. We want to communicate with the providers, and on that provider, we want to build or manage resources.Provider:You list the provider block and a few arguments that are used to authenticate with the provider in the provider block.1. Create the provider.tf file:Create a new file named `provider.tf` in your Terraform project directory. Open the file in a text editor. 2. Configure the Azure Provider:Inside the `provider.tf` file, add the following code to configure the AWS provider:Resources:You describe what you wish to build in your provider in the resources blocks. Each resource block has its own set of necessary and, for the most part, recommended parameters.The fact that the parameters don't overlap between suppliers is crucial to understand.The code for AWS resources differs from the code for Azure resources as a result. Following is an example of how to create a resource in AWS using Terraform:1. Create the main.tf file:Create a new file named `main.tf` in your Terraform project directory. Open the file in a text editor. 2. Define the Azure Resource:After adding an AWS provider, add the following code to define an AWS resource in the main.tf file. For example, let's create an AWS S3 Bucket Resource:In here you can see we want to make a resource with the type “aws_s3_bucket” and with the name “example_bucket”. In the block we give the information that is needed to create such a resource.Working with TerraformTerraform has three main commands which are used to initialize, plan and apply resources.Once you have created your infrastructure according to your requirements, you will have to run these commands to create resources in Azure.These commands are called:Terraform init Terraform plan Terraform apply Terraform Init:Initializes a Terraform project in the current directory. Downloads the necessary provider plugins and sets up the backend. This command should be run once when setting up a new Terraform project or when making changes to the provider or backend configurations. Terraform Plan:Generates an execution plan based on the current Terraform configuration and state. Shows a preview of the changes that Terraform will make to the infrastructure. Helps you identify any issues or potential problems before applying changes. Terraform Apply:Applies the changes defined in the Terraform configuration to the infrastructure. Creates, modifies, or deletes resources according to the desired state. Terraform will prompt for confirmation before making any changes. TakeawayTerraform makes it feasible to use a single Infrastructure-as-Code tool to develop, manage, and apply infrastructure across several platforms.The infrastructure layer is another area where Terraform clearly focuses.This indicates that it offers skills like the ability to display updates, manage provider development, and manage your on-premises and cloud infrastructure in a single language.
Creating and Managing Amazon Web Services (AWS) with Terraform: A Hands-on Guide

When you hear the term "Customer Experience" (CX), do you instinctively relate it to UX design or customer care?Well then you need to hear this too: that’s not the case!In its truest essence, the full breadth of customer experience extends far beyond the responsibilities of UX designers and customer care teams.Crafting an extraordinary customer journey necessitates a holistic, well-integrated, organization-wide approach.And for large enterprises seeking sustainable business growth and a competitive edge, integrating customer journeys across channels, processes, and tools is not just beneficial, but essential.Cultivating a Customer-Centric Organizational Culture: Embedding CX into the Company’s DNAIn the grand scheme of enterprise operations, customer satisfaction must not be viewed as just another department.Instead, it should be regarded as a foundational aspect of the company's culture.Customer experience needs to be a strategic priority championed by everyone in the organization, from top-level executives to frontline employees.The successful execution of CX strategies demands a shared vision, a sense of collective responsibility, and an unwavering commitment across all departments.It is about creating a work culture that continually seeks to align actions and initiatives with customer needs and preferences.From marketing campaigns to sales processes, product development initiatives, technology implementations, and operational procedures – each facet of the business plays a pivotal role in shaping the overall customer experience.This necessitates an end-to-end commitment, with all departments contributing to a holistic, superior customer experience, for all the right reasons.The following encapsulate all the ways that user experience strategies, including those aimed at customer engagement and customer journey mapping, can not just be integrated but made optimal use of in large enterprises.Ownership and AlignmentCustomer experience is a strategic priority that should be owned and driven by the entire organization, from top-level executives to frontline employees.It requires a shared vision and commitment across departments to align their efforts towards delivering exceptional customer experiences.End-to-End Customer JourneyCustomer experience encompasses every touchpoint and interaction a customer has with the organization, from pre-purchase to post-purchase stages.It goes beyond the design of user interfaces and customer service interactions. It involves product development and marketing, sales, technology, operations, and more.Each department plays a vital role in shaping the overall customer experience and bringing together their insights for various areas of the customer journey mapping effort, as well as for customer-focused marketing and customer lifetime value.Consistency and ContinuityCustomers expect a consistent and seamless experience across all channels and interactions.It is crucial for organizations to integrate their systems, processes, and data to ensure a unified and frictionless customer journey.A wide range of functional expertise is required to gather customer insights, identify real pain points, and innovate solutions.Various departments can contribute their unique perspectives and expertise to uncover valuable customer insights and drive innovation in products, services, and processes.Organizational CultureShifting the organizational mindset towards customer-centricity is critical for successful customer experience transformation.It requires a cultural shift top-down, that values customer satisfaction and puts the customer at the center of decision-making.This cultural change must permeate throughout the organization, driven by leadership and reinforced through training, incentives, and performance metrics.For a more in depth understanding of integrating a more agile culture within your people, tools, and processes, be sure to read this article: Explore the Neglected Side of Agile Insights and Innovation.The Strategic Payoff: Short-Term and Long-Term Benefits of Customer Experience TransformationCustomer experience transformation yields both short-term and long-term benefits for large enterprises.Understanding these benefits can help organizations prioritize and invest in customer experience initiatives.The potential rewards of such a transformation are significant, spanning from immediate gains to long-term profitability:Short-Term Gains: Immediate Returns on InvestmentHeightened Customer Satisfaction: Enhancing various customer touchpoints can lead to a significant improvement in customer satisfaction levels. Happier customers are more likely to remain loyal, make repeat purchases, and advocate for the brand, resulting in increased customer retention and acquisition. Boost in Average Revenue per User (ARPU): Satisfied customers are more likely to upgrade their services, purchase additional products, or opt for premium features, thereby contributing to an increase in ARPU. Incremental Growth: Delivering exceptional customer experiences can stimulate positive word-of-mouth and encourage customer advocacy, attracting new customers and driving incremental revenues. Long-Term Rewards: Driving Sustainable and Scalable GrowthCustomer Loyalty and Retention: Superior customer experiences foster loyalty and ensure long-term customer engagement. This reduces customer churn and contributes to stable, recurring revenues. Increased Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Focusing on enhancing customer experience can significantly augment CLTV, as satisfied customers tend to have longer relationships with the organization and make repeat purchases. Deep Understanding of Customer Needs: By engaging in CX transformation, organizations can delve deeper into their customers' preferences and pain points. This rich understanding can guide the development of customer-centric products, services, and strategies, offering a strong competitive advantage. Competitive Differentiation: In today's fiercely competitive market, CX can be a potent differentiator. Organizations that excel in customer experience are more likely to stand out from the competition, attract new customers, and retain existing ones. Customer-Centric Innovation: A customer-focused approach encourages innovation that aligns with customer needs and preferences. By incorporating customer feedback and insights into the innovation process, organizations can develop new products, services, and experiences that truly resonate with customers and create value. TakeawayIn conclusion, customer experience transformation goes beyond the responsibilities of just the UX designers and customer care teams.It demands an organization-wide strategic commitment to deliver an exceptional customer journey.By adopting a comprehensive approach and involving various functional areas, organizations can realize a wide range of benefits, from improved customer satisfaction and revenue growth in the short term to customer loyalty, differentiation, and customer-centric innovation in the long term.The strategic power of customer experience, therefore, is an indispensable asset for large enterprises in today's customer-centric business landscape.
Mastering CX Excellence Part 1: The Strategic Significance of Customer Experience For Large Enterprises

When you search for the term “infrastructure-as-code” (or IaC), you’ll quickly find a list of the most popular IaC tools out there:ChefPuppetAnsiblePulumiCloudFormationTerraformHeatAnd while each tool has its own benefits, the difficult part is determining which one to use.All of these tools are capable of managing infrastructure as code, in addition to sharing other commonalities:They are all open-source, have large contributor communities, and work with various cloud providers (except for CloudFormation, which is closed-source and AWS-only). They all provide enterprise support. They are all well-documented in both official documentation and community resources like blog posts and StackOverflow questions. So, how do you make a decision?For us, we do have a top pick: Terraform.In this article, while we will talk about all of these IaC tools, we’ll also find how Terraform compares with the rest and reveal why we prefer it over others.Terraform vs OthersThere’s another challenge when choosing the best IaC tool.Most online comparisons between these tools do little more than list the general properties of each tool, making it sound like you could be equally successful with any of them.While technically correct, this is not helpful; it's a little like telling a programming newbie that you could build a website just as well with PHP, C, or Assembly — a technically correct statement, but one that leaves out a lot of information that would be extremely helpful in making a good decision.In this article, we'll go over the specific reasons why Terraform is our top pick over other IaC tools.Why Terraform: The Trade-OffsAs with all technological decisions, it comes down to trade-offs and priorities.And while your priorities may differ from ours, we hope that sharing our thought process will assist you in making your own decision.The following are the main trade-offs we considered:Configuration Management vs Provisioning Mutable Infrastructure vs Immutable Infrastructure Procedural vs Declarative General-purpose Language vs Domain-specific Language Master vs Masterless Agent vs Agentless Paid vs Free Offering Large Community vs Small Community Mature vs Cutting Edge Using Multiple Tools Together Configuration Management vs ProvisioningChef, Puppet, and Ansible are all configuration management tools, meaning they are intended to deploy and manage software on existing servers.CloudFormation, Heat, Pulumi, and Terraform are provisioning tools, which means they are meant to supply servers (along with the rest of your infrastructure, such as load balancers, databases, networking setup, and so on), leaving the chore of configuring those servers to other tools.But, if you are not utilizing server templating tools, a configuration management and provisioning solution combined is an excellent option.For example, using Terraform to provide your servers and Ansible to set up each one is a popular combo.Mutable Infrastructure vs Immutable InfrastructureMutable infrastructures allow regular updates and changes after the software is deployed, while immutable infrastructures do not allow changes after the software is deployed.Procedural vs DeclarativeChef and Ansible support a procedural approach in which you write code that explains how to attain a desired end state step by step.Terraform, CloudFormation, Pulumi, Heat, and Puppet all support a more declarative approach, in which you write code that defines your intended end state, and the IaC tool determines how to attain that state.General-purpose Language vs Domain-specific LanguageChef and Pulumi enable you to manage infrastructure like code by using a general-purpose programming language (GPL): Pulumi supports a broad range of GPLs, including JavaScript, TypeScript, Python, Go, C#, Java, and others, whereas Chef supports Ruby.To manage infrastructure as code, Terraform, Puppet, Ansible, CloudFormation, and OpenStack Heat all employ a domain-specific language (DSL): Terraform makes use of HCL; Puppet makes use of Puppet Language; and Ansible, CloudFormation, and OpenStack Heat make use of YAML (CloudFormation also supports JSON).DSLs have some benefits over GPLs:That is simpler to learn More concise and clear Greater consistency GPLs offer some benefits over DSLs as well:Sometimes there is no need to learn anything new More sophisticated toolset and a larger ecosystem Greater strength Master vs MasterlessChef and Puppet, by default, require you to maintain a master server for preserving the state of your infrastructure and distributing changes.By default, Ansible, CloudFormation, Heat, Terraform, and Pulumi are all masterless.To be more specific, some of them rely on a master server, but it's already a part of the infrastructure you're utilizing and not an extra component you have to maintain.For example, Terraform interfaces with cloud providers via their APIs; therefore, the API servers are similar to master servers in certain ways, except that they don't require any additional infrastructure or authentication processes.Agent vs AgentlessChef and Puppet require the installation of agent software (e.g., Chef Client, Puppet Agent) on each server to be configured.There are some challenges that come with this:Bootstrapping Maintenance Security Ansible, CloudFormation, Heat, Terraform, and Pulumi do not require any additional agents to be installed.To be more specific, some of them necessitate the use of agents, which are often already deployed as part of the infrastructure you're utilizing. Amazon, Azure, Google Cloud, and all other cloud providers, for example, install, manage, and authenticate agent software on each of their physical servers.You don't have to worry about any of that as a Terraform user: you simply give instructions, and the cloud provider's agents execute them on all of your servers.Ansible requires that your servers execute the SSH daemon, which is standard on most servers.Paid vs Free OfferingCloudFormation and OpenStack Heat are absolutely free: the resources you deploy with those tools may be expensive, but you don't have to pay anything to utilize them.Terraform, Chef, Puppet, Ansible, and Pulumi all have free and commercial versions: for example, you may use Terraform's free and open-source version by itself, or you can combine it with HashiCorp's premium product, Terraform Cloud.Large Community vs Small CommunityWhen you select a technology, you are also selecting a community. It's tough to make an exact comparison between localities.The table below compares popular IaC tools based on data I gathered in June 2022, including whether the IaC tool is open source or closed source, what cloud providers it supports, the total number of contributors and stars on GitHub, how many open source libraries are available for the tool, and the number of Stack Overflow questions listed for that tool.(Note: The data on contributors and stars comes from the open source repositories for each tool, but as CloudFormation is closed source, this information is unavailable).Mature vs Cutting EdgeAnother vital thing to consider when selecting a technology is maturity.The table below displays the first release dates, current version numbers (as of June 2022), and my subjective assessment of each IaC tool's maturity.Pulumi is the most recent IaC tool in some comparisons and, arguably, the least mature: this becomes clear when searching for documentation, best practices, community modules, and so on.Terraform is a bit more mature these days: the tooling has improved, best practices are better understood, there are far more learning resources available, and it is a far more stable and reliable tool now that it has reached the 1.0.0 milestone than it was when the first and second editions of Terraform: Up & Running were released.Chef and Puppet are the most mature and oldest tools.Using Multiple Tools TogetherDespite the fact that I've been comparing IaC tools throughout this article, the reality is that you'll most likely need to use a combination of tools to build your infrastructure.The sections that follow show three common combinations that I've seen work well at a variety of companies.Provisioning plus configuration management Provisioning plus server templating Provisioning plus server templating plus orchestration Provisioning plus configuration managementAs an example, consider Terraform and Ansible.Terraform deploys all underlying infrastructure, such as network topology (e.g., virtual private clouds, subnets, route tables), data stores (e.g., MySQL, Redis), load balancers, and servers.You then use Ansible to deploy your apps on top of those servers.This is a simple strategy to begin with because no additional infrastructure is required (Terraform and Ansible are both client-only programmes), and there are several ways to enable Ansible and Terraform to operate together.Provisioning plus server templatingTerraform and Packer are two examples.Packer is used to package your apps as VM images.Terraform is then used to deploy servers with these VM images, as well as the rest of your infrastructure, such as network topology (i.e., VPCs, subnets, route tables), data stores (e.g., MySQL, Redis), and load balancers.This is also a simple technique to begin with because no additional infrastructure is required (Terraform and Packer are both client-only programmes).Furthermore, because this is an immutable infrastructure solution, maintenance is simplified.Provisioning plus server templating plus orchestrationTerraform, Packer, Docker, and Kubernetes are a few examples. Packer is used to produce a VM image that includes Docker and Kubernetes agents.Terraform is then used to deploy a cluster of servers, each of which runs this VM image as well as the rest of your infrastructure, such as the network topology (i.e., VPCs, subnets, route tables), data stores (e.g., MySQL, Redis), and load balancers.Finally, when the server cluster powers up, a Kubernetes cluster is formed, which you can use to execute and manage your Dockerized apps.The benefit of this strategy is that Docker images develop rapidly, you can run and test them on your local computer, and you can use all of Kubernetes' built-in capabilities, such as multiple deployment strategies, auto-healing, auto-scaling, and so on.The disadvantage is the added complexity, both in terms of extra infrastructure to run (Kubernetes clusters are difficult and expensive to deploy and operate, though most major cloud providers now provide managed Kubernetes services, which can offload some of this work) and several extra layers of abstraction to learn, manage, and debug (Kubernetes, Docker, Packer).Final TakeawayConsidering everything, the table below compares the most popular IaC tools, depicting the most common or default configuration of the various tools.However, it’s important to note that, as discussed earlier, these IaC tools are flexible enough to be used in other configurations as well (e.g., you can use Chef without a master, you can use Puppet to do immutable infrastructure, etc.).Want more expert insights into what an ideal DevOps culture looks like and how it can help? Check out this article: 6 Reasons Why You Should Adopt a DevOps Culture in Your Business
Managing Infrastructure As Code: Terraform Explained

As a team, we recognize the importance of designing good experiences for everyone.And as the world becomes more and more impacted by advancements in technology and the evolution of digital experiences, our design team decided to actively play a responsibility in ensuring everyone is accounted for.Making it a priority during the first quarter of this year, our designers have been taking a course on Digital Accessibility from the W3C to learn the ins and outs of digital accessibility and how we can adopt it to design inclusive experiences.This fourth round of the Ask A Designer series is dedicated to shedding light on these learnings, as our designers answer questions that help us understand how Accessibility can be adopted.Question 1What does digital accessibility mean to you?Name: Grace XuTitle: Sr Graphic DesignerResponse:Digital accessibility is not just a nice to have, but a must have. It is mandatory for some but beneficial to everyone.Equal access to digital information has to be something that every designer strives for, and it goes beyond meeting federal or even international laws and policies on this matter.This is a basic human right and these accessibility practices empower my ability to empathize and understand others who use and experience our digital products from a different angle, one that we often don’t consider but absolutely should.Name: Usman KhanTitle: Product DesignerResponse:Digital accessibility is the important practice of designing and developing digital content and technologies that are accessible to all people, including those with disabilities.This includes making sure that digital content, including websites, mobile applications, electronic documents, and multimedia, is accessible to and intelligible by all users, regardless of their abilities or limitations.The use of technology that can be accessed by assistive devices like screen readers and the provision of clear, easy-to-read text are a few examples of how this is done.Another is the provision of text replacements for non-text information (such as photos or videos).All things considered, It is very important because it ensures that all individuals have equal access to digital content and technology, which can help to promote inclusion, independence, and participation in society.Name: Pranavi LMKTitle: Associate Product DesignerResponse:Digital accessibility ensures that everyone has equal access to information: every website and application must be built with this in mind.Digital accessibility is essential because it empowers one and makes them independent in this digital world.Designing a website that is accessible to everyone makes them feel included and is a professional moral to follow.Making a website/app accessible means adding interactive elements like buttons/controls that lets users access the information through clicking, scrolling, voice commands etc.Accessibility exists on a large scale.When it comes to using digital products, users have a wide range of requirements and preferences, so there is no one-size-fits-all accessibility definition.But as designers, It is our responsibility to try and assist as many people as possible.Name: Usama JavedTitle: Product DesignerResponse:Accessibility is all about people. It is about ensuring all users can access the same information, regardless of the impairments they may have.Whether a visually-impaired person uses a screen reader to access a webpage or someone has a cognitive disability that requires straightforward content and navigation, there are many reasons to make your digital presence accessible.Digital accessibility is when technology has been designed in a way so that it can be accessed by all types of people.This includes electronic documents, websites, software, hardware, video, audio, and other digital assets.Question 2What kinds of tools do you use to check for accessibility?Name: Grace XuResponse:The WAVE Evaluation Tool is pretty robust for most web cases, the contrast checker is the one I use the most! However I also want to shift the focus away from tools and more on how we need to keep in mind that tools won’t give you all the answers on how to make something accessible. For example, a tool can inform us that a piece of alternative text is missing from an image, but it can’t tell us if in the case there is alt text, that what it has displayed is actually appropriate or helpful for users who need it. We need to use manual testing as well to fully see if our work is actually compliant and always consider it in every step of the design process.Name: Usman KhanResponse:The WAVE tool is pretty good and it can help to identify a wide range of accessibility issues, including missing alt text for images, low contrast text, missing form labels, and more.It can improve the overall checking of accessibility in several ways:Easy to understand results: The WAVE tool provides a detailed report of all accessibility errors, warnings, and features. This report is color-coded to make it easy to understand which issues need to be addressed first and provides clear guidance on how to fix each issue. Real-time testing: The WAVE tool allows you to test web pages in real time, so you can see accessibility issues as you make changes to your website. This makes it easy to test and fix accessibility issues as you work on your website.Overall, the WAVE tool is a powerful tool that can help improve the accessibility of the website. By using it to identify and address accessibility issues, I can ensure that the website is accessible to all users, regardless of their disabilities. Name: Pranavi LMKResponse:I use https://webaim.org/resources/contrastchecker/ and https://coolors.co/contrast-checker/112a46-acc8e5 to check color contrast.Webaim has other articles, checklists and resources to check your design accessibility. It has resources that lets you do manual testing even for screen readers.Name: Usama JavedResponse:One tool I use is Getstark, which is a tool that helps ensure that my designs are accessible to users with visual impairments. This tool checks for issues like color contrast, font size, and other factors that can impact how easily users can read and understand your content.Another tool is Contrast Checker, which helps with color contrast.This tool enables you to check whether your text and background colors meet accessibility standards, which is particularly important for users with visual impairments.Last but not the least, There is the Lighthouse tool. It is built into Google Chrome that can help you test the accessibility of your site.It provides a comprehensive report that includes accessibility, performance, and SEO metrics.Question 3How do you integrate accessibility into your work?Name: Grace XuResponse:One thing I’ve committed to memory are the most common forms of assistive technologies and how people use it to interact with digital products.I try to imagine what they would do and if there is a production link to our product then open up one of these tools and try it myself.I also think that you never stop learning as some things come with experience; overlook a part of your design’s accessibility and once that’s pointed out as being inaccessible, you won’t forget the second time.Thankfully there are always multiple checks along the way, and no digital product would get released without evaluation from devs, POs, content, and even an organization accessibility champion in our case.Name: Pranavi LMKResponse:I always make sure I do not forget the basic principles, like the size of the text, button, elements and color contrast. These are the general guidelines to start with making a design universal. I try to put myself in the shoes of the user and see if the design is accessible or not. It is good to review the accessibility beforehand with the team and developers which will save time and give more insights. I cross check my design with the web accessibility checker.Name: Usman KhanResponse:I always make sure that along with normal people, there will be people with disabilities who can use my product.Here is a quick example on how I keep track of accessibility while I am working on a website by:Using proper heading tags (h1, h2, h3, etc.) to create a clear and logical content hierarchy. Ensuring that all images have alt text that describes their content and function. Ensuring that all forms are labeled correctly and are accessible to screen readers. Using high-contrast colors and fonts that are easy to read for people with visual impairments. Name: Usama JavedResponse:Good question! I always ensure that I follow basic guidelines and principles of accessibility to ensure that designs meet the accessibility requirements. There are some other important key things which i follow while creating designs for products:I use proper color contrasts because it is very important to ensure that there is sufficient contrast between text and background colors.I provide alternative text for images.It allows me to understand the context of images and other visual elements.I understand the needs of the users with disabilities throughout the design process, from ideation to implementation.Question 4What was eye opening for you in your training?Name: Grace XuResponse:“Good design makes a website, application, or any other product or service, one that we all want to use – it just works better.” Having teams of people who care about digital accessibility will create products that are better for everyone who experiences it. The course showed many types of differently abled people and how they use assistive technology or omit certain technologies we commonly use to achieve the same goals that you and I would. It made me poke around my frequented digital websites, apps, tools more and see where the gaps are and notice how often many of these accessibility issues are simple to solve.Name: Pranavi LMKResponse:The training undoubtedly showcased various disabilities and the assistive technologies that are available to enhance their access to the digital world. Screen readers, motion tracking software, screen magnifiers, and braille display are new technologies that I got to know of. I learnt that accessible products help in boosting businesses by increasing SEO, Customers. There are laws that protect and demand digital products to be accessible for the differently abled.Name: Usama JavedResponse: The training emphasized the importance of good design in creating products that are user-friendly for everyone. By having a team of people who prioritize digital accessibility, businesses can create products that work better for all the users. During the training, I was introduced to many different abled individuals and how they use assistive technology to achieve their goals. This made me more aware of the accessibility gaps in the digital products I use regularly and how simple solutions can make a big difference.Overall, the training emphasized the importance of creating accessible products that are usable for everyone. By understanding the needs of differently abled individuals and incorporating digital accessibility into the design process, businesses can create products that are better for everyone.Name: Usman KhanResponse: This training helps me understand the importance of website design that is accessible to everyone, regardless of their abilities. By designing accessible websites, I can now create a better user experience for everyone, including people with disabilities, and help organizations reach a broader audience. Additionally, the course teaches about accessibility standards and guidelines, helping organizations avoid legal and financial consequences associated with non-compliance. I can now confidently become an advocate for web accessibility and promote its importance across my circle.
Ask A Designer Round 4: Considering Accessibility and Designing Inclusively

Design Thinking is not new.It started thousands of years ago when our ancestors were looking for answers from the open world by observing it, interpreting it, bit by bit adapting to it, and quickly pivoting when a critical threat is observed by their sensory knowledge.Because of the Design Thinking approach, we survived extreme weather conditions and the deadliest of predators, and equipped ourselves with the right tools and ways of survival.We transitioned from hunter-gathering, to growing crops and into creating industries and digitizing them.From a cosmological viewpoint, we are merely designers, experimenters, and doers who proceed with caution.Design Thinking helps surface the uncertainties that have some level of doubt attached to them, and then we address those uncertainties through an iterative way of proceeding with caution.We shouldn’t forget, however, that design thinking has also been the buzzword for a decade now where small to enterprise-level organizations are continuously dedicated to establishing design thinking as a panacea.But when organizations fail to realize the situational application of Design Thinking, they generate waste in the name of experimentation.Shall Design Thinking Be Used in Every Situation?Instead of using Design Thinking in every situation, there is a way to identify which situations require Design Thinking.This can be achieved through the ‘Uncertainty Index’ for a given requirement.Instead of using Design as a buzzword for showing some level of upskilling within the organization, these can be used selectively and more efficiently to solve the right problem for the right people.Otherwise, it can become devastating if not used for the right problem.The conceptual understanding of Design Thinking has been improving, where Product Managers and Designers have started to factor in different uncertainties to make it an effective method of solving customer problems.What Are These Uncertainties?At mobileLive, we believe in adopting the most effective approach to address uncertainties while minimizing waste, by identifying and researching our customers' and clients' true needs.To achieve this, we suggest selectively using a set of uncertainties that can be applied to any given problem or need.Progressive companies typically consider multiple uncertainties to ensure that design thinking is only used where it can uncover real needs.If the company has relevant historical data, research, or expert opinions on the problem at hand, they assign an uncertainty threshold to determine whether the problem falls below the threshold and can be solved using a tried and tested approach to product development.This approach saves time and cost while still achieving the same level of product development as a design thinking process.With the ‘Uncertainty Index’, uncertainties of all kinds associated with a problem, a product, or service can be mapped in a singular view.This helps us to be able to gauge better if the problem at hand warrants a design thinking approach to solving the problem, or if conventional methods need to be used for better outcomes.The Seven Uncertainty IndexThe following are the seven types of uncertainties for which a quantitative or qualitative threshold can be defined and practiced across the Products cross-functionally:1. Customer PreferenceInsufficient or inaccurate data on customer preferences, such as incomplete or outdated market research or survey results Limited understanding of customer needs and pain points can result in misaligned products and services that do not meet customer expectations Rapidly changing customer preferences due to shifts in consumer behavior or the emergence of new technologies or trends Inconsistent or unreliable customer feedback and satisfaction data that can lead to inaccurate conclusions about customer preferences Lack of clarity or articulation of customer expectations, which can make it difficult to develop effective marketing strategies and product roadmaps If there is minimal uncertainty related to customer preferences, it may indicate that a design thinking approach is not necessary.Instead, product strategists can focus their efforts on leveraging existing data and research to inform their product development decisions.This can help to optimize resources and ensure that solutions are aligned with the needs and preferences of the target customer base.2. Market VolatilityRapid changes in consumer demand and supply due to changing market conditions Shifting consumer preferences and behaviors, including emerging trends and fads Technological advancements and disruptive innovations that can quickly change the competitive landscape Intense competition and pricing pressures, including the emergence of new competitors or business models Economic and financial instability, including changes in interest rates, exchange rates, and other macroeconomic factors that can impact market dynamics If there is a low level of uncertainty related to market volatility, it may be an indication that the market is relatively stable and well-understood.In such cases, design thinking may not be the most appropriate approach to use, as the focus should be on leveraging existing knowledge and data to drive product strategy and decision-making.However, even in relatively stable markets, there may still be opportunities to innovate and differentiate, and a design thinking approach can still be valuable in identifying and capitalizing on these opportunities.It is important to assess the level of uncertainty related to market volatility on a case-by-case basis and to use a range of tools and approaches to identify and minimize these uncertainties.3. Regulatory AmbiguityAmbiguity in regulatory requirements and compliance standards Lack of clarity in legal frameworks and guidelines Uncertainty about how regulatory bodies will interpret and enforce regulations Compliance costs and risks associated with regulatory non-compliance Potential reputational risks associated with regulatory violations In cases where the regulatory landscape is relatively stable and clear, design thinking may not be necessary as existing regulations can guide decision-making.Similarly, in situations where the regulatory requirements are well-defined and leave little room for interpretation, other methodologies such as legal or compliance-focused approaches may be more appropriate.However, if there is significant uncertainty surrounding regulatory requirements, design thinking can be useful in exploring potential solutions and identifying areas where further regulatory guidance may be needed.It's important to assess the level of regulatory ambiguity and determine whether design thinking is the most suitable approach for addressing the specific challenges and opportunities at hand.4. Technological UncertaintyRapid pace of technological change, which can make it difficult to keep up with new developments and trends Uncertainty around the commercial viability of emerging technologies, including questions around market demand, scalability, and return on investment Complexity of emerging technologies, which may require specialized skills and expertise that may not be readily available in-house Risk of technological disruption that can create new threats to established business models and markets Potential for emerging technologies to create new opportunities and business models, including the potential to improve operational efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and create new revenue streams When faced with uncertainties related to technological disruptions, it's important to assess the level of uncertainty and the potential impact on the product.If the uncertainties are conventional and there are proven solutions or approaches that have been successful in the industry or by the organization, then design thinking may not be necessary as product strategists can rely on conventional methods.However, if the uncertainties are more complex and disruptive, with no clear examples of successful solutions or approaches, then design thinking can be a valuable tool to help product strategists explore alternative solutions and develop more innovative products that can better meet the needs and preferences of their target customers.5. Channel UncertaintyIncomplete understanding of customer behavior and preferences across various channels, which can lead to suboptimal channel selection and poor customer experience Uncertainty around the most effective methods to reach and engage customers through different channels, which can lead to inefficient use of resources and missed opportunities Limited knowledge about the costs, benefits, and risks associated with different channels, which can make it difficult to optimize channel selection and ROI Uncertainty about how different channels will evolve and their future viability, which can make it difficult to develop a long-term channel strategy Lack of clarity about the potential impact of emerging channels on existing channel strategy, which can make it difficult to effectively allocate resources and adapt to changes in the market If there is minimal uncertainty with the channels, using design thinking as the default approach may result in unnecessary time and resource waste trying to reinvent the wheel.However, with the rapid introduction and expansion of digital channels, it is crucial to remain present and relevant while exercising caution. In such cases, applying design thinking can help to identify opportunities for innovation and differentiation, ensuring that your organization stays ahead of the curve and delivers value to customers in new and impactful ways.6. Financial ViabilityLimited understanding of the lifetime value of customers and the impact of customer acquisition costs on profitability Uncertainty about the scalability of the product and its ability to generate sufficient revenue to cover development costs and sustain the business over the long term Limited knowledge of the market size and growth potential for the product, and the potential impact of competitors or substitute products Uncertainty about the financial impact of potential legal or regulatory challenges, such as patent infringement lawsuits or regulatory hurdles Limited understanding of the financial implications of potential product failures or recalls, including the costs of customer refunds or compensation, legal fees, and damage to the brand's reputation If there is minimal uncertainty related to financial viability, it may not be necessary to use a design thinking approach and instead bank on the existing financial models and data.7. Organizational AbilityLack of organizational agility and ability to adapt to changing market conditions and customer needs Limited capability to attract and retain top talent with the necessary skills and expertise Insufficient investment in training and development programs to build necessary competencies and capabilities Inability to effectively manage and integrate acquisitions or partnerships Limited ability to implement and execute strategic initiatives and goals due to siloed or bureaucratic organizational structures If the uncertainty related to organizational ability is low, then it may not be necessary to use a design thinking approach as product strategists may already possess the necessary skills and expertise to develop and execute the product strategy effectively.However, if there is a higher level of uncertainty in this area, it may be critical to adopt a design thinking approach to identify the right organizational skillset needed and to develop strategies to retain top talent possessing those skills to ensure successful product development and execution. The main aim remains to deliver with certainty.Reducing Uncertainties Through the Uncertainty IndexThe uncertainty score can be determined by going through each of the five uncertainties listed under the seven main uncertainty categories.Any organization can set a rule of thumb to kickstart the design thinking process when an uncertainty score of a category is found to be above the uncertainty threshold.Once uncertainty is mapped, the goal is to reduce it through research, rapid prototyping, and pivoting.Analyzing uncertainties with the scope of the ‘uncertainty index’ requires domain expertise and cross-functional collaboration, but rest assured, it will save a lot of wasted efforts in terms of time and money later in the product development and launch cycle.This example below definitely calls for sophisticated data elicitation and research using design thinking principles.Final TakeawayIn conclusion, the uncertain business environment makes it challenging for organizations to make strategic decisions.Design thinking can be an effective approach to navigating uncertainty and creating customer-centric solutions.However, it is important to assess the level of uncertainty associated with the problem at hand before deciding to use design thinking.The uncertainty index can be a useful tool in this regard, helping organizations to evaluate various uncertainties such as customer preferences, market volatility, including uneven competitive landscape, emerging technologies, channel uncertainty, regulatory ambiguity, financial viability, and organizational ability.By carefully considering these uncertainties and using design thinking where appropriate, organizations can make more informed decisions and better position themselves for success in the marketplace.FAQsIs design thinking a panacea for all kinds of problems?No, design thinking is not a one-size-fits-all solution for every problem. It is a framework that is best suited for complex, open-ended problems that require creative solutions.Can design thinking be misused as a buzzword to create the illusion of innovation?Yes, it is possible to misuse design thinking as a buzzword without actually achieving any tangible results. It is important to approach design thinking with a genuine intention to solve problems and create value.Are there situations where design thinking may not be appropriate?Yes, there may be situations where design thinking may not be appropriate. Those problems with low levels of uncertainty usually don’t require the design thinking approach such as when the problem is well-defined and has a clear solution, or when time and resources are strictly limited.Can design thinking be used as a substitute for domain expertise?No, design thinking is not a substitute for domain expertise. It is a complementary approach that can be used in conjunction with the domain expertise to generate innovative solutions.Is it important to involve stakeholders in the design thinking process?Yes, involving stakeholders in the design thinking process is critical to ensuring that the solutions generated are relevant and meet the needs of the end users and all entities in between. The associated uncertainties spread across different disciplines within an organization to be well understood, followed up and reduced.Is it important to evaluate the problem for uncertainties before using design thinking?Yes, it's very important to evaluate the problem for uncertainties as it helps in identifying potential challenges and opportunities that may affect the outcome of the process. This evaluation can also help in adjusting the process to accommodate any unforeseen obstacles.Is it important to evaluate the success of design thinking initiatives?Yes, it is important to evaluate the success of design thinking initiatives to determine their effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
Reducing Uncertainties With Design Thinking: The 7 Uncertainty Index

Toronto, ON, May 9th, mobileLIVE, a Toronto-based technology services company, achieved Platinum Club status with Canada’s Best Managed Companies program by retaining its Best Managed designation for seven consecutive years or more.Celebrating its 30th anniversary, Canada’s Best Managed Companies program awards excellence in private Canadian-owned companies. To attain the designation, companies are evaluated on their leadership in the areas of strategy, culture and commitment, capabilities, innovation, governance, and financial performance.“It has become increasingly important for businesses to foster collaborative workplaces where employees are empowered to make valuable contributions to their organizations,” said Derrick Dempster, Partner, Deloitte Private and Co-Leader, Canada’s Best Managed Companies program. “This year’s Best Managed winners, including mobileLIVE, embrace a people-first mentality, enabling employees to cultivate important capabilities and integrating diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives into their core strategy. By prioritizing employee wellbeing and championing professional development, these companies are harnessing their talent pool’s fullest potential and in a stronger position to attract the talents needed to embrace the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead.”Canada’s Best Managed Companies is one of the country’s leading business awards programs recognizing innovative and world-class businesses. Every year, hundreds of entrepreneurial companies compete for this designation in a rigorous and independent evaluation process. Applicants are evaluated by an independent panel of judges with representation from program sponsors and special guests.“We are thrilled to be named a Best Managed Platinum Club member,” said Jahan Ali, CEO and founder at mobileLIVE. “This win is a testament to the hard work and dedication of our team, the success of our business philosophy, and our commitment to excellence in every aspect of our business.”The Best Managed assessment process is rigorous and comprehensive, evaluating a company’s overall performance and practices in areas such as strategy, leadership, innovation, culture, governance, and financials. Companies that achieve Best Managed status are recognized as industry leaders, demonstrating their commitment to long-term growth and sustainability. The 2023 cohort of Best Managed companies share common themes such as having a people-centric culture, targeting effective ESG strategies, and accelerating operational digitization.“CIBC is proud to sponsor Canada’s Best Managed Companies, a program that has been celebrating leading organizations that are working towards building a better future, for the past thirty years,” said Blair Cowan, Executive Vice-President, Head of Commercial Banking and Real Estate CIBC. “Companies such as mobileLIVE, which successfully deliver innovative solutions for longer-term growth and investments, are a testament to our country’s high standards of excellence.”
mobileLIVE is now the Best Managed Platinum Club Member

First brought into practice by a team at Google Ventures, the idea of “sprints” came about as a quick solution to solve the problems of startups that they invested in.They particularly needed “quick” solutions and wanted to be able to solve these problems in a short time because of challenges like:High stakes: The solutions require a lot of money and time, which most startups lack. Limited time: There’s often a deadline and the solution needs to be presented fast. As the word “sprint” suggests, teams need to work quickly and efficiently towards attaining a workable solution. Feeling stuck: If there’s a deadlock in the creative process, a design sprint acts as a catalyst that can pull teams through such situations and give them a creative boost. These were just the challenges that the team who invented “sprints” faced, and today, sprints are adopted across the globe amongst teams in various industries.In the design industry, in particular, design sprints are adopted to solve complexities quickly, and in this article, we’ll break down design sprints into a 5-stage holistic process.What is a Design Sprint?The “sprint” is an effective method of solving complex problems, prototyping ideas and testing them with users.This method can also be used to test new ideas in a product and see what the customer acceptance would look like.Product teams can improve their product development process and create successful solutions in a short amount of time with design sprints.The Process: 5 Phases of a Design SprintTo look at it from a holistic angle, the design sprint process is divided into five different phases:Phase 01: Understand the problem Phase 02: Sketch all possible solutions Phase 03: Decide on the most optimal solution Phase 04: Create a usable prototype Phase 05: Test the prototype with users and gather insights Phase 01The first phase is structured around discussions to create a path for the sprint week and to create a map of the challenge being faced.A long term goal needs to be set for the product.This will act as an anchor point for a mindset towards solving the problems that are preventing the team from achieving that goal.All the key stakeholders (designers, developers, business, project managers, etc.) need to be a part of the team because you need people with different skill sets and experiences to examine the problem — everyone brings something unique to the table.The map represents the user going through your product to achieve the intended goal.All the touchpoints that get the user closer to the goal are noted.Along with visualizing all the steps that the user takes, the map also helps identify if there’s friction between the touchpoints and provides a structure for our sketches & prototype.Now imagine that the goal is achieved.Can we identify any issue that the user might face while going through this journey?These will be put in the form of “How Might We questions (HMW)” instead of simply jotting down the statement e.g. How might we educate the user about this new feature?Put the questions within the respective journey phase (discovery, learning, using).The last part of this phase involves prioritizing the HMW questions and targeting a user.The example shown above has only one user, but in case there are multiple user personas involved, the key stakeholders in the team have to decide which user to focus on for the current sprint.This can be done using dot voting. Phase 02After defining the challenge in detail, the next step is to come up with solutions.The first thing to look out for is if there are other similar products out there and look for inspiration.Afterwards, the team members can ideate upon the solutions by creating sketches and flows.When everyone is done, all the team members can present their solution.Phase 03After everyone explains their solution, its time to choose the most optimal one.This can be done by discussions, which can become very exhaustive because team members will have to critique each other's solution, but it's important to get this right.An optimal solution would be something that most efficiently solves the problem and is also viable for the design and dev team to create.Image credit: Sprint - By Jake KnappA storyboard needs to be created around the chosen solution. This will help us set the mood for prototyping.The storyboard will essentially cover the user journey from discovery of the product to the exploration and usage of the new feature, which is the intended goal.Think of this as a more detailed map (from phase 1), which covers all the touchpoints, hence creating a clear roadmap for the prototype.Phase 04A prototype will be created based on the storyboard that should be realistic enough for testing, such that during the testing phase, the user should be able to properly interact with the prototype without any hiccups.The prototype shouldn’t be very high fidelity because the solution may not work. Extra time, therefore, shouldn’t be spent over something that has a high chance of disposal/changes.Phase 05The final phase of the design sprint is intended for testing the prototype.The format of the interview boils down to this:A friendly welcome and some open ended questions to learn more about the user Introduction to the prototype Detailed task that would require the user to start from the beginning and interact with the prototype till the end A debrief to capture the user’s impressions regarding the prototype Use this feedback to make any amends in the prototype, if required.Final ThoughtsIn the design sprint methodology, research is given very little time.Great products are a result of extensive research, and therefore I’ve tweaked the design sprint approach such that the research in phase 1 and 2 is given much more time.The design sprint is no doubt a high energy task where everyone is excited and ready to roll.But once it's completed and action points are drawn from it, oftentimes there’s a gap that remains till execution.The decision maker (a part of the sprint team) may lose power to allocate teams and budgets for the new project.There may also be structural changes in an organization, or outsourced execution, which means that the team that conducted the sprint are not the ones who develop the whole thing.The design sprint, therefore, needs to be optimized for large companies, in a way that the execution gap is accounted for within the sprint plan.To learn more about how you can integrate design sprints into your design workshops, be sure to give this article a read: Design Thinking Workshops: Choosing the Right One For Your Team
Solving Complexity in Sprints: A 5-Step Breakdown of Design Sprints
Owing to its recent rise in popularity, you've likely heard of design tokens.As a concept, understanding design tokens is quite simple: A design token is a code-based way to maintain how design systems look.For a designer, that means:Faster design changes Improved communication Reduced documentation headache More cross-platform consistency Easier handoffs to developers And while, for the right teams, design tokens can do wonders, it would be a mistake to get into it and try to implement design tokens without the right knowledge or practices.What Are Design Tokens?In essence, design tokens are variables.Think X = Y, where ‘X’ is a design attribute and ‘Y’ is the value.It’s important to note that there is much more to these values than reducing them down to “variables”, but for the sake of understanding design tokens better, this analogy will work for our purposes.For example: ‘borderWidth = 8px’ means that a border’s width will be, you guessed it, 8 pixels. (Pixels are what we see on our devices. These words you are reading right now are being displayed as pixels by your device.)These variables or “design tokens” can help to speed up the design and development process by automating updates, removing guess work, improving documentation, and documenting design decisions.For the right teams it can boost productivity and efficiency by removing some of the tedium that comes from maintaining design systems and documentation.Why Use Design TokensI’m sure you can already see how design tokens can improve your design system:Rapid design changes: Designers and developers can quickly change the look of the design by manipulating the token’s values. Consistency across platforms: Design tokens help ensure consistent design elements across platforms, reducing the need for back-and-forth between designers and developers. Reduced documentation headaches: Documentation can be updated automatically with design token changes, reducing the likelihood of errors and inconsistencies. Future-proofing your design system: Design tokens provide a flexible, modular foundation for your design system that can be easily updated and adapted over time. Additionally, design tokens are gaining in popularity.As I am writing this, there is a W3C community group working to establish a set of standards for the industry to use.The W3C or The World Wide Web Consortium is responsible for creating and maintaining the standards for the world wide web. It’s thanks to them that teams no longer need to spend hours ensuring web apps appear the same across web platforms.This is something that you are going to want to consider with your design systems.Developer Hand-offAh, the joys of handing off design tokens to development!While design tokens offer immense benefits to the design process, communicating and implementing them across platforms can be a daunting task.The first challenge is understanding and communication.Designers and developers need to be on the same page when it comes to naming conventions and values to ensure consistency in design. Here’s an interesting video to understand how design systems help improve and speed up the development process.Secondly, implementing design tokens across platforms can be tricky. Different platforms may require different formats, and converting design tokens can result in discrepancies in values.And if that wasn't enough, managing design token changes can be a headache.With multiple stakeholders involved in the process, keeping track of changes and ensuring everyone is using the most up-to-date design tokens can feel like a game of whack-a-mole.But fear not, there are ways to overcome these challenges and streamline the handoff process.For a deeper dive into how designers and developers collaborate, be sure to catch this insightful conversation between our developers and design teams: Ask A Designer Round 2: Questions For Designers, From Developers.How To Navigate the Challenges of Design TokensHold a workshopResearch! Learn about how design tokens were created and how organizations are adapting them to their needs. Look into the W3C Design tokens community group to understand the standards that are currently being developed. Bring together your stakeholders, developers, designers, and other key personnel Ensure that everyone understands the goals and intent behind adding design tokens to a design system. Make sure to document your decisions! Discuss a naming convention. This step is trickier than you may think. Designers and Developers need to create a common language for discussing the project. If thats not a common practice already, it will take some time to get everyone on the same page. Document. Your. Decisions. Agree on an implementation plan, start small and with a few components to work out any process gaps. It is easier to adjust 3 variables than it is to adjust an entire design system. Consider the future of the project as well, the work you do will have a direct impact on the results in the future. Again, make sure you are documenting this work. DocumentationDocumenting the decisions that build the foundation of your design system is ALWAYS the prudent thing to do.After all, who hates leaving a meeting and realizing you cannot remember key decisions?This opens the team up for misinformation to creep in and disrupt the flow. Were we using a 8pt system or 10pt system? Designer A says 8pt, Developer 1 says 10pt. It's anarchy!Make it easier with documentation tokensWhen it comes to documentation, Design Tokens for Figma can expedite the style documentation thanks to its handy documentation tokens.But what it cannot document is the reasoning and structures that go into creating the style guide.Adding design tokens to your system gives you and your team an opportunity to look at what is currently serving your design practice and determine if it is still serving you.Best Practices To Introduce Design Tokens To Your Design SystemIn order to offer the best chance at organizational adoption, here are a few best practices that will help navigate the nuances of design tokens:Create and enforce clear naming conventionsEstablishing a common language between all involved in a product isn’t always an easy feat. Even in the design community, you hear different terms for the same design patterns: Modal aka pop-up, overlay, or ********dialogue box. Consider the experience a new team member will have onboarding into this system. Use naming conventions that are intuitive and that work for your team. Avoid abbreviations and again, document the decisions that went into it. Be kind when reminding someone of correct naming conventions. Habits are hard to break, so as you start implementing design tokens don’t expect 100% adherence from the start. Maintain a centralized Design Token LibraryConsider using a cloud-based 3rd-party platform such as Storybook as a repository for your design components. This will allow team members to access the design system components from anywhere increasing visual design consistency. Create clear guidelines for how design tokens should be organized within the library to ensure naming and organization consistency. This can also help stakeholders and developers navigate through Figma using wayfinding. Regularly update and review design tokensSet a regular review schedule to ensure that design tokens are regularly audited and updated as needed. Solicit feedback from team members and stakeholders to identify areas where design tokens may need to be updated or added. Document any changes made to design tokens to ensure that all team members are aware of updates and can access the most current version. If you find that you aren’t making much headway with design token adoption, I find it helpful to take a step back and ask “why”.Sometimes you will need to tweak your approach or perhaps your organization lacks the design maturity to support design tokens.Once you have a clearer understanding of the underlying issues, you can begin to address them.When NOT to use Design TokensWhile design tokens can be a valuable tool for maintaining consistency and efficiency in the design process, they're not always necessary.If you're working on a small project, a project with constantly changing requirements, or a project with highly unique visual elements, it may not be worth the effort to create a full library of design tokens.In those cases, it may be more efficient to define visual elements on a case-by-case basis.The key is to evaluate each project on a case-by-case basis and determine if design tokens are the right choice.Real-World Examples of Design Token ImplementationDesign tokens are the secret sauce that many companies are using to create consistent and cohesive design experiences across their products and platforms.From IBM's design language to Salesforce's Lightning Design System, these tokens are being implemented in a wide range of products and services to streamline the design process and ensure visual consistency.Even companies like Shopify and Airbnb have jumped on the design token bandwagon, using these powerful tools to create a consistent look and feel across their websites and mobile apps.So if you want to stay ahead of the design curve and ensure a consistent user experience, it's time to start incorporating design tokens into your design system.TakeawayLet's wrap up this informative piece on design tokens.Design tokens are like the MVPs of the design world, enabling rapid design changes, consistency across platforms, and future-proofing your design system.However, implementing design tokens can have its challenges, such as communicating and implementing them across platforms and managing design token changes.To overcome these challenges, hold workshops, document decisions, establish clear naming conventions, and maintain a centralized design token library.So, start implementing design tokens like a pro today!
Design Tokens: Creating a Single Source of Truth for Your Design System

Developers know that the more they test their code, the better their chances are of developing high-quality software.And with Test-Driven Development, or TDD, they’re not only able to validate their code but also automate their testing process in order to keep the code simple, clean, and bug-free.But even though TDD has been around for several years, there is one big misconception about what TDD is actually about.Is TDD just about testing code?We’ll uncover the answer to this question, the true essence of TDD, and how you can use it to improve the quality of what you develop in this article.What is TDD and What it is NotContrary to popular belief, it’s not a method, but more of a mindset toward designing or developing your code.Before getting into how TDD works and what process is used to implement it, it’s crucial to break some of the misconceptions around what TDD is:TDD is NOT just another method of testing code or a QA replacement Writing unit testing is a method of practicing TDD For each function, you write code to validate your expected flows TDD will increase your development cycle Most people think TDD is about testing code, whereas in reality, TDD goes far beyond simply testing code.Usually, when we think about testing, the process goes that we write the code first and then test it. TDD offers a whole different approach to software development.In TDD, the cycle is reversed: you don’t write the code first, but instead, you write your tests.TDD is about driving development by test. “Life is a highway, I wanna ride it all night long.”What does Rascal Flatts have to do with TDD?You write code, and when it fails, you keep writing until it eventually passes; your code is your highway.So, as the name suggests, TDD is about driving development by test, where you write your test first and then write your code instead of the other way around.If anything, this further strengthens the concept that TDD is not about testing the code, but rather it’s about an approach to software development where the main focus is ensuring that our code is doing what we expect it to do.TDD is a way to verify everything you create. All dev activities are organized around the need to verify what it is that we create. In TDD, therefore, the primary focus is to be able to verify that whatever we create is of good quality and that it can provide the intended results. The essence of TDD is to work incrementally on your design The Value of TDDCode is weird, unusual, complex, and fragile. One tiny error can invalidate the result.Even the strongest developers make mistakes – after all, they’re only human, and minor mistakes can happen by anyone.It’s also interesting to note that the very nature of TDD is to iterate and improve. Step by step, TDD makes it easy to introduce new features incrementally, and in each iteration, we can catch and resolve the defects found during testing. Researchers have found that most problems found in production are caused by simple programming mistakes.“Approx. 60% of all the issues found in production are due to trivial mistakes.”A simple mistake can cause entire systems to fail.A study of 198 production failures found that 58% of the failures were due to trivial mistakes that could've been caught before deploying to production. This means that if we checked that our code actually did what we thought it did, we'd improve our reliability by over 50% - substantial cost savings and, most importantly, improved user satisfactionAnd while we do have tools that catch some mistakes, and our IDE will give us great feedback that is fast and efficient and maybe highlight some errors, the IDE won’t catch all kinds of issues.In software development, TDD is a huge step forward because of this very reason: it ensures that we catch the issues that the IDE could not catch earlier.How TDD worksThere’s a lot that TDD has to offer, and understanding its most significant benefits requires a look into the way it works. The following is a summed-up version of the workings of TDD and what happens at each stage:Writing and checking that the test failsWe can check the mini specification by executing before writing the behavior and checking that it fails. Before even writing the behavior, the focus should be to write the test and to make sure that the test fails. Of course, the first time, the test will fail because there’s no code.If it fails, that’s a good sign – it means we wrote something useful, so now our next focus can be fixing the test. Improving quality with each iterationWhen we fix the test, what we really want to do is implement our behavior. But then, in the very first iteration, we won't be trying any fancy things or getting creative with the code. At this stage, we just do the bare minimum to pass the test, and once it has passed and we’re good with it, then in the second iteration is where we can bring in our creativity. This is where we can add more quality, improve our code with every iteration, and, most importantly, ensure it fulfills our intent. Writing code to fulfil the intentNext, we write some code to fulfill that intent, and we write just enough code to get to the passing test with that failing specification – the bare minimum to meet that mini specification. Run test again to confirm it passesNext, we run our test again to confirm it passes. Now we are in a stable state. All our specifications are passing. Safety checkOnce we run our test, we have the safety check that guarantees that if anyone tries to change the code or wants to modify it, we can run it and still be able to catch any issues with our approach. This safety check guarantees that our test will detect any issues before it goes to production. The open “code” road is ahead of us to express our intent in the form of test mini specification, and here’s where we divide and conquer: we test mini specifications for one behavior, and then we test another one. Following this, we accumulate and record all the requirements we intend to implement. TDD gives us an independent path verification that the coding actions matched our intent. It offers a way to verify that what we have coded matches and implements our intent.Evolving Your CodeNow, we have more time to improve our code and bring more quality and refinement to the code. This is true since we have our tests embedded in the CI/CD pipeline and ready to catch any defects that could have been introduced by the changeTo make our tests/ code more expressive, we can start changing and modifying it to make it more general, readable, and simpler. And to do so requires a three-step process known as the Red-Green-Refactor cycle.The Red-Green-Refactor CycleWhat is the Red-Green-Refactor CycleIn the Red-Green-Refactor cycle, the process of TDD is broken down into three stages:Red: Write a test that failsGreen: Write code and see it passRefactor: Make the code greatWhy use Red-Green-RefactorThrough the cycle Red-Green-Refactor cycle, we try to improve the quality of the code to reach a stage where the code is:Easy to read Easy to change Workable Testable Easy to maintain in the future Simple and efficient And also to achieve the following attributes of good code:Modular Loosely Coupled Cohesive Separation Of Concerns Information Hiding TakeawayWith TDD, it has become easier to achieve the attributes of good code, as mentioned above.When we try to refactor our code to achieve these attributes, TDD gives us the assurance that we have already tested any changes that we want to make, and if any issues arise with our code, they will be detected before production.The outcome of the TDD approach is a unique test, and these unique tests can be integrated into the continuous Integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) process. With this integration, what we want to achieve – and what TDD helps us achieve – is that whenever someone changes the code, the process of TDD will run. As part of that, we can find any defects or issues before the code goes into the QA environment and, of course, before it goes into production.In software development, TDD is one of the top approaches to tackling complex development and ending up with clean, workable code. To learn more about other methods and what is best suited for your business, this article about TDD, BDD, and DDD is not one to miss!
Test-Driven Development: Improving Efficiency with a Mindset Change

When was the last time you were tasked with test automation but ended up spending more time and effort on maintenance?If you’re reading this article, chances are you’re familiar with test automation and may have even conducted it yourself. In case you’re not, this article on The What, When, and Why of Test Automation will give you a quick refresher on what it is and why/when you should use it.However, if you’re like other newbies, you may have managed to design a framework, but then you’d spend a lot of time, effort, and resources on simply maintaining it.That right there is what happens when you do test automation without knowledge of the best test automation tools and practices.And if you read further, you’ll find precisely what the best practices for test automation are and how they can get any beginner started with test automation in the most efficient way.Framework SelectionTest automation is heavily dependent on tools, low-code or no-code.Therefore, selecting the right tool is essential for high ROI with test automation. Here are a few points you should consider while choosing a test automation tool:Scope of testing: Will you be testing web-based applications or mobile-based applications? Or both. In order to test only web-based applications, there are several tools like Selenium or Cypress that are pretty powerful. In contrast, for mobile-based applications, Appium is still considered the go-to tool. Available support: Whenever opting for a test automation tool, one should always consider the level of documentation and the degree of support you can get from the respective community, if you ever need it. Since Selenium and Cypress have been the favorite tools among the testing community for quite some time, the level of support you can get from the community is incredible. Tech stack: Another factor to consider while selecting the automation tool is the tech stack your dev team uses to develop the application under test. Since you’d want to keep and execute your E2E tests in the same repo and environment, respectively, it only makes sense to use a tool that uses the same stack. For example, if your application is being developed using Angular, you might want to use Protractor, which was developed specifically for testing Angular applications. Open Source or not: Depending on budget constraints, one may choose to use open-source tools such as Selenium or Appium for automation purposes. However, it is important to remember that all open-source tools are not inferior to their commercially available counterparts. Available Features: While choosing the tool, you should check if the automated testing tool supports record-and-playback test creation as well as manual creation of automated tests. Does it include features for implementing checkpoints to verify values, databases, or key functionality of your application? Does your tool integrate with your CI/CD pipeline, such as Jenkins or Azure? Or a source control such as Git? Does the tool have the ability to test enterprise applications? Does your tool offer out-of-the-box support to test packaged applications like SAP, Oracle, and Salesforce? Selecting the Right SelectorsUsing the right kind of selectors to get your elements for your automated tests is the only solution for flaky tests. If you select un-reliable or generic selectors, your tests are destined to fail. For example, using Xpaths or generic class names as selectors will result in flaky tests and a lot of maintenance for the test suite, as they’ll be invalid whenever there is some change in the UI of the page under test. In my personal experience, I’ve found the CSS & JQuery selectors more reliable and effective.Let’s assume we want to get the following element:Which of the following selectors do you think is more reliable?Xpath: //*[@id="container"]/a[1]CSS: a[href="https://youtube.com/]Which Tests Should You Automate?It is impractical to automate all testing, so it is vital to determine what test cases should be automated first. Good test cases for automation are ones that are run frequently and require large amounts of data to perform the same action.You can get the most benefit out of your automated testing efforts by automating the following:Repetitive tests that run for multiple builds Tests that tend to cause human error Tests that require multiple data sets Frequently used functionality that introduces high-risk conditions Tests that run on several different hardware or software platforms and configurations Tests that take a lot of effort and time when manual testing Test Cases that touch a key piece of functionality and should be run before release Test CoverageHere we’ll not be talking about test coverage in terms of unit testing but the different types of testing you should cover as part of your automation test suite even if it weren't required. Here are a few that, in my personal opinion, should be covered as part of best practices implementation:Accessibility Testing: Without going into too many details about accessibility testing, as in what it is or why it is important, the borderline is your application will perform better if it follows the WCAG guidelines, and while it should be part of development itself, nonetheless it should be part of your automation testing. With tools like the AXE engine, it is very easy to integrate the accessibility test cases within your existing test suite. API Calls: Even though APIs are tested separately by the QA and the development teams, it is always better to check the API calls on runtime while they’re being made from the application. For example: If you need to test a login page, sometimes the errors on the FE are very generic, and they’ll not tell you more than ‘Something went wrong.’ Still, as a tester, while you need to observe if something goes wrong, you also need to identify why it did. In this scenario, if you’re inspecting that API call made on clicking the login button, you’ll get the exact response and status code back and can quickly identify what exactly happened based on it. Client-side Performance: While server-side performance is important and is covered extensively during testing, client-side performance is equally essential and, most of the time, is left untested. A general client-side performance audit will tell you things like the FCP and LCP, which is the time your application takes to load the first item versus the page's main content. The easiest way to implement this is by using Google’s lighthouse integration. Visual Testing: I’ve covered this topic in detail in my other article on Visual AI and Autonomous Testing, but just for introductory purposes, with modern AI/ML tools available like Applitools and Percy, it doesn’t make sense to keep validating your application’s look and feel via coding assertions. Implementing Visual AI testing in your automation suite will save much of your time and resources, especially with maintenance. Test Structure & StrategyWhile designing your test automation suite, you must take into account the importance of a good test structure and strategy that can benefit not only the live development but also its maintenance. Following are a few points that have helped us in the past:Test suites: Structure your tests in the form of test suites that can be independently configured and executed. If each test case represents a piece of a scenario, such as the elements that simulate completing a transaction, use a test suite. Self-contained /Independent: While writing your tests, make sure they’re self-contained, meaning that they should not depend on their successor tests to pass in order for them to pass. We’ve seen many examples where teams build their tests to run in a sequential order while it's opposite to what the automated test suite is supposed to be: flexible, agile, etc. Data-driven: Always make sure your tests are data-driven in order to ensure the reusability of the work that has already been done. By using a data-driven approach, you can generate test cases just by changing the data stored in external files. Page Object Model: In some cases, when your application under test is prone to frequent UI changes, it is a good idea to implement POM for your automated tests. It not only ensures the reusability of the component but also helps in the readability and maintenance of the test code. Dedicated Automation EnvironmentThis might not be possible for each team or project. Still, since we’re talking about the best practices, I have to mention Dedicated Automation Environment, as having one will only increase the productivity and overall efficiency of your automation framework and hence the crucial time and resources of your team.It has been observed many times before, more than I hate to admit, that tests frequently fail due to unannounced changes deployed to the environment in which the tests were executed, especially when multiple teams are working with the same dev or test environment. Therefore, having a dedicated environment that is up to date with the latest changes that are supposed to go live in the next release is essential for non-flaky tests.Testing Cross-platform and On Real DevicesMore often than not, it is observed that testers design their tests to execute only on a single platform. It could be a platform like a desktop against mobile or in terms of a browser like Chrome vs. Firefox, while as a best practice, your tests should be designed in a way that they can be executed against multiple platforms, and they should.To have ample test coverage for a web application, you should ensure you execute your tests against all the popular browsers and on all the popular devices such as desktops, tablets, and mobile. Moreover, if you require more realistic results, your tests should run on real devices instead of emulators or simulators. This task can be humongous and expensive if done manually or even using local resources hence making use of cloud platforms such as Browserstack or SauceLabs can be beneficial.ExecutionThis is where all your preparation and work come to life. This is also the most critical step to automate, which most of the testers fail to do. It is often understood that integrating the E2E tests into the existing CI/CD pipelines is a DevOps job that is somewhat true but not always. I like to do it myself, as it gives you more control and ownership of your tests. Anyhow, whoever does it, ultimately, it should be done, and the following are a few points to remember while making doing so:Parallelize the automated test cases that are independent. For example, if a test suite contains 5 tests that are self-contained, none of them should wait for the previous test to finish before starting. Use multiple machines and servers to run your tests in parallel. It can decrease your execution time from ~25 to ~5 minutes. To increase the speed of your release while maintaining the quality, configure your tests to run on each pull request from a child branch to the main branch. This will ensure that none of the new changes are breaking any existing functionality and that the code is safe to merge. If your team doesn't push out frequent releases, it might be a good idea to execute your test cases based on a cron-job to ensure nothing unexpected breaks the application. For example: Run the tests every other day at noon or every first Monday of the month. ReportingFinally, in the last step, if there is no thought-out plan for effectively collecting and analyzing the test results, the automation effort can be all in vain. Therefore, a well-defined process will save teams from many conflicts and resources in refining the application.Automation should serve to reduce the amount of time QA teams have to spend verifying test results. Set up adequate reporting infrastructure using the tools that will generate high-quality test reports after each cycle. If possible, assign your tests different but relevant tags to group and filter them out easily in the reports. A good test summary report should be created after each cycle and shared with all the stakeholders via multiple mediums, such as Email & Slack.TakeawayEach application of any complexity will likely have its own combination of testing requirements, and none of the discussed points together will ever be in play.It is still essential to know the best practices for making the right decisions early on. Study these practices, and implement them in a way that best suits your software, business, and users.If you want to take your application of test automation a step further to practice better, faster QA, this 30-minute video will give you all you need!
Best Practices for Test Automation: Framework Selection, Test Coverage, and more

UX, UI and Product Designers work within a space of continuous learning. The very nature of what we do is iteration!In a highly competitive field, good designers look to expand their knowledge and keep up with the latest tools in order to best serve their users.So I asked designers from our team about how they stay sharp and what methods have worked best in their experience.Question 1What suggestions would you give to keep up with the latest knowledge and advancements in technology?Name: Adriano RenziTitle: UX ResearcherResponse:I try to check how technology may evolve by attending scientific conferences and reading scientific journals and being part of discussion panels related to interaction, information architecture and AI. Many presented researches anticipate by 2 to 5 years what will come in the future.Name: Rahul JacobTitle: Product DesignerResponse:As the tech industry evolves rapidly, attending conferences, tech events, and joining online or in-person communities can help with gaining knowledge and adapting to new technologies. It is also important to spend some time every day following news from technology focused publications and online tech news sites. Connect with tech Influencers, tech companies devoted to technology and emerging trends through social media.Name: Osama NadeemTitle: Product DesignerResponse:I have subscribed to many designers/content creators on youtube, blogs and I follow tech leaders on platforms like linkedin where I get many updates regarding what’s happening in the tech industry.Name: Umer FarooqTitle: Principal DesignerResponse:I used to look around articles especially on IDF and try to find if it’s timeless. Trends come and go but there are certain workflows, behaviors you can learn by participating in communities. I can relate to Figma as I lost the train because of my too much involvement with Adobe XD. A lesson well learnt and now catching up well with Figma, the best design tool.Name: Dana MitchellTitle: Sr. Product DesignerResponse:Step one would be to identify what technology you want to keep up with. Go with what you are passionate about or technologies that pique your interest. Step two is figuring out how you want to keep up to date. I leverage videos, audiobooks, and podcasts for my learning. Lastly, step three, use that knowledge. Write articles, design flows, edit a video, whatever format it takes! By using your new knowledge you will anchor it in your mind and create a personal design process that is dynamic and designed to grow with you.Name: Cordelia FongTitle: Sr. UX DesignerResponse:I tend to actively keep up and devote time to reading the tech news daily. Attending conferences and workshops, networking with designers are also a priority, following great leaders and participating in online communities.Question 2Are there design leaders or blogs you regularly follow?Name: Adriano RenziTitle: UX ResearcherResponse:I like to check what is happening in projects from Ben Schneiderman, Floridi, Resmini, Benyon, Agner, Nigel Cross and Resú. They are usually very active in continuous publications on technology. I do not look for design blogs because they usually present no reference of their facts.Name: Rahul JacobTitle: Product DesignerResponse:I consider Don Norman to be one of the most influential design leaders when it comes to user experience and usability research. In addition, I find John Maeda to be a true inspiration since he is the pioneering voice of simplicity that encourages people to use technology to simplify their daily lives rather than complicate them.Dribbble, UX Collective, Medium, Smashing Magazine are all excellent resources for finding great articles, stories, content, inspiration, research, as well as for thinking critically.Name: Osama NadeemTitle: Product DesignerResponse:Among many designers that I follow, I admire Don Norman, Anudeep Ayyagari, Eric Keneddy and Joe Natoli. I like how Don Norman has a very simple yet effective way of explaining things, Anudeep Ayyagari has a rather funny tone which is also pretty interesting. Eric Keneddy’s UI course that I took a couple of years ago was very impactful and is still very relevant and Joe Natoli has a very unfiltered and impactful way of explaining things.Name: Umer FarooqTitle: Principal DesignerResponse:My all time favorites are Normans, Nick Babich, Mark Hassenzaal, Frank Spillers. The guys are so expressive and communicate ideas in a seamless fashion that you don’t feel burdened.Name: Dana MitchellTitle: Sr. Product DesignerResponse:Not a blog but podcasts! While not specific to emerging technologies in design, there are a lot of podcasts, like The Way of Product Design, Design Better Podcast, 99% Invisible, etc. have helped me to build a better design practice. Hearing design leaders speak about their problems or projects and the solutions that came with them helped to expand my knowledge of what is possible in product design.Name: Cordelia FongTitle: Sr. UX DesignerResponse:My favorite design leaders are Luke Wroblewski (Mobile First), Steve Krug, Don Norman and Kim Goodwin. I followed a few blogs when I started as a UX designer: CareerFoundry, JustinMind, UX Mastery, UX Matters. They provided such great depth of information on UX careers.Question 3What are your main sources for continuous learning?Name: Adriano RenziTitle: UX ResearcherResponse:Conferences (HCII, AHFE, SPGD, FTC), Journals (Ergodesign Journal, Philosophy and technology, Design de Informação), Theses (Esdi, PUC-Rio), Books (Mihaly Csikszenntmihalyi, Resmini, Nielsen, Rosenfeld, Morville),Name: Rahul JacobResponse:Every once in a while, I check if there are any tech-related crash courses, webinars, online tutorials, and networking events occurring. In addition, I reach out to my friends, coworkers, and colleagues who have the most knowledge on a topic for recommendations: articles, books, lectures, or other resources.Name: Osama NadeemTitle: Product DesignerResponse:I consume lots of content on youtube and I’ve subscribed to many design specific channels there. I also read articles on medium and have followed people on linkedin who post useful design learning resources. Whenever I come across some content and I don’t have the time to skim over it right then, I save it in my Notion workspace and revisit it later. I also try reading books, but that doesn’t happen too often.Name: Umer FarooqTitle: Principal DesignerResponse:I prefer watching rather than reading. There are many channels out there to follow and everyone is doing some seriously amazing work.A recent addition was a guy from Canada called Faheem.Name: Dana MitchellTitle: Senior Product DesignerResponse:My source changes based on my intent. I find that, as a designer, any social media algorithm will eventually serve me design-focused content. You like one of Zander Whitehurst’s “Supafast” videos and the algorithm will serve you more like it. This is a fantastic way to take small “sips” of new knowledge, which makes learning more approachable. However, I do have a more targeted approach when it comes to learning specific skills and I will seek out anything that can help me achieve my goals. Articles, tutorials, videos, documentation, whatever!Name: Cordelia FongTitle: Sr. UX DesignerResponse:LinkedIn learning, courses, books, blogs and attending events.Question 4What design books do you recommend?Name: Adriano RenziTitle: UX ResearcherResponse:Information Architecture by Rosenfeld, Pervasive Information Architecture by Resmine and Rosatti, Arquitetura Pervasiva by Luiz Agner, Lean UX by Gohelf, Seiden, Flow by Csikszenntmihalyi, Les Technologies de l'intelligence by Lévy, Designing Interactions by Moggridge.Name: Rahul JacobTitle: Product DesignerResponse:The Laws of Simplicity by John Maeda, The Design of Everyday Things by Don Norman, 100 Things Every Designer Needs to Know About People by Susan Weinschenk, and Start With Why by Simon Sinek.Name: Osama NadeemTitle: Product DesignerResponse:The Design of Everyday Things by Don Norman, Just Enough Research by Erika Hall, Giving A Damn about Accessibility by Sheri Byrne Haber, Don't Make Me Think by Steve Krug, and Refactoring UI by Adam Wathan & Steve Schoger.Name: Umer FarooqTitle: Principal DesignerResponse:Don’t Make Me Think by Steve Krug and The Design of Everyday Things.Name: Dana MitchellTitle: Sr. Product DesignerResponse:Inspired by Marty Cagan, The Mom Test by Rob Fitzpatrick, Stories That Stick by Kindra Hall, Think Again by Adam Grant, Actionable Gamification by Yu-kai Chou, and Atomic Habits by James Clear.Name: Cordelia FongTitle: Sr. UX DesignerResponse:Many of you may have known these books, but these are still my top 3: 1) The Design of Everyday Things by Don Norman 2) Don’t Make Me Think: A Common Sense Approach to Web Usability by Steve Krug 3) The Elements of User Experience: User-Centered Design for the Web and Beyond by Jesse James GarrettQuestion 5Do you find your personal interests influence your professional space? What inspires you as a designer?Name: Adriano RenziTitle: UX ResearcherResponse:Not really. But I find my enthusiasm and learning interest to influence people around me.Name: Rahul JacobTitle: Product DesignerResponse:Looking back at my childhood, I’m glad I was exposed to Music and Art because it taught me valuable lessons that I don’t believe I would have learned otherwise. Through music and art, I learned how to think outside the box, discover better ways of doing things, boost confidence, productivity, self-esteem, and well-being.Name: Osama NadeemTitle: Product DesignerResponse:I’ve always been fascinated about how things work, that mindset has enabled me to look at problems keenly and that is always my approach when it comes to design. My personal interests such as music and gaming always keep my brain creative because both of them allow me to think outside the box and be creative. These two are among the attributes that keep me motivated as a designer.Name: Umer FarooqTitle: Principal DesignerResponse:I prefer to spend time watching seasons especially with the backdrop of WW2 and keenly observing the culture, the food, the language and how people use to behave in certain circumstances etc. A good designer can always get inspired from whatever content he digests every day.Name: Dana MitchellTitle: Sr. Product DesignerResponse:My inspiration as a designer is to creatively solve problems to improve the lives of people. With my personal interests being balanced between mentoring new designers and expanding my skills as a novice potter, I find that these interests feed directly into my professional work. Mentoring has improved my ability to speak about design and to convey my ideas more effectively while pottery has taught me to let go of my work and accept that not everything is going to make it out of the kiln how I want it to.Name: Cordelia FongTitle: Sr. UX DesignerResponse:Curiosity and finding your passion. I tried things that interested me. Find out what I am good at, and I experimented with Illustration, Sketching, Painting, Interior Design, Fashion Design, Jewellery Design, Advertising Design, Website Design, and which led me to where I am
Ask A Designer Round 3: Staying Curious

When was the last time you considered “team happiness” as a KPI for yourself?As a manager, it’s vital to be very aware and conscious of how your team feels at work. Are they happy with what they’re doing? Do they have enough opportunities to grow and develop their skill set?Having a culture of open and transparent communication within any team can have very positive effects on its function.Open communication helps foster trust among team members by creating a safe environment where they can share their thoughts and ideas.It can also boost the team’s productivity, creativity, and innovation. Above all, if practiced regularly, this can create a continuous feedback loop that can help the team to improve, leading to better decision-making and smoother achievement of their goals. Combined with values of honesty and support, this can enable managers to build hyper-successful teams.Then again, it is important to understand that communication is a two-way street, and sometimes, growing teams and managers fail to look at it that way. The team lead, or the manager would always be the one to provide feedback and consider it to be sufficient.Instead, managers should engage in open dialogue and actively seek feedback for communication with their team members. This will help them understand how they are perceived and identify any concerns their team members have.Not only will this activity make them more effective in their roles, but when each teammate feels that they have a say in how the team is run and that their opinions are valued, their motivation and commitment to the team will increase massively.Open collaboration is not just limited to the team and the manager, but it should also be encouraged amongst all stakeholders involved to ensure success of any project. To achieve this, be sure to check out this article on DesignOps.Focus Areas For ManagersFor managers, we can identify the following areas upon which they can measure their perception within their teams and seek improvement:Team Happiness: Do their team members enjoy working together under their management? Growth & Upskilling: Do managers provide enough opportunities for growth and development for their team members? Leading through an example: Do managers manifest the qualities in themself that they expect of their team members? Support: Do managers provide the right support to their team members in their work? Open to feedback: How open are the managers about their shortcomings or listening to their team members about their own mistakes? Transparency: Do the managers communicate proactively and transparently? Culture: Does the manager create an inclusive culture for everyone in their team to thrive? Recognition: Does the manager put an effort to recognize their team members when they do good work or just focus on the criticism? A lot of answers to the above questions can be found by simply maintaining open communication with your team, like in this candid conversation with designers.Feedback Form TemplateNow to put these in practical terms, here is how someone can use the following template to get feedback from their team members.Instructions for the respondents:Keep the survey confidential and anonymous, so people can comfortably respond. Illustrate the intent of the survey, which is to get feedback from people for self-improvement. Don't confine the responses to p options or a grading system. Keep the answers open and let people express their sentiments. Here is an example:The QuestionnaireFor the questions of the feedback survey, it is a good idea to give examples of positives and negatives that can help the team members understand better what they should be looking for in terms of support from their managers. It is also a good idea to enable the shuffle option in the questionnaire if possible to randomly sort questions to remove fatigue bias for some questions.Are you happy or proud to be a member of your squad/ team? Do you feel connected with your peers? Does <> provide you with enough opportunities for growth and advancement in your career? Examples can be discussion around opportunities or asking you to practice certain things that can improve you as a professional. If this has happened, highlight something that you disliked or liked about this. Does <> inspire or motivate you to do your best work? If yes, How? Example: Either by his example or sharing inspirations or talking with you or something else. How would you describe the level of support offered by <>? Example: Does <> support you in your well-being, work challenges, work-life balance challenges, growth challenges, etc.? You can also mention areas where you may have felt a lack of support from <> and would like that to improve. How comfortable do you feel in giving feedback to <> or sharing anything that you don't feel good about? What is <>'s general response when you have shared something difficult with him before? Do you feel that you are treated fairly without bias? How would you rate transparency in terms of messaging, policy sharing, and general communication from <>? What could be improved? Describe your squad's culture in fewer than 20 words. You can also mention if you don't see any culture or a culture you would like the team to strive for. Are you encouraged to lend others a helping hand if they are stuck with some task or take help from others and be comfortable about it? How strongly do you feel valued at work? Does <> recognize your good work or exclusively focus on criticizing? How likely would you recommend a close friend, family member, or someone you care about to work in the <>'s team? [BONUS Question] What is something <> can start doing, do more of, or stop doing to support you to continue doing great work? TakeawayConstructive criticism that doesn’t discourage, but in fact motivates team members effectively will always prove to be a successful method.And as great as achieving effective communication can prove to be, it’s vital to make conscious and tangible efforts in the way of doing so.With the feedback form template and questionnaire provided above, you should find it easier to actively contribute towards improving communication and collaboration within your team.For a more in-depth guide on how you can enhance the growth and performance of your design teams, read this detailed article on Designer Career Ladders.
Empowering Your Team through Feedback: A Manager’s Guide For Effective Communication in the Workplace

Many product development teams often face one very common yet very significant challenge; scaling unified experiences across multiple channels, and accomplishing that without significantly reinventing the software itself.The main culprit behind this problem? Usually, a lack of reusability maturity across the organization. In the initial phases, most startups are heavily focused on shipping out the first version of their digital product as early as possible and collecting feedback early on in the process. While this is understandable, given that startups often have tighter timelines (and budgets!) compared to an enterprise-level business, it does impact the product itself.Usually, as a direct result of focusing too much on a fast rollout, many important architectural decisions can (and do) take a lower priority than shipping out the product itself. And to make matters worse, these gaps continue to compound and become harder to deal with the longer they stay on the back burner.It is important to note that the engineering teams (in most cases) are not to blame for this situation or the problems that subsequently arise from it. Regardless of the extent of their competence, a product’s architecture is directly impacted by decisions taken very early in the development process, especially where there is very little foresight available into the future.However, before a product can truly enter its growth stage, it could prove prudent to take a step back and address the underlying issues that could be impeding the needs associated with the growth stage of the product’s lifecycle.What makes reusability so important? Accelerating time-to-market When leveraged correctly, reusing components can create space for faster development and save product development teams more time since many of the necessary building blocks will already be available to them, making the need to build everything from scratch redundant.Centralized maintenance Any software periodically requires updates to function optimally. With reusability in the mix, any time a piece of software needs updating, developers need only to update it in the centralized master component, instead of manually updating each section of the software. This allows not just for easier maintenance but also speeds up the process in parallel.Lower operational costs One of the most important long-term benefits of reusability is that it allows development teams to increase their efficiency, helping them save time both in terms of development work as well as eliminating redundancies and duplication.New business lines Reusability at the system level can help firms discover new business lines. For example, with the exposure of the existing system functionality to new customers, especially those that live outside of the eco-system e.g. API integrations, SDKs, etc.Reusability maturity frameworks From a product developer’s perspective, there can be several suitable reusability frameworks and models. However, choosing the right one is crucial to product success. Based on my professional experience, two such frameworks can prove very helpful in a broad range of situations.First, the reusability framework pioneered by Koltun and Hudson (1991). This framework evaluates reusability maturity on an organizational mindset level. It does so primarily by taking into account the various processes and internal practices that the development teams within the organization tend to follow.The second framework that I have found to be very effective solely focuses on the assessment of reusability maturity in the context of the software itself. These assessments can include:Level 0️ – No reusability: Cut and paste. Manual update at all instances.Level 1️ – Object & Function Reuse: Small-scale software components that implement a single well-defined object or function may be reused.Level 2️ – Component Reuse: Components of an application from sub-systems to single objects may be reused.Level 3️ – Application Reuse: An application may be reused either by incorporating it without change into others or by developing application families.Level 4️ – System Reuse: Complete systems, which may include several application programs.Software Reusability Maturity modelMoving up the reusability maturity curve The impact of leveraging the assessments of a reusability maturity framework is to determine where you stand on the reusability maturity curve. From that point, the next logical step is to try and move up the curve. One way to do this is to establish a roadmap and identify the next necessary steps along this roadmap. It is important to remember that, regardless of your position on the curve, the phrase “build once, reuse everywhere” should be a north start for development teams.For example, in the second framework examined above, moving between Level 0 and Level 2 would primarily require teams to consistently adopt and adhere to better programming practices. In this case, product managers could consider using a design system as a possible solution in promoting the reuse of components across different areas of the application.A design system can help to create a comprehensive library of components, allowing product teams to efficiently and consistently deliver a unique brand experience through a single application.Levels 3 and 4, however, may need more sophistication in key decisions, especially at the architectural level. Products may require you to make certain changes to the tech stack or move towards complex cross-platform options, based on what would best meet your requirements.The correct architecture would then allow product teams to collate various application components and then republish them separately as SDKs or separate platform services.Microservices architecture can enable product development teams to build specialized APIs which can also be reused outside of the core application. This, in turn, could help to create entirely new business channels, for example, by exposing the existing service to 3rd parties for integrations.Final Thoughts This blog does not mean to imply that achieving reusability maturity is the solution to all product problems. In fact, working with reusable software code can prove somewhat challenging for many developers. But there is the fact that with software components reused across different sections of the same app or multiple apps, you can create additional space to consider and test out different scenarios for each release, minimizing the impact on the rest of the modules in the software.Therefore, moving up the ladder of the reusability maturity curve is more likely to help with product sustainability through the growth and maturity stages in its life-cycle.
Understanding Reusability Maturity Assessments
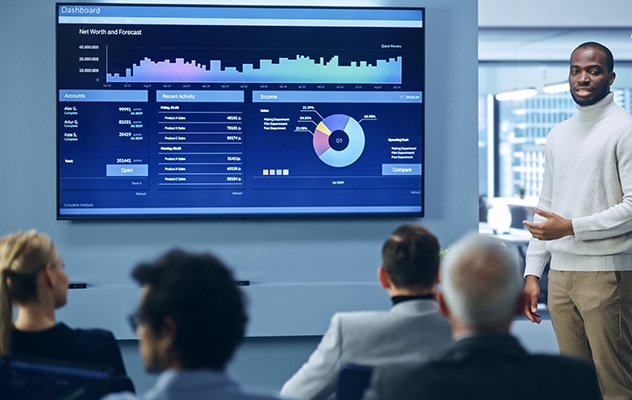

If you’re someone who thinks of frameworks as a scam — you’re not alone.Many people have come to associate product frameworks with trouble rather than a solution to real world challenges — a conception that has formed over the past few years.Unfolding the Stigma Around Product FrameworksThe stigma around product frameworks stems from companies and individuals that offer “frameworks” only as a means to lure users towards their products — a mere stepping stone in their marketing efforts.As a result, what we’re left with is a wide variety of frameworks — for every topic, and in every industry — with little knowledge on how to actually use them.And today, it seems the situation has gotten quite out of hand; I recently came across a framework for relationship counseling that contained “metrics” to track all violations caused by your partner. And of course, these would be discussed in weekly review sessions.So, it was inevitable that frameworks, originally meant to provide a well-organized structure to any process, are now more often than not looked at in a negative light, especially in the product community.Most aspiring product managers have fallen prey to the facade of flashy frameworks that only cause more trouble than offer any viable solutions.But we’re not here to completely discredit product frameworks! After all, at its core, the true purpose of a product framework is to offer a template of practices you can follow to bring structure to any process.However, without certain measures of caution, using your product framework would always be a gamble.4 Things To Consider When Using Product FrameworksThe success of your product framework will always depend on certain factors. And being cautious about each of them will significantly improve your chances of success with your frameworks.1. Find the right framework for your productNot every framework you come across will be suitable for you and your product.As a standard practice, it is critical to perform your due diligence in seeking out the framework that best suits your needs and fits your product well.In your research for the right product framework, you’ll also likely come across two frameworks with contradicting guidance on how to use them.This doesn’t necessarily indicate that either one of the two is a scam; they just might not be relevant to your situation.A good way to identify the right frameworks is to watch out for non-credible sources and seek out frameworks that have actually been tried and tested by others with similar use cases.2. Get appropriate and authentic trainingProduct frameworks are far from being straight-forward and easy to adopt right away.Most frameworks you find will require some level of familiarizing and training.There are some complex product frameworks for which you’ll find dedicated training programs online as well. But even this is being exploited and turned into a scamming business, so it’s important to be wary of what you’re getting yourself into.I’d like to emphasize here that there is no need for any paid certification to get started with using a product framework. In today’s world, most of the information and guidance you’ll need is already available out there — free of cost.All you need to meticulously do is filter out the authentic ones from the rubble of unreliable ones.The best way to do this is to:Get a sound understanding of any framework you pick for your use-case. Understand the limitations of your chosen framework, where it is most effective, and where it fails Review all original material available about the concept wherever possible (look for the original author of the information to check its authenticity). Connect with other community members and learn from their experience of the product framework: what worked for them? What didn’t? 3. Avoid getting blindsidedNo framework you find out there will be 100% perfect!Product frameworks are meant to be an aid to your process — not a stringent rulebook that is rigid and impedes the progress of your product team.Anyone that considers product frameworks as the “absolute truth” would be a fool.For every product, every team, and every circumstance, there will be different and distinct requirements. There’s no guarantee that what worked for companies like Google, Facebook, or Amazon will work for you — so it’s best not to get too excited and try implementing it on your own use-case.It’s good to trust your gut and base your decision on what the framework actually brings with it, what it recommends, and whether or not it aligns with your fundamental principles.Before getting started with a product framework, make the effort to truly understand what you can modify about your process in accordance with the guidelines and what cannot be changed for your specific framework.4. Don’t over-rely on frameworksAlways remember: there’s no critical need to use frameworks — and using them just for the sake of having a framework in place is possibly one of the worst reasons to invest your time and effort into getting a framework.The end goal in product management is always to solve customer problems, and do so effectively. Whether or not you have any particular framework in place holds no importance to the customer.If, for example, you already have a prioritization method or product prioritization framework that works for you better than MoSCoW or RICE, it’s completely fine to continue using that.Product frameworks are very helpful when it comes to adding an overall clarity to your process and approach, and even more so for newcomers who need concrete and clear guidelines before handling any abstract task.TakeawayProduct managers want to solve customer problems, and product frameworks are tools that help you solve problems in pretty much every situation.For any process, and at any given point in time, there will always be multiple tools that you can choose from and use. But the important thing here is to identify and choose the right tool that works well with you and your product and actually helps you execute your processes more efficiently.As with any tool, it’s important to know how to use the framework effectively before getting started.Product frameworks are created to address pre-defined problems, but in the real-world, your situation will always be unique and the tools you use may require adjustment in accordance with your circumstance.Finally, there’s absolutely no obligation to continue with an existing tool. If you have another method that does the job better, don’t take the added burden of additional costs to use the tool.Learn what works, gauge your own limitations, and apply methods and product frameworks that actually align with your needs.
4 Things To Get Right When Using A Product Framework

To build and manage a product in the digital world today heavily relies on data and analytics.With data guiding important decisions, there remains no doubt that data-driven decision making will continue to dominate as the modus operandi for digital businesses.In this article, we’ll cover three techniques that can help you make data-driven decisions.But first, let’s understand why using data to make decisions is such an important part for successful product companies.Why are data-driven decisions important?While data has always been integral to any business in any form, never has it been more important to extract, collate, and analyze this data efficiently.With massive amounts of data now generated on a daily basis, there are several reasons successful organizations play such close attention to user data analytics:1. InnovationCompanies that recognize the importance of data-driven decisions don’t just look at it as a digital “trend”. They treat it as an essential asset for the business; with data guiding important decisions, digital insights are seen as an opportunity to seek more knowledge and drive a culture of innovation within the organization.2. CompetitivenessWith a higher dependency on data, you gain the ability to evolve your business in accordance to emerging trends.Not only does this increase the adaptability of your organization to keep up with the latest patterns in the industry, but such adeptness also helps you use data to make better decisions that ensure you stay ahead of your competition.3. Improved communicationWorking with key insights and user data analytics is a great way to keep your organization aligned with important KPIs that contribute towards business growth.By being on the same page, your organization can perform as one cohesive unit that never loses sight of what needs to be achieved and which kind of user data is needed for it.4. Consistent growth and opportunitiesOne of the prime benefits to businesses that leverage user data analytics is that of consistent growth and discovering fresh new opportunities.Being able to consistently make data-driven decisions empowers your organization to narrow down on key insights, performance metrics, and actionable benchmarks that keep you ahead of the curve by continually encouraging growth.What is an example of a data-driven decision?To understand how businesses have come to recognize the importance of data and user data analytics, let’s take the example of a business with a large base of millions of active users.Netflix, a giant in the content streaming industry, leverages user data to achieve consistent customer retention.Despite increasing competition in the industry, Netflix has found ways to prioritize the user experience by studying their behaviors, preferences, and watch patterns.With such deep insights, the streaming service is able to recommend relevant and accurate content suggestions to each user, significantly improving their experience on the platform, which keeps customers coming back for more.What are some key factors when making data driven decisions?With a good understanding of all the ways user data analytics can help in your business, it’s vital to keep the following factors in mind for data-driven decision making:Organize your data effectively Format your collected data properly, before jumping into the analysis. Remove outdated information or irrelevant data that is not aligned with your goals, and get rid of duplicated data to remove confusion and arrange the data systematically.Overcome your biases Keeping yourself aware of factual data will limit your bias and help you make more informed decisions that aren’t based on guesswork. It is one of the best practices in data-driven decision making to collaborate with colleagues and consider other perspectives by seeking out more conflicting information.Ensure data literacy Only educating yourself on data won’t suffice; you should ensure that every stakeholder that contributes towards important business decisions is well-versed in working with data. This can be done by making your data more user-friendly and easily understandable, and also by analyzing who in your organization has the capability of working with data.For more tips on how you can effectively manage data, read about our 3-tiered approach in this article on The What, Why, and How of Data Management In the Age of Digital.3 Techniques To Make Data-driven DecisionsNow, let’s walk through some of the most useful techniques that are great for making data-driven decisions.There are several other techniques to drive better decision-making with user data analytics, but the following are found to be most effective:Funnel analysis Cohort analysis Event-based tracking Funnel analysisA funnel analysis is a technique for figuring out how many people proceed through each phase in order to reach a particular outcome on a product.The series of phases is known as a "funnel" because the standard shape used to visualize the movement of users resembles a kitchen or garage funnel.There are some great benefits of using a funnel analysis:Identify the exit pages with a significant volume of visitors Figure out the sources of your best visitors Aid in decision-making for team members and stakeholders Let me share an example of a funnel analysis done where we are looking how many customers started the session on the app, then viewed the ingredients and submitted the review.In the image above, we can see that around four people started the session and 85% of the customers viewed the ingredients.This further dropped until the write review step, showing that there’s an overall 62% conversion rate from session start until the “write review” step.This is how funnels help to understand the drop, on which you can further do different analyses to understand what’s causing the drop and how you can mitigate that.Cohort analysisHow do you analyze your user base to study various types of users when not every user feels the same way about your account?Cohorts are a means to divide up users into subsets based on a shared trait.Let's take the simple example of a blog website.To begin with, imagine a scenario where every person who visited the account for the first time is compared to how they behaved the next time they visited and interacted with it.Then, we evaluate this user behavior at two distinct times, testing for the same characteristic, which is first-time users, as you continuously push out updates, and analyze how various update types affect first-time user behavior.Now, let's say you published some extremely interesting material in January and February and noticed a rise in interaction.But in March, you added some pretty awful, enormous graphics to the landing page, and noticed a decline in retention.First-time user study is useful in such situations because it helps eliminate the prejudices of customers who have some brand loyalty and will continue to use the product despite poor UX.The goal here is to compare behavior and responses to various activities performed using the first-time experience.Cohorts become important in this situation.You need to compare KPIs as you push out new features, factoring in the KPIs you are measuring first. Conversions and retention are the KPIs that individuals most frequently consider when discussing cohorts.In other words, are your users turning into paying clients or are they only returning to your product itself? You can determine what features and KPIs are driving behavior in this way.Event-based trackingLet's look at event-based tracking now.This is the technique I would emphasize the most on because it’s the one that businesses do the least.By examining each and every interaction a user has with your product or your screen without clicking, you can now get into the mind of the user. And using instrumentation is the only way you'll be able to gather this data.Instrumentation should be a consideration for your engineers when they design your product. It's a difficult process because you're adding a lot of instrumentation in addition to writing code and releasing a new feature.But bear in mind: you're not being an effective product manager if you have to do this after launch. The post-launch process is highly expensive, and you've already lost a lot of really important data.Event-based tracking enables you to dissect particular elements of the user experience. How many times, for instance, was a picture loaded? How many times did the same error message appear, or how many characters were entered?This type of analysis enables you to guarantee that your customer experience is excellent. Consider what the client is doing when you create your instrumentation and how you want to instrument it. And some of these are actually rather difficult; it's not always simple to perform.I collaborate with a few of our customization teams, and a lot of these initiatives involve technology hurdles you need to consider right away. Consider your technology choices before moving on with the project.TakeawayIn this article, we explored the many ways data-driven decision making can drive incredible benefits for your business, both externally and internally.On the external front, user data is definitely something to be leveraged if you want to remain competitive in your industry and become a giant, like in the example we saw.Within the organization, staying on top of user data analytics will help keep your teams aligned and focused towards clear, common business goals and place benchmarks and KPIs that all contribute towards your journey to success.If you want to learn more about data-driven product management and which stages of the product life cycle can benefit from the use of user data analytics, don’t skip this article here: Do Products Drive Data or Does Data Drive the Product?Meta description:Data is vital, but useless if you don’t know how to use it right. These 3 effective techniques improve how data is used to drive better decisions for your business.Excerpt:In a world of cut-throat competition in every industry where businesses operate in the digital space, missing out on key user insights and relying on guesswork can prove to be fatal for your business. Leaving things to chance when it comes to understanding what your users really want from their experience with your product can be detrimental. On the other hand, carefully studying your users, their behaviors, and their interactions has endless benefits — both on the outside and within your organization. In this article, Associate Product Manager Ali Ayub Khan reveals three of the most effective techniques that help you drive better data-driven decisions every single day.
3 Techniques To Make Data-Driven Decisions with User Data Analytics

For any organization where design is a core part of the service portfolio, building a design team is a gargantuan task.While filling in the designer roles and laying down designer responsibilities is one big part of it, there lies another immense responsibility on the organization: to provide promising designer career paths for its people.This means building something strong from the ground up, but at the same time, creating a solution that is flexible to your organization’s distinct needs and goals.What is the Career Path for a Designer?When deciding the career path for a designer, the first step is to start by building a career ladder for all designer roles within the organization.At this stage, your objective should be to make sure that the ladder answers the following questions:How do we offer our designers opportunities to grow as individual contributors and people managers? How do we make sure that our titles are standard with the best practices in the industry? How do we ensure consistent titles across all designer roles? In the search for answers to these questions, we came up with the following career ladder:The Dual-Lane Designer Career LadderAlong the product and design career ladder, there are multiple elements and steps that the designers go through.And understanding the hierarchy of these designer roles and their impact is step one.What is the hierarchy in designer roles?Every designer starts as an associate, learning and growing their way to mid and senior levels.After the senior level, designers can decide to pursue either the individual contributor or the leadership path as both offer very different levels of designer responsibilities and role expectations.Of course, designers can opt to switch their paths: An individual contributor can always become a manager and a manager can go on to become an individual contributor at any time of their career.But, with that being said, this usually comes with a big change in their day-to-day responsibilities — and that’s what’s important for designers to understand.Transparent role expectations and designer responsibilitiesNext, it’s important to give designers the tools they would need to succeed in their current roles and help managers have better conversations with designers around the subject of growth and development.In our quest to learn from some of the best standards and examples from the design community and defined clear role expectations for every role.For each designer role’s expectation, we tried to include a good mix of hard and people skills.Below is an example of our product design role expectations.Annual assessmentsNow to add accountability and dialogue to the mix, we’ve seen that running skill assessments once a year is a good way to take first-hand input from every designer, key designated client-side stakeholders, and the team leads. This feedback is then assessed against the designers’ role expectations, and key designer KPIs.We also have the designers fill out the same skill assessment for their own selves when they join the team.In these assessments, we urge designers to be as honest as possible:Ranking as ”Improving” (low) anywhere is seen as an opportunity for growth and not as a sign of weakness.This is the same principle you can follow when discussing the results of yearly assessments that are done from clients and other stakeholders.For the rating of each skill, we use the following grading system that we learned from our amazing friends at Salesforce.The word scale makes a lot more sense than the number scale and reduces subjectivity when it comes to rating designer skills.The assessment results from different stakeholders are received, aggregated, and shared with each designer and their design leads. This process end-to-end is duly managed expertly by our Design Ops team.The leads then engage in conversations with designers to help them better understand the expectations of their designer roles.It helps to break the expectations into achievable goals and help the team members get better at what they do in their designer roles.The leads are also responsible for creating opportunities for designers to help them polish their skills in areas where client-side opportunities are not sufficient.This conversation is carried over to the weekly one-on-ones between the designer and their lead and they both work together for the designer’s career growth.Above is a hypothetical example of what a designer assessment result looks like. Different colors represent scores from different stakeholders.The further a point is from the center of the radar determines the level of proficiency in each skill. 0 in the graph is mapped to Non-Scoring, 1 is improving, 2 is achieving and 3 on the graph is excelling.In the above chart, the designer is perceived to be excelling in visual design by one stakeholder and perceived to be achieving in visual design by their other stakeholders.Looking at the assessments, we commend the designers for being great at so many things.Then, for the following year’s learning and development program, we start by focusing on areas where we see our designers not excelling or fully achieving expectations and define priorities from there.Seeing designers excelling at multiple ends also gives us an indication that the designer has started to outgrow their current role.For example, in the above evaluation, we would want to work with the designer on their Product Thinking, Mentorship, Culture, Design Thinking and Facilitation skills as starters and then move on to strengthening their other skills.One of our key learnings when we implemented this at our organization in recent years has been that transparency and good communication are the key to any initiative’s success. With these assessments, we also try to create an opportunity for open and clear conversations.Case in point: Here is a recent communication that I shared with my team on how they can make the best of their assessments in a very positive way and use this information to their advantage.TakeawayDeveloping such processes within the organization is an achievement in itself:It feels amazing to look back at all that is achieved along the way, and while this is by no means complete, it’s an opportunity to always take feedback from people all over the organization and use it to improve our processes.For us, the next step is replicating the same model for other roles of Designer, Research, and many more across the Product-Design career ladder. This is also an opportunity to build a model where designers can give feedback on the leaders of their team, thus maintaining a healthy atmosphere built on constructive criticism and focused towards design success.
Designer Career Ladders: Enhancing the Performance and Growth of Design Teams

For frontend developers, the ease and simplicity of the development process has a significant impact on the quality of their output.And, while in a simple UI layout, either vertical or horizontal arrangements of cells are easily created with the UICollectionViewFlowLayout, which is the default layout for UICollectionView, there remains one very pressing challenge for frontend development:As times passes, the layouts are getting much more difficult to implement as the UICollectionViewFlowLayout lacks some important functionality, thus forcing developers to create custom layouts to achieve those functionalities in an enhanced way.What can developers do to keep up with the growing heterogeneity of layouts and build custom layouts with ease?Fortunately, we do have a successor to the old UICollectionViewFlowLayout, as introduced by Apple in WWDC 2019!Here’s a solution that moves away from the delegate approach and uses a much simpler closure-based approach.But before that, let’s try to wrap our heads around the UICollectionViewFlowLayout.What is UICollectionViewFlowLayout?Look at UICollectionView as the foundation of a lot of apps.The UICollectionView is used to arrange cells/ UI views in Scrollable Content inside it, and the given layout determines how the elements will be arranged. By default, the UICollectionView Flow Layout is either in horizontal or vertical scrolling, which is the most widely used layout.The UICollectionViewFlowLayout object organizes items from a simple layout into a grid, and for each section, it accounts for optional header and foot views. You are required to provide an estimated height and width for the cell, otherwise the cells will use auto-layout and the end result is not the best, in most cases.The biggest plus point of the UICollectionView over the UITableView is the capability of horizontal scrolling, as well how multiple cells can be arranged in a column, unlike UITableView.But, like we saw earlier, it comes with a catch: The UICollectionFlowLayout works quite well with simple layouts, but with designs becoming more heterogeneous, there needs to be a solution that supports building custom layouts — without the challenges that come with it.Boilerplate code and problems of self-sizing cells are just a couple of issues that make building complex and advanced designs an uphill task.UICollectionViewFlowLayout and its DrawbacksThe default layout for UICollectionView is sufficient for designing a simple layout, but it has the following drawbacks:The Layout Scroll can either be Horizontal or Vertical The UI Flow uses Delegates as a datasource, which is an outdated method of implementation It only provides animation for Inserting or Deleting a single item at a time The object has to be fetched using IndexPath, which can cause the application to crash in case of out-of-bound access The selected object has to be casted It is only suitable for simple UI Designs Switching layouts with animation is not possible Cells cannot encapsulate their layout variations programmatically One of the most pressing challenges of the Default UI Flow is that it is only limited to Continuous Scroll or Paging Scroll behaviour.In the UICollectionView, if you want to achieve paged central scrolling behaviour or scroll with cell hugging behaviour, a third-party custom layout has to be used. Either this, or you would have to implement your own solution, which, in most cases, might crash if not written properly.If you want to achieve Horizontal Scroll View within a Vertical Scroll View, there is a way to embed UICollectionView in UI Table Cell and use UITableView. We’ll learn exactly how a little further into the article, but before we get into that, let’s quickly refresh our knowledge of the main difference between UICollectionViewFlowLayout and UICollectionViewCompositionalLayout.What is the Difference Between UICollectionViewFlowLayout and UICollectionViewCompositionalLayout?The UICollectionViewCompositionalLayout is essentially a more advanced and enhanced version of its predecessor, the UICollectionViewFlowLayout.In a UICollectionViewCompositionalLayout, data is presented in a static manner in multiple rows arranged in a single group, up and down, and the sections are composed of single and multiple groups.Depending on the user interface you want to achieve, you can see for yourself and decide which layout of the two suits you more: for simple layouts, for example a list of items that don’t need any designs, a UITableView would work just fine.However, if you’re looking for more ability to customize within each cell, the UICollectionView is what you should use.To put it in the simplest way possible, the UICollectionView organizes the collection of data/ views, presenting it in layouts that come with the customizability that is missing in UITableView.In the UICollectionViewFlowLayout, embedding the UICollectionView in the UI Table Cell and using the UITableView as the top most view will help achieve the Horizontal Scroll View within a Vertical Scroll View.And while this may sound easy to accomplish, there are certain things you must look out for when doing so:You have to conform to Delegates for both UITableView and the UICollectionView, which will make the code very messy It is memory-intensive and might cause memory leaks It’s hard to contain the complete code in a Controller The MVVM paradigm may need to be modified Gladly, during WWDC 2019, Apple introduced compositional layouts with the goal to simplify the development process of complex layouts in our applications.Here’s where the solution from Apple comes in and saves the day. Meet the Compositional Layout.What is the UICollectionViewCompositionalLayout?During WWDC 2019, Apple introduced a new, more modern and advanced way to implement more complex layout in simpler ways.This was known as the Compositional Layout, which was released with the purpose of simplifying the development process of complex layouts in the UI for iOS applications.Compositional layouts are a type of collection view layout that are designed to be flexible, composable, and significantly faster so as to allow you to build whatever visual arrangement you want.It lets you combine, or composite, each of the smaller components of the design into a full layout.The Compositional Layout comprises one or more sections that compartmentalize your layout into distinct visual groups. Each section is composed of groups of individual items, the smallest unit of data you want to present. A group might lay out its items in a horizontal row, a vertical column, or a custom arrangement.How Compositional View Solves the Challenges of the Default UI FlowThe Compositional Layout for iOS design comes as a solution owing to the multitude of advantages that it boasts over the older UICollectionView for iOS layoutIt is declarative in nature It supports both Delegates (older approach) as well as the new Diffable Datasource New Complex animations come out of the box using Diffable Datasource Snapshots Item can safely be retrieved directly for diffable datasource and doesn't need to be casted Layout variations can be encapsulated within the cell programmatically Easier on device hardware performance and supported by Apple itself Support layout switch with animations TakeawaySome of the biggest enhancements that the Compositional View offers for frontend UI development, particularly to overcome the challenges of UICollectionView for iOS, include:It supports both Horizontal as well as a Vertical scroll at the same time It achieves this by adding new Groups in each section, making code much more readable, easier to understand, and cleaner It supports 6 types of scrolling behaviours out of box, including Central Scroll (suitable for Carousel View). Considering the importance of breaking down the frontend UI development process to make it simpler, more efficient, and most importantly, flexible and adaptive to increasingly advanced iOS designs, there remains no doubt that the Compositional View offers benefits that can go a long way to improve life for frontend developers. Want to learn more about MicroFrontends and Microservices? Read this article here!
How Compositional Layouts for iOS Design Revolutionized Frontend Development

What do small businesses with small teams need during their product’s life cycle?Scaling their teams and operations is undoubtedly one of the biggest aims for startups. But scaling using the legacy Agile Scrum frameworks that these small-sized teams are so used to can make scaling an uphill battle.When it comes to a small business scaling up, the Agile Scrum framework will fail as the business endeavors to add more resources to the team. The Agile Scrum framework is designed for small teams, and a lot of startups end up making the mistake of adding more resources while using the same Scrum framework, resulting in agility loss.What, then, can startups do to bring about agile and digital transformation without slowing down their operations?How Do You Transition From Company to Agile?Often at the growth stage, one of the biggest problems teams run into is organizing and structuring their processes. This leads to a number of problems that end up significantly slowing a team down.As they consider business agility transformation, it is crucial for product owners and managers to try out different agile frameworks meant for larger teams so they can ensure the same agility when they are scaling.Scaled Agile frameworks aim to solve these structuring and organization problems by introducing processes meant for multiple small teams working towards a common goal. This helps teams manage their backlog and also stay agile enough to adapt to changing customer needs.At times, however, in hopes to adopt agile transformation, teams slow themselves down by jumping on one scaled agile framework without knowing what works for their team and what doesn’t. This leads to a lot of frustration that, in my opinion, can easily be avoided.If you’re a small business scaling up that is used to the legacy Scrum framework then what exactly are the best options out there for agile and digital transformation?The answer to this question largely depends on what works best for your team, but it helps to look at the best, most popular, and well-reviewed Scaled Agile frameworks.In this article, let’s explore our top three popular frameworks and what teams should focus on while scaling Agile transformation.3 Popular Scaled Agile Frameworks For Digital TransformationSAFe FrameworkThe Scaled Agile Framework® (SAFe®) is a framework for implementing AGILE operations at an enterprise level.SAFe lays out a set of organizational and workflow patterns that are needed to implement agile practices at an enterprise scale. The SAFe framework offers structured guidelines on how to plan and manage work, the roles and responsibilities of everyone involved, and the values that must be upheld.The framework is based on creating structure, roles, and processes around multiple scrum teams working together. These teams are called Agile Release Trains (ART) and come with extra roles and responsibilities that need to be filled. The teams coordinate on delegating epics, features, and user stories among themselves and complete work in time-boxed sprints along with all required sprint ceremonies. These sprint ceremonies are quite the same as the legacy scrum framework e.g. Sprint Planning, Retrospective, Backlog Grooming, etc. Teams are also free to use either Kanban or Scrum to finish work in their sprints and every team maintains its own backlog of work.SAFe is also the most widely used framework for big corporations' developing and shipping software.If you are looking to scale your organizational processes and structure, SAFe really is the best option. It doesn’t only focus on building multiple teams working on a single product, but rather on building the key organizational principles, values, and roles that help companies scale and build lean product portfolios. Read this article to learn how to implement SAFe as a Scalable Agile Framework.LeSS Agile FrameworkAnother popular framework is LeSS, also known as Large Scale Scrum, which follows the “do more with less” philosophy.The LeSS framework focuses on scaling existing scrum procedures, always starting with one small scrum team and then scaling to multiple teams working on the same product backlog.Less is considered much more lightweight than SAFe because it comes with fewer roles, which makes it a much easier process to adopt for agile transformation than SAFe.The LeSS framework focuses on legacy scrum practices but applies it to multiple teams working on the same product.Unlike SAFe, in LeSS there is a singular product backlog rather than a team backlog and just one Product Owner. All teams plan and pick their items in Sprint Planning 1 where work is presented to the dev teams. This is followed by Sprint Planning 2, where dev teams discuss development strategies for features and integration of their development into a single product during release time.Contrary to SAFe, in the LeSS Agile framework, inter-team coordination is also a responsibility of the teams rather than a role dedicated solely to it. This framework is often referred to as barely sufficient by some while it works great for some teams.LeSS really is a great choice when it comes to affordability due to its lower implementation cost. For some teams, a single Product Owner really proves to be an efficient link between business and tech because they understand the framework, challenges, and product vision and strategy.Scrum of ScrumsScrum of Scrums is a framework that focuses on divide and conquer.It helps organizations take a large workforce and create teams of four to five people working towards a common goal. The framework believes in smaller teams as it helps to build practical and personal relationships, which in turn results in velocity.Scrum of Scrums also has separate product owners for each team and the ceremonies are exactly the same as Scrum. The framework also comes with extra roles to ensure coordination between different teams. These roles are Chief Product Owner and Scrum of Scrum Master, who solely works on coordination in daily 15 minutes scrum meetings.The Scrum of Scrums framework is quite lean but does not undermine the importance of coordination roles.The framework is also quite flexible, allowing you to quickly discuss and switch up processes for greater efficiency. The coordination roles constantly discuss impediments daily and try to resolve and change processes, which allows for open discussion on problems and their solutions, unlike in other frameworks.Which Agile Frameworks Are Right For My Team?There really is no one size fits all solution here: what works for one company will not work for other companies, simply because of different cultures and mindsets.Usually, a lot of research, trial, and testing is required to create and pick the processes that work for you. Sticking with one framework religiously will slow you down. These frameworks focus on delivery & outcomes, which is great for larger enterprises and teams and help establish predictable outcomes and clear goals.However, for small businesses scaling up, the recipe for success is delivering value to customers as fast as possible.Most popular frameworks also come with their own set of frustrations and problems, which people openly talk about.For example, we talked about the SAFe framework and how it works but one of the biggest problems that people report with the framework is the unnecessary roles and complex processes. People who have worked in this framework often report that it is a waterfall method in disguise and the delivery of actual work and value to customers is quite low. The jargon and processes are so complex that teams spend more time organizing themselves rather than actually working, let alone being able to work with agility.On the contrary, the LeSS framework is regarded as barely sufficient as it is a simple and lean framework and relies on fewer roles. If the team dev leads are not used to communicating and coordinating, then the absence of a team's product owner can be very difficult on everyone.LeSS is also quite notorious for not solving developer problems as it often is not the focus of the single product owner; sometimes product owners are just swamped with a lot of challenges that demand their attention, and the developer challenges are neglected.Scrum of Scrums focuses on building smaller teams but it often leads to an imbalance of resources. Finding the perfect performing squads can also be quite a hit-and-miss.This just proves that no digital transformation framework alone is perfect and in order to achieve efficiency, teams need to invest time into discussion and trial.What are the Steps to Scale a Small Business?For all the challenges that come with the aforementioned Scaled Agile Frameworks, what exactly should then growing startups focus on instead of jumping to adopt a Scaled Agile framework?I really believe that before scaling, product teams really need to look at themselves and ask whether they are agile enough to scale.Scaling with what is right for your squadWorking on your single scrum team is very important as the first team really is a brand ambassador of your values and culture.Agility is a mindset and your team is like a car engine. Every person is a crucial component of this engine and to perform well, the team needs to have the right mindset. After that, the team will scale efficiently no matter what.It is also quite important to develop practices that help to build the foundational work ethic for your squad.For example, how efficient are devs in communicating on tickets? Does your team document a lot of stuff? What onboarding processes do you have for new team members? These processes are important baselines for establishing success in adopting frameworks.Every team has its own pace and comfort in which they perform best, so it is important for teams to continuously discuss and monitor their performance to make adjustments. Continuous discussion around process improvement is key and all stakeholders should be able to voice their opinions.If you’re still not sure if you’re ready for Agile transformation with Scaled Agile Frameworks, use this Agile Culture Checklist to keep your team grounded and efficient as you scale up.Agile Culture Checklist1. Customer/User obsessionWe’re all here for our users and customers, developing products for them.Successful companies are always obsessed with making their customer/user experience the best there can be.Customer obsession is a valuable principle that is quite common in all frameworks and it helps squads develop better features, which in turn helps the product grow.2. Looking out for each otherA great agile squad is like a well-oiled engine and in order to keep this engine running smoothly, one thing teams need to do is always look out for each other.Building personal relationships within your squad will help keep your velocity always high.A great example of this is sick or parental leaves. Whenever a squad member has to take time off work, unprepared teams will struggle.However, a team with the right agile mindset will share the work and responsibility of the team member not present. This helps the team to always move forward and take charge when they need to.3. Always flexibleFlexibility is one of the core principles agile teams need to practice.Today’s markets have gotten increasingly competitive and startups always need to be delivering value fast, as changing market scenarios can make or break businesses.Teams who are flexible constantly innovate and stay ahead of the curve by adapting to any situation they are faced with.I believe teams that fully practice these principles should consider adopting frameworks while always staying true to these principles.All said and done, let's see how mixing and matching processes from different frameworks can really be the best way to scale for companies.Takeaway: Mix, Match, and Perfect!There is no hard and fast rule to adopt a single framework and stick to it. Studying the different processes and roles within different agile and digital frameworks can give you the best insights into what can work for you.If you’re a small business looking to scale, you can start with small teams like in Scrum of Scrums as then the teams can focus on building better personal and practical relationships. Having product owners for every squad might not be feasible for you, so try splitting the responsibilities to two or three central product owners.There are several principles that are common within these frameworks, and hence mixing and matching processes works as many things are interchangeable.Teams can also experiment to empower their developers so they can also be better at managing work, allowing for less reliance on coordination roles as your tech leads will then be comfortable communicating with stakeholders.All these experiments and trials can happen within the sprint cycle and you can even monitor two squads simultaneously with different processes to see what is working better for you. You can also add or remove meetings you think the squads need. Creating a feedback channel for all processes and meetings will help validate your experiments.Finally, it really does not matter if you adopt a popular framework because, with the knowledge and resources available, teams can literally invent their own new frameworks.Using this approach of mixing and matching while staying true to your agile values is the foundation of success when scaling your operations, structures and processes. Agility is a mindset and that is what you should be preaching across your business. To learn more about how an Agile culture can be adopted across the organization, you’ll find a lot of value in this article that discusses the role of People in Agile.
Scaling Agile Operations: 3 Agile Frameworks for Digital Transformation

In the product development life cycle, user experience research plays a significant role.But knowing how and when it should be implemented for the best results in any new product development process is a very critical piece of the puzzle.How Does UX Research Fit into the Development of a Product?User experience is central to every brand.Even more so than your product itself, the experience that your users have at every touchpoint and interaction will define whether or not you can not only capture their attention but also convert and retain them as happy customers.To deliver the highest level of customer satisfaction, it’s vital to know who your customers are, what are their preferences, their wants and needs, and what could potentially convert them (or drive them away). This is where the UX research process kicks in.When Should User Research Be Included in Product Development?Ideally, user experience research (or UX research) should be utilized very early on in product development.With that said, it can also be useful at later stages of the project and for upcoming releases.To best understand the true impact of user experience research in the product life cycle, it helps to consider each of the four stages of the product life cycle separately and learn the exact UX research methods that can be used at each stage, along with the outcome that the UX researcher will achieve by implementing these methods.What are the Stages of a New Product Development Process?Whenever you’re faced with any new product development process, it will comprise four main stages:Research and Discover Ideate and Design Build and Test Deploy and Measure At each stage of the process, it’s important to really focus on your end users and adopt a customer-centric approach to product development. Here are 4 Customer Research Methods for Customer-Focused Product Development.We will be looking at each stage of the product life cycle in terms of how UX contributes towards them and what methods should be used to achieve certain outcomes at each of these stages, both pre and post-release of your product.UX Contribution in the Pre-Release StagesStage 1: Research and DiscoverResearch is always the first step in discovering and comprehending the End User.Whenever you’re looking at a new product development process, the first step is to establish a core team, learn and align on the company's objectives, and always empathize with the customers. This will assist teams in comprehending the customer's perspective, pain points, and actions.The following are a few approaches taken by professionals in user experience design to help businesses avoid mistakes in the early stages of the product life cycle:UX research This includes things like in-depth interviews, surveys, focus groups, and field studies. After conducting research, designers create personas, experience maps, user scenarios, etc. through a data modeling approach. These procedures can aid businesses in better comprehending their target audience of users and the issues they face. This will make it simple to address them in the final product.Workshops for brainstorming The attendees of these workshops come from various departments.The confrontation of various points of view encourages discussion and provides the ideal setting for challenging existing concepts and coming up with new ones. This, in turn, may help in aligning everyone on the vision for the project.Competitive research When you examine the products of your rivals in terms of user experience, you could seek out potential areas for enhancement. Stakeholders will be able to gain an advantage in solving customers' problems and ensure that their product will not be a duplicate of an existing app by conducting competitive research in the product design process.Stage 2: Ideate and DesignIn this stage, the entire product team works together to make sure the product is of the highest possible quality at the best possible time for marketing.Designs are developed that represent a solution that UX researchers and teams have arrived at after brainstorming and ideation.Some of the practices that UX designers can follow to help deliver the highest quality of experience include:Map out the user flows and information architecture It is necessary to develop a well-thought-out structure, navigation, and user flows (a user's path to completing a task). By doing this in the product design process, designers can ensure that end users can easily navigate the features and contents of the product.Create wireframes Before any visual design is applied, the interface of the app is laid out in wireframes as a skeleton. Wireframes are a quick way for UX designers to convey their thoughts and ideas in the form of an interface because they require less time to produce (especially low-fidelity sketch versions).Create high-fidelity and test prototypes Additionally, wireframes can be transformed into functional prototypes, allowing designers to evaluate their concepts prior to beginning UI design work. By doing so, businesses can avoid wasting time on bad ideas, and designers can begin working on high-fidelity designs as soon as the results of the prototypes are clear.In the next step, we’ll come to actually delivering the product to your customers after the strategy has been established and everyone has a clear understanding of what the product will be and who it will serve.Stage 3: Build and TestAt this stage, designers are expected to collaborate closely with the development team to release a customer-focused solution that drives value and creates an unforgettable experience.This is when the high-fidelity designs are in place and the designers are prepared to “hand off”:Handoff between Designer and Developer! The Developer, Designer & Tester huddle together where the designer walks everyone through the Design Features and Their Planned Functionalities from the Element Level to the Component Level, describing Their Expected Behavior.Sharing the designs through UI slicings is one of the suggested practices to accomplish this, which essentially entails annotating each component and element to convey it smoothly to other stakeholders involved.For more insights into how Designers and Developers collaborate, check out our latest Ask A Designer segment, where developers question designers on things they’ve always wanted to know!UX Contribution in the Post-Release StagesStage 4: Deploy and MeasureDuring this phase, the entire team works together to implement a user-focused solution where they learn, iterate and deploy in a sprint cycle to achieve a customer-centric product that delivers value and satisfaction.After the product has been introduced to the market is when you come to the final stage of the product development life cycle, where you will Observe & Validate whether the product is a good fit for the market.The following are some of the actions that can be taken to enhance the user experience of a product:Perform a UX audit Performing a product audit can prove to be the best course of action for a business that wants to go a step further to enhance their product experience. By doing this, designers can offer advice on a product's accessibility and usability issues, which could boost conversion rates and other crucial business metrics.Build new features with feedback from actual users Another great part at this stage is that you can use the information and data you have gathered about a product's performance whenever you want to improve on it to meet your users’ needs.Even if a product is just an MVP, it may be easier to identify usability issues. You can get real-world feedback on your product through user testing, which is sometimes impossible to get through even past mockup testing.Additionally, you can also gain insights that will assist you in designing additional product features.TakeawayUser experience research can be advantageous for businesses of all sizes, digital and physical products, and at all phases of a product life cycle.The earlier in the product development life cycle you can introduce UX research, the more benefits you will reap.“UX comes into play as a Prerequisite & Not as a Peripheral when you speak about Focusing on End Users!”With that said, this action can always be taken at any time; it’s never too late!If you’re still considering the value of incorporating the expertise of a design specialist for your next product development process, here’s a detailed introduction to Enhancing the Product Life Cycle With Great User Experience.
Implementing User Experience Research in the Product Life Cycle

mobileLIVE is proud to celebrate another solid win this year! Our company has been officially included in the 2022 Best Workplaces in Ontario. mobileLIVE received this honor after a thorough and independent analysis conducted by Great Place to Work®.The list is based on direct feedback from employees of the hundreds of organizations that were surveyed by Great Place to Work®. To be eligible for this list, organizations must be Great Place to Work-Certified™ and have exceptionally high scores from employees on the Trust Index survey.mobileLIVE is humbled and honored to have scored high on the Trust Index. This score proves our approach is in the right direction: empowering employees, valuing diversity, and nurturing innovation throughout our workforce. At mobileLIVE, our people are the real drivers behind success, and this is a win for each of our valued employees.About Great Place to Work® Great Place to Work® is the global authority on high-trust, high-performance workplace cultures. A global research and consulting firm, Great Place to Work® provides the benchmarks and expertise needed to create, sustain, and recognize outstanding workplace cultures. In Canada, Great Place to Work® produces both industry and demographic-specific Best Workplace™ lists and represents the voices of 500,000 employees across industries. This is part of the world’s largest annual workplace study, recognizing the world’s Best Workplaces in a series of national lists including those published by The Globe and Mail (Canada) and Fortune Magazine (USA). Visit us at www.greatplacetowork.ca
mobileLIVE recognized among the Best Workplaces in Ontario® 2022

A big part of any organization’s growth now relies on providing a great user experience.And hence, some of the biggest product development companies now focus a great deal on user experience design. In the product life cycle, UX design provides multiple benefits, making it easy to see why and how good user experience design should be an integral part of the process.What is a Product Life Cycle?The product life cycle refers to the set of strategies that are used at different stages during the product’s development for purposes of sales and marketing.If we look at the product life cycle through an abstract lens, we find five distinct stages in the product life cycle:Conceptualization and Technology Development Product Development Market Introduction Market Acceptance Growth Normal Market Cycle Apart from this, the product life cycle can also otherwise be defined as amount of time that a product spends from being introduced into the market until the time it is taken off the shelves.The product life cycle assumes that most products have different life spans, and therefore, at each stage of the cycle, the business faces a different set of advantages and disadvantages.This is why, when working on any product, it’s crucial to be a critical thinker to identify all edge cases that you could face during future processes of new product development.There needs to be a lot of focus on the current and future consequences of the product, and to overcome such situations, businesses can adopt different processes and strategies to approach design, development, and marketing.What is User Experience Design?User experience design (or UX design) is simply the experience of your customers during their interaction with your product or service. How easily users can navigate through this experience and how simple (or complicated) it is for them to achieve what they want is all a part of user experience design.The user experience can make or break your customer experience — and hence be a deciding factor when the question arises of whether your customer will want to stick with your product or move on to the next best option.So, when it comes to achieving great user experience design, it's important to make this consideration throughout the product life cycle to improve product growth and increase revenue streams.How the Best Design Performers Increase Revenues in the Product Life CycleIf we refer to extensive research from McKinsey on the subject, companies with top-quartile design scores outperformed the industry-benchmark growth by a ratio of as much as two to one.You will be amazed after looking at the graph below about how shareholders got the revenue after implementing the design into their businesses.(Image reference taken from McKinsey)Why is UI/UX Design Important in the Product Life Cycle?The potential for design-driven growth is enormous in both product and service-based organizations.Customers can feed opinions back to the companies in real-time, allowing the design to be measured by customers themselves — whether or not companies want to listen.(Image reference taken from McKinsey)Although UX requires a lot of work and time, there are several techniques that play an important role in the product life cycle.Without UX, most teams end up facing several issues and difficulties after the product is released. This is where UX comes in, helping with not only avoiding any issues but also ensuring you identify them during the product life cycle and not after release.What Does the User Experience Design Thinking Process Look Like?As UX affects every aspect of the product being built, the UX or Experience Designer is involved throughout the product life cycle.Essentially, the UX designer designs the end-to-end experience of the product, which includes the complete design thinking process depending on the nature of the product.The design thinking process always varies from product to product. Your process could change if you are working on an existing product and you want to add some new features.The UX designer’s task is to be aware of all the problems and pain points with viable solutions, and convey those results to any and every element with which it is associated within the product life cycle.Working as a UX designer is really important in the product lifecycle to understand why we need to define the problem, discover pain points, ask important questions like the whys and whats, and conduct user research before getting into the design phase.Sometimes, there might also be the need to convince other stakeholders about why conducting user research is important for your product. The trickiest part is how you do it; there could be a lot of challenges such as:How to discover and understand the actual problem statement? How can we manage time constraints? What if people find the experience difficult or useless? What will the consequences be?User experience design starts by conducting user research. Moderated and unmoderated usability tests are conducted to validate design assumptions specified in the requirements defined at project kick off.User research helps the team identify their target audience and create a user persona to represent their users in order to validate design decisions throughout the product life cycle.Next, they design the user journeys in order to gather feedback and optimize their designs around that feedback. They keep refining their designs even after product delivery to make sure that the product is user-friendly.How To Practice Good User Experience Design in the Product Life CycleGood user experience design means that from UX research to launch and till the time the product life cycle ends, the customer is kept at the center and considered at every stage for the product design.If we consider the problem above, user experience design contributes largely towards overcoming it.UX research helps in identifying the pain points earlier so that you can solve any problem you may run into.In turn, designers can start at the beginning of the product life cycle with research and can focus on the end user of the product. It helps designers to reveal customer issues and narrow down on how the product solves them.By conducting UX research with your target audience through a set of interviews and more, you can design user personas, journey maps, user scenarios, prototypes, and simplify the overall user experience process. Here’s another article that will give you a clearer understanding of Why Ignoring UX Research Is A Mistake.Good user experience design plays an important role in the product life cycle when designers approach it with the actual pain points of the users, support it with user research, brainstorm the ideas together as a team, and create seamless flows.Takeaway: Key Benefits of Integrating UX in Product Life cycleIncorporating user experience design into your process is always beneficial, whether you're launching a startup, developing a product, or questioning the performance of an existing one.In most cases, the sooner you incorporate the expertise of a design specialist into your project, the better your chances will be of achieving effective and agile UX product development.“UX comes into play as a Prerequisite & Not as a Peripheral when you speak about Focusing on End Users!”Using the right UX methods and principles at all stages of a product's life cycle can reap many benefits for product development companies. Some of the most valuable benefits evident to us across the product development life cycle include:UX research helps stakeholders to understand their target audience and problems, making it easier to address them in the finished product. User experience design allows much better work engagement and lets product managers plan ahead of time. The UX designer gets a better perspective of how the product is, enabling them to stay consistent across the product features. Implementing the UX process into products increases the sales, user engagement, and adoption rates. It also increases the customer’s emotional bond to a company or a product. It will always be beneficial for a product development company to bring in a UX expert into the product development life cycle so that UX design can be involved into the product process early on. Take your User Experience Design a step further by designing cross-channel experiences for your customers with these 9 UX Design Heuristics!
Enhancing the Product Life Cycle With Great User Experience Design

Designers and developers have very different roles, but in most cases, their paths cross while working on the same project.For example, if a website needs to be created, a designer is tasked with delivering the visual impact that the user interface will have on the viewers. On the other side, the developer will be managing all the backend capabilities and ensuring that the designs and wireframes are materialized.And while this shows us that the relationship between designers and developers is key, oftentimes their processes aren’t as collaborative as should be.So, in an effort to improve communication and bring down some of the barriers that hinder collaboration between design and development teams, in this Ask A Designer feature, we invited our developers to put our designers on the hot seat — asking them things that developers want to know about designers!Question 1How is your experience communicating with developers?Response 1:Most of the projects I work on will involve developers in some way – either in setting up a new page in Contentful, or creating/modifying components.— Véronique Janosy, Senior Product DesignerResponse 2:In my experience, collaboration, open-mindedness, inclusion, proactiveness, and a healthy relationship between design and development are key essential characteristics required to ensure that the design details are correctly translated into the code for a successful, visually appealing, and functional product development.For a pixel perfect design, every detail including measurements of canvas sizes, margins, paddings, hover and focus states, no-data or error states needs to be communicated or annotated to the development team for smooth coding.At the end of the day, both designers and developers are working towards achieving the same goal.— Rahul Jacob, Product DesignerResponse 3:Given that the design requires a collaborative environment within multidisciplinary teams, and in particular, an efficient communication between Product designers and Developers, it is always considered that communication is the key value in succeeding in any product’s project. In my collaborative design projects from the beginning, I always tended to build a good relationship with my team members, especially the developers, to improve the process of the design of the product. In my experiences throughout the years, I tried to learn the basic programming terms and on top of that learned the developers’ concerns regarding creating a new design to be able to provide feasible ideas that they could also be able to create.— Ella Rabiei, Senior Product DesignerResponse 4:Developers and I work closely with each other; often communicating on Slack or via daily standups and scrum meetings. We discuss ux issues such as error handlings or variants of a component like having different states of buttons and behaviors in the Design System and talk about problems and solutions. I deliver ux clarifications includings scenarios in the form of design patterns and guidelines and support developers where needed. It’s all about collaboration and teamwork.— Rebecca Kim, Lead Product DesignerQuestion 2When tasked with a new feature, do you research the feature(s) while keeping the developer and standard libraries like Angular / React Material, PrimeNG/PrimeReact, Angular/React Bootstrap, etc. in mind?Response 1:I don’t research features available in any libraries, but I always engage developers whenever developing something that I’m not certain about, since they are the experts in the field. A lot of actions and features we use have already been used on the site, so I don’t need to verify those, but I will set up a call or start a conversation about a feature if I’m not sure. I also want to make sure that when I write tech specs I include any information that will be essential for the dev team. After handing over a new or modified component spec sheet, there is always a walkthrough with developers, at which point we can discuss any questions or concerns that have not already been addressed prior.— Véronique Janosy, Senior Product DesignerResponse 2:When it comes to new features, I always take the less is more approach. As a product designer, I am always empathic with the users, as they rely on their products to be intuitive, functional, reliable, and usable for their needs to be met quickly and effortlessly.Any time I start working on a new feature, I use existing libraries as a starting point. It is always important for me to design components that are practical and long-lasting so that they can be reused or managed in the future. As a result, the design is easier to maintain on the backend while looking good on the frontend, which increases its longevity.It’s a win-win for everyone!— Rahul Jacob, Product DesignerResponse 3:Yes, but not the library source in particular. When it comes to design of a new feature, I would talk to the developers to learn about developing and coding restrictions and the alternatives that I can use of; there are always multiple new features that need to be created, and it would be hard for the designer to go through all the libraries in person to see if it would work for them, that is why the direct collaboration with developers can help the designer to process the feature and make the decisions correctly regarding that.— Ella Rabiei, Senior Product DesignerResponse 4:Yes, I do research the features, prioritizations, IA, design approaches, and page layouts focusing on synthesizing and communicating high-level strategic insights. Developers are highly-skilled and knowledgeable and may offer new and different perspectives that could unlock unrealized potential. For example I ask developers' thoughts how the sophisticated backend system works that is captured in information architecture and workflow in ux.With the collected information, I adopt user research methods and conduct Usability Testing, User Interviews, or Focus Group for ux findings. With the ux findings, I look into the Design System in terms of the UI component quality like a complex form and table, so it allows me to reduce the risk of any variation between products.— Rebecca Kim, Lead Product DesignerQuestion 3Is the web app multi-themed, responsive, and/or multilingual? How many layouts do you share with the developers, and what format (XD, Figma, etc.)?Response 1:The work I do is aimed at one theme (brand). All the components I build are designed to be responsive, and I provide mockups and tech specs for 4 breakpoints, which handles the majority of the scenarios. My client works with Sketch for design, and Abstract for version control, so I share out Abstract links to the developers, which allows them to inspect each component fully.— Véronique Janosy, Senior Product DesignerResponse 2:Each project I work on incorporates responsive design to adapt to the viewports of these devices: desktops, tablets, and mobile.I work primarily with an app called Abstract that lets me import Sketch files and create a centralized repository for the team's most up-to-date design work and supporting documentation. Developers can seamlessly transition from design to development with this app. It allows developers to compare changes, view measurements, specs, inspect, and download assets through a link or directly from the app.— Rahul Jacob, Product DesignerResponse 3:Yes, the process of the designing a product requires designers to create/build responsive designs which would follow the guidelines and rules; it is very important to evaluate and test the design on different platforms to see if the message of that specific product is clear without any distortion, failing to do so, would cause a confusion and difficulty to the developing team and as a result the product would fail. The number of layouts highly depends on the number of scenarios in a particular product project, in general we as designers would provide all the potential scenarios for developers. In each design team, there are a variety of applications that product teams could use to work together. In my current work, we use the Abstract and the Sketch apps to communicate our ideation and designs; there have been some situations where we had lost our access to either of these apps and I would provide developers with exported versions of the design, such as SVG, PDF and PNG to move forward with our process.— Ella Rabiei, Senior Product DesignerResponse 4:Yes or No, it depends on the context, constraints, business requirements, and user needs. If yes,define the layouts based on responsive breakpoints (Desktop, Tablet, Mobile) in Design System including with light and dark themes in Figma. share with the developers UI elements and functions including documentations around the look and usage of each component in the component library. support multilingual languages. For example, when translating English into French or Spanish, the translation will generally be about 15 % to 30 % longer than the original. I will make sure if it suits the copy in different languages. If the translations break the design layout, that requires discussions to come up with solutions such as adjusting font sizes, text truncate ellipsis, or alignment and text placement. — Rebecca Kim, Lead Product DesignerQuestion 4Do you keep accessibility in mind before designing features?Response 1:Yes, it’s a must! I do think that more education is needed around accessibility, across other areas of the business. It does seem that while design and dev are aligned on the importance of accessibility, stakeholders need to be educated so that they value it as well. At the end of the day, with certain businesses, design can always be overridden by stakeholders.— Véronique Janosy, Senior Product DesignerResponse 2:I always incorporate accessibility into my design process so that every user has access to the same information, regardless of their visual, auditory, cognitive, or motor impairments. As a result of keeping accessibility in mind, it expands the potential audience, improves usability, and meets accessibility standards. “Always build with accessibility in mind.”— Rahul Jacob, Product DesignerResponse 3:Yes! Absolutely. The accessibility is one of the most important features in product design and it is considered as one of the main reasons why a product would reach the public approval or it would easily fail.— Ella Rabiei, Senior Product DesignerResponse 4:Yes, I keep accessibility considerations in mind before designing and while designing features. The accessibility considerations are:Design simple experiences Interaction models (eg. is the functionality a link or a button) Color contrast and complementary colors and visual cues Create distinct and recognizable UI elements with familiar design patterns Work with content team and developers to communicate my design decisions and intent Test with real people early and often — Rebecca Kim, Lead Product DesignerQuestion 5What is your approach in dealing with accessibility?Response 1:Luckily, in design system work, our base components, colours, typography and interactions have already passed accessibility tests and been approved by our Accessibility team lead, so design needs to focus mostly on experiences and making sure those meet accessibility standards. By reusing existing components and sticking to the design system as much as possible, you can ensure a good base.— Véronique Janosy, Senior Product DesignerResponse 2:Often, accessibility is misunderstood as being primarily for those with disabilities. However, this is not the case. To benefit all users, designers must approach all projects with an accessibility-first mindset.Here are a few key areas to consider before designing your next feature or project:Color Selection and contrast Typography, font size and spacing Page structure, layout, and hierarchy Focus states, hover states and indicators Use of labels or instructions with form fields and inputs Descriptive text alternatives for images and videos to understand context — Rahul Jacob, Product DesignerResponse 3:If I would be asked to work on a completely new product without any developed design system, I would personally check the colors, typographies, layouts, and different component dimensions on different platforms by using accessibility tests tools and other design methodologies, such as observation method and secondary research method to create a feasible product for the product’s intended customers. In my current design team, we work with a design system platform which has already been developed and is also going through the accessibility checking processes over and over to make sure all the components are following the most recent guidelines and could result in products’ success.— Ella Rabiei, Senior Product DesignerResponse 4:Accessibility should be considered before the project starts. When I do my design research, here are some practices I use:consider accessibility, annotate, and document my decisions for an inclusive experience. Work with developers to refine decisions further. Ask myself: Are the needs of people with disabilities being met in the business requirements? Have I annotated my designs to clearly communicate to developers how a design is to be built? — Rebecca Kim, Lead Product DesignerSpecial thanks to developers Kashif Ullah, Waqas Niazi, Shahid Ullah Khan, and Talha Gillani for participating with these questions to ask our design team.TakeawayIn an age where so much relies on the interconnectivity of multiple functions working in unison to ultimately create the best user experiences, smooth communication and collaboration proves to be a valuable asset.Recognizing the importance of bridging the gap in communication between designers and developers, we brought both together and let the conversation flow, not only till our developers got all the answers they wanted, but going beyond and deepening this vital relationship!
Ask A Designer Round 2: Questions For Designers, From Developers

If there’s one big transformation we’ve witnessed with the onset of the digital era, it’s that user experience design has come a long way.The late 80s and early 90s saw a much-needed shift from the traditional way of designing objects to the idea of interfaces as design artifacts, accredited to acclaimed designer Gui Bonsiepe (1995). One of the first to see interfaces as a communication object, Bonsiepe saw interfaces as a “bridge” between humans, the product, and the objective.Ten years later, with faster microcomputers integrated into cell phones, cars, cameras, houses, appliances, etc., capable of communicating with other devices through not just one touchpoint of the customer journey but diverse technological possibilities of connections, it became clear that the “bridge” in user experience design goes far beyond interfaces.What are Cross-Channel Journeys?Cross-channel journeys refer to the experience a customer has on not just a single customer touchpoint but across a combination of multiple different channels.The human-computer interaction evolved into human-information interaction, and multi-channel interactions are increasingly transforming into a cross-channel customer journey.In the cross-channel customer experience, the user experience as a narrative journey involves actions in the physical and digital worlds pervading through many different digital devices, all linked together by a dynamic system ecology.In the digital customer journey experience, these connections, across multiple touchpoints in the customer journey, bring together short narratives into one whole story.What is Cross-Channel Journey Optimization?Cross-channel journey optimization is where the customer journey map is integrated with various techniques and tactics to cater to the customer via every channel on which they’re present.Usually, usability evaluations concentrate on the experience of users interacting with a single system.However, the whole experience, especially now in today’s digital world, trespasses the system and includes moments that are both precedent and subsequent to the direct interaction with the system.To truly optimize this cross-channel journey, user experience research and design will determine the quality of the customer experience you can offer to your users.What is Cross-Channel User Experience (UX) Design?From a UX design perspective, products and services must go beyond the good usability of systems and understand the users’ complete journey.Storyboarding is one method in UX design that helps UX teams align on the vision for the design they work on, with the single end goal of mapping out the user journey. To learn all about the What, When, Why, and How of Storyboarding in UX Design, read this article here.Businesses must understand the whole journey to plan customer touchpoints and create a service/product experience that is available on various different channels — a pervasive cross-channel experience.To achieve this cross-channel customer experience, user experience research plays a critical role in the UX design process.How to Conduct UX/UI Research and Why It Matters?UI/UX research is conducted through a variety of both quantitative and qualitative user experience research methods.When it comes to digital customer journeys, user experience research is one of the most integral parts of the UX process because it helps extract critical insights from early adopters. Understanding how users will perceive your product/service can be an aid when it comes to decreasing the learning curve for users and identifying opportunities for improvement. Learn more about why User Experience Research matters and what it can do for you here.Why UX Research is Essential To Plan Better Cross-Channel ExperiencesDifferent from a multi-channel experience, where users can connect to a product/service through different channels, the cross-channel experience will pervasively cross through channels and physical ambiance to create one experience.Connecting the dotsCross-channel contexts take the user experience to new amplitudes, and it is imperative to adapt usability principles to a narrative experience scenario, as the technological evolution and users’ interaction with devices and environment have been gradually changing and are expected to evolve to an even more integrated cross-channel experience with the metaverse.Although usability tests and measurements focus primarily on interactions with isolated devices, several user experience research methods can surface information about users that help understand their mental model, interaction needs, and cultural-interaction references to better comprehend their journey of experience and map contexts that could take users to interact with your product. Through generative research methods, UX strategists can connect these dots, build experience mapping and prepare a project with multiple possibilities of interaction.Planning for a better user experienceThe journey of your user will start well before they connect with your product/service, with several contextual scenarios leading them to your product.Mapping possible precedent actions and contexts of use can help understand what triggers the full journey of users and direct your product/service to be there when they most need it.Vague assumptions based on intuition have little role in the digital industry and can lead you down the wrong path, wasting precious time and resources.This is where user experience research comes in as the key to gathering the knowledge necessary to project a cross-channel experience:Knowing who the audience is for your product. Many times, this varies far from the initial assumptions. Thinking outside digital devices. Interaction with isolated devices is a very narrow perspective of the full scenario. Understanding the context of use that led people to use your product. What are the precedents that ignite interest? Planning how your product can help and create value for users. The product needs to be an ally, not a difficult step to reach a goal. Continuing the UX journey beyond your product. Plan for a smooth transition and a positive impact on the customer. Users will reach your system through diverse devices, and so the interaction must be planned in a way that offers a smooth journey with many touch points, blending the spaces in one full experience.Understanding this full experience will enable a better connection with not just service design strategies, but business strategies as well.UX Design Heuristics: Guidelines for Cross-Channel Customer ExperienceHeuristic evaluation in UX has always been centered around the user; how easy and user-friendly your interface is for the target customer contributes largely toward customer satisfaction, and even more so in the presence of cross-channel experiences.Therefore, the following set of UX heuristics (or guidelines) aims to help guide products for a better integrated, UX-pervasive experience. These are guidelines that can, and should, be applied to any service system that intends to provide an experience with interoperability between devices and systems:1. Place-makingPlace-making refers to the self-localization of users when using the system during their customer experience journey. Visual interaction, hierarchical layout, and structure, as well as physical environment, should facilitate the users’ understanding of where they are in the journey and where they can go from there.2. ConsistencyThe system must present visual, typographic, information, action, and interaction consistency. If a user utilizes different devices to execute partial actions of the whole experience, each touchpoint access must present the same rules and responses to the actions.3. ResilienceThe flexibility of the interaction flow and touchpoints should be adequate for different users and different journey and search strategies from different contexts of use.4. ReductionEven if the back end of the system is complex in its structure, the options and the contents must be presented to the users in an objective way and with simple usage, providing reduced interactive actions and minimum cognitive workload in their journey.5. CorrelationThe system must help users find information and content naturally. There must be a correlation of data between distinct points of interaction and devices. When users move from one device to another, the interoperability of information must be in unison.6. Equivalency to cultural conventionsIt is important to understand users’ references regarding technology, processes, functionality comprehension, and interactions — all of these can be used as a base in the development of a new system.7. Visual intuitive contentUsers must recognize functionalities, steps, hierarchy, pathways, and information with minimal memory load – this means making objects, actions, and options easy to recognize and understand by the user.8. Natural, intuitive, and direct interactionsAny touch point of interaction with the system should be as intuitive as possible, by direct gestural manipulation or simple vocal commands.9. Contextual ergonomicsPhysical environments, contexts of use within the journey of experience, and human physical limitations should be considered while projecting touchpoints of interaction with the system.TakeawayUndoubtedly, the digital landscape has evolved to a point where we can all safely agree that user experience has taken center stage in nearly every industry.But does the evolution of digital experiences stop here?From what we can witness today, business interactions in the digital world are constantly evolving, pushing the boundaries of user experience design.The onus is on UX researchers and strategists to respond and adapt well to these changes, integrating user experience research methods and journey optimization techniques to offer a complete cross-channel experience — meeting the customer where they are.
9 UX Heuristics For Cross-Channel User Experience Design

Across any industry in today’s digital age, what is the single most important differentiator that sets apart market leaders from other businesses?Many will answer that with “customer experience”. And they would be right.Experience has always been the key differentiator in identifying the right market leader in any industry. An enhanced customer experience has a proven potential of a 200% increase in conversion rate for the business. Concurrently, 89% of customers switch to a rival business as a result of a poor experience with a brand.But how do enterprises account for the customer experience in the product development cycle?Before we dive into that, it’s important to know what stages constitute the entire Product Development Cycle.What are the Stages of the Product Development Cycle?From ideation to commercialization, the product development cycle goes through multiple stages as the product matures. Broadly, the product development cycle constitutes 5 major stages:Ideation Research Planning Prototyping Release In this article, we aim to understand how a customer-focused product development approach can be integrated at each stage of the cycle, what customer data analytics need to be tracked, and what research techniques can be adopted to gather these customer insights.What is Customer-Focused Product Development?In the product life cycle, there’s a common perception that as soon as a product is launched, the product development cycle is concluded.But the lifecycle of product development doesn’t culminate with the release.Instead, there's a lot of work that needs to be conducted in the way of customer journey research to ensure that a customer-focused strategy is truly implemented in the process.What Factors are Important in Customer-focused Product Development?“Research is creating new knowledge.” - Neil ArmstrongCustomer wants and needs are prone to constantly changing as the market gains maturity.A great product is one that continues to evolve as it matures with the customer at the center.To implement a customer-focused product development approach, the co-existence of product delivery and customer research is vital — something that should be leveraged not just during but also after the shipment of the product or feature.Designing for the Right Reasons with Customer ResearchDuring a flight, before the plane takes off, an airline assistant always demonstrates the security protocols, even though every passenger receives a separate leaflet with the same details.This is a classic example of how observing an aware frequent flyer using the safety jacket reveals undocumented context.The same concept applies in product development that uses customer journey research to follow a truly customer-focused strategy.How Many Types of Consumer Research Are There?There are four different types of research that can be leveraged in the product development cycle.Each type of customer research comes with its own set of distinct benefits at specific stages of the cycle:1. Exploratory researchWith varying customer needs that evolve with each passing day, oftentimes product teams can end up with unique problems — as well as the demand to understand the problem first to decide on the best approach with which to move forward.Such situations require a very quick response and a clear segregation of what is known and what still needs to be learned.Why do it:Exploratory customer research helps product teams be aware and mindful of the challenges that a particular industry faces.Learning from both successful and failed launches can be identified early via exploratory research, which helps build empathy with clients and customers alike. With empathy at the core, a product can be designed well for an organization as well as customers.When to do it:Exploratory customer research is done at the very beginning, before the product life cycle is kicked off. This can be when there’s aNew domain (a new market/customer group sharing a common problem or need that needs to be addressed) New client (with unique business objectives along with new ideas to mature) Pre-sales initiative (by reaching out to an existing client base with ideas to implement with respect to emerging customer needs or technological advancements) Exploratory research may kick off the following activities:Industry benchmarking Competitive analysis Portfolio overview (Internal Competitive analysis) Evaluate across a 2×2 diagram to define maturity and usefulness Stakeholder interviews 2. Generative researchAn important contributor in the product life cycle, generative customer research paves the way for new ideas, new understandings, and new directions.For teams focusing on a single problem, particularly while designing UX, generative research helps explore many possible solutions and approaches. This mindset can lead product teams into many different directions, as it should. That being said, it is essential to have defined KPIs for success where each activity is tracked for its progress with clear success metrics.Why do it:Generative customer research helps strengthen relationships with clients by engaging in their core business problems.Two prime benefits include defining the success of the product and relationship building activities, as well as collaborating in upfront research.When to do it:Post major release Following a workshop It may kick off the following activities:Design sprint Suitable when there is flexibility in budget, scope, and timeline Often involves process changes outside the software Facilitated workshops Focussed collaborations involving the entire team Frequency should be once a month to collaborate on product direction and function Contextual inquiry Context is critical Requires a seasoned practitioner Ideally should be an environment where the product is going to be used/ or being used Output should be a well-defined service blueprint Card sorting Helps in discovering how people categorize information 3. Formative researchFormative research brings a bigger perspective to the table by analyzing both the qualitative and quantitative aspects together.Why do it:Formative research in UX helps evaluate the current state of the product, finding areas for improvement (e.g., building a new product or feature enhancement) and designing actionable output in the form of roadmap planning.Formative research can be carried out in the form of following activities:Heuristic evaluation: Expert reviews to check how the usability of an existing product holds up against a set of predetermined design principles. User interviews: Under expert guidance, you can conduct one-on-one user interviews to garner direct insights of the customer, highlighting the existing pain points or ideal journeys. Prototyping: An early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process, following the Rules of Prototyping: Build quickly, make many, and provide only essential details. Prototyping can be done in the form of Storyboards, Role-plays, Walk-Throughs, and Touchpoints. Some synthesis techniques for formative customer research can include:Personas Journey Maps Diagrams 2 x 2 Matrix Finally, the outcome analysis is done by asking six questions:Is it useful? Why/why not? Is it desirable? Why/why not? Is it easy to use? Why/why not? Is it functional? Why/why not? Is it sustainable? Why/why not? How does it compare to the alternatives? 4. Summative researchSummative customer research focuses on the evolution of the market and the respective product offerings. It helps identify failures at the early stages as well the adaptation measures needed, both with clients and users.Summative research comprises the following techniques:Usability testing Testing in development environments (anything before the production) Analytics review (to review metrics that can help in the evaluation of the forecast vs the performance of the product Out of all 4 of the customer research techniques discussed above, Formative and Summative research are the two types that are most crucial for designing a successful product from both a delivery and inception perspective — how the product works and whether it works as intended.With all said and done, for a deeper understanding of how user research contributes to the success of a product, read this article on Why Ignoring User Experience Research is a Mistake.Takeaway: Building Better Products with the Right Customer ResearchProduct experience plays a critical role in helping brands retain customers and build strong relationships, leading to a loyal customer base. Knowing how to incorporate customer feedback into the product development phases can be critical in helping product teams come together on the right unified goal of having a real impact in the life of their targeted customers.Being able to feel and realize this impact will prove integral to creating a better product experience for all stakeholders involved.To learn more about how you can take personalization a step further in your customer experience strategy, read this article on 6 Hyper-Personalization techniques that large enterprises can adopt for a much more enhanced customer experience!
Customer-Focused Product Development – with 4 Types of Customer Research

Toronto, ON—October 4th, 2022 – mobileLIVE, one of Canada’s fastest-growing IT services companies has been awarded the prestigious Great Place to Work – Canada® 2022 certification. This is the second consecutive year the company has been recognized for its people-driven culture.“Our second consecutive GPTW certification reflects our continued commitment to prioritizing employee physical and mental well-being, collaboration, and development. It is an honor to be recognized as a great workplace, by both the good people at GPTW as well as our talented and diverse workforce” said Jahan Ali, CEO & Founder.Each year, the Great Place to Work Institute® Canada conducts a thorough, independent, and extensive analysis, including anonymous surveys and employee feedback. The certification is awarded to Canadian businesses that are considered fair, unbiased, and inclusive among the majority of their workforce.Since its inception in 2010, the culture at mobileLIVE has nurtured talent and inclusivity across its workforce. With 400+ employees from varying ethnicities, cultures, and social backgrounds, the company continues to empower its workforce through empathy, collaboration, and development.About Great Place to Work®: Great Place to Work is the global authority on high-trust, high-performance workplace cultures.Through proprietary assessment tools, advisory services, and certification programs, Great Place to Work recognizes Canada’s Best Workplaces in a series of national lists including those published by The Globe & Mail (Canada) and Fortune magazine (USA). It offers benchmarks, frameworks, and expertise needed to create, sustain, and recognize outstanding workplace cultures. Visit at www.greatplacetowork.ca or find them on Twitter at @GPTW_Canada.
mobileLIVE gets its second consecutive Great Place To Work® certification

The buzz about data-driven product management is something we’re very familiar with.Long gone are the days when you could only rely on intuition — data is now everyone’s friend, and product managers have spent a considerable amount of time operating in a data-driven manner.This has also contributed towards the rise of big data analytics tools and other product data management systems and strategies.Having said that, while the importance of data and how it is used in product management is not lost on us, there is one big question to be answered:Where does this data come from?What Drives Product Data Management?What specific data do you need to drive your product?Product and data are both drivers in product management; we get data from the product and the same data helps product managers make the right decisions for that product.Understanding that the relation between product and data runs two ways is the first step in product data management.We know where data comes from and how it plays a key role for your product, but what are the most significant stages where data is the key for decision-making?Data-Important Stages in the Product Life CycleData plays a part at nearly every stage of product management.Specifically, there are three main stages in the product management life cycle where data should be central to making key decisions for the product:Acquisition Retention Expansion 1. AcquisitionAcquisition is one of the first few steps in product management.In order to achieve better acquisition for your product, it’s essential to track the right metrics.There are several acquisition metrics that are useful in data management for products, but some of the most important ones you’ll need are listed below:Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)We are all aware that acquiring new customers is much more expensive than keeping the ones you already have.So, how much does it cost you to bring in a new customer? And what is a reasonable cost per new customer for your company?Calculating client acquisition cost, a crucial parameter that enables you to enhance your marketing initiatives and increase overall sales, will help you find the answers to these concerns.The formula to calculate this metric of customer acquisition data is as follows:(Sales Cost + Marketing Cost) / Total new customersCustomer Lifetime Value (CLTV)At times, a customer may stick around for a few years, buying more of your product until they no longer require it or they switch to a different business.How much revenue will a customer generate while they remain a client?The formula to find this metric is as follows:Average total sale x Sales over time x Average customer lifespanConversion RateNot every visitor to your business will make a purchase.They might look around your website or app, but they may not buy anything.You want to make it more likely for people to buy something, sign up for your mailing list, or do anything else you want them to do.The formula to use to gauge how many of your visitors actually convert into buyers is as follows:Number of conversions / Total visitors2. RetentionThe first step in developing long-term consumer loyalty is typically customer retention.Customer retention refers to the ability of a company to convert new consumers into recurring customers.Retention is critical to the success of your product; and to achieve it, cultivating loyalty amongst your consumers will always cost less than acquiring new customers.According to Harvard Business Review, acquiring new customers will cost your business 5 to 25 times more than retaining current customers.Therefore, for the best chance at achieving and improving retention, the top metrics you should consider are:Customer Retention RateThis is the easiest metric to use to gauge customer loyalty and the volume of recurring business you are bringing in.There are a number of additional indicators alongside customer retention rate that you can track to get a more comprehensive picture of how your product is doing.Customer retention is calculated for a specific period of time. Depending on your specific needs, it can be calculated for weeks, months, or years.It is usually reflected as a percentage, and the formula for calculating customer retention is as follows:(Customers at end of defined period - Total new customers during defined period) / Customers at start of defined period * 100Customer churnThe rate at which customers discontinue using your products or services is known as your customer churn rate.This can typically happen when a customer decides not to renew their subscription, stops doing business with you, or ends up doing something else instead of continuing with your product.Much like customer retention rate, customer churn is also calculated for a specific period of time, again, totally dependent on your needs.The formula for it is as follows:(Existing customers at start of defined period - Existing customers at end of defined period) / Existing customers at start of defined periodNet Promoter Score(NPS)A measure of customer satisfaction called Net Promoter Score (NPS) quantifies how probable it is for customers to recommend your product to others.This value shows how satisfied and devoted a customer is to your brand.Although a high NPS can't ensure customer growth and retention, it can help identify product advocates that are most likely to generate referrals.Low customer satisfaction is reflected in a low NPS, which may suggest that some sort of intervention is required to improve things. Here’s the formula for NPS:Percentage of Promoters - Percentage of Detractors3. ExpansionAs with any product manager, your aim will also be to keep clients loyal and coming back for more business throughout the growth stage of the customer lifecycle.To keep your customers satisfied and engaged with you — and in turn making them a profitable customer — you would upsell, cross-sell, and offer expert services, training, and whatever else you can think of.In an ideal world, you'd also like to see them become brand ambassadors for your product. If they are incredibly pleased with your product, they will assist in spreading the news and provide you with some priceless word-of-mouth advertising.Expansion is majorly based on the results that you get from retention metrics.But there are a couple of key metrics that help with the expansion phase:Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)Undoubtedly one of the most crucial levers for long-term growth is expansion revenue.This indicator, also known as expansion monthly recurring revenue (MRR), counts the money gained from repeat business through upsells, add-ons, and cross-sells.ProfitWell recommends that at least 30% of your revenue should come from expansion for a healthy product.According to the Product-Led Growth Flywheel framework, expansion revenue corresponds to the user journey's adoration stage, when your loyal customers start exploring new applications for your product.Net Revenue ChurnSimply put, some of your customers will stop using your product.And so, you will regrettably almost always need to disclose some churn.When you do that, the net churn is a better indicator of your product's health than gross churn rate, since it provides a more holistic picture.Customer churn is generally a less effective metric for growth than revenue churn. This is because, as much as we try denying it, losing your most profitable customer hurts much more than losing your favorite one.Owing to this, if you only use one churn figure, it should be the net revenue churn, which represents the sum of money lost after deducting any new, expanded, or reactivated revenue. The formula to calculate this is:(Revenue lost in defined period - New & Expansion Revenue) / Revenue at the beginning of defined periodTakeawayData management is a huge part of product management that can be approached in multiple ways and requires a deep understanding of the what, why, and how of data, data collection, data management, and big data.Across the entire product life cycle, and particularly at the most vital stages, product data management will define the quality of decisions made pertaining to your product.In doing so, to avoid getting stuck in the web of massive amounts of data, it’s best to know exactly which data you need that will have the most impact on your product.FAQsHow do you acquire customer data?There are several ways to collect data for product data management. Direct observation of customer behavior and preferences, focus groups, surveys, interviews are all the most commonly used methods. Once the customer data is collected, there are multiple ways to assess that data; exploratory data analysis, qualitative data analysis, predictive analysis, etc. are all methods that can be used to further analyze the data.What is the main focus of product management?The core focus in product management is to provide the most value to the customers while also generating value for the business. It combines product vision, strategy, and a deep understanding of the target market and customers to align on a product roadmap. Product management is a function that provides direction throughout the product life cycle — from developing the product to customer acquisition, retention, and expansion.What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data?Qualitative data is information that is not represented in numeric values, but rather in descriptive terms. Quantitative data, on the other hand, is quantifiable information that can be measured and represented in numeric terms. While qualitative data is more about gauging factors like customer motivation and intent, quantitative data collects vast amounts of information through questionnaires, polls, surveys, etc.What are the three components of CLV?The Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) measures a customer’s average revenue over the period of their relationship with a company. The three components that make up the CLV are: 1) continuous margin after deduction of costs like retention spending, 2) constant probability of retention per time period, and 3) discount rate.
Do Products Drive Data or Does Data Drive the Product?

DISCOVERY & SOLUTIONING WORKSHOP FOR USER-CENTRIC TRAINING DOCUMENTATION An eGuide OVERVIEW In product development, ignoring the digital customer onboarding process can become one of the biggest reasons that drives your customers away. After all, no matter how great your product is, if your customers don’t know how to use it — or find it difficult to — they’ll quickly move on to the next best option. Despite that, while most companies will claim they spend time to create training documentation and support for the digital customer onboarding process, they often go at it with a waterfall approach that can have significant costs involved, including time lost due to delays that can otherwise be avoided. So, as a digital onboarding solution, we realized that an agile approach is necessary to create user-centric training documentation that is accessible, easy to understand, and best serves the customers’ needs. Training Documentation eGUIDE 1In this eGuide, we‘ve revealed a way to kickstart the process of creating user-centric training documentation alongside product development rather than after it. You’ll learn a 10-step process of how to approach the initial stages of discovery and solutioning in a more structured manner and in a way that aligns all stakeholders on how the training documentation should be created. Training Documentation eGUIDE 2 WHAT’S IN THIS EGUIDE HOW TO USE THIS TRAINING DOCUMENTATION GUIDE This eGuide can be used to organize a three to three-and-a-half hour workshop for the initial stages of Discovery and Solutioning to create Training Documentation. The workshop can be conducted in person or remotely on Miro. To synthesize insights from the workshop, we have also provided a template for an Output Report that you can use to present as a summary report to the audience after the workshop. The template for this report as well as other resources are provided at the end of this eGuide. Training Documentation eGUIDE 3TRAINING DOCUMENTATION WORKSHOP FROM PLANNING TO EXECUTION IN 10 STEPS Step 1: Finding the Right Team Step 2: Preparing for the Workshop Step 3: Orientation and Introductions Step 4: Familiarizing with Miro Step 5: Workshop Questions and Goals Step 6: Identifying Stakeholders and Steps in Training Journey Step 7: Mapping Stakeholder Needs in Training Journey Step 8: Lightning Demos, Presentation and Voting Step 9: Overview, Suggestions and Voting for Documentation Formats Step 10: Conclusion and Discussion Training Documentation eGUIDE 4 STEP 1 FINDING THE RIGHT TEAM Identify key participants for your workshop. You should include people from the Product, Marketing, Support & Success, Operations, and Learning & Development teams (if available). Training Documentation eGUIDE 5STEP 2 PREPARING FOR THE WORKSHOP STEP 2 Learn about the product/application for which you have been tasked to create training documentation. Do a quick industry research and competitor analysis to understand other perspectives. Then, shortlist some training documentation formats that can be used for the product. Schedule the workshop for 3 and a half hours (breaks included) and send invites upfront. Training Documentation eGUIDE 6STEP 3 ORIENTATION AND INTRODUCTIONS Initiate the workshop with a quick intro of the hosts and what the workshop is meant for. Lay down the goal of the workshop and align participants on why everyone is there. Ask a representative from the Product team to quickly describe the vision and strategy of the product to refresh everyone's memory. This will serve as the North Star throughout this exercise. Training Documentation eGUIDE 7STEP 4 Let everyone add some details about themselves on the Miro board, so that they can not only introduce themselves but also get acquainted with Miro in the process. FAMILIARIZING WITH MIRO Training Documentation eGUIDE 8STEP 5 WORKSHOP QUESTIONS AND GOALS In this section, we try to understand the vision of this exercise and identify the risks in achieving that goal. Training Documentation eGUIDE 9STEP 6 IDENTIFYING STAKEHOLDERS AND STEPS IN THE USER JOURNEY Ask the team to list down all the stakeholders (both internal and external) who will be consuming the training documentation. Get the team to map down all the steps in the training user journey, like: ● Before launch, ● At the time of launch, ● Post launch, ● Pre-purchase, etc. Training Documentation eGUIDE 10By this point, your team could probably use a breather, so this is the perfect time for a 10-minute break. You can use this time to map the information (Stakeholders, Training Stages) from the previous section on to the board.STEP 7 MAPPING STAKEHOLDER NEEDS IN TRAINING JOURNEY Ask the team to identify and list down the training needs of all stakeholders at each stage of the training journey. Training Documentation eGUIDE 11STEP 8 LIGHTING DEMOS, PRESENTATION AND VOTING At this stage, ask everyone to browse the Internet and research to find other examples and ideas (at least 3 per person) of Training Documentation. Encourage them to go beyond their immediate industry. Identify "BIG IDEAS" that can inspire. Put a sticky note beside it to sum up the idea. At the end, ask everyone to present their ideas and conduct a voting exercise to shortlist ideas (in the next step). Training Documentation eGUIDE 12Take another breather here before the workshop moves into the final stages of overview, other suggestions, and final voting. A 10-minute pause here will help participants reorganize their thoughts before going into the concluding discussions.STEP 9 OVERVIEW, SUGGESTIONS AND VOTING FOR DOCUMENTATION FORMATS Present some popular and relevant training documentation formats to the team based on your research before the workshop. Present pros and cons for each format. Ask the team for any additional ideas not covered previously and add them to the list. Lastly, vote on the formats. Training Documentation eGUIDE 13STEP 10 CONCLUSION AND DISCUSSION Review the content covered in the workshop and give everyone some time to share anything they would like to add that was not already covered. Thank everyone for their time and conclude the workshop. Training Documentation eGUIDE 14POST-WORKSHOP RECOMMENDATIONS REPORT Use the "Recommendations Report" template (provided on the Miro link at the end of this guide) to summarize and synthesize your workshop insights and to propose recommendations for the Training Documentation formats. Training Documentation eGUIDE 15HELPFUL LINKS This eGuide covers only the Discovery and Solutioning stages of the entire process of creating Training Documentation. Here’s the link to the Miro template you can use when you conduct the workshop: https://miro.com/miroverse/training-documentation/ Discovery and Solutioning are only the initial two steps of our 5-step Process of Creating User-Centric Training Documentation for Effective Digital Onboarding. To learn more on our 5-step process to create user-centric training documentation, please refer to this article: https://www.mobilelive.ca/blog/create-user-centric-trai ning-documentation-for-effective-digital-onboarding Training Documentation eGUIDE 16ABOUT MOBILELIVE We’re your full-service digital team obsessed with helping you make smart investments and reduce time-to-launch. Our team of experts specializes in designing experiences, building products, and scaling technology with flexible engagement models, outside-in views, bespoke solutions, and a succession of early wins while never losing sight of the big picture. 100% client retention since day one 40+ iconic & Fortune 500 clients 20+ industry awards & distinctions http://www.mobilelive.ca contact@mobilelive.ca Training Documentation eGUIDE 17
Discovery and Solutioning Workshop for User-Centric Training Documentation

With the wave of Digital Transformation every business is trying to ride, how do you keep up with the wave of users that comes with it?Online and self-serve systems have seen a massive rise with the growth of digital platforms, and an even bigger push with the COVID pandemic. These systems became the need of the hour to limit human interaction, and so technology evolved to a point where providing a seamless and swift digital experience became a standard.But despite that, many corporations still can’t take full advantage of these new technologies and often end up losing potential customers simply because their legacy systems can’t keep up.The Challenge of Adopting New Technologies For Large EnterprisesDue to a dependency on mission-critical legacy systems — predominantly owing to high replacement costs — enterprises are forced to build digital systems on top of the existing legacy systems. This results in two architecture layers with different service-level agreements (SLAs).But while digital APIs deployed on the cloud can scale automatically to sustain any workload, these legacy systems would eventually crash under heavy load, causing loss of business opportunities.In this article, we’re diving into a real-world application of the Command Query Responsibility Segregation (CQRS) design pattern and event sourcing to prevent this issue of overloaded legacy systems.CQRS Pattern to the RescueLet’s dissect the problem stated in the previous section.As we understand it more deeply, we find the root cause behind the need for CQRS and event sourcing patterns: modern digital APIs have the ability to produce a much higher volume of transactions than legacy systems can support.Can we have an architecture where the legacy system is required to process only a subset instead of all the transactions?The CQRS software architecture pattern offers a good solution.The command query responsibility segregation separates the write and read transactions in such a way that digital APIs can commit to one system and query from another.The diagram below shows how the CQRS pattern changes the architecture to send a subset of transactions, "write actions", which usually represent a tiny portion of all the transactions generated by a digital system.Usually, the CQRS pattern is coupled with event sourcing patterns that facilitate data synchronization between the source operational data store and the target read-only data cache in near real-time.The data cache is a high performing database that is located close to the digital APIs to reduce latency. The data model is designed to maximize read performance instead of data integrity since this is a read-only data store.Once the changes above have been implemented, we notice a huge performance increase in the read transaction. We can also observe that the backend systems were able to cope with the seasonal spikes in volume.Implementation Strategy for the CQRS PatternGiven the complexity of the CQRS design pattern, it is preferable to implement it in phases, focusing on the most critical APIs first.When we were using the CQRS pattern, my team had an urgency to fix the issue completely. Hence, the phased approach was rolled out.We’ve realized it works well, and using it for every single API that the digital systems use is found to deliver a reliable experience.But as with any new technology, there can be challenges with the implementation of the CQRS pattern.Two Challenges with CQRS ImplementationThe CQRS pattern has its benefits, but it also comes with many challenges that we need to take into consideration before making a decision to implement it.The two biggest challenges we faced while implementing command query responsibility segregation with event sourcing pertained to:Testing Race Conditions Challenge #1: TestingThe CQRS pattern impacts the most valuable corporate asset in the digital world: customer data.Any defects that are not detected and fixed in a non-production environment may have a drastic impact on customers. For instance, a CQRS defect can result in a privacy issue where a customer gets access to some other customer data.In order to avoid such issues, testing in non-production environments alone is not sufficient.For our project, we went with the traditional approach of testing in non-production and allowing for a period of business readiness testing in production. Then, we launched the system to the customers.As a result, there were many corner cases and special data that we never accounted for that caused some serious issues in production.Solution:A better approach would have been to run the old and new system side by side for some period of time and automatically validate the output from both systems for the same requests in production. The diagram below outlines this approach.Challenge #2: Race conditionsThe operational data store is the source of truth and is updated by many systems, amongst which is the digital system itself.When the update happens from the digital system, the customer expects the new information to reflect on all the views immediately.With the CQRS implementation, this may not be feasible since there could be a delay in updating the data cache and hence the digital APIs would still read the old data.Solution:To get around this race condition, the write transactions that are initiated from the digital system had to also mark the data in the cache as stale and save parts of the write transaction response that can be used for temporarily presenting the latest version of the data on the user interface.TakeawayDespite the challenges that came with it, when we implemented the CQRS pattern, the benefits were evident:An enhanced user experience An increased system availability during the transaction spike period However, with that said, the CQRS pattern is still relatively nascent.While it may seem to be a disruptive solution for a very pressing issue in legacy-based systems, implementing the CQRS pattern should always be taken on a case-by-case basis and with preparedness for the challenges that could arise with it.FAQsIs GraphQL a CQRS?CQRS is a design pattern used in programming that treats data in queries and commands separately. While GraphQL also defines input and output object types separately, aligning with the concepts of CQRS design patterns, CQRS GraphQL is a query language that standardizes data queries.Is CQRS an architecture or pattern?CQRS is a design pattern that can be applied in software architecture. It is an architectural pattern that separates commands and queries in the application architecture.What is the difference between CQRS and event sourcing?The implementation of CQRS happens through a segregation of commands and queries. On the other hand, for implementing event sourcing, the sequence of the events is used to track any changes in data. Event sourcing is a practice to store domain events.How do you implement CQRS?The implementation of CQRS lies in the segregation of commands and queries, meaning it is executed using separate models for read and write. It’s best to implement CQRS in phases and coupled with event sourcing patterns.
Surviving User Overload: How CQRS pattern helps build digital APIs on legacy systems

Have you ever ended up abandoning a product because it forced you into multiple, seemingly unnecessary security layers?Let’s take an example of what I’m talking about. In fact, I’ll share four examples of how security layers meant to “enhance security” can cause more harm than good.Product Security Layers That Do Not WorkComplex Password PolicyBack in my college days, this is what the password policy of our IT department looked like:A default password was set up for every student, which looked something like this: Press@123 All students were required to change this password every month This was a classic example, and not the only one, of a complex password policy that both required symbols, numbers, upper and lower case letters, and also required the users to reset the passwords at an interval of every few days.As a result of this, most users would end up using the same passwords across various websites and, in worse cases, saving their passwords in unencrypted notes.This wasn’t the only consequence of the complex password policy adopted by my college IT department:A massive worldwide online hack took place during those days, due to which a staggering 8 billion login passwords were leaked.I, along with some friends, downloaded and analyzed this dump of account login passwords. A key observation we made while analyzing these passwords, which belonged to university students, professors, and even cyber security experts, was that every time these users were asked to reset their passwords, they would only increment the last number in the password.If this event proved anything, it was how user behavior could easily render such complex security measures redundant and useless.No ‘Show Password’ OptionApple users, in particular, will be able to relate to this issue the most.The unavailability of a ‘show password’ option often results in users opting for other, non-secure ways to avoid typing errors when inserting their passwords. Oftentimes, users are more likely to simply copy and paste their passwords from other non-encrypted places where they've written down these passwords, mostly their notes.Another consequence of a missing ‘show password’ option is that users end up creating short, less complex passwords that are easy to remember as well as type out without mistakes.Fortunately, to prevent such counter-productivity, many platforms have equipped users with the capability to ‘show password’, which is enabled as a default feature so as to minimize errors and enhance the user experience without compromising on the security of their passwords.Frequent LogoutsIn efforts to prevent misuse of account information, a lot of applications and platforms frequently log out the users after a certain time of inactivity (or, as per their own respective policies, even every week or month, etc.).While the need for such policies is evident in sensitive cases like banking and finance apps, these measures can hamper the user experience and end up being an overkill for other use-cases, like HR software or other internal applications.Thankfully, as a solution to this dilemma, we have technologies of Face and Touch IDs to deal with such concerns as they don’t compromise on the user experience while keeping security intact.Prohibited Multi-device LoginsThere are also some applications that will automatically log you out from one place if you try to log in from another device or IP address.This, again, hampers the usability of the application and can be off-putting for users.A better implementation of this, rather than automatically expiring the user sessions, is where users are allowed to add and remember any new device that they log in from. Once they go through the verification for the new device, they can simply ‘remember’ that device, so they don’t have to log in every single time.Product Security and User Experience: Finding the BalanceThe dilemma of choosing between amping up product security versus accounting for better usability and an improved overall user experience is one that we often face in our daily work.According to Avi Douglen, founder and CEO of Bounce Security, AviD’s Rule of Usability posits that:“Security at the expense of usability comes at the expense of security.”The Pessimists Vs. the OptimistsThere are two sides to this dilemma that stems from product security and usability:The Pessimists:These are the Security and IT teams whose belief lies with Murphy’s Law, meaning that what can happen will happen. So, being preemptive, the Pessimists will want to ensure Government-level security for all apps.The Optimists:On the other hand, there are The Optimists. These are the Design, CX, and Sales teams whose primary job is building products that engage the customers and are easy for them to use rather than adding more barriers and complications for the user.Which of these two sides comes out at the top?Neither, because both of them have weight, and both are (usually) valid in their own ways.Is the Minimum Viable Secure Product (MVSP) Worth It?For Product Managers, the most vital thing they need to achieve is to find a balance between usability of the product and its security. This sweet spot between the two is what has come to be known as the Minimum Viable Security Product.Exactly where this balance is achieved will always vary according to the situation and circumstance at hand.For example, some products involve Personally Identifiable Information (PII) or other data that is of high sensitivity. In this case, a product manager may need to lean more towards The Pessimists and adopt a layered security model, endpoint security controls, or another stringent product security framework.With that said, what is of utmost importance here is to not ignore either side of the coin.Often, finding this balance between product security and usability may require you to adopt measures that are costlier.From personal experience, and having learnt the hard way, I’ve found that identifying and choosing such a solution that does the job of keeping both usability and security intact is often worth the added cost.I’ve also found that oftentimes security teams can get lax and suggest a security measure that damages the user experience, while better alternatives do exist that can at least come close to achieving similar levels of security.All that would be required to achieve the latter rather than the former is some added effort (e.g., HTTPS, local storage encryption, app bundle encryption, etc.).TakeawayIn the presence of so many innovative solutions that product teams now have at their disposal, balancing product security with product usability is not the impossible, gargantuan task that it was previously believed to be.In some cases, you might need to encourage and challenge design teams to innovate for an enhanced user experience amidst security constraints. It’s safe to say that seeing how long we have come with technological advancements, solutions like Passwordless logins, Face IDs, Touch IDs, MFA, SSO, and more have made it possible to achieve the right balance between security and usability.FAQsWhat is the Minimum Viable Secure Product (MVSP)?Minimum Viable Security Product (MVSP) is the baseline of the minimum security measures and checks that a product must meet to ensure security. Much like the need has grown from simply providing an MVP to instead creating a Minimum Viable Experience, so has Minimum Viable Security become more relevant and required.What is the Minimum Viable Secure Product checklist?For any software, application, or enterprise-ready products and services, a Minimum Viable Secure Product checklist is a baseline for security measures that can be implemented at various stages of the product and sales cycle. These security controls help manage the security levels for things like requests for proposals, self-assessments, third-party security, vendor compliance, licensing, etc.
Minimum Viable Security: Balancing Product Security and Usability

If there's one thing all UX designers, product designers, and anyone working with design can relate to, it's the plethora of questions that they have to deal with on a daily basis.And our designers were no exception to this.So, in an open conversation with no holds barred, we decided to sit with five designers from our design team to discover:what these questions tend to look like, how designers deal with these queries regularly, and the uniquely distinct perspectives of each UI/UX designer in the field of user experience design. For the sake of this article, we chose three questions to ask each of our five designers:Question 1: What is the most common question you are asked by clients?Question 2: How do you negotiate deadlines with product owners and stakeholders?Question 3: What is your approach when presenting your work?Question 1What is the most common question you are asked by clients?Response 1:Would you recommend this approach based on UX? What is your UX opinion if we do this particular thing? Can we do A/B testing to make a final decision? How can we improve this particular journey based on UX? Can you provide some feedback on the current pages and let us know your thoughts on improvements? What is the best practice for serviceability check for user experience? — Ella Rabiei Senior Product DesignerResponse 2:"Typically, the most common question designers run into is, "When will this be ready for review?""I find that there are generally 2 kinds of questions that a client will ask; "What is the cost? (in time, funds, effort, or stress)" or "Can you explain your thinking?". While these questions may seem like an oversimplification (as it probably is), understanding the underlying intent of these questions helps me, as a designer, ensure I'm providing answers that are effective and concise.Being pedantic and looking at my typical question above, that boils down to "How much time with this cost the project". And why not? Time is as finite a resource as a budget is."— Dana Mitchell Senior Product DesignerResponse 3:"When can you have this done?"This raises an important point, which is that often the emphasis is placed on quantity/output rather than quality. It also highlights the client's lack of understanding of the UX designer's role, which is a weak link in the chain of product design."— Véronique Janosy Senior Product DesignerResponse 4:"How fast can you finish? Will it be quick? Can you do it sooner?"— Carlos Salguero Senior Product DesignerResponse 5:We want to do a redesign. Where do we start? We want to add a new feature to this page. Can you implement this solution? We have these requirements, and we are looking for this solution. When can you deliver this? "Clients need help to uncover problems. Like most humans, they are very good at communicating solutions. My job is to help them find the best solution by first identifying the problems. This is called problem-solution fit. A solution must fit a problem. If the solution does not fit a problem, it is not worth doing it. Furthermore, the solution must be appropriate and not perfect."— Amir Abura Lead Product DesignerQuestion 2How do you discuss and deal with deadlines while working with Product Owners (POs) and stakeholders? If the requested deadline is too tight, how do you negotiate?Response 1:"The POs mostly set a deadline and try to adjust it with the designer's capacity. Depending on the situation, there are several ways to deal with it:If the deadline is for "Tomorrow morning" and it is mid-day already, it depends on the task's value. If it is a small design request, like updating a specific page, I would do it while working on other tasks. If the task is a major design request, I'd let my manager know that I need to pause some of the work to deliver the task, and I would try to see how I can expedite the design process and, if possible, use some of the currently designed pages as my placeholders. To negotiate, I always try to look at the big picture and see how I can accommodate the client's request and my current capacity; I'd also ask to see if there is any possibility of pushing the deadline to some days in the future to avoid the conflict between the deliveries. I'd also ask POs what goals they are trying to achieve with the requested design and try to deliver it in semi-high fidelity mocks instead of high fid versions." — Ella Rabiei Senior Product DesignerResponse 2:"For myself, the easiest way to prioritize is to directly ask what the priorities are. When I have several tasks on the table and not nearly enough time, I start by giving each task a rough time estimate and lay out what I will be able to accomplish in the given time frame.Armed with this knowledge, the PO or stakeholders are better able to understand what my current workload is and decide what the focus will be, hence setting the expectations for the deadline and ensuring that everyone is on the same page.Alternatively, it could be agreed to reduce the amount of work involved; instead of creating a high-fidelity design, a wireframe could be produced instead. Concessions like this allow for the work to begin and start the iterative design process on its merry way."— Dana Mitchell Senior Product DesignerResponse 3:"I'm very up-front about it. If it hasn't been mentioned during the brief, I'll always bring it up; this helps me to prioritize and also to avoid nasty surprises later. More often than not, somebody's got some kind of date in mind–whether it's a hard date that developers need assets by or a more general one, like "sometime during Q2"– and that's a good starting point. Knowing the timeline helps me field questions like "when can you have this done?", since I already know what the projected timeline is. If a timeline is too short, I voice my concern to the PO, and then we work together to reprioritize whatever's on my plate. I always try to remember that there are only so many hours in a workday, and I try to be as honest as possible when it comes to my workload and capacity. When stakeholders are up-front about deadlines, then I can be better prepared to manage expectations."— Véronique Janosy Senior Product DesignerResponse 4:"I explain the intricacies of the work and only negotiate if PO is being reasonable and understanding. Otherwise, UX requires a minimum of 2 weeks and a couple of grooming sessions to consider a wireframe "ready for sprint"."— Carlos Salguero Senior Product DesignerResponse 5:"There is no perfect solution. There is only an appropriate solution given the time and resources available. This is how I negotiate. What can we do now with the time given and resources available? And more importantly, is it worth it? Is there a problem-solution fit? My job is to provide this analysis, so the PO has more info to make a decision: let's do this now and iterate after or let's not do this now and spend more time on the problem."— Amir Abura Lead Product DesignerQuestion 3What is your approach when presenting your work?Response 1:"This question is a bit general when it comes to the audience; I'd try to respond in different scenarios:In General: I'd prepare a fictional or real scenario that includes the research data based on the actual product/design subject and gather the most common/potential pain points plus the written ideation on how to resolve the problems or create a better environment to avoid the potential problems. Then I'd prepare the low-fidelity mockup to discuss the user journey and the product's process path. And once I showcased it, I'd prepare the high-fid mocks to present the finalized idea with showing the details for the solved/improved path, and at the end, I'd present it to the client, including POs, Stakeholders, marketing executives, etc. To the POs and the Dev team: After updating the mocks on Abstract, I'd share my screen in our review session to present the changes/ ideas/ new outcomes on fictional scenarios. I would receive the feedback and comments and will apply them to the design before presenting to the stakeholders. To Stakeholders: mostly happens after the [presentation to PO's] session, once everything is updated, the POs would proceed with presenting the design." — Ella Rabiei Senior Product DesignerResponse 2:"Whenever presenting my work, the first thing I do is prepare myself for feedback. Feedback is a vital part of any design process, but it's not always easy to swallow. I prepare myself to stay grounded and receptive.Next, I consider the audience to whom I am presenting. The goals of each team within a project, myself included, will be different; the artifacts created will be used differently by each team, and I try to keep that under consideration. At the end of the day, my goal is to help set clear expectations to ensure that everyone knows what we are driving towards."— Dana Mitchell Senior Product DesignerResponse 3:"In my job, I don't have to do any kind of formal presentation. I'll usually present what I have to the PO, who will then bring back my work to marketing. The PO acts as a buffer between design and marketing because the interactions can get pretty intense. So when presenting to the PO, I pretty much just tour the component, noting where the design followed or deviated from the original requirements and explaining why. I may have a few different options to present, and the PO and I will usually discuss which one we align with.When presenting to developers, I start by introducing the purpose of the component (if it's a net-new component) or, if it's just a variant, I'll be sure to lead with that. I then talk about the various technical aspects of the component and how it may be similar to or different from either its parent component or a similar one. I then open the floor for questions."— Véronique Janosy Senior Product DesignerResponse 4:"I put myself in my audience's shoes. How can I make this easy for anyone to understand? I make flows, add arrows, include annotations, and, if time allows, create a prototype with all possibilities."— Carlos Salguero Senior Product DesignerResponse 5:"Present the problem, evidence, explorations, and the best solution that fits the problem with the time and resources available. Again there is no perfect solution. Only an appropriate solution that benefits the customer and the business in the present moment with the resources, technology, and time available."— Amir Abura Lead Product DesignerTakeawayAs with any designer, I, as a lead designer myself, have always been at the receiving end of the aforementioned questions, amongst many others.Therefore, this effort was made to not just bring these questions to light but to truly get to discover the perspectives and thoughts of other product and UX designers as well.After all, it's a designer who can best understand another designer, and this candid discussion with my design team provided an opportunity to uncover their unique, creative personalities that make them so good at what they do.FAQsWhat does a UX designer do day to day?In their daily lives, UX designers often work with Product Owners (POs) and other stakeholders to capture the project requirements, conduct research, ideate, design, and demonstrate how a new feature or product is going to work and why any design changes would be required.Does UX design require graphic design?Graphic design is one of the many aspects of UI and Product Design. Having a foundational understanding of graphic design is what drives good interfaces: understanding visual hierarchy, good typography, understanding how to use color, etc.Is UX design in demand?While it is a relatively nascent field, UX design is very much in demand with an exceptional career outlook. In fact, the demand for UX designers continues to grow, leading to the field of UX design being included in one of the 50 best jobs in 2022, according to Glassdoor, amongst other similar rankings.Is UX design coding?Coding is not required, but understanding HTML/CSS code is an asset as a UX/UI or Product Designer. It helps in communicating with developers to speak their language.
Ask A Designer: An Open Conversation with Product & UX Designers

Since the start of this decade, large-scale transformations in business strategy and technology have become standard features across industries and business models. Over the past two years, a significantly large (and rising) number of enterprises have begun adopting a Multi-Cloud strategy.IBM's 2021 global study on cloud transformation also confirms this rapid change. The study found that the use of single-cloud systems declined to a mere 2% in 2021, compared to 29% in 2019. Most companies are either already running Multi-Cloud architecture or will be moving there within the next few years. So it seems fairly obvious that in the years ahead, hybrid or Multi-Cloud will remain the most dominant type of IT infrastructure across industries and business models.In this blog, I aim to discuss what keeps driving organizations to the Multi-Cloud strategy and what challenges they face during this transformation. But before we dive into further details there, let's first examine what we mean by Multi-Cloud.What is a Multi-Cloud Strategy?At its most basic, I would say a Multi-Cloud strategy is simply utilizing two or more public or private clouds. For example, a company utilizing AWS or GCP, or Azure and AWS, can be said to be adopting a Multi-Cloud strategy.Is this strategy applicable to any type of enterprise? Not exactly.I would say a Multi-Cloud strategy is usually a better fit for larger enterprises. Particularly because of the significant costs and complexity involved in running and maintaining the architecture. For small to medium organizations, I would typically recommend Hybrid Cloud as a more appropriate solution option.What Does Hybrid Cloud Mean?Picture a business running a local data center. This business could also be extending some services or replicating its local data center services into a public cloud in parallel. This is precisely what you call a Hybrid cloud model. But there can be further segmentations in the terminology involved. For example, a hybrid strategy where there is a local data center as well as more than two or three public clouds. The combination of these is called Hybrid-Multi Cloud.Why Are More Businesses Turning to Multi-Cloud?Many businesses already have a dual cloud vendor strategy because they want to be more competitive while keeping the cost down. It may sound like a generic motivator, but that does not invalidate the fact that it keeps driving so many enterprises in that direction.FlexibilityThere are also several more specific drivers for organizations to adopt Multi-Cloud strategies. From my perspective, I really feel it's the flexibility to pick services that different vendors offer compared to others that adds to the eagerness to shift.SecurityAnother key aspect, I would say, is from the security standpoint. Cyberattacks continue to be a huge concern for businesses anywhere, causing companies to lose billions in terms of data breaches, confidential information, and reputational damage. It is significantly difficult to bring down a Multi-Cloud environment using a denial-of-service attack or DDOS attack, in my experience. Therefore, the added security would most definitely prove a key motivator for businesses to shift in that direction.Data RecoveryThe third aspect I'd say is data recovery or disaster recovery. Businesses need only to slip up once to become the victims of a significant data breach. So it makes a lot of sense to have contingencies that protect against that. A multi-cloud strategy lets you can create one of the most reliable architectures, which, in turn, can mitigate the fallout from a single-point failure in parallel.In a nutshell: the ability to do best of breed, improved security, disaster recovery, and data availability all contribute to the rapid rise of Multi-Cloud adoption across industries.The Top Challenges When Implementing a Multi-Cloud StrategyWith any new technology and its adoption, there are almost always some challenges. This is no different when it comes to Multi-Cloud. As a technology, it is safe to say that it's still evolving, and organizations are already invested in it. The biggest hurdles they currently face include:A Lack of Industry StandardsOne of the key challenges that many companies face is that there is no industry standard that regulates architecture guidelines, principles, or best practices that need to be implemented.A Lack of Holistic ToolsIn addition, there aren't many tools in the market that can help support or monitor a Multi-Cloud environment. Also, when it comes to provisioning, deploying, and testing the technology, you often don't see too many tools either.Problems with Identity BrokeringLet me use an example for this one. Say you are running an application in a local data center that has typically been authenticated by an active directory. This has to stay in contact with or receive some information from your AWS file system, for instance. AWS, on the other hand, uses an IM service or identity management that authenticates any request that is coming in before it is executed. Translating an AD token or AD authentication to authenticate automatically in AWS is called identity brokering.From an application standpoint, identity brokering is a big challenge in the Multi-cloud environment because each service provider might end up using their application to identify the request and response.Recommendations to Enterprises Implementing a Multi-Cloud StrategyIn my line of work, I can see in the industry there is a new adoption called "infrastructure as code" or IaC. This is one of the ways that you can address admin tasks, from provisioning to deploying, like:Configuring, Testing the virtual machines, Creating containers, Deploying containers, Creating serviceless functions, etc. All of that can be automated by IaC, and this code can then be run by virtually anybody. What this results in is an automated CI/CD pipeline spanned across a Multi-Cloud environment. So, to see more success when implementing Multi-Cloud, I would recommend every business leverages IaC.Specialized Tools for Multi-Cloud ManagementI've already talked about how there aren't a lot of tools that assist in managing and monitoring Multi-Cloud. But I have come across a select few that can help with Multicloud monitoring.The most useful ones are Flexera and Embotics. They are fairly closer than other comparable ones when it comes to managing Multi-Cloud environments. IBM Cloudpark is another fairly good choice, and it sees a lot of use for data insights.For certain use cases, you can also combine tools. Terraform combined with Ensemble, for example, can act as a powerful IT automation tool. This can automate many IT tasks in the context of public and private cloud environments.But, from experience, I would still say I have observed a significant demand from enterprises for a holistic platform that can be used to allocate workload strategy and manage business containers in a hybrid Multi-Cloud environment. Unfortunately, we have yet to see a comprehensive tool that can act as a unified management platform.TakeawayThere is no question about the benefits a Multi-Cloud or Hybrid Multi-Cloud environment brings to a business. The real hurdle is the need for a unified infrastructure management tool. That's what we really need to comprehensively and holistically manage these environments. While there isn't a tool that can claim that title yet, I would say it is only a matter of time before we witness a major cloud provider getting around to releasing it. After all, why not, right?I have come across many companies and vendors trying to get there. There are several third-party tools that are already in development. Azure and AWS have already implemented tools to aid with Hybrid Cloud management. In essence, nothing is really stopping them from making a Multi-Cloud management platform as well. Or to go a step further and create a unified infrastructure management platform. Once that happens, that tool could prove a significant game changer in overcoming challenges to implementing and managing Multi-Cloud architectures. Who knows, maybe that could be a watershed moment right around the corner!
What’s Driving Large Enterprises to Multi-Cloud?

Holding your customer’s attention when they have no time is a big challenge.Particularly in today’s digital age, with average attention spans that only last a few seconds, driving business outcomes now relies heavily on employing the right user engagement strategy.But before jumping into the various types of user engagement strategies used for improving customer experience and retention, let’s quickly understand exactly what a user engagement strategy entails.What is a User Engagement Strategy?A user engagement strategy is a plan to:Grab your customers’ attention, Improve their experience of using your product, and Make them engage with the product offering on a regular basis. Such engagement tools enable us to not only increase customer loyalty and lifetime values, but also optimize the customer experience and boost customer retention for the long term.User Engagement StrategiesThere are many ways to hold your customers’ attention and engage them long enough to make sure they have a great time using your product.The user engagement strategies highlighted in this article are ideal for growth marketing and product success, and are proven ways to garner customer loyalty and retention:Customer Journey Mapping Hyper-Personalisation Integrating Analytics Rewards and Customer Loyalty Program Chatbot 1. Map Your Customer JourneyTo effectively develop and implement a user engagement strategy, it is crucial to understand who your target audience is and how they use your product.A good way to do this is through customer journey mapping.In this user engagement strategy, you map out your product’s customer journey and understand all the different ways a customer can interact with your digital platform or app. This allows you to unravel any challenges the user may face and discover more about your users’ needs and behavior, which is instrumental in identifying opportunities for engagement.Illustration 1.1: Common touch points surrounding a customer journey map that a visitor takes to start the buyer journey process.Additionally, analyzing your customers’ behavior will allow you to segment your target base and create customer personas. Collecting this knowledge is the first step in creating a tailored user engagement strategy to interact with each persona according to their distinct preferences.2. Create Hyper-Personalized OfferingsIn today’s day and age, providing personalized experiences has become an essential user engagement strategy. And it makes sense why – customers have grown to want products that are tailored to their needs.Personalization can be something as simple as showing customers a location-based ad or using their first name in an email.It could also become something much more complex, by applying nascent technologies such as machine learning and AI to offer hyper-relevant services.A good example of personalisation in the Telecommunication industry is when a customer who regularly purchases data add-ons to meet his monthly needs is offered an exclusive package to upgrade their plan at a discount. Usage behavior, interests, location, device information, etc. could be used to create a unique offer for each customer that best meets their needs.Push notifications are also essential when it comes to a successful user engagement strategy and plan. Using these notifications effectively can help improve awareness and usage for your product features. Location-based notifications or offers can allow you to give the users of your product a contextual experience that would be hard to match.3. Track Business AnalyticsThere is no way of knowing whether your customer engagement strategies are working or not if you don’t have specific success metrics in place and aren’t tracking them on a regular basis.Therefore, it is essential to close the customer loop by listening to their feedback and incorporating it into improving your product offering.Data driven decision-making can allow you to identify behavioral trends and understand how the customers use your product in order to address their needs.Tracking your daily active users (DAU) as a % of your monthly active users (MAU) can give you an estimate on the number of days your customers use your product in each month.Segmentation and analytics play a pivotal role in driving the marketing strategy for an organization. Quantitative insights can help build your brand persona and also help identify the USPs of your product. This can be used to create acquisition and retention campaigns to increase usage.Understanding the onboarding process for your platform and the use of conversion funnels to identify the relevant drop-offs can also play a crucial role in helping uncover design or product level issues that might be hampering your overall user engagement.The use of analytics tools can significantly impact the growth of engagement on your platform. Using these tools can enable you to segment your user audience based on multiple attributes i.e. age, location, interests. These segments can then be targeted with the use of available communication channels or push notifications, thus generating not only interest but also customer retention and loyalty to your offering.4. Design a Customer Loyalty ProgramAnother effective user engagement strategy is to engage your customer through a customer loyalty program that rewards them with points, discounts and gifts in return for frequently engaging with your platform.These programs can prove to be very effective as they not only improve customer retention, but also increase customer switching costs by boosting customer loyalty. Having a loyal customer base can generate word of mouth and referrals for your product, which can attract the desired audience to your platform.Illustration 1.2: Customer loyalty programs improve customer engagement and boost retention rates.5. Implement a ChatbotChatbots are a proven tool to increase conversion rates, especially when it comes to digital platforms.An AI-powered chatbot has the ability to analyze data and appropriately reply to users based on preprogrammed recommendations. The program can also be engineered to trigger specific messages based on customer attributes such as location, time, or engagement levels.Bots can also help users choose products they like, answer FAQs, or even act as a trouble-shooter to decrease churn rates.Additionally, another key advantage of using chatbots as part of your user engagement strategy is their ability to offer minimum service levels even during after-hours when a call center representative is not available. This helps create an additional channel through which key customer information can be collected so that they can be contacted later.TakeawayThere’s no doubt that the digital age of today has transformed the way businesses operate and seek out customers.Therefore, in efforts to keep up with such transformation, it is now more crucial than ever to adopt smart approaches and strategies that put the customer at the center of your engagements with them.User engagement strategies like the ones discussed above all help you hold your ideal customers’ attention, improve their experience using your product, and keep them coming back for more.Remember, the right user engagement strategy will pave the way for transforming your target audience into loyal customers that stick with you for the long haul.FAQsHow to optimize user engagement?There are many user engagement strategies that help optimize user engagement for your product, digital platform, or app. Some great ways to do this include customer journey mapping, hyper-personalization, integrating analytics, customer loyalty programs, rewards, and chatbots.How do you increase product engagement?Product engagement can be increased by incentivising customers (e.g. through loyalty programs and rewards), using and studying user data to create personalized notifications and offers, and streamlining and optimizing the overall user experience through customer journey mapping.
Improving Customer Experience with the Right User Engagement Strategy

What do you do when you need people to come together and be on the same page for a new concept at your organization?Some back and forth via emails? Putting in requests for meetings where the conversations are driven by PowerPoint pitches? Having one discussion at a time, and that too only led by the extroverts or people with titles and power?What about the value that the rest of the individuals at your organization can bring into these discussions? How do you cultivate an environment for brainstorming and a healthy exchange of ideas where every individual is a part of the conversation and contributing towards a purpose?Contrary to the conventional ways of doing business that organizations have ingrained as common practice, there is a better solution. The latest research around creativity and innovation offers a much better way of aligning everyone on a shared goal: Design Thinking Workshops.Design Thinking WorkshopsDesign Thinking Workshops help organizations combine the power of individual thinking with the cross-pollination of ideas and critical thinking. These workshops can truly accelerate innovation by transforming the way teams collaborate during design ideation to design and redesign products and services for their customers.The design thinking workshop framework acts as a catalyst, bringing out the best ideas to light and speeding up innovation in the design thinking process.Design thinking workshops are much more advanced than simply encouraging participants to talk about what needs to happen. Instead, they steer participants on HOW to do it.Simply put, these workshops take design thinking ideation a step above and actually help you get things done - quickly and more effectively.Which brings us to our next question: What do different kinds of design thinking workshops achieve, and which is the right one for you? Let’s help you choose the best one for you in the next section.Types of Design Thinking WorkshopsThe type of design thinking workshop you need for your project is contingent on several factors:Why you need it to happen Who are the participants What is your end goal Depending on your situation, here’s a quick comparison of all the workshops before we jump into each one in detail:Now, let’s try to understand each workshop, its requirements, and outcomes in detail so you can pick the design thinking workshop you need:Discovery WorkshopBest suited for the early stages of a project, a Discovery Workshop is a customized design thinking workshop designed to frame the problem from the end user’s perspective.During this workshop, the focus is on the business goals, target user personas, their needs, journey maps of these users and opportunities for improvements in these journeys.Who should attendBusiness & Sales Team Leads Product/Marketing Team Lead Solution Architects All other stakeholders critical to defining the problem Why should we do itDiscoveryDiscovery workshops help uncover users’ problems, pain points, and needs through curated activities; developing user personas and mapping the current user journey helps identify and uncover any pain points along the way. ContextA deeper dive into the problem space provides context and a better understanding of the backend processes within the organization. Understanding the context more clearly also helps define the business success metrics. Solving the RIGHT ProblemsThis kind of design thinking workshop builds a shared vision and identifies the root causes of the problem. It also helps reframe the problems into opportunities to serve customers better. Through discovery workshops, you can prioritize the opportunities that are best aligned to the business and users’ goals. Defining ways to help validate ideas and concepts before committing time and budget to them saves resources. Quite often, these workshops help reframe the problem by shifting the focus from the solution to the problem. It is vital to spend sufficient time understanding the problem and gauge if that is the right problem to be solved. If we solve it, will it result in achieving the business goals? How is it doneDiscovery workshops are conducted through customized workshops and a set of activities that fit your needs and schedule.What do we get out of itA common definition of project goals, success criteria, target users, and their journey of interaction with your products or services A short document detailing the workshop findings and possible next steps for engagement Often these workshops result in a defined scope for the project and can be followed up with a proposal for engagement Designed forSmall-medium size organizations Small groups of key decision-makers Developing new products and services Kickstarting and setting the scope for a large engagement Aligning stakeholders Creating alignment around the problem trying to be solved Typical durationA few hours to a full day (depending on the complexity of the problem)Ideation WorkshopIf you have already understood the problem and defined the success criteria of the project, it never hurts to have a second opinion on the approach to solve it. Ideation jams with customers can be a fun way to creatively solve the problems at hand.An Ideation Workshop is a collaborative and rapid idea generation session intended to create as many ideas as possible to address the challenges at hand by empowering participants to think creatively.Who should attendStakeholders Business System Analysts Product Managers Designers Solution/Tech Architects Why should we do itCo-creationIdeation workshops help bring a diverse range of insights and minds to generate as many ideas as possible. Fresh IdeasInspiration is taken from solutions in the same problem space and adjacent areas to spark creativity. Subject matter experts and those from your organization are invited for TED-style keynotes, which bring everyone up to speed and provoke the thought process in that direction. To explore ideas and make informed decisionsIdeas are not only proposed by participants, but they are also evaluated by them in order to narrow down on the most impactful solutions. How is it doneIdeation workshops comprise a disciplined framework that uses the best practices of ideation and innovation by providing time for individual brainstorming, building on top of ideas, connecting dots — then intelligently voting to shortlist the best ideas to move forward with.What do we get out of itUnderstanding and exploration of the problem space Explore multiple solutions to address the challenge Established set of ideas that can be explored and refined to find solutions Set of experiments that can be conducted as next steps Designed forThose looking for an outside-in view or second opinion on solving technology product, people, or process challenges Solving problems that demand creative and critical thinking Problems that are easy to lose focus on Establishing common ground amongst stakeholders Typical durationA few hours to a full day (depending on the complexity of the problem)Future WorkshopsDesigned to explore the “art of the possible,” Future Workshops help align key stakeholders around the future vision of the company by taking a wide view of what’s already established in the market and what are the trends.Working our way back, this vision is then translated into a high-level roadmap, for the present, for what’s next, and for the future.Who should attendC-Level or Decision Makers Key Management Business and Sales leads (VPs) Why should we do itUncover & DiscoverAssessing the current issues of customers and the business, future workshops aim to uncover problems, pain points and needs from both sides and create a shared vision of the future for your organization. Alignment & Buy-InSuch design thinking workshops help align all stakeholders’ understanding of the vision and garner buy-in. Ideate, Evaluate & EnvisionThey help generate solution ideas according to the timeline, evaluating them based on feasibility and user and business values for establishing a product roadmap. How is it doneCollaboration is the vehicle that sparks the discussion on design ideation for user experience to the table through activities and diverse team effort.What do we get out of itA shared vision of the future and what’s possible A detailed description of the short, mid, and long-term goals to get to the future vision A document detailing all the workshop findings and the next possible steps for exploration Designed forOrganizations/functional units interested in a long term roadmap and strategy for transforming business Exploring what major trends are in the market, what has worked so far in the industry and what hasn’t Determining what the ideal future looks like and what is the first steps to get there Planning to add new features or functionalities on an existing product(s) Typical duration2 to 4 hoursDesign SprintThis engagement takes you through the complete design cycle from problem defining and framing, solution brainstorming, solution defining and visualizing, solution viewing and visualizing of concept-solution in a rapid sprint spread over a week or two.Who should attendDesigners Developers Product Owner VP of Product Actual users (if possible) Why should we do itDay 1: To UnderstandMap out the problem space and create a shared vision. Day 2: To Ideate/sketchGenerate a broad range of ideas and narrow down on possible solutions. Day 3: To DecideDetermine what to prototype to answer sprint questions. Day 4: To PrototypeBuild one to two prototypes required to validate the idea. Day 5: To Validate or deliver the finalized solution (e.g. artifacts) and relevant documentsTest with five target users or review with the client to get valuable feedback. Deliver the finalized solutions, including a concept brief, prototype, and a process document. Design Sprints are aimed at understanding the context, validating ideas and releasing an MVP quickly in the market. These workshops also cater to helping everyone on the team understand the value other team members can bring as well as the struggles they face.How is it doneWe take you through joint daily sessions (outlined above) to move from the problem to the solution stage; providing direction, review, feedback, and ideation along the wayWhat do we get out of itAbstract to Concrete: Turning abstract concepts and ideas into tangible prototypes (digital or physical experience) with user feedback Business goals and objectives Personas & Journeys: User personas and journeys documenting pain points, challenges, and opportunities for improvement Wireframes and mockups for digital experience Development/Implementation estimates with a +/- 50% confidence Designed forStartups Small business or a smaller team Client or business who a relatively simple problem Client or business who has a clear direction for the solution Client or business that needs to test and validate ideas for MVP quickly Typical duration1 to 3-week engagementShape It UpShape It Up is a complete end-to-end engagement that takes you through the entire design cycle, from discovery to user experience design, technical solution design and hand-over to development.This engagement allows us to work with product owners and business heads throughout the entire cycle leading you along the way and ensuring any outcome is aligned with your business goals and meets user needs.Who should attendEveryone who is related to the project, affected by issues or outcomes, and diverse teams are encouraged to participate:Designers Developers Business Analysts C-level executives Management, Product management Sales, customer services Even real users Why should we do itThis is the most comprehensive engagement and is highly effective in producing the best solutions based on defining the right problem, understanding the customer and business needs, as well as other realistic factors that need to be considered before making a huge investment. Understanding that stakeholders at your organization manage multiple projects at any given time and it may not be feasible to bring everyone together for a dedicated design sprint in a short time frame, this engagement adopts a mixed model approach. It consists of a few workshops and deep-dive sessions with relevant stakeholders. This vision is then translated into a solution that is reasonably “shaped up,” and development teams can be engaged for implementation and rapid rollout. How is it doneShape It Up workshops and regular joint working sessions to assess, gather, and frame the right problem and solution collaboratively as well as deliver the concept, MVP and a product roadmap along with a technology solution documentation.What do we get out of itProject documentation containing the process, findings, research, concept designs, and technical development Personas, experience and journey maps, mockups and interactive prototypes Solution system architecture, a product roadmap, other technical documents that are required for product development and management Designed forBusiness at any scale A complex solution that requires customer interfaces, middleware or backend systems integrations B2B, B2C, B2B2C solutions or products Typical duration1 to 2 months (depending on the complexity of the problem)Remote WorkshopsRemote workshops are meant for dispersed teams located in remote locations and time zones. For stakeholders and team members in such situations, there are several frameworks for remote collaboration that can be used. These help facilitate remote design workshops using virtual tools that provide a great deal of value, but at the same time are not bound by physical or geographical limitations.You’ll find a deeper understanding of remote workshops in this article, which will provide you with all you need to know to conduct them, what virtual tools and processes you’ll need, and how to make the most out of remote workshops while working from home.TakeawayWhile design thinking workshops can prove to be largely impactful for alignment, they’re not the end-all solution.The real value from design thinking workshops is in their implementation and facilitation. Without applying the frameworks of these design thinking workshops in their true sense, you would simply end up having just another “meeting” — wasting time, energy, and resources.To successfully experience a workshop, there needs to be a willingness to participate, the effort to prepare, and the dedication to follow through with the outcomes.The design thinking workshops we covered in this article are designed to take you from the abstract to the concrete. Within a few hours, instead of taking weeks to materialize ideas in traditional ways of working, these workshops will help facilitate your team to ideate design thinking and draw focus on the present, bringing to light important information, ideas, and actionable next steps. This is the “concrete” foundation that will serve as the stepping stone to move out of the problem and into the solution space.FAQsWhat is the design process in UX?The process of design ideation for user experience comprises multiple, distinct steps that include user research, testing, validation, implementation, etc.What is human centered design thinking?Human-centered design thinking accounts for the humanistic approach to design via a deep sense of empathy for the target users. It uses the everyday emotions, thoughts, and behaviours of the people using the design as the North Star to creatively approach situations and find the best solutions to the problem at hand.What are the steps of the design thinking process?The design thinking process is an end-to-end journey that covers every step from ideation to implementation. It covers problem identification, UX research, design ideation, solutioning, prototyping, testing, and improving iteratively.What does design thinking work for?Design thinking is used to identify and solve problems creatively and iteratively. The approach prioritizes the end users’ need, above everything else, by observing their interactions, everyday behaviours, thoughts, and emotions to truly empathize and innovate for the best solutions.Meta description:In a jump from traditional ways of working, design thinking workshops offer a creative way to build solutions. But which is the right one for you? Find out here.
Design Thinking Workshops: Choosing the Right One For Your Team

How much time do you dedicate to your UX research process?When it comes to approaching any project, there’s no doubt that UX and Product Designers are fully aware of how critical it is to conduct research in order to put the user experience at the forefront.But the issue arises when clients or other stakeholders in the project are not on the same page.One of the first things stakeholders will do when a project comes in is to propose an idea and a solution, and concisely put it as, “Our mandate is X”. When this happens, the rest of the team is expected to focus all their attention towards the proposed solution, rather than actually spending time to fully understand the problem at hand. At this stage, instead of assuming they know what the user wants because they themselves are the user, it’s more crucial to ask questions like:Why are we doing this?What is the root problem?The design process we follow may be unclear to the client, but as UX and Product Designers, there are certain things we can do to share our knowledge and perspective with others so they can better understand the value of UX research to be done at the beginning of a project.The Consequences of Insufficient UX ResearchInsufficient UX research is where the quality of a project is compromised.No matter how much time you spend on creating great visuals, if your users are going to struggle with using your designs, instead of solving your users’ problems, you’re going to end up creating new ones:Increasing the learning curve for usersIgnoring the user experience research means you're making no effort to truly understand your users or even the scope of work. Without proper UX research, it’s difficult to familiarize yourself with what your target audience struggles with. You're more likely to end up increasing the learning curve for your users and driving them away.Losing key insights from early adoptersA lack of UX design research can impair the ability to find early adopters. Early adopters are a vital part of the project as they can lend a lot of critical insights about the usability of a feature and provide you with an accurate picture of the pain points — and gain points — of your target customer.Difficulty in identifying opportunityAnother element most clients/stakeholders don’t take into consideration when allocating time and resources to UX research is that of opportunity. Identifying and evaluating your competitors helps UX teams understand what already exists in the market and where there is space for improvement and innovation. Without such competitor insights, you could risk losing out on opportunities to enhance your business strategy and have an edge in the market.The Value of Investing in the UX Research ProcessThe UX research process can include both quantitative and qualitative UX research methods that can take up several forms, like:Card sorting, Focus groups, Interviews, Competitive analysis, etc. These are all useful UX research tools that help shape the strategy and define the goal(s) of a project. Having the correct data accessible to the team will pave the way for making solid decisions and ensuring you are focused on the appropriate users for your design.Without this user experience research, your team is in danger of leaping to assumptions instead of solving actual problems for the target users. You could also be putting yourself at risk of scope creep when discoveries arise later down the road.Knowing all the benefits of investing in UX design research, stakeholders may still lack the design maturity needed to carve out the required time and resources for the UX research process. This is where you should start thinking about controlling the risks.Risk Control With Limited Resources For UX ResearchAll too often, UX research gets sacrificed due to time or budget.That being said, if you find yourself in such a situation, there are certain methods you can employ to mitigate the risks that come with not allocating enough resources for user experience research:Using available dataTake whatever data you do have available. Analyze what you have and make your best guesses.Post-launch plan to track metricsIf you can’t validate your hypotheses now, build a post-launch plan so you can test and track metrics.Creating proto-personasBuild proto-personas based on your best guesses to get a shared understanding of what you do know about your users. It will help identify critical tasks and create a focused project scope.Mini-interviews with small groupsConduct mini-interviews on the down low, if possible. This is an informal method to test ideas and could be done within 10 minutes among a small group of users (around 10 people).While these methods may have some drawbacks, they’re still quite helpful in terms of providing a fair amount of guidance for your project if you’re in a pinch.Educating Clients and Stakeholders on the Value of UX ResearchFor many organizations, there might be a lot of difficulty in trying to change or update their process. At the same time, there might be others who believe they're already operating well. Some might even prefer sticking to the practices they're accustomed to, relying on analytics tools to retrieve data.Whichever kind of situation you’re in, there’s no doubt that any kind of change will be faced with some degree of concern and resistance. But, whether as a UX or product designer, you can go the extra mile to demonstrate to your client or stakeholder how research is an integral part of the process – one which serves as a means to understand the users’ problems and goals.UX research also helps define the scope of work so that teams are able to plan their MVP and the proceeding phases. Cutting UX research tools and techniques out of the project can have a detrimental impact on the quality of the final product.Investing in user experience research equips you better to validate your hypotheses and ideas so you may better understand your users’ needs.TakeawayIt’s essential to convey to stakeholders how assumptions about the users are causing more harm than good to their overall UX design process. The current bias found in most organizations needs to be put aside: business goals are NOT the same as user goals, and managers, project owners, and designers are NOT the end users. The end users are the people outside of your organization who will use the product - your actual customers.So what you need to ask yourself is: Are you building the right product for your user?Without knowing who your user is, you will fail to answer this question. Without knowing what works and what doesn’t, you’ll fail to build the right product.Fortunately, user experience research is a solution that gives us not statistics but valuable and vital insights that will prevent you from compromising on the quality of your product.And while you won't see this shift to more investment into UX research happening overnight, leading the discussion on the benefits of UX research can surely be a starting point for any project.FAQsWhat is the role of a UX researcher?A UX researcher's role is to study and find key insights about target users, like user behaviours, wants and needs, challenges, and motivations. Using both quantitative and qualitative UX research methods, a UX researcher will thoroughly research what users expect from products, services, applications, and websites and convey these insights to UX designers so they can design experiences that are more user-friendly.Why is UX research important?UX research is an integral part of the UX design process as it helps give a direction to your strategy as well as better define the goal(s) of a project that is more aligned with the users' wants and expectations. UX design research is a way to ensure that your designs aren't just based on your assumptions about what the user wants but accurate insights about what the users' actual problems and goals are.What does the UX research process include?The UX research process includes both quantitative and qualitative UX methods and various UX research tools to study the users and be able to extract the required insights about their behaviours, wants, needs, challenges, and expectations.What is the value of UX research?The value of UX research to the overall UX design process is most significant when it comes to addressing vital questions about the project, like what the goals are, what is the true challenge for users that we are trying to solve, and what users expect from the solution, etc. User experience research helps UX teams design solutions that are well-aligned with the actual situation of the end user rather than simply relying on assumptions about the users.
Why Ignoring User Experience Research is a Mistake

Is the MVP approach becoming irrelevant? The Minimum Viable Product approach (or MVP approach) for launching and scaling products has long been used by companies. But these days, you’ll see more MVPs failing to deliver on their promise.And that happens because the core focus is still on the minimum viable PRODUCT and not the minimum viable EXPERIENCE of the customer or user.That’s not to discredit the benefits of building an MVP lean product. The approach still:Is the quickest way to get feedback on your product idea and iterate to scale Helps minimize the risk of effort when compared to a product with all the intended features Aims to maximize the feedback from the customers with the LEAST effort. So what’s wrong with it?Why is the Minimum Viable Product NOT Viable Anymore?The usual approach for most companies is to work backward from their grand product vision by delivering a major part of the desired product. However, this minimum viable product approach doesn’t work anymore and is becoming irrelevant due to several factors:Saturated Competition in Most MarketsWhether it is the food delivery space or the ride-hailing market, competition is tough. Customers are more willing — and quicker — to switch for a better feature or customer experience. A great example of this is how a new player in the ride-hailing market called ‘InDriver’ has been able to capture the majority share by offering users the ability to negotiate a fare with the driver. Competitors like this make it tough for companies to stand out from the crowd and acquire customers.Customers’ Patience is DiminishingFor digital products, it is much easier to build and get your product in the hands of customers as the distribution costs are extremely low and acquiring customers is easy. However, the problem with this approach is that you can also lose customers just as fast. Customers these days are switching to faster and better competition for a better user experience than they currently have.Preference for Experience Over FeaturesIt is getting trickier to succeed with the minimum viable product approach as customers are less willing to stick around for just the functionalities and features of a product alone — and that is all the MVP focuses on. The MVP approach revolves around building a great product with the least features, but to make MVPs succeed, a lot more is needed to be packaged with the product to make customers stay, like complete customer journey mapping for one of the features being used, or a full-blown product catalog. MVPs generally succeed when they have an engaged user base that is willing to live with a satisfactory user experience and missing features in order to have a clear roadmap of improvement and feature launches that they want from your MVP.Failure to Build Desirable Brand ExperiencesThe minimum viable product approach is also failing these days as most MVPs that are being pushed into the market generally have a degraded brand experience. Tech companies, for example, focus on putting out innovative features faster so they can keep their targeted user base of early adopters engaged. In doing so, they often fail in acquiring early and late majority users because they fall short in building a desirable brand experience around their products, since their core focus is always on shipping the features.Enter: The Minimum Viable Experience (MVE)Where the MVP fails to account for the user experience, building a Minimum Viable Experience comes in.The MVE approach focuses on the whole customer experience. At its core, MVE looks at the experience of your users/customers, either with a replacement or with an existing product. It asks the very important question of “what is the minimum experience we can deliver that will still satisfy our customers?”Creating a minimum viable experience revolves around an end-to-end experience that resonates with the customer. It is akin to a full-stack effort: all elements like brand position, marketing, and design experience are in place to give early customers a great reason to try the product and get excited about it.The following chart explains the key elements of creating a successful Minimum Viable Experience, capturing the augmented emotional value as the experience matures:Minimum Viable Product Vs Minimum Viable ExperienceIn the minimum viable product approach, the product is launched faster and iterations are super fast as well.But customers want products that specifically fulfill their personalized needs — and this is the driving factor when engaging with early adopters, who will essentially convert into influencers for your brand. That’s why the Minimum Viable Experience vs traditional MVP argument is gaining so much traction these days.It’s not like product managers following the MVP approach don’t try to address all possible customer touchpoints. The problem is that all these touchpoints typically reside within the product. Therefore, the experience that a user gains from the product is limited to only one channel: the product, which itself is already at its minimum viability. However, this may not prove enough to satisfy the unique needs of modern users, which will ultimately impact the experience they derive from the product.To acquire early adopters and offer an experience that transforms them into advocates, these touchpoints need to extend beyond the main channel (or product). For example, leveraging social media channels, apps, helpdesks, and so forth to address a user’s product queries is a more effective way to address their need than a silo of information within the product.This is where the MVE approach proves most effective. It can not only meet user needs, but also help to capture useful metrics, analytics, behavior, and use it to keep evaluating the product and improving MVE.MVE In ActionIf we take a look at recent successful start-ups, one thing a lot of them will have in common is a core focus on the customer experience. A significant instance of this can be seen in the fintech space, where new companies are focusing on building a great customer experience around handling money by introducing convenient features that customers have been looking for all this time.The international money transfer app, Wise, which has a target market for freelancers earning foreign currency or remote workers, is a good minimum viable experience vs minimum viable product example. Customers can avail special exchange rates and minimal transaction fees as well as the ability to have an official account number or routing number in any country they want. This kind of experience has helped Wise quickly rise to the top of the international money transfer app market because it focused on the core needs of its target market and on offering a good customer experience around that.Their winning strategy? A deep focus on building the experience around essential money transfer features; instead of shipping the most features required for a money transfer app, they focused on creating a USP by doing the essential features in the best way.TakeawayIn the age of digital startups, if you lose focus from your customers and fail to understand their preferences and expectations from digital experiences, this article should be enough to show you how you’re missing out by not giving them the seamless user experience they wish to see.Fortunately, the MVE approach serves as a tool that you can use to understand your customers better and focus on building features that matter most to the customers, and the successful companies of today are doing just that.Amongst the biggest companies that have adopted and succeeded with the MVE approach is Apple, which is well-known for introducing features quite later than the competition but always providing augmented value to their customers solely through user experience.Have you tried building products using the MVE approach yet? If not, now’s a better time than any to get started because your customers will continue to put the user experience above the actual functionality of the product.Get in touch today to learn more about building the perfect MVE.Frequently Asked QuestionsWhat is the purpose of a minimum viable product?A product built around the MVP approach is intended to validate the product idea and attract early adopters very early in the product life cycle.What is MVP in product management?MVPs are designed with enough features and functionality to attract users before launching the full-scale product, offering a better idea of product success early on.What is a good minimum viable product example?Jeff Bezos initially founded Amazon as an online bookstore, which helped to validate the e-commerce purpose before it began transforming into the e-commerce giant it is today.Why do MVPs fail?Sub-par UX, ineffective pricing, addressing the wrong problem, and the presence of competing products can lead to MVP failure.What is an MVE?The MVE approach prioritizes user experience over functionality, aiming to create advocates among early adopters.Is MVP, MVE, or MAP the best approach?MVP, MVE, and MAP (Minimum Awesome Product) are all lean development approaches. MVP places a greater emphasis on features, while MVE gives more weight to user experience. MAP borrows elements from both MVP and MVE to create products that customers will refer to as “awesome”.
Is the Minimum Viable Product Irrelevant?

Would you be surprised to find that product companies lose over HALF of their users (52% to be exact, according to one study) during the first 90 days of their digital onboarding?While that is an alarmingly large number, I wasn’t surprised.That’s because I (and many others who design products) know this is often purely the result of poor digital onboarding, customer engagement, and support experience.And that begs the question…Why Is User Onboarding the Most Important Part of the Customer Journey?Digital onboarding, or user onboarding, is when your customers interact with your product or service and become more proficient in using it. This digital customer onboarding process is where users begin to familiarize themselves with your product, gauge whether or not it's easy to use, and decide if they want to adopt or abandon it. Product documentation can, quite literally, make or break this part of the customer journey.Each year, product teams spend millions of hours building new features that are never adopted by the majority of users, hence leading to very poor user adoption rates.Each year, support and success teams also spend thousands of hours creating product documentation that no one reads.In this article, you will learn how to create user-centric product training and support documentation in five steps using our learnings from Design Thinking so that you can help onboard new and support existing users efficiently.Challenges When Creating Effective Documentation for Digital OnboardingIn most companies, oftentimes teams will wait for the finalization of the features, screens, user journey, and the product itself before they begin the documentation work.There are several challenges when using this waterfall approach, such as:Delays in the readiness of the product training and support documentation. Greater risk of lack of due diligence from the team before creating the product training and support documentation Overlooking last-minute changes in the product training documentation, with the usually large volume of work pending the final stages. Greater risk of duplicated or redundant information as teams may not be in-sync so late in the process. Increased difficulty in tracking/communicating information scattered and buried across various tools (confluence, JIRA stories, release notes, Slack/Teams, etc.). Long-form documentation is harder to retain and not very effective for onboarding and supporting busy end-users. Information retention decreases with larger volumes. With an average attention span of less than 8 seconds, users retain information better when delivered in bite-sized chunks and through more engaging formats. Creating documentation that is ineffective. As a result of skipping the pre-work step, the documentation may not meet or support the requirements of the end-users. In certain cases, the product and support teams may end up creating documentation that delivers poor customer adoption rates because of a reduced focus on the user’s requirements. This can impair product performance, uptake, and ultimately, the success of new rollouts. Our 5-Step Process of Creating Training and Support Documentation for Digital OnboardingMany teams consider the training documentation to be separate from the product, which, based on my experience, is the first mistake they make.Just as digital onboarding is not isolated from the user experience, product documentation cannot be treated in isolation from your product.Product Training Documentation, or Product Documentation (as it should be properly addressed) is, and should always be, considered a key part and feature of the product.Just like any other feature, product documentation has an important role to play in the overall Product Mission, Strategy, and Goals. Therefore, any product documentation should always:Be developed keeping the needs of the end users in mind Have its own KPIs and metrics to measure its success and adapt as needed using data-driven decisions Follow all the stages of product development (see Figure 1).Figure 1. 5-step process to creating successful product training and support documentation.In the next few sections, we will cover all these stages in the context of developing product (training and support) documentation to support better user onboarding outcomes.DiscoverIn his famous book, INSPIRED, Marty Cagan talks about the four big risks in product development:Value risk Usability risk Feasibility risk Business viability risk The first step to building successful products is all about minimizing these risks. And creating training and support documentation that delivers more efficient digital onboarding is no different.In order to do that, it is imperative to first understand the problem your product is solving (the what) and for whom. The how is what you intend to create as an end result. We take a top-down approach to achieve that end result (see Figure 2).Figure 2. Product Documentation, like any other feature, has a part to play in the overall Product Mission, Strategy, and Goals and should be prepared in alignment with the overall Product Strategy.By aligning your approach with the product strategy, the documentation you end up creating can play its part in helping you achieve your product goals.Take, for example, PackageX, which solves the last yard delivery problem with the goal of making the mailroom operations more efficient. One of the key KPIs, when I was managing the product, was to reduce the end-to-end time it took for a mailroom supervisor to process mail. With this in mind, we spent most of our efforts training the users on more efficient workflows rather than simpler/more intuitive workflows to achieve the same result.In essence, along with the specific documentation KPIs, the product goals should remain the north stars throughout the digital customer onboarding process.Identifying What to Include in Product TrainingUnderstanding your target users is the most important consideration you have to make during this step. Most of the steps you’d need to take here are the same as in a standard user research exercise for a product (and you can definitely reuse some of the existing information already available from the product discovery stage). But you might want to extend the scope of your target audience to both internal and external stakeholders.While the main users of your product are often limited to the ones who are interfacing with the product on a day-to-day basis, the product documentation caters to a more diverse audience.In the case of most B2B products, it has a key role to play during the purchase cycle to help the key stakeholders make the buying decision in comparison to other available options.On the other hand, it also caters to the needs of the internal team to consult as needed during the team onboarding and query resolution process.Understanding the training needs of all the different stakeholders at each step of the training journey allows you to get a holistic view of the requirements that should feed into your plan (see Figure 3).Figure 3. Training Journey Needs Matrix captures the training needs of all the product stakeholders (both internal and external) along their digital onboarding and usage journey.Design and SolutioningIn light of the needs of all the stakeholders captured above, at this step we move forward to find the solution to solve for success. Designing the training and support experience for a product is often constrained by a number of factors and will vary from product to product. There is no one-size-fits-all solution in this case.For example, if you feel that your product’s features can easily be copied by your competitors, you often don’t want to make your training guides public to everyone. In such cases, the entire digital onboarding and training experience is usually designed for in-person interactions with your user (e.g. on-call or in-person demos) or accessible only through a secure login (e.g. a private knowledgebase).Combining the needs with the constraints at each stage of the training journey will help you design an experience that is valuable for your users, as well as feasible.In this stage, you may also need to define the different formats and mediums of training and tools to be used at each step of the training user journey (see Figure 4) during their digital onboarding. For example, a user looking to purchase a product subscription will have very different needs versus a user who has already been using a product for a year. The training needs can be different at each step, so each step demands its own full attention.Figure 4. Training Formats Canvas builds from the Training Journey Needs Matrix and establishes how each product documentation format will play its part in covering the user needs at each training stage.While it’s very tempting to propose different formats/mediums for each step or need, it can very quickly become unsustainable for your teams to keep all the different formats updated and in sync with the latest product updates.Therefore, finding the right balance between reusability and specialized solutions for each need is absolutely crucial.In the case of multiple formats and mediums, duplication can become a valid concern. However, designing a master content reusability architecture that allows asset sharing between different formats will play a huge role in avoiding duplication of work by your teams. This can further improve the digital onboarding experience for customers.It is also important to choose the right documentation tools to develop and distribute the content to your users at each step of the training journey. The combination of the right tool, the right architectural decisions in content creation, and the right digital onboarding solution will enable you to manage future updates to your content efficiently.Develop and TestHow many times did you have to delay the launch of a feature because the support content was not ready or released a feature with the support content getting pushed separately?Most companies create training documentation for digital onboarding in a traditional waterfall manner, where a feature is developed first by the development teams, and the documentation work begins after that, or very late in the process.This approach is often preferred by teams who fear duplication of work because of changes along the way. But the downside is that it often causes communication slippages, resulting in delays in documentation readiness as too much work is left towards the end.This goes back to the root cause of the product teams not considering training and support documentation as another feature of the product but only as an after-thought.Product documentation should therefore be developed in a truly agile manner, in sync with the product development (see Figure 5). The team preparing the product training documentation (usually the support and success team) should be embedded into all the development teams’ scrum ceremonies to collect first-hand information, starting with the backlog grooming and sprint planning sessions to generate their own documentation and sprint backlog.The day-to-day changes in the sprint plan are captured through a presence in the daily standups and weekly demos to ensure that the final draft of the documentation sprint is in perfect sync with the development release.Figure 5. Agile documentation generation in sync with the development stream.Before initiating mass content development for digital onboarding, it is important to structure the document hierarchy and establish documentation guidelines to follow throughout the process to ensure consistency between different team members.On a broader level, the guidelines for an effective digital onboarding solution should at least cover the following areas:Content templates and structure to follow for each type of format (including sections and components to use, and for what specific purpose) Style guidelines (fonts, colors, etc.) Language and accessibility best practices Naming and versioning conventions Content reuse strategy (often starting from the more comprehensive format to the lesser one) Content archiving plan Role differentiation Glossary - system terms to use Content localization plan Review process Publishing checklists During the development process, in addition to the peer reviews and proofreading stages, I have found usability testing of the documentation to be really helpful. Getting early feedback from the actual users often helps identify blind spots early in the process.Sample Test Scenario 1As a user, you want to learn about X topic. Without using the search option, can you find the relevant section of the documentation?This often helps identify the issues in the documentation hierarchy. If the user ends up taking a lot of time navigating to the right section, then you probably need to reorganize your sections so that it is more intuitive to locate relevant information.Sample Test Scenario 2As a user, you are facing a problem Y and you land on article Z. How long does it take you to find the answer you are looking for?I often frame such questions to test the templates, identify any clutter and improve the signal-to-noise ratio.Other tests include verifying the verbiage and system terms used in the documentation. These tests can be carried out as early as the Design and Solutioning stage.ReleaseAs it always happens in startups launching MVPs, while working with one of my previous teams, we launched a product with very minimal training documentation. The idea was to handhold the initial users until there was enough bandwidth available for that work.However, as many friends with startup experience can relate, when you push an item down the backlog queue, it, more often than not, stays buried under the pile.In our case, it wasn’t until another six months before we were able to publish it for our users. When it was launched, it took us considerable effort to create awareness and promote adoption and ensure the digital onboarding went smoothly.Here are some of my learnings from that experience:Readiness: Ensure that your training documentation is ready from Day 1. After that, it will be very hard to inculcate the self-serve habit in your users if they have been spoonfed too much in the beginning. Visibility: If the training content is hosted on a separate URL, make sure that it has some visibility inside the application as well, e.g. Help icon redirect. Communication: Whenever possible, ensure recurring communications are sent out to new and existing users on all communication channels (push notifications, emails, text, social media, website, etc.) with self-serve links. Reinforcement: The sales and support teams should be trained to reinforce the adoption of the product documentation by pointing the user to relevant resources during their digital onboarding journey instead of sharing answer excerpts directly. Evaluate and IterateAs the famous saying goes, you can only improve what you measure.Like any other product feature, product documentation should have its own KPIs and be evaluated regularly to determine ways to improve its efficacy for digital onboarding.Below are some key metrics that often come built-in with most online tools and can help you evaluate and improve the performance of your product training documentation as well as the product:Adoption and Awareness: No matter how much visibility you ensure for your help content, there will always be users who would say they never knew about it. A bi-annual survey to evaluate the awareness of the product documentation can be useful to gauge where you stand. Engagement: This is primarily dependent on the choice of your formats and tools. Most online knowledgebase tools provide insights into article views, time spent on each article, clicks, videos played, etc. However, better engagement (views) doesn’t necessarily signify better content. It might often be the case that a poorly written article on a very common challenge in the application gets a lot of views but doesn’t help anyone with the resolution. Therefore, it is essential to interpret the engagement metrics in combination with the effectiveness metrics. Effectiveness: To actually understand the effectiveness of a particular content piece, the most reliable metric is often the reduction in support tickets related to that category. You can also collect immediate contextual feedback from the users on each content piece in the form of upvotes or ratings (also supported by most online tools).Moreover, oftentimes the terms used in the help content do not resonate with your users. While the search engine often helps to an extent by extending search results based on synonymous terms, it is entirely possible that the users don’t get the information they are looking for during their digital onboarding, even if it is already there. Even worse, it is also possible that you and your team had a blind spot and overlooked a particular help topic entirely. In such cases, it is helpful to observe the data of search terms coming from your users and evaluate them against the number of responses or the clickthrough rate on the responses.In addition to the quantitative metrics, digital onboarding can further be optimized by getting qualitative feedback from the users every now and then and adapting the content for the digital onboarding process with an aim to improve the above metrics.Moreover, training documentation can also be used as a tool to improve other product KPIs. For example, you can leverage application usage analytics to identify problem areas during digital onboarding, where the users are getting stuck, or where the users need more help and use the training documentation to overcome these issues by creating more awareness about them.In the same manner, the analytics from the training documentation and digital onboarding process can also feed back into the product. For example, if there is a particular article or section of the help documentation that is getting high engagement, maybe it’s time to relook at the UX or the journey in the application itself.The feedback and evaluation from this stage should feed into the documentation stream backlog and be used in retrospective and planning sessions to update the content strategy, the writing procedures, and, of course, the content itself for smoother digital onboarding.TakeawayFor any new product or feature you launch, digital onboarding will undoubtedly define how well your customers respond to what you’re offering. As we discussed above, product training plays a critical role in ensuring that this digital onboarding journey of the user is efficient and boosts the customer adoption rate rather than leading to abandonment.Let’s summarize the five steps we used to create user-centric product training documentation in an agile manner:Discover Design and solutioning Develop and Test Release Evaluate Our approach borrows from design thinking concepts to create this documentation, keeping all types of users in consideration and user understanding and adoption as the focal point during the whole process. The best kind of product training documentation for digital onboarding is that which addresses the users directly using your product as well as those who are looking for your product, so it’s vital to approach documentation with this lens, understanding the different needs of your users.The next time your team gets into product development, instead of overlooking the digital onboarding and training experience and following traditional methods of documentation that won’t help users understand your product, use our agile five-step approach instead to engage with customers.
User-centric Training Documentation For Effective Digital Onboarding

Whenever you’re tasked with a new project, what’s the first thing you do?Surely, whether you’re a UX designer, a manager, or a stakeholder in the project, your first step would almost always comprise the ideation phase.But while most companies will follow through with the ideation process, there’s one very important step they’ll often skip – and in my opinion, it’s definitely NOT something to miss out on if you want to get a clear direction for the project right at the beginning.I’m talking about storyboarding for user experience design, and in this article, you’ll learn exactly what a UX storyboard is, how to build one, and why it is essential to create a logical story that has:a strong plot a structured narrative a focus on the main goal you’re trying to achieve What is Storyboarding in UX Design?A storyboard is a powerful visual communications tool to improve user stories by making them more authentic, emotional, simple, and clear. The underlying philosophy being that visual representations offer a far easier way to see elements making up the “big picture” than a text-based document.First used in the early 1930s by filmmakers and animators at Walt Disney, a visual storyboard served as a means to graphically represent scenarios that contain a sequence of a few events. IN UX design, storyboards are therefore a natural fit when it comes to representations of user interfaces, user events, new features, etc.One of the first storyboards used by Walt Disney in the 1930sSource: Disneyparks.disney.go.comStorytelling and Storyboarding in UX DesignA UX storyboard helps strengthen your research phase by exploring and visually predicting the user experience and interaction with a product over time, giving designers a clear sense of the user’s priorities and goals even before the product or service is launched.Storyboarding is a quick way to demonstrate how someone might interact with a future service or product. Through visual storytelling, you can easily set the ground for the whole team to come together and quickly grasp the essential aspects of the project – like the target audience, the occasion, and the goal.A storyboard starts off with a simple rough sketch and ideally includes not more than four to six scenes to show the story – that’s what makes it so easy to work with and what makes it important to carry out right in the early stages of the ideation phase so that the entire team can get a direction for the project from the very beginning.Besides having a strong visual presence that boosts engagement within the team and helps store information in the brain long term through visual elements, storyboarding in UX design also breeds an emotional connect and appeal. This equips team members better to put themselves in their target audience’s shoes and visualize the user experience.It’s important to note here that storytelling and storyboarding in UX design is not the same as mapping out user journeys:What is the difference between user journey and storyboards?The most important distinction between a user journey and a UX storyboard lies in their content; while storyboarding in UX design comprises visual representations of the main events of a scenario, user journeys are far more detailed and contain complex, textual information about the process that your customer will be going through in order to achieve a goal.To understand this distinction more simply, look at a UX storyboard as a tool that captures a fragment of the entire user journey.A UX storyboard is, most of the time, a rough, informal illustration to set the context of the project by providing a scenario (story) visually so that the whole team can get the right direction of the project from the get-go before getting into action.A user journey, on the other hand, doesn’t just draw on high-level emotions or ideas of one particular situation but, in fact, extensively details the insights from various stages of the user’s journey of experiencing the product/ service till the time they achieve their goal with it.When and Why You Would Need To Use Storyboarding in UX DesignStoryboarding in design thinking is done early in the design process, typically during the ideation or discovery phase. The main reason for early storyboarding is to gather insights from the team and see if everyone is striving towards the same goal while ensuring that the user needs are being considered explicitly. Storyboarding in UX design, in turn, creates a way for teams to collaborate and find new solutions for users by staying aligned on a shared thinking and vision about the user experience.That answers WHEN storyboarding should take place, but what about WHY it’s even needed?Here are some of the biggest reasons why storyboarding in UX design can be the most vital step in your ideation process:Human-centered Design ApproachWhile storyboarding in UX design, the people are central to the design process. Stories put a human face to user data, analytics, and research findings.User FlowDesigners always think about their users and put themselves in their shoes to see how users interact with the product. This approach enables the designers to fully understand any existing interaction scenarios as well as test predictions about potential new ones.‘Pitch and Critique’ MethodSince storyboarding in UX design is a collaborative effort, it provides everyone a chance to contribute to the activity. This results in a clearer picture of what should be developed and promoted as new design concepts. Each scene of the UX storyboard should be analyzed to allow team players to leave their reviews and create insights.Iterative ApproachStoryboarding is heavily reliant on an iterative approach; sketching out a UX storyboard helps designers experiment with a variety of things with very little or no cost at all when it comes to testing multiple design ideas simultaneously. Since these sketches are so quick and rough, nobody gets too attached or connected to the ideas that are generated.How Do You Create A UX Storyboard?While it’s mostly an informal activity, you can still structure your storyboard in a way that helps you and your team fully reap its benefits.Structure of a StoryboardBefore you start directing your storyboard, you will need to ensure that you understand all the basics of the story.Understanding the story in its entirety and then breaking it up into pieces can help you approach it in the best and most convincing way possible. For a story to be considered well-structured, it should have a comprehensive beginning, middle, and ending, in addition to the main elements that every storyboard must comprise.A UX Design Storyboard illustrated in 4 scenes to showcase each stepMain elements of a UX storyboardThe CharacterYour character – or the persona – is the central figure or hero of your story. Everything associated with your persona is very crucial, for example, behavior, feelings, expectations, and decisions made by the focal person. It is also essential to reveal the mindset of your character completely in order to illustrate the situation best. Address questions like:What is the problem faced by the main person? How is the problem resolved? What are the needs/wants of the main character? What are the goals/clear outcomes to be achieved from the whole scenario? The SceneYou will need to have a realistic, recognizable, and relevant environment for your persona to live and thrive in this scenario. The scene is the space that the character finds himself or herself in.The Plot and NarrativeThe plot needs to be highly convincing, simplistic, and realistic in nature. The narration of the story must be focused on the goal of the character in the plot.Your plot should start with an event and end with a benefit or a solution to the problem that the persona will be facing in the scenario There must be a clear conclusion to the persona’s journey so that lessons are learned and assimilated by the project team.To structure your plot better, you can use Freytag’s Pyramid, which shows the following five acts:Exposition Rising Action Climax Falling Action (or final suspense and resolution) and Denouement (Conclusion) Freytag’s Pyramid TemplateFreytag’s Pyramid Template indicating all steps in beginning, middle, and end stagesTakeawayIn this entire article, we discussed what a UX storyboard is, when you would need a visual storyboard, how storytelling and storyboarding in UX design are carried out, and why storyboarding is needed.To sum up this entire lesson on storyboarding in UX design, here are some key takeaways to keep in mind before you get into your next project:A UX storyboard assists in getting a good understanding of the people you’re designing for. One cannot understand good design if they do not understand people. Storyboarding in UX design is an outstanding visual tool for designers to bring conceptual ideas to life before they start ideating with their team. Designers put themselves in the user’s shoes, visualize their product journey, and address the pain points through visual communications tools such as a UX storyboard.
Storyboarding in UX Design: Learning the What, When, Why, and How

The Quick Starter Guide to GraphQLNeed a better query language for APIs? If you're a developer or a professional associated with the field, chances are you've heard of the term "API".And while it’s one of the most frequently used words in the world of development these days, most individuals, despite coming across it or using it, won’t be familiar with exactly what an API is.What is an API?API stands for Application Programming Interface. As the name implies, it is an interface via which developers, users, and consumers can interact with data.To understand how an API works, try comparing it to a bartender: You order a drink from the bartender, they locate the right liquor, ice, and other ingredients, and prepare it for you. No big deal about that, right?Building an API hasn't been as difficult as it sounds since the dawn of the contemporary web. However, learning and comprehending APIs, on the other hand, has always been a challenge.Developers form the majority of individuals who will use your API to build something or merely consume data. Therefore, your API should be as simple and straightforward as possible, if you want them to remain feasible.A well-designed API is simple to use and understand. It is also user-friendly, which is something to keep in mind when you get started with creating your API.REST Vs. GraphQL APIsFor a long time, REST has been used to create APIs.But with using REST APIs – and the reason that has ignited the REST vs. GraphQL APIs comparisons – comes the slew of issues that come with it.While using the REST design to create an API, you’re very likely to run into hurdles like:1) Too many endpoints 2) Information repeatedly being over and under-fetched 3) Increased difficulty for developers to learn and understand your APITo address these issues, Facebook designed GraphQL, which, in my opinion, is the greatest method to design APIs these days.In this article, you'll not only learn what a GraphQL API is and why you should begin learning GraphQL right away, but also how to use GraphQL to develop a well-designed, efficient, and powerful API.What is GraphQL?GraphQL, or "Graph Query Language," is a query language for APIs, as the name implies. It allows the client (frontend) to request data from an API.Since GraphQL is open-source, it has garnered a large community of users and is being adopted quickly by people and businesses.In fact, that's probably why you've heard of it as well – due to the open-source GraphQL APIs. The earlier you learn how GraphQL works, the sooner you'll be able to experience the beauty of practicing it.Getting Started: How GraphQL WorksOur first goal with this GraphQL starter guide is not to teach you how to set up a GraphQL server but to learn how GraphQL works in practice.So for that, we'll use GraphPack, a zero-configuration GraphQL server.To begin our project, we'll make a new folder, which you can name whatever you wish. For the sake of this guide, let's name it "Graphql-server".Type the following into your terminal:mkdir graphql-serverYour system should now have npm or yarn installed. If you’re unfamiliar with these, npm and yarn are package managers for the JavaScript programming language. The default package manager for Node.js is npm.Next, type the following command within your newly created folder:npm init -yor you can use yarn:yarn initNpm will generate a package.json file for you, containing all of the dependencies you installed as well as your commands.Now, we'll install the one and only dependency that we'll be using.Graphpack allows you to quickly set up a GraphQL server with no setup required. Since we're just getting started with GraphQL, this will make it much easier for us to continue learning how GraphQL works without having to worry about server configuration.Install it like this in your console, within your root folder:npm install --save-dev graphpackAfter you've installed Graphpack, browse to the package.json file and add the following code to the scripts section:"scripts": { "start:dev": "graphpack", "start:build": "graphpack build" }We're going to make a folder called src, which will be the sole folder on our entire server.Create a folder called src, and then create only three files within that folder.Make a file called schema.graphql in the src folder, and put the following code into the first file:type Query { hello: String }Our full GraphQL schema will now be stored in this schema.graphql file, and I'll explain what that is later.Create a second file in the src folder now. Create a new file called resolvers.js and paste the following code into it:import { users } from "./db";const resolvers = { Query: { hello: () => "Hello World!" } };export default resolvers;The instructions for converting a GraphQL operation into data will be provided in this resolvers.js file.Finally, make a third file inside your src folder. Name this db.js and paste the following code into the third file:export let users = [ { id: 1, name: "Adil Sikandar", email: "adil@gmail.com", age: 28 }, { id: 2, name: "Shahid ullah khan", email: "shahid@gmail.com", age: 29 } ];Since, in this tutorial, we’re not using a real-world database, this db.js file will simulate a database we can use for the purpose of learning GraphQL.Now our src folder should look like this:src |--db.js |--resolvers.js |--schema.graphqlYou should be able to see this output in your terminal if you run the command npm run start:dev or, if you're using yarn, yarn start:dev.Now, you can access localhost:4000 – this means we're ready to begin creating our first GraphQL queries and mutations, but before jumping into those, let’s quickly address some commonly used terms associated with GraphQL.GraphQL SchemaGraphQL has its own set of languages for writing schemas. The Schema Definition Language is a human-readable schema syntax (SDL). No matter what technology you use, the SDL will remain the same, and you can use it with whatever language or framework you wish.This schema language is quite useful since it makes it very clear what types of APIs will be offered, which you can figure out by simply looking at it.Types: Learning How to Use GraphQLOne of the most vital characteristics of GraphQL is types.Types are unique objects that represent the look and feel of your API. If you're creating a social media app, your API should have types like Posts, Users, Likes, and Groups.There are fields that exist in these types, and each field returns a certain type of data. For example, if we're going to make a User type, we'll need fields for name, email, and age.Type fields can be anything, but they must always return a data type such as Int, Float, String, Boolean, ID, a List of Object Types, or Custom Object Types.Let’s construct our first Type. Open your schema.graphql file and replace the existing type Query with the following:type User { id: ID! name: String! email: String! age: Int }This is where the primary principles in GraphQL will kick in, and you’ll learn about them next.Queries & MutationsThe way you acquire data from the server is through queries.And the method through which you’ll be able to modify data on the server and receive updated data (create, update, delete) is known as mutations.QueriesTo put it another way, queries in GraphQL are the means through which you can obtain data.One of the most appealing qualities of GraphQL queries is that you will only receive the data you require – not more, not less.This has a big impact on our API in terms of avoiding the issue of over-fetching or under-fetching data like what would happen with REST APIs.In GraphQL APIs, we define our first type Query. This is where all of our questions will end up.To begin with this, we'll create a new type called Query in our schema.graphql file.type Query { users: [User!]! }Understanding this is fairly straightforward: the users query returns an array of one or more Users. Because we used the “!”, it will not return null, indicating that it is a non-nullable query, and meaning it should always provide a response.We might, however, retrieve a specific user.To do so, we'll construct a new query called user. Put the following code within the Query type:user(id: ID!): User!type Query { users: [User!]! user(id: ID!): User! }As you can see, we can pass arguments with GraphQL requests. In this scenario, we'll use the ID to search for a specific user.By this point, you might be questioning how GraphQL knows where to acquire the data. This is why we need a resolvers.js file, which instructs GraphQL on how and where to obtain data.To get started with that, open the resolvers.js file and import the db.js file that we just built. Your resolvers.js file should look like the following:import { users } from "./db";const resolvers = { Query: { hello: () => "Hello World!" } };export default resolvers;Now, we’re going to make our first query.import { users } from "./db";const resolvers = { Query: { user: (parent, { id }, context, info) => { return users.find(user => user.id === id); }, users: (parent, args, context, info) => { return users; } } };export default resolvers;To see if the queries are working properly, go to localhost:4000, type in your address, and paste the following code into it:query { users { id name email age } }All of the users should be returned to you.Alternatively, if you wish to return a specific user, type:query { user(id: 1) { id name email age } }MutationsOnce you’ve got a good understanding of GraphQL queries, mutations come as the next step.Mutations are the technique used to edit data on the server and update data back in GraphQL.In GraphQL, we'll make our initial type mutation, and all subsequent alterations will be contained within this type.To begin, open the schema.graphql file and add a new type called mutation:type Mutation { createUser(id: ID!, name: String!, email: String!, age: Int): User! updateUser(id: ID!, name: String, email: String, age: Int): User! deleteUser(id: ID!): User! }Create a new mutation object like this in the resolvers.js file, below the Query object:Mutation: { createUser: (parent, { id, name, email, age }, context, info) => { const newUser = { id, name, email, age };users.push(newUser);return newUser; }, updateUser: (parent, { id, name, email, age }, context, info) => { let newUser = users.find(user => user.id === id);newUser.name = name; newUser.email = email; newUser.age = age;return newUser; }, deleteUser: (parent, { id }, context, info) => { const userIndex = users.findIndex(user => user.id === id);if (userIndex === -1) throw new Error("User not found.");const deletedUsers = users.splice(userIndex, 1);return deletedUsers[0]; } }Our resolvers.js file should now look something like this:import { users } from "./db";const resolvers = { Query: { user: (parent, { id }, context, info) => { return users.find(user => user.id === id); }, users: (parent, args, context, info) => { return users; } }, Mutation: { createUser: (parent, { id, name, email, age }, context, info) => { const newUser = { id, name, email, age };users.push(newUser);return newUser; }, updateUser: (parent, { id, name, email, age }, context, info) => { let newUser = users.find(user => user.id === id);newUser.name = name; newUser.email = email; newUser.age = age;return newUser; }, deleteUser: (parent, { id }, context, info) => { const userIndex = users.findIndex(user => user.id === id);if (userIndex === -1) throw new Error("User not found.");const deletedUsers = users.splice(userIndex, 1);return deletedUsers[0]; } } };export default resolvers;Next we'll see if our mutations are operating properly. Go to localhost:4000 and type in your address, then paste the following code into it:mutation { createUser(id: 3, name: "Adil", email: "adil.sikandar@mobilelive.ca", age: 28) { id name email age } }With that, it should give you a new user. If you wish to experiment with novel mutations, I recommend that you do so! To see if it's still working, try deleting the same user you created.TakeawayAs you’ve probably learned by now, GraphQL is a relatively new yet extremely powerful technology.Exceeding far beyond the traditional REST API model, GraphQL offers the ability to create better and more well-designed APIs, disrupting the existing API economy and changing the game for developers at large.With a landscape as volatile as what we’ve been witnessing with the progress in development and technology, learning GraphQL and how it works is the only way to prepare ourselves for when, eventually, REST APIs are replaced by GraphQL.Meta Description:Building APIs has long been done on REST, but that doesn’t come without its challenges. That’s why we need GraphQL, and here you’ll learn all about the GraphQL API.Excerpt:Developers may have heard of GraphQL, but traditionally, it’s been a long-standing practice to use REST when it comes to building APIs. While REST has been widely used, the pace at which GraphQL is being adopted by people and businesses is telling of the benefits of GraphQL over REST and how this powerful technology solves the biggest shortcomings of traditional API models. In this quick starter guide, you’ll learn how GraphQL works, what is a GraphQL API, and how you can get started with using GraphQL right away.
GraphQL- The Quick Starter Guide

“Hi Kelly! Can we do an early beta launch of our product? Let’s move up the timelines by two weeks and launch it! This way we can call it more Agile too.”Peter, an eager and driven manager with a lot of experience in managing teams of product managers and scrum masters, expected to engage Kelly in a discussion on being more Agile.However, Kelly doesn’t fully agree, neither with the approach nor with terming it as being more “agile”.“Peter, I’m sure you wouldn't want to give your customers a product with incomplete user journeys. We prioritized just these three features for the launch and completing these will be the bare minimum we can achieve from our products. Shipping products with bad experiences will make the LEAST Agile sense.”, Kelly retaliated at Peter's suggestion for reducing timelines.Kelly is a seasoned product manager who, since joining the company four years ago, has expanded her portfolio to be the major contributor to company revenues. Working on this project for the last eight months, she has been trying desperately to upskill the cross-functional team to be more Agile.In theory, this is the same direction that Peter and his organization are moving towards in efforts to increase innovation and experimentation. Peter, with his diverse experience, has successfully delivered multiple programs in both conventional and digital products for the company over the years.But as far as this product launch is concerned, Kelly and Peter are on two very different pages about what Agile practice actually looks like:“Kelly, this is not the Agile thinking the management is trying to preach. You’re talking about the same old waterfall mindset. Agile means, quick, very quick, and in doing so if things get a bit dirty, it shouldn't matter. We already researched the product in depth and now I feel you are not confident about it anymore.”, replied Peter.Kelly argues that the research has established the product need, but if shipped with incomplete information and journeys, they risk running into the first mover disadvantage. Trying to explain this to Peter, she responds that two weeks is not going to make a major difference. “I am not encouraging perfect and flawless products but at the least we should offer complete user journeys to our customers.”By this point, Peter has already lost his patience. “Okay, here’s the deal. I have already promised the management that we will deliver the product earlier than planned. Either you commit to this or I can ask for someone else to deliver it.”, he threatens.This whole situation sums up what the ’Agile Paradox’ looks like, and it’s not just Peter and Kelly who have fallen victim to it – this is exactly the dilemma that many organizations undergoing Agile Transformation face. Organizations, while being deeply focused on Agile processes, roadmaps, strategies and efficiency, tend to ignore the behavioral, softer side of Agile: The People.And while companies think they’re practicing Agile, in reality, they’re far from understanding what Agile actually is, and what it is not.What Agile Is NotIn principle, Agile is NOT the organizational ability to practice, but rather, it is the dire need of organizations to reduce uncertainty pertaining to customer preferences, technological innovations, changing market dynamics, regulatory dissonance, and, most importantly, the organizational ability & skillset to deliver in a less risky environment.To enable organizations to deliver the most certain and viable product, the product is shipped in bits and pieces that are complete in themselves in serving one or more customers’ needs.What Must Businesses do for a Successful Agile Transformation Strategy?Agile shouldn’t just be undertaken as a strategic stint to overcome the ever-increasing costs of product development. It should be taken as an iterative approach where changes in processes are accommodated as you design the culture or the organizations, deriving behaviors that are consistent with agile practices, and defining structures that help with ‘Kaizen’s continuous improvement’ – or in other words, ‘Investing in People’. How do lean-thinking people and Agile teams enable organizational agility?Simply put, organizational agility can be achieved by taking these steps:Breaking down a large problem into smaller ones Then, through ‘Service Design’, identifying the most impactful ones to be solved for the customer Then using ‘System Design’ to identify the most impactful ones for the business Finally, delivering those smaller problems in an iterative manner, and continuously improving the ones already delivered in parallel to the newly identified ones.Agile People Over ProcessesWithout investing in your people, you might be able to somehow implement Agile through process enforcement, but you won’t be practicing it in essence, and hence your Agile transformation strategy would not be sustainable.Understanding that Agile is not just about Agile processes, but in fact it is about Agile people over processes, is the first step in the right direction if your organization is building an agile business strategy. But how do you truly implement and practice the Agile strategy framework within your culture and people?These interconnected soft elements are the very basis for building a truly Agile organization:Autonomy Unsolicited collaboration Strategic alignment Clarity in roles and communication TrustAutonomyThe core focus of an Agile strategy framework should be on giving autonomy to your people.Your Agile adoption strategy can only be successful when smaller connected groups of people at the execution level of the organization are able to take decisions with just the right amount of strategic guidance. This includes all decisions pertaining to product design, research and development. So, while the managers still play the lead role, this role is principally to provide directions and guidelines and to check the work of the people – the executioners – by shifting accountability on them.Hence, in a truly Agile set-up, the decision-making would be based on the expertise of the people, and regardless of the strategic ambition of your Agile work processes, this autonomy has to be given, in one way or another, to the people who are actually executing the job.Unsolicited CollaborationMany organizations that have successfully created guilds, tribes, and squads in efforts to enrich their culture with a more “collaborative” spirit are actually failing at sustaining these formal and informal groups.The reason behind this is the lack of an environment to facilitate purpose-driven collaboration with autonomy in the hands of the people doing the work. Most of these organizations will create forums where people are tasked with sharing the same functional expertise at least once a month, but most of the time this doesn’t work unless there is a major push from the leaders.If these collaboration forums, instead, become the center of cross-functional or functional value-addition, they’re much more likely to sustain and perform without a formal process dictating these interactions.In the Agile way of working, such unsolicited collaboration that is others-driven rather than process-driven, will serve as a constant source of learning, equipping your people with the ability to make adjustments to their work as they carry out their tasks. Strategic AlignmentIt is important to understand that Agile is not just the measure of the organizational capability to act fast, but also a primary driver for achieving strategic ambitions through innovation and experimentation. While keeping the main focus on strategic enablers, organizations can work swiftly towards validating and invalidating uncertainties to make sure the strategic objectives at the end of the day are crisp and clear.When devising an agile strategy, all elements that are necessary to the success of the organization should be considered a part of the strategy. If we consider the element of collaboration discussed above, in an Agile framework, these collaborative forums would actually be showcasing how people are achieving business success and strategic goals of the organization at large, not simply chasing the assigned KPIs by their managers.This is what makes your Agile transformation strategy sustainable, and such strategic alignment is what every organization must strive to implement within their teams.Clarity in Roles and CommunicationCommunication in Agile teams is vital, especially when providing clarity across the roles, defining the responsibilities of the people, and ensuring that the people who are actually doing the job are well aware of their KPIs, their practices, and get enough time to work on their tasks.Agile processes are focused towards removing impediments in processes – like duplication of efforts and siloism – while bringing clarity in the roles for each individual.Such clarity can only be achieved autonomously through establishing a culture that is visited and evaluated unbiasedly at regular intervals. This Agile practice improves the use of communication channels for various organizational needs, focusing on the training and development of people and redefining formal and informal communication mediums and organizational structures to strengthen the agile-based culture. TrustTrust is an outcome of all the four variables discussed above, and it is definitely not built by top-down directions.In fact, trust is built through collaboration that is unsolicited in nature, complimented by autonomy and clarity in the roles of the people towards the strategic ambitions of the organization. Once this trust is instilled and ingrained in the organization at different levels, agility is established.TakeawayWhile most organizations focus on Agile processes, tools, and education, there is another world of soft elements of Agile that focuses on people, their behaviors, communication formalities, trust, and servant leadership.The leaders of the organization cannot ignore their people, and without instilling the right culture and values across your people, you cannot establish or implement a sustainable Agile transformation strategy. Trust is built when your people are not accountable to serve the leadership, but rather the overarching strategy of the business – and It is only when you set up such a high-trust team that you can truly be self-sustaining.So, let’s be Agile, but not at the cost of people.
Explore the Neglected Side of Agile

Unlock the Hidden Features of Bootstrap 5 (and How To Use Them)ALT text: Unlock the best Bootstrap 5 new features and how to use themOne of the most widely used open-source frameworks – and a very popular tool amongst web developers – Bootstrap launched its much-awaited fifth version with the intention of creating a more "future-friendly" tool, according to the official launch announcement from Bootstrap.Does Bootstrap 5 live up to the expectations of frontend developers and designers?Before answering that question, let's take a quick refresher on Bootstrap 5.What is Bootstrap 5? Bootstrap 5 is the latest major release from Bootstrap, which is an open-source framework for HTML, Javascript, and CSS. In a massive leap from previous versions, Bootstrap 5 can also be used with SCSS – a more advanced version of CSS-Cascading Style Sheets.In simple words, the framework helps create responsive websites and applications, and Bootstrap 5 takes it up a notch by:Helping create websites that are more appealing from a UX perspective, Catering to accessibility standards, and Automating the process of development, making it much faster, easier, and cleaner. When was Bootstrap 5 Released? After several alpha and beta versions released prior to the stable rollout, Bootstrap 5 was officially launched on May 5, 2021.Unlocking the Hidden Features of Bootstrap 5 This latest and major version of the free frontend framework came with a lot of new exciting features; some of these were instantly recognized by frontend developers and designers – but those weren’t all.In this article, we're not looking at the most evident features that Bootstrap 5 offers but rather the hidden, lesser-known capabilities that most developers may not be aware of.Automatically Set Foreground Color according to Background While developing a website or an application, there is an accessibility requirement that a good contrast is needed between the color of the text and the background color that the text is written on.The latest accessibility standards, as set out by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), require a minimum contrast ratio of 4.5:1 for any text that comes over a background on a website.To meet these accessibility standards, you would need to set the foreground colors based on the background. Without Bootstrap 5, developers would have to monitor and determine the best contrast ratio manually using the color contrast function. That changed with Bootstrap 5 because developers now have the capability to automatically set the foreground color (dark or light) based on the W3 contrast ratio.This is quite the handy feature for developers as it not only automates their manual effort but also frees them from worrying about contrast errors while manually setting up the foreground colors.Most importantly, at the end of the day, with this capability, developers and designers can ensure compliance with global accessibility standards.Let’s watch this feature used in action. Consider that we are creating a card that can have a background color from any of these theme colors:$theme-colors: ("primary": $primary,"secondary": $secondary,"success": $success,"info": $info,"warning": $warning,"danger": $danger,"light": $light,"dark": $dark);Note: This is the standard Bootstrap way of storing values in an Object in the form of key-value pair: $variable : ( “key” : value ).ALT text: Black/white text with blue, yellow, red, and green backgroundIn order to set the foreground color (black or white) as per the contrast ratio (set using the min-contrast ratio variable), we’ll use the following function (from function.scss).$min-contrast-ratio: 4.5;@function color-contrast($background, $color-contrast-dark: $color-contrast-dark, $color-contrast-light: $color-contrast-light, $min-contrast-ratio: $min-contrast-ratio) {$foregrounds: $color-contrast-light, $color-contrast-dark, $white, $black;$max-ratio: 0;$max-ratio-color: null;@each $color in $foregrounds {$contrast-ratio: contrast-ratio($background, $color);@if $contrast-ratio > $min-contrast-ratio {@return $color;} @else if $contrast-ratio > $max-ratio {$max-ratio: $contrast-ratio;$max-ratio-color: $color;}}@warn "Found no color leading to #{$min-contrast-ratio}:1 contrast ratio against #{$background}...";@return $max-ratio-color;}Note: This function is present in the function.scss file and is derived from the W3C community of formulas.For our card styling, we’ll use this function to set the foreground color simply by using the background color value in the argument:@each $color, $value in $theme-colors {.card.bg-#{$color} {$card-background-color: $value;color: color-contrast($card-background-color,$body-color);}}As a result of this, what we get in the compiled output is the class generated for the card background (for example, .bg-primary), which will, in turn, decide which foreground color (dark or light) should be automatically set to this card (based on the contrast ratio).This feature offers a major utility to developers, as it removes the risk of contrast errors while setting up the foreground colors.Minimize Codes For Bootstrap 5 Maps Another addition to the list of Bootstrap 5 utilities, developers now have the ability to automate the process of creating huge maps with several values.Previously, with large sets of values, creating these maps would be a manual, time-consuming process prone to human errors. By automating this process using the new Bootstrap 5 utilities of SCSS for loop and map-merge methods, developers can save a lot of time and manual effort.To understand this Bootstrap 5 utility better, let’s take this example where we want to extend the values in an existing spacers map and add up to 30 more values. Your final map should look like this:$spacer: 1rem;$spacers: (0: 0,1: $spacer * 0.125,2: $spacer * 0.25,3: $spacer * 0.375,4: $spacer * 0.5,5: $spacer * 0.625,6: $spacer * 0.75,7: $spacer * 0.875,8: $spacer,9: $spacer * 1.125,10: $spacer * 1.25,11: $spacer * 1.375,12: $spacer * 1.5,13: $spacer * 1.625,14: $spacer * 1.75,15: $spacer * 1.875,16: $spacer * 2,17: $spacer * 2.125,18: $spacer * 2.25,19: $spacer * 2.375,20: $spacer * 2.5,21: $spacer * 2.625,22: $spacer * 2.75,23: $spacer * 2.875,24: $spacer * 3,25: $spacer * 3.125,26: $spacer * 3.25,27: $spacer * 3.375,28: $spacer * 3.5,29: $spacer * 3.625,30: $spacer * 3.75);Each value is 0.125 units more than the previous one.From here, if we create such a map manually, it will require a lot of time and human effort. With Bootstrap 5, however, we can automate it using a loop:$spacers: ();@for $i from 0 through 30 {$spacers: map-merge($spacers , ($i: '$spacer' + '*' + #{$i*0.125}));}@debug $spacers;When you run @debug $spacers, it will show you the values in the $spacers variable, as seen above.What has happened here is that we've created a complete map writing only a single line of code no matter how many entries there were.Using the same technique, we can also simplify the process of creating maps for other property variables.Consider this example where we want to produce $position-values. This is how we want our required output to be:$position-values: (0: 0,25: 25%,50: 50%,75: 75%,100: 100%);We can produce this map with a single line of code using the for loop and map-merge method while adding as many entries as we want:$position-values: (0: 0);@for $i from 1 through 4 {$i: 25 * $i;$position-values: map-merge($position-values , (#{$i} : #{$i} + '%'));}@debug $position-values;Note: In for loop, if "through" is used, the final number is included; if "to" is used, it is excluded.In this case, we’ve slightly modified the logic and adjusted the $i value according to the requirement before using it in the map-merge function.Note: You can always use the @debug function to see the content of variables during compilation.The same method can also be used to create a border width map:$border-widths: (1: 1px,2: 2px,3: 3px,4: 4px,5: 5px);$border-widths: ();@for $i from 1 through 5 {$border-widths: map-merge($border-widths , ($i: #{$i + "px"}));}@debug $border-widths;The logic here is relatively simple, as all we needed was the addition of syntax “px” with the value.Make Utility Classes Responsive Further extending its capabilities from its predecessor, version 4, Bootstrap 5 also provides responsive utility classes. In Bootstrap 4, these were fixed values.Bootstrap 5 uses a SASS-based utility API to generate these utility classes, with the output stored in the $utilities variable as a Map through which various utility classes can be used.This contributes in a major way when code is being written for a website to be viewed on different devices. Taking the various mobile or desktop views into consideration, developers would often have to create specific classes for the respective device view.With this feature of responsive utility classes in Bootstrap 5, developers now have the option to automatically generate classes that can be used on mobile or desktop or tablet, catering to both a "medium screen" and a "large screen".$utilities: map-merge($utilities,(// scss-docs-start utils-vertical-align'align':(property: vertical-align,class: align,values: baseline top middle bottom text-bottom text-top,),// scss-docs-end utils-vertical-align// scss-docs-start utils-float'float':(responsive: true,property: float,values: (start: left,end: right,none: none,),),… more lines))Let’s consider that you want to use the width property from this $utilities map:'width':(property: width,class: w,values: (25: 25%,33: 33.33%,50: 50%,75: 75%,100: 100%,auto: auto,),),The class that is generated for html use is .w-25 or .w-33 giving the CSS value width:25% or width: 33%.If, for example, we wish to use the width property for a certain breakpoint (tablet or desktop only), the required class should be .w-md-25 or .w-lg-33 working at tablet or desktop breakpoints only.All you would need to do is set the optional responsive value to "true", which is false by default, and we'll get the required responsive classes:'width':(responsive:true,property: width,class: w,values: (25: 25%,33: 33.33%,50: 50%,75: 75%,100: 100%,auto: auto,),),What's essentially happening here is that the API in Bootstrap 5 is doing all the work that previously, developers would have had to do manually through functions in older bootstrap versions.Define State Properties Since this rollout of Bootstrap has inherited some object-oriented features that weren't previously available, it now also offers the capability to define state properties. This speeds up and improves a previously very time-consuming and tedious process where developers would have to write a separate code and input values manually to apply the same command that would be used on multiple variables.This is possible with Bootstrap 5 because the utility API has a state option, which, when set, gives developers the option to produce pseudo classes, like “hover, focus”.Let's take an example of the navigation menu on a website. If you want to add the ability for an item in the navigation bar to change color when a user hovers on it, and then apply the same command on other items in the navigation bar as well, all you would need to do with Bootstrap 5 is to simply write "state: hover" in the "Opacity" property in $Utilities Map and mention the values once. This will then produce the hover classes, which can be used in the html of menu items, making the coding much cleaner as well as reusable.$utilities: ("opacity": (property: opacity,state: hover,values: (0: 0,25: .25,50: .5,75: .75,100: 1,)));Output:.opacity-0-hover:hover { opacity: 0 !important; }.opacity-25-hover:hover { opacity: .25 !important; }.opacity-50-hover:hover { opacity: .5 !important; }.opacity-75-hover:hover { opacity: .75 !important; }.opacity-100-hover:hover { opacity: 1 !important; }TakeawayBootstrap has historically been a popular tool amongst developers, but with the new Bootstrap 5 components, small and large companies alike are quick to recognize the value of adopting this free tool. Perhaps the biggest and most evident benefit offered is the ability to automate development using the SCSS functions and mixins that reduce the code while minifying output files mostly by using inheritance and other object-oriented programming (OOP) features.From accessibility to automation, Bootstrap 5 utilities have undoubtedly reached a whole other level in terms of making the development process much smoother and more efficient, particularly for frontend developers and designers.
Unlock the Hidden Features of Bootstrap 5 (and How To Use Them)

Committed to service excellence and driven by a culture of innovation, the company maintained the Gold Standard recognition for overall business performance.Toronto, ON—May 10, 2022—For the sixth year in a row, mobileLIVE is once again recognized for overall business performance and sustained growth. This year, mobileLIVE not only earned the prestigious Canada’s Best Managed Companies designation but also maintained its status as a Best Managed Gold Standard company.“Now in its 29th year, the Best Managed program seeks to recognize companies who combine strategic expertise and a culture of innovation with a steadfast commitment to their communities,” said Derrick Dempster, Partner, Deloitte Private and Co-Leader, Canada’s Best Managed Companies program. “This year’s winners demonstrated an increased focus on environmental, social, and governance issues. They maintained an unwavering dedication to their core purpose, enhancing client relationships and cultivating a healthy corporate culture.”Winning the Best Managed award puts mobileLIVE amongst the best-in-class of Canadian-owned and managed companies – companies that have achieved sustainable growth through demonstrated leadership in areas of strategy, capabilities and innovation, culture and commitment, and financial management.“By prioritizing employee well-being and championing their professional development, we are on course for continuous improvement,” said Jahan Ali, CEO and Founder of mobileLIVE. “Today marks a very important milestone in recognizing these priorities. With innovation at our core and the right culture, we are driving sustainable growth.”Every year, hundreds of entrepreneurial companies compete for this designation in a rigorous and independent process that evaluates the calibre of their management abilities and practices. Applicants are evaluated by an independent judging panel comprised of representatives from program sponsors in addition to special guest judges. 2022 Best Managed companies share commonalities that include (but are not limited to) putting their people and culture at the forefront, focusing on their ESG strategies and doubling down on accelerated digitization.“The pandemic has changed the way businesses operate and these winners have responded by transforming and pivoting their companies so that they are leading the way forward for the future,” said Dino Medves, Senior Vice President and Head, CIBC Commercial Banking (a sponsor of Deloitte). 2022 winners of Canada’s Best Managed Companies award will be honoured at galas across the country. The Best Managed program is sponsored by Deloitte Private, CIBC, The Globe and Mail, Salesforce, and TMX Group. About Canada’s Best Managed CompaniesCanada’s Best Managed Companies continues to be the mark of excellence for Canadian-owned and managed companies with revenues over $50 million. Every year since the launch of the program in 1993, hundreds of entrepreneurial companies have competed for this designation in a rigorous and independent process that evaluates their management skills and practices. The awards are granted on four levels: 1) Canada’s Best Managed Companies new winner (one of the new winners selected each year); 2) Canada’s Best Managed Companies winner (award recipients that have re-applied and successfully retained their Best Managed designation for two additional years, subject to annual operational and financial review); 3) Gold Standard winner (after three consecutive years of maintaining their Best Managed status, these winners have demonstrated their commitment to the program and successfully retained their award for 4 -6 consecutive years); 4) Platinum Club member (winners that have maintained their Best Managed status for seven years or more). Program sponsors are Deloitte Private, CIBC, The Globe and Mail, Salesforce and TMX Group. For more information, visit www.bestmanagedcompanies.ca
mobileLIVE maintains Best Managed Gold Standard, awarded Canada’s Best Managed for Sixth Consecutive Year

What are UX Metrics? Types of Metrics Three UX Metrics For Usability Testing UX Metrics Test Plan Template TakeawayWhen we talk about UX & design, we often discuss research, research-led design, usability studies, and user experience trends. However, while we often finish these discussions with several exciting learnings, we find all of them battling for our attention.How do you prioritize your work and understand the value a design change could bring to you?The simple answer? UX Metrics.What are UX Metrics?Metrics help support design changes while also allowing UX teams to choose the most critical problems in their product usability. Usually, this framework is used to measure the enterprise user experience so that we can talk with the users and gather vital information from them.A metric is a measure that we can track, and in this context, a 'measure' is the detection of change. Similar to the multitude of metrics that businesses use, such as sales and retention rates, there are several types of UX metrics.(Diagram by Mark G Brown)Types of MetricsConsider UX metrics as your key performance indicators (KPIs). The KPIs for UX/UI design are of different types, each of which focuses on a distinct area:Usability MetricsThese are descriptive metrics that look at how easily users complete a task or event. Commonly tracked indicators like ease-of-use rating, time on task, task success rate, etc., are used to measure the ease of task completion. Advanced usability metrics may also track interaction patterns.Engagement MetricsThese measure user perception: how users interact with your software, app, or website. They include page views, scrolls, event streams, the time it takes per interaction and the attitude of the occurred interaction.Conversion MetricsThese measure the outcome of the experience by focusing on smaller groups of users that you can engage for prolonged and retained use of your product to get insights like conversion rates or Net Promoter Score (NPS).Three UX Metrics For Usability TestingYou might be familiar with some common usability testing metrics and the frameworks that use them.However, in this article, we’re only talking about the ones that:Are both time and cost-efficient and were found to be the most effective at providing accurate results – without needing a large sample size of participants!These methods listed below were handpicked after we tried them out and used them to conduct our own usability testing on a very complex Enterprise Product that we were working on.1- Single Ease Question or SEQ (Post Task Questionnaire)The Single Ease Question (SEQ) is a UX performance metric that uses a seven-point scale to rate how difficult users are finding a task. Here’s an example of what this scale may look like:ExampleOverall, how difficult or easy was it to complete the task? Rate your experience using the seven-point scale below.During usability testing, users are given a post-task questionnaire with this rating scale right after attempting a task to best capture the user’s impression and experience of the task. Since most usability-study sessions will involve many individual tasks, each task followed by such a questionnaire will allow you to extract and record several subjective answers from each user.Collecting Responses of SEQ through Google FormPost-task questionnaires should be short – ideally one to three questions – in order to allow minimum interference with the user flow during a testing session.The SEQ Google Form Survey looks like this.Interpreting SEQ ScoresOnce user responses are collected, you can track the answers using this UX Metrics Scorecard.You can then interpret these scores on an SEQ Percentile Rank Scale:On average, SEQ scores fall between approximately 5.3 and 5.6, which is above the midpoint of 4 on the seven-point scale.One issue of the SEQ as a diagnostic tool is that the questionnaire can lead to users finding it hard to recognize and differentiate the complexity of finishing a task from the actual problems experienced while completing it. So, it is recommended to ask a follow-up question: “What is the primary reason for your score?”Benefits of Using SEQThe SEQ method is very useful for two reasons:Since it is conducted right after task completion, the SEQ method gathers users' immediate thoughts and impressions, as the experience is still fresh in their minds. Hence, the participants can clearly assess how they felt during the experience without any other tasks or thoughts hindering their memory. With the data being collected right after every task, the SEQ method allows easy comparison of the most problematic issues in your workflows for every task.Post-task questionnaires should be short – ideally not more than 1 to 3 questions – in order to allow minimum interference with the user flow during a testing session.Note: There are many user testing platforms like User Testing, Usabilla, or Maze that can help you measure task time and success. The UX metrics methods quoted above are what we used for an Enterprise Product.2- System Usability Scale or SUS (Post Test Questionnaire)A post-test questionnaire, the System Usability Scale contains ten different questions. Each of these questions has five responses – from strongly agree to strongly disagree – to gauge the usability and learnability of the system.ExampleAs the name suggests, this post-test questionnaire is given out at the end of a session after participants have completed all tasks in the usability test.According to an article on perceived usability published by the Nielsen Norman Group, post-test questionnaires "reflect how your users perceive the usability of your website or app as a whole". They are meant to capture this assessment from the perspective of the user, including "their lasting overall impressions". The impressions on your users of the experience as a whole are subject to something known as the peak-end effect, which is that "the most intense and last parts of the experience, either positive or negative, impact the participants' recollections and evaluations the most".Conducting Usability Session by SUS through Google FormTo conduct the usability session by SUS, here’s the Google Form Survey you can use.The formula used to score SUS is as follows:For odd items: subtract 1 from the user response. For even items: subtract user responses from 5. This will scale all values from 0 to 4 (with 4 indicating the most positive response). Add up all of the converted responses from each user and multiply the total by 2.5. This will convert the range of all possible values from 0 to 100 instead of from 0 to 40. Formula:Interpreting SUS ScoresJust as we did in SEQ, a UX Metrics Scorecard is used here as well, which looks like this.Based on research, a SUS score above 68 would be considered above average, and anything below 68 is below average.In order to have the usability of your site be in the top 10% of all sites, you'd require a score of 80 or higher, while a score of 73 would put you only in the top 30%.The best method of interpreting your score is through the process of normalization, in which the scores are converted to a percentile rank. The grading scale below shows how the percentile ranks can be associated with SUS scores and letter grades to interpret the results.Benefits of Using SUSWith references in more than 1300 publications and articles, the SUS method has made its mark as an industry standard.Some of the noted benefits of using SUS, according to usability.gov, are:It is relatively a very easy scale to apply to participants It provides reliable results even when administered on small sample sizes It is very valid in that it effectively differentiates between usable and unusable systems. 3- Usability Metric for User Experience (UMUX)A result of research at the Intel Corporation in 2010, the UMUX method came about as a replacement for the SUS to create a tool that was not just shorter than the SUS but also conformed to the ISO 9241–11 definition of usability (i.e., effectiveness, efficiency, satisfaction).Interpreting Score of UMUXA result of research at the Intel Corporation in 2010, the UMUX method came about as a replacement for the SUS to create a tool that was not just shorter than the SUS but also conformed to the ISO 9241–11 definition of usability (i.e., effectiveness, efficiency, satisfaction).The UMUX method is used for testing perceived usability via a four-item questionnaire. Scores are measured on a seven-point option scale, which goes from Strongly Disagree (1) to Strongly Agree (7), and the scores range from 0 to 100.Interpreting UMUX ScoresThe UMUX is best used after a usability test in the following way:Determine what method you will use to distribute the questionnaire. A pen and paper will suffice for in-person testing, but you can use an online survey tool for remote testing. While scoring UMUX, odd items are scored as [score — 1], while even items as [7 — score]. The scores are summed up, and the total is then divided by 24 and multiplied by 100.To conduct a usability audit, we always let users know as much as possible about all the scenarios, tasks, participants, and facilitators, as well as provide them with brief information within the given time.UX Metrics Test Plan TemplateHere is a sample usability test plan template to use before conducting Usability Testing.TakeawayThere are many factors that come into play when deciding what metrics will work best for you; the ones discussed in this article were shortlisted because they were found to be the most time-effective and easily compatible with smaller sample sizes of participants.As is the case with many other UX researchers and designers, budget-friendliness was also a very important reason we ranked these methods at the top. If cost-efficiency is something you’re concerned with, you’ll appreciate this article about Usability Testing on a Budget.All in all, UX performance metrics are vital in UX research, particularly as a KPI for UX UI design. But it is also equally important to understand why UX metrics are used and which ones to use at what stage of your usability testing process will ultimately pave the way for you to achieve your main goal: consistently providing an unforgettable user experience.
Top 3 UX Metrics For Testing Product Usability

Part 1: The Challenge and Our North Star The Challenge Every now and then, we see designers wasting their time creating UI flow diagrams inside slide decks and whiteboard tools to show UX/UI design to executives or senior management. Designers are also at times found giving walkthroughs of their design files to every member on their team, then to all product managers, then to all developers, then to all the people who missed those calls, and it goes on and on until the end of time. When we have designers working repeatedly on these things, it impacts not just the designers but the whole organization. We want the designers to work on more important things: solving user and product problems. When this starts to happen, the designer’s valuable time and energy are reduced to doing these repetitive tasks. Design Ops to the Rescue One of the key areas of Design Ops is to alleviate problems exactly like this. Our North Star here is to completely eliminate the handover process of design with stakeholders. In an effort to achieve this, we need to bring everyone to the same table and have the same language that everyone speaks and understands, which is what DesignOps achieves. This will have two immediate benefits: Eliminate (reduce) time wasted by designers doing side tasks. Build confidence with stakeholders. Stakeholders feel more comfortable trusting their designers when they can understand their work and process as well. The design department will no longer be seen as a black magic box that no one really knows how it operates. The shared language will help the stakeholders understand how design files are organized and documented, so they can go and find anything whenever they need it without bugging designers. The documentation on design decisions in best cases eliminates the requirement for tedious walkthroughs, one of the biggest benefits of DesignOps. Laying the Foundations As a first step, we set up two keys or legends to identify the state of the design and document the design files. State of Design Very similar to project management statuses, we introduce the states of UX/UI design. The key allows anyone coming into the design file to understand their status. This can be used not only to identify design files as a whole but also the pages, user flows, and individual screens. Our first set of statuses look like this (these can be modified and adapted to any team’s needs, but we have found this to be most productive in our case): ✍️ Working on it Anything that designers are currently working on can be denoted by this status. 🚧 In-progress Things that are not yet finished but also not being actively worked on can be denoted by in-progress status. ✅ Pretty much done This status is important to indicate your progress on work. Statuses like these will build confidence with your stakeholders. 🔸 Please review for approval With this time you are inviting the product manager or other stakeholders to review your UX/UI designs and decisions. 👍 Ready for presentation UX Designs that have been approved by product managers and the internal team will be ready for executive presentation. 🔹 Approved Designs approved by all the stakeholders can be marked with this status. 🔒 No further changes Use this state when a design has been officially locked and you want to hand it off to developers. This will mean that no more changes will be catered to on the design and it is locked until delivery of the project. 🔻 On hold Designs that get deprioritized due to any reason can be marked as on hold. 📦 Archived or legacy Any old or deprecated design can go under the archived or legacy label. 🎆 Magic Lab All the amazing ideas and designs can find their place in the magic lab. These are proposed pieces of design that designers want to showcase or show off but are not part of the main user flow. Documenting Design Taking this a step further, we also set up comment keys. These can be used to document design decisions, clarifications, ideas, concerns, and more as raised by designers and stakeholders during the design process. The comment key we generally suggest to use looks something like this: The status and comment key is part of the Figma File System, a subset of the Figma Design System by mobileLIVE. This can be downloaded free from the Figma community. This is available as ready-to-use components that you can plug in any of your design files and start using them.
Design Ops Series: Improved Designer and Stakeholder Collaboration

TORONTO, ON – Nov 16, 07:45 ET mobileLIVE, a digital transformation consultancy specializing in experiences and the technology used to perfect them, is proud to be named a Great Place to Work®-Certified Company. “Investing in our people, prioritizing a culture of learning, and empowering and enabling the professional and personal goals of employees is ingrained in our culture,” says Aftab Ali, Director Human Resources. “We understand that in our line of work, fostering innovation and supporting the people who spark it is critical to driving change and solving the challenges our clients turn to us to solve. We give our employees less to worry about while enabling them to do more, professionally and personally. It’s simple in concept but far-reaching in impact.” This certification is determined after a comprehensive independent evaluation by the Great Place to Work® Institute Canada and an extensive employee survey conducted anonymously. Additionally, recognized organizations must be headquartered in Canada, with a majority agreement that people are treated fairly, regardless of personal characteristics (such as gender, ethnicity, age, sexual orientation). “Becoming an employer of choice is not only a foundational aspiration of ours but strategic and critical to achieving our vision for the future,” said Jahan Ali, CEO and Founder. “This certification serves as an indicator, directly from the people who matter most, that we are on the right track. It’s the experience our people provide which is a big driver for our growth and never losing clients, and why it’s so critical to provide an equal experience to employees.”
mobileLIVE Becomes Great Place to Work® Certified™

Client demands are always changing, and if the last decade is any metric to go by, we know they will continue to evolve for the foreseeable future. To stay competitive now requires companies to have multiple permutations of their offering and an agile approach to continuous improvement. The traditional REST API model doesn’t cut it anymore; what companies need is fast pace in development, and with GraphQL that’s exactly what they get. Join Luca Maraschi, CTO mobileLIVE, as he very elaborately walks us through the journey of what GraphQL does, why it is important, and how it differs from REST.
GraphQL and the API Economy: Beyond the Traditional REST API Model

Customer expectations are always changing; however, digital has not only accelerated the rate of that change but elevated those expectations. Needless to say, this has caused challenges for business, with BFSIs being particularly hard hit. The Googles, Facebooks, and Amazons of the world have spoiled customers, providing them with seamless experiences, on-demand, wherever and however they want. And now, it’s time Financial Institutions and other BFSIs do the same, and I’ll show you how below. But before you can solve the problem, you need to understand it. The Problem For Banking Customers For banks, credit unions, and insurance brands, and BFSIs in general, the shift of consumer preferences towards digital solutions poses one of the biggest threats to their core modus operandi: in-person customer appointments. And while physical bank visits were not an issue felt by banking customers previously, their perspectives have changed on two significant fronts: Experience over products More customers now prefer that their experience should be better, more efficient, and faster, prioritizing it over the products that they receive, which are pretty vanilla in their construct. Convenience over privacy Customers are also willing to let go of a little bit of privacy in exchange for more convenience, better integration of financial or banking softwares, and faster action for the services they’re choosing. Changes in Customer Behaviour With customers getting so used to getting all of their tasks done instantly and in a few clicks, BFSIs are lagging in adopting such efficiencies in their customer engagement models. As a result of such fundamental changes in customer expectations from the industry, we’re now witnessing alarming statistics in customer acquisition rates as experienced by banks, financial institutions, insurance companies, and BFSIs that are trying to shift their processes to a digital framework: 51% of customers drop off from their onboarding journey with a bank due to the length of the process. 46% of customers leave their applications midway because the user interface is not friendly enough to proceed. 41% of those who start the process digitally never return if they log out or if the sign-up process is too long and requires too much information. In addition to changing customers’ tolerance levels towards their banks, such variables contribute largely in showing BFSIs that they have a lot of catching up to deliver the differentiated experiences that their customers have already become so used to receiving from interacting with other non-financial services. The Industry Perspective on Digital Experiences When we look at financial institutions and BFSIs as a whole, it’s no news that it’s a heavily regulated industry. While that in itself is not a challenge, their use of decades-old practices, processes, and financial softwares is still being followed. Such institutions have never viewed it as a customer journey but rather a journey that happens internally within the bank and involves the customer’s file to move physically from one department to another. In simply trying to make such a process seamless and convert it into a frictionless onboarding journey for the customer, many issues come to the fore. Organizational Challenges Before looking at how financial institutions could begin to address these bottlenecks, we need to consider some of the grave organizational challenges that exist as well: Disconnect at the first touchpoint Whether the customer’s first touchpoint is a website or app, in the case of a digital channel, or to visit the bank and talk to a teller for non-digital channels, this is where most of the disconnect happens. Systems failing to cope up with expectations On a system level, the challenge remains to cope with increasing customer expectations, be it an internal system or a legacy system with the customer. Old and outdated processes The fact also remains that the processes and financial softwares adopted by these institutions are simply too old to convert and involve too many layers in pushing the customer’s application from one place to another. The true picture that this paints for financial institutions is that of struggle: breaking the numerous silos, being unable to implement automation, and using non-modular technology, rather than using modern technologies like banking softwares that offer convenience in accordance with the current needs in the digital world. That being said, one sliver of hope we’ve seen in the last three to four years is that the right technologies have become available to remove nearly all such hurdles. With such technologies at hand, processes like identity verification and document scanning and organization can all be reduced to a matter of a few seconds and done purely digitally rather than taking days and manual interaction with people. This is where successful institutions are now setting themselves apart, and the reason why achieving the optimal customer onboarding experience has become more critical than ever before. How Banks Can Address the Challenges Most banks resorted to addressing the digital shift by taking the same system and flow of process and creating an online facsimile of it. With research showing us that 85% of customers drop off between clicking on an ad to starting their application online, it’s evident that these ways aren’t working. We see such high drop-off rates because the customer onboarding process isn’t being adapted to digital, rather just shifted to it. Even if financial institutions didn’t – or didn’t need to – think about these earlier, certain factors are unique to a digital journey and need to be taken into consideration: Capturing the customer as soon as they come in How can the institution position the journey and capture customer information so that even if the customer drops off, they can be contacted again to help move their application forward? A lot of organizations are rewarding customers to return and complete their journey, an incentive that is doing wonders in the way of new customer acquisitions. Upgrading to new systems Most core banking softwares are quite archaic and need upgrading, and to run a digital workflow, institutions will need new systems rather than relying on the same old financial softwares. Speeding up the process With digital experiences, the pace of action is one of the most critical factors, and the question becomes of how fast banks can get the customer in and through the system and convert them into revenue-generating customers. The 5 Stages of the Customer Journey Digital Onboarding - The 5 Stages of the Customer Journey Understanding that the customer journey cannot remain in the background anymore needs to be prioritized above all else. From an organizational point of view, it can be broken down into five stages: Acquisition of Data Whether customers fill-up the form themselves or their information comes from third-party portals, capturing their documents and organizing them in as little time and clicks as possible is the first stage. Verification Is the customer who they say they are? Depending on the product offered, there are different Know Your Customer (KYC) regulatory requirements. Risk Assessment Once customer information is verified, an automated risk adjudication process is conducted. Payments Are customers paying directly, or are payments integrated with third-party payment providers? Provision of the Service The customers are issued a digital card to add to their Apple or Google wallets to get started with using the service as soon as they sign up. Interestingly, from the first to the last stage, this entire journey can be 100% automated, without human intervention, and in most cases done almost instantaneously. The experience needs to be easy, fast, and frictionless. In 5-minutes, a customer can and should be able to activate their account, with a digital card added to their device, all without ever having to set foot into a branch. Takeaway Every organization hoping to enter the digital era needs to break from or evolve their traditional processes, and this, although harder, is especially important for financial institutions. The question is, how to create a solution that balances customer expectations and business objections; and it will be those who can most effectively achieve that, who will be the most successful in the future.
How Financial Institutions Can Exceed Customer Expectations

Experiences that make you feel the same way regardless of where they happen – that’s what sets apart a business from a brand. Omnichannel experiences will continue to guide digital interactions that are: Faster More personalized Customer-driven And our experts show just how that can all be implemented. Bringing together their brand, design, and technology, this one-hour session about unravels implementing omnichannel experiences, the challenges that come with it, and the potential it will unlock for the future of digital businesses.
Omnichannel Experiences: Solving the Implementation Challenges

While the preference for digital channels isn’t diminishing, customers’ tolerance for long, complex sign up processes is, and that means financial institutions are now facing challenges like: Dropping customer sign ups Increasing cost of acquisition Rising cost of abandoning signup Fortunately, this can be fixed with faster, frictionless, and completely E2E digital onboarding, and you can discover how here. In this extremely insightful, one-hour session, BFSI experts Ghazanfar Ahmed (Director of Digital Innovation) and Danysh Hashmi (VP BFSI) let us in on exactly how banks, credit unions, and insurance brands can achieve a better Digital Onboarding experience for their customers. Join them as they discuss key industry drivers and market challenges, designing customer-driven experience, and the technology needed to support it all.
BFSI: How to Create Frictionless Digital Onboarding Experiences

Any experienced product developer will tell you that a bold vision and strategic planning are not enough to bring your envisioned product to life . That approach focuses too heavily on the destination; overlooking the critical journey of how to get there. And for that, we turn to a roadmap. A product roadmap is the bridge between your long-term goals and short-term struggles; and today, we’ll dive further into the concept of roadmapping and why it can take you on a journey to your next product. What is a Roadmap? Agile roadmap The concept of a roadmap is commonplace, especially if you’ve even been involved in a long road trip like the one from Toronto to Montreal depicted below. Note, it does not say a specific time of arrival; rather a window. That is because there are several stops along the way; and given any number of variables at those stops, it’s difficult to say with certainty how long each of those stops will take. After all, what if there’s a huge line for the bathroom? However, the roadmap does help answer some critical questions: Which is the fastest route? Will you stop along the way; and if so, where? How do you know you’re moving in the right direction? The prerequisite for gaining any benefit of a roadmap is a destination; and when talking about product development, that destination is the product. And the roadmap is how you ensure that journey ends up where it needs to be while addressing strategic objectives along the way. The Importance of Roadmaps for Product Development The same that applies to road trips apply to product development The value of a good roadmap applies equally to road trips as it does to product development. And while there are numerous frameworks for creating one, as long as it keeps you on course and gives you a better understanding of where you’re going and why. An incredible tool for implementing product strategy and aligning stakeholders on a shared vision; a product roadmap provides not only the journey the product will take but how that strategy will be executed, communicating the product’s evolution by mapping its major releases onto a timeline. Roadmapping in Action That’s exactly what was done for our engagement with one of our clients. The client was in the process of executing an important digital transformation initiative when they began to voice some concerns: How would the journey look like, and how can we communicate to executives that the teams are moving in the right direction? How would the product evolve in the future? How would the three teams work together to deliver integrated business goals; what were their dependencies? Executives were unclear what the individual teams were trying to achieve, how much was done, and what was next What would be in the releases and when would they take place? Which release to focus on now and why? Which features to prioritize and what associated user stories to use for the first release What they were missing was a connection between the vision and execution, and the solution for that is nothing but a good roadmap to plan out its major releases. An exercise was done to identify the milestones along the way, and eventually, they were able to create their first roadmap in the following format. The items or business goals in these three columns were strategically placed to inform the team of the goals to focus on NOW and which ones to focus on later. This format helped them emphasize the order of things with business goals rather than their due dates. It also allowed product owners to prioritize features and associated user stories, which helped them to achieve the goals mentioned in the NOW column. Roadmap in Action Multiple sessions were conducted with all stakeholders, and we helped them understand the purpose of a roadmap that would help them overcome the challenges they had identified. After that, the following structure was produced. This structure identified the releases for the NOW column business objectives: releases for the NOW column The results of the roadmapping exercise above were as follows: Aligned the vision with business goals and objectives. Even though everyone already had this information, it was not presented in such a way that could be understood by all of them. Identified and agreed on the KPIs on the business objectives. Identified the features from all the teams involved (presented with different colors) to achieve those objectives. Identified what the journey will look like by mapping out releases. Identified which features need to be delivered for each release goal. Understood what the user stories are associated with the identified features for each release. Not all user stories needed to be considered for the release goal. Introduced goal-oriented thinking instead of just delivering outputs through user stories. By following the format of NOW, NEXT, LATER for the roadmap, the program could communicate better with the key stakeholders and was able to establish transparency. The roadmap was able to solve the challenges the client was facing and also help them identify what to focus on. Roadmapping During COVID-19 As mentioned before, the concept of road mapping is not only applied for product development or a road trip. It’s frequently used by governments as well. Here’s an example of what Ontario followed as part of the province reopening during the pandemic: The Roadmap to Reopen is a three-step plan to safely and cautiously reopen the province and gradually lift public health measures. The plan is based on: The province-wide vaccination rate Improvements in key public health and healthcare indicators Creating A Roadmap For Your Perfect Product There is no specific date involved in the plan, but it does highlight goals to achieve. As the Ontario Premier, Doug Ford, clearly mentioned in one of his interviews: “Roadmap is a plan about how we are going to reopen the province, not when.” Build Your Own Roadmap It should be clear at this point how crucial a roadmap is for any serious product development effort. Which is why I want to leave you with exactly how to create your own:Identify and articulate product vision Identify business objectives/outcomes to achieve along with metrics Focus on goals and benefits, not on timelines Collaborate with all stakeholders for alignment Consider rough estimates to check the feasibility of the goal Review it regularly and adjust as required By creating a roadmap, you have better communication and easily identifiable goals that help you achieve the product you have envisioned.
Product Roadmapping: For Agile Planning & Product Development

Now that the social experiment of working from home is over, how many of us can say we want to go back to work? For most organizations, replicating physical workspaces to the virtual landscape was not an easy task; in fact, it was one that came with a range of unforeseen challenges. But with virtual tools, collaboration strategies, and the latest inventions of modern technology, most of all Virtual Reality, organizations, both big and small, are able to not only manage their teams efficiently, but engage them in ways that can make remote collaboration all the more enjoyable. And just like everyone else, my colleagues and I have also had to find different ways and virtual tools to keep our team members engaged and inspired during the pandemic as we tackled remote collaborations with people we had never met before. We recently held a virtual talk in which we discussed the strategies that have enabled our teams to have successful remote collaborations in the new virtual reality. Remote Collaboration versus Regular Meetings Before we get into the virtual tools, collaboration strategies, and practices that can make your project successful, it is important to understand what the term ‘remote collaboration’ encompasses. This is the process of different teams working together, regardless of their geographic location. While the purpose and content are the same in both remote and regular meetings, the element of body language is missing in the former. In face-to-face meetings, you have the facility of being able to judge the body language of your peers. Not being able to fully gauge the response of your team members across the screen can affect work performance and company morale. While pre-pandemic collaborations would include face-to-face meetings, conferences, and workshops, remote collaborations consist of group chats for work projects, virtual interactive meetings and workshops, and virtual tools as well. In order to have a successful online collaboration, you need certain virtual tools that can help team members connect and also boost their innovative thinking, even in a virtual reality. So instead of having boring Zoom meetings in which at least one team member is likely dozing off, engaging the team in a much more interactive virtual activity, like an online workshop, can prove to be far more beneficial. Virtual Tools for Collaboration Workshops Collaborative workshops are the best way to brainstorm new ideas since they are more focused toward one specific topic or project. With every team member tending to one problem or project, you will have better outcomes. The word ‘workshop’ may sound daunting – but don’t be intimidated by it. You do not require big teams in order to have a fun and constructive workshop; it can be with as little as three people – even as you work in your new virtual reality of working from home. Workshops foster innovative thinking as they allow you and your team members to be more hands-on. It also allows for more visuals which can definitely make the entire process less snooze-inducing. Remote collaborative processes like workshops prompt your employees to be more vocal. Every single one of your workshop attendees will be required to participate in some way, so it is an effective way of improving communication between team members. This is especially so because a workshop offers the opportunity for everyone to be heard, as opposed to conventional meetings where only someone higher up in the company hierarchy, like the CEO, would be the loudest person in the room. With everyone participating, you can identify what each team member excels at so that you are playing with each other’s strengths. Virtual Tools Now that you know about the advantages of having a workshop, let’s talk about some virtual tools that will facilitate you in the process. These are some of the soft wares I have found useful for creating workshop boards on: Miro is a whiteboarding platform that allows various teams to work together for an online collaborative process. This virtual tool has a suite of features, from digital sticky notes and a Template library to a canvas that never runs out of space. The ability to integrate this with other platforms like Google and Jira to quickly export documents serves as an added benefit, making this one of the most efficient virtual tools for such remote collaboration. Mural is another virtual tool that allows you to have a seamless collaborative workshop online. You have visual communicative features like flowcharts, drawing, sticky notes, and some interactive tools like timer, voting, and celebrations. Google Jamboard is a user-friendly virtual tool, and the best part is that if you are using other Google Suite products like Google Sheets and Google Meet then you can just integrate the Jamboard with them. You can have up to 50 collaborators on Jamboard at one time, making it another valuable addition to the list of virtual tools we have at our disposal. Collaboration Strategies in Action Your Role as a Facilitator It’s important for you to think about the role you will play as the facilitator. It is a crucial job, one that can greatly determine the success of your virtual workshop. But don’t worry – I have some collaboration strategies for you that will help you shine in your role in this virtual reality we’ve found ourselves in. As a facilitator you must allow creativity to flow while maintaining the structure of the workshop. There are two aspects that you must keep in mind as you prepare for your workshop: Firstly, since you have to guide the workshop you must fully understand and convey to your audience that the purpose of the workshop is to dive deeper into the problem or topic that the workshop will be addressing, and it’s okay for participants to not have a high-level understanding of the topic. As the facilitator, it’s more important to answer questions and help everyone come out of the workshop with a better understanding of the topic and unveil the root of the problem being addressed. Secondly, you have to empathize with the people working with you. When I prepare my workshops I try to keep in mind that my team members are also nervous about taking on a remote collaborative process and will need me to keep them motivated and engaged through the process, as well as guide them on working with the virtual tools being used. Rules Give Your Collaboration Structure Even before the workshop starts you can connect with your virtual collaborative team by sending them an intro board that has the names of team members and the other details such as the mission and aim of the workshop. You can also include tips and shortcuts in this intro board, especially for those who are not familiar with the tools of a virtual workshop. This ensures you don’t waste time in the actual workshop trying to guide team members. A quick tip to achieve this is to send out a short 5-minute tutorial video that explains, with a practice board, how the tools are to be used. This helps participants get used to the tool that will be used in the workshop beforehand. It would also be helpful for you and your team members if you added the rules of the workshop. Here, I must emphasize on two rules: Stick to the topic, and Respect the time Stricter time management is required in virtual collaboration meetings; focus on these two rules so you don’t lose time or track of the meeting. Another rule that you should have for yourself is to encourage out of the box thinking and let your participants be expressive. Also keep in mind that sometimes there are stretches of silence as team members are thinking or working on something on their own. This can feel awkward for many but it is the facilitator’s responsibility to assure the team members that this silence is normal and not uncomfortable. What can help at this time is a playlist that can uplift the mood of collaborators – it might even help the creativity flow! The most important rule of all is that everyone in the workshop, including you, feels comfortable enough to share their ideas. Socializing is a Key Part of Remote Collaborations Once the rules have been laid out, don’t just jump straight to work. Remember, if your team members are awkward with each other, you won’t be able to foster any innovative thinking. Have some ice-breaking activities that will allow your team members, especially cross-functional ones, to get comfortable with each other. Not only do such sessions help with getting the participants familiarized with each other, but can also be done as a quick warm up exercise on the topic of the workshop before they begin. If your ice-breaker is based on the theme of the workshop, it’ll help get the conversation going. Team members can upload pictures of themselves, and play a game in which each of them writes a truth and a lie on a sticky note and lets the other team members guess which is which. If you really want to kick things off, you can also ask them questions, like giving them four different meal options and letting them choose what they would order by writing it on a sticky note, or ask them their favorite part about the topic to be discussed and asking them why they think so. Socializing done, let’s start the real work! First, set the goals and expected outcomes of your collaboration. This means establishing two points: Why are we here? What are we trying to achieve? Your collaborators should have all the information about the purpose of the workshop and with that, you need to ensure that the outsiders have complete context of the problem they are taking on with you. Once everyone has all the information, let the discussion flow. Remember, you have many virtual tools and features at your disposal so don’t hesitate to use them. Best Practices and Tips For Virtual Collaboration How Can You Improve? An important part of having workshops is receiving constructive feedback. My peers and I find that having a post-workshop survey allows us to identify our strengths and weaknesses. So use a survey to find out how your participants felt about your workshop. In the survey you can ask questions such as: Have you achieved the goals you had before coming to the workshop? What did you think of the time management/activity design? How was the facilitation? You can share the survey at the end of the workshop, when memories are fresh, and give them a few minutes’ time to fill them out. If you want honest feedback, ensure your participants that the surveys are anonymous. Playback Session Now the workshop may be over, but there is still some work left! We suggest you have a playback session. This allows the team to get back together for a second session and review the workshop results. The teams know exactly what work they have produced and if it matched the expectations or hypothesis they had set. You can also decide what the next steps are going to be. A playback session is another interactive way of ensuring that your team members are all on the same page with each other, so it will include a recap session in which you may include short clips or screenshots of the main discussion points of the workshop. A section on synthesis and key findings would allow everyone to discuss the details of the ideas produced in the workshop. Finally, you can organize the ideas into actionable items and then work towards what the next steps can be. The Future of Remote Collaboration The pandemic has forever changed how we work. Whether it is in offices or at schools, work from home will become more frequent, at least in a hybrid capacity if not completely. But the shift to virtual workspaces will continuously demand innovation of better ways to recreate human interactions and make them as comfortable and convenient as possible. With the introduction of 5G, virtual meetings, conferences, seminars, and workshops will run a lot smoother, with less lagging, call dropping, and other connectivity issues. One thing that I’m personally excited about is that many companies are looking into VR processes that will allow you to attend meetings virtually, either as an avatar or hologram. We may feel isolated right now, but technology is growing by leaps and bounds. With holograms and avatars, you could freely interact with new team members from any corner of the globe, and this is just one of the many advancements that prove to us that despite not being physically present at work, we do not have to do without the social elements of collaborating with each other.
Remote Collaboration For Successful Innovation

While my career choices might make me appear biased, I truly believe that few practices will carry as much importance in the future as Service Design. In truth, service design isn’t new. However, as our world moves towards all things digital and finds that transition accelerated by historic and uncontrollable forces – like the pandemic – there has been a keener interest in what exactly service design has to offer. Much like the world had to evolve and transition to digital quite rapidly, so too did the practice of service design adapt and evolve to help architect and orchestrate that transition, or at least, many of the success stories. And seeing how at the heart of service design is incorporating a variety of perspectives, I’ve included a few of my peers’, taken from a virtual talk we shared, to show how service design can improve ever-evolving digital experiences by evolving alongside them. Changes in Service Design An Internal Perspective Service design is all about going out into the world and observing how people interact with services, gathering data and plotting the best course forward. And to address “the elephant in the room,” as Patrick Bach, Director of Service Design at CIBC, put it, research and the way it is conducted has been forced to change significantly. Ethnographic interviews are a great example, notes Patrick, something he and his team would historically conduct in-person, and in some cases even fly across the country for, have all had to shift to virtual. He admits that while many elements do translate well to a Zoom call, getting to the heart of research questions isn’t without its challenges. Virtual poses many obstacles, especially to participatory and activity-based research, while the lack of a traditional conference room setting has forced teams to reimagine how they collaborate and co-create. “One of the ways we’ve adapted is around how we communicate. So it used to be these very physical walkthroughs; we would print things over large sheets of paper and get everyone to walk around, annotate, and reflect. In the virtual world, we’ve been embracing the format of video, so instead of creating a journey map or service blueprint, we’ve been converting those things into something more portable, repeatable, and reusable.” I couldn’t agree more with Patrick, and will come back to this point later. An External Perspective Video does allow for many opportunities for collaboration and connection; however, not everyone is so quick to embrace it. “Let’s take observational research, for example,” says Judy Mellet, Director of Service Design & Strategy at Telus Digital. “We are on a project where we try to observe what happens in an installation process in the home where a customer might be comfortable in some ways letting you into the house and observe them and they see you as perhaps somebody that may be able to support them through that process. They are less wanting to be observed over video, and it’s just a dynamic; they feel like they’re being watched.” Service design beckons professionals to dig deeper for ways to improve, revamp, and evolve how specific processes or activities are carried out. It proposes new and reimagined ways of achieving the same, if not better, results – and it appears organizations and enterprises are ready to embrace. Judy goes on to remark that evidence of this can be seen in how the nature of requests from businesses of service design are evolving. Rather than asking to fix one specific problem, the demands are more transformational, reimagining entire concepts or approaches. And to me, this is the real proof of its value – when applied to transformational initiatives. Growing Appeal of Human-Centred Design An interesting observation is that the pandemic pushed customers and stakeholders into becoming the end-users of a complex and broken system. Suddenly, everyone knew what it was like to be on the wrong end of a bad digital experience. So how do we fix it? The answer is human-centred design, and by putting it at the centre of all transformation projects, we’ll best be able to craft an experience that justifies the systemic journeys and buy-in processes that are becoming the norm of digital life. This has seen the demand for service design increase and, to echo Judy, so too have the project sizes, as organizations realize, in some cases the hard way, that their digital experiences simply weren’t good enough. Communication & Collaboration Adding to Patrick’s point earlier, professionals are now more driven to develop new digital tools to overcome their biggest problems, which couldn’t be more evident than in collaboration and communication. Virtual tools now complement physical walkthroughs otherwise conducted in more tangible ways. For instance, where experience mapping was previously being done on physical walls with location and size limitations, virtual walls are now being used that are more conducive to collaborative research and come with fewer physical restrictions. This is not to say that such virtual activities weren’t in play before the pandemic hit; rather, it’s their prevalence and adoption that have increased. Not only does everyone have to have access to them now, but being a part of such an environment has led to better and more efficient ways for everyone to play their part within an organization. Industry Impact & Opportunities Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals The role that service design can play in healthcare is just now being paid its due attention because workers are faced with challenges and questions unlike ever before. A new scale of awareness is now observed, with individuals partaking in conversations like which vaccines they can get, where they can get them from, and where they currently stand in the process. Such a level of individual engagement has opened up a large window of appreciation for service design principles and how they can be applied to solve all such concerns. Telecommunications & Banking Where driving sales and engagement with customers has always been a priority, sectors like banking and telecommunications were severely impacted as a result of the pandemic. Powerful, yes, but these industries driven by sales and customer engagement saw a massive disruption in their processes. Now, as offices and retail are reopening, we are seeing these industries finding some resistance in going back to the old ways and much value in staying on the course forced upon them. It appears much of the “quick patchwork” intended to tie us over is being revisited, refined, and will likely make an appearance (or at least some facsimile) in whatever the “new normal” turns out to be. Real Estate Another industry is real estate, where historically, physically visiting a property site was vital. Beyond virtual tools and walkthrough technologies, service design thinkers created completely new ways to translate physical interactions into immersive virtual journeys that took the customers from point A to point B via a seamless digital process. Why Service Design? It’s Adaptable & Malleable What makes service design so relevant and effective in today’s global landscape is its multifaceted nature. There are numerous service design methods, principles, and applications that can adapt to any given situation to the degree with which it is required. Rather than offering a single solution to a specific problem, service design takes up a problem-fit approach to really tackle challenges as they come along. It Breeds Innovation & Human-Connection Being applicable to a range of different projects makes service design a huge facilitator for innovation. It drives out-of-the-box thinking because it urges users to think along bigger lines for better solutions. And the value of service design is not going to fade away when and if we “go back to normal.” The new norm will be a different one, and service design has the potential to assist organizations with rethinking the best ways to design this new reality, keeping the people who will be living it at the forefront. Practically speaking, our own service design team comes in at the start of engagements, rethinking how the business is currently serving customers and the quality of the experiences being offered. It’s imperative to translate the context of the customer in such situations, but transferring the same level of empathy across all user testing channels is challenging. In my opinion, the onus is on service designers to augment themselves throughout the end-to-end process so that they can reimagine these experiences and prioritize human-centrism every step of the way. Take Away While I know I am not alone in this opinion, I’m doubtful we’ll ever go back to the way things used to be. Already, hybrid work models are being implemented, businesses are shifting and transforming to digital at an accelerated speed, and the demand for better digital experiences is increasing at an exponential rate. And it’s those reasons why service design is so largely at play now across the globe. It’s also why service design will continue to support the efforts of future-focused businesses in not only improving their digital experiences, but crafting them (and their organizations) in such a way that the interest and journey of all parties involved are best served.
Service Design: Improve and Evolve Experiences

Develop, test, and deploy pieces of the frontend independently Add, remove, or replace elements of the frontend without rebuilds Build the components of the frontend using different technologies Craft the truly omnichannel experiences customers demand You know why Micro Frontends are so appealing and what challenges they solve; and now, you can learn how to scale them. In this one-hour session, join Luca Maraschi, CTO of mobileLIVE as he shares how to create the elevated customer experiences that are driving revenue for Ikea, Starbucks, HelloFresh and more.
Scaling Micro Frontends: The Why and the How

Toronto, ON – June 7, 2021 – mobileLIVE’s singular purpose to accelerate digital transformation has just gained momentum with the appointment of Luca Maraschi as their new Chief Technology Officer. As CTO, he will be responsible for architecting the technology roadmap for our clients, lending his deep expertise on cloud computing, distributed systems, designing platforms at scale, and for scale to provide a holistic framework for transformation. “Technology is far from being utilized as a real tool to leverage acceleration. In the short term, layering on more and more technology can solve the problems in front of you, but it also weighs you down, causing bigger ones all around you. Suppose your goal is agility, speed, and efficiency? It would be impossible to accomplish this through that approach. First, you need to reassess and reimagine your processes, remove points of friction, and realign your people and perspective for organizational, not just project efficiency.“ LUCA MARASCHI, CTO of mobileLIVE From his time as a Technology Leader advising Fortune 500 companies through their transformation journeys, inspiring hundreds of developers to create the next generation of platforms and products, and his reputation of removing complexity and replacing it with value that is felt by both user and organization as a whole proceeds him. As an active contributor to numerous developer communities and author of several open-source tools, the proof of what he can do is all around him. “I met Luca several years ago and was instantly impressed not only with his technical knowledge but how he utilized his unique experiences to approach challenges with simplicity and efficiency in the forefront,” says Hussain Qureshi, President of mobileLIVE. “When I discovered such alignment between his approach and our own, I knew he was the person to lead our technology teams and drive the transformational efforts of our clients.”
Luca Maraschi Named New CTO at mobileLIVE

If you are looking to launch a device in Canada, whether it’s IoT, a tracker, wearable, 5G, mobile – whatever, you’re going to want to have it tested and certified first. And in this 30-minute video, you can learn how having the most common questions answered, including: Where do I start, and should I do it alone? What tools do I need, and what’s the end-to-end process? How long does it take, and what does it cost? What type of certification do I need, and what comes next? And more! The mobileLIVE Device Certification & Testing Lab professionals have been helping Fortune 500 brands and SMBs launch their products in Canada with certification, testing, and team augmentation for more than 10-years. And in this video, they will show you precisely what you need to get your device certified and launched in Canada.
How to Certify IOT, Wearables & Mobile Devices for the Canadian Market

Despite a challenging year felt across the globe, the company maintained its drive, culture, and future vision. Toronto, ON – May 5, 2021 – mobileLIVE is being recognized for its commitment to strategy, culture, innovation, and sustained growth, earning Deloitte’s Canada Best Managed Companies for a fifth, and perhaps, most memorable, year in a row. “The entire world felt the impact of the pandemic, and we were not immune. It was challenging, but being an agile organization by nature with digital in our DNA, we were able to pivot quickly,” said Jahan Ali, CEO and Founder of mobileLIVE. “Good planning, clear and communicated strategy, and a resilient culture helped us respond, not react to events as they unfolded. That is why maintaining this designation is something not only myself, but our entire organization is proud of and will continue to strive for.” Going into its 28th year, Canada’s Best Managed Companies is the country’s leading business awards program, recognizing excellence in Canadian-owned and managed companies with revenues exceeding $25 million. These companies are judge across 4 pillars, including: Strategy & Execution Culture & Commitment Capabilities & Innovation Governance & Financials “This past year has posed numerous challenges for Canadian business and has touched each and everyone in some form or another – including this year’s Best Manage Winners,” said Kari Lockhart, Partner, Deloitte Private and Co-Leader, Canada’s Best Managed Companies program. “They should be extremely proud of this designation and use it as a catalyst to continue the work they do each and every day. Their unwavering commitment to their people, and their adaptability amid a year of turmoil, have led them to this achievement and it mustn’t go unnoticed.“ Each year, several sponsors join Deloitte in celebrating Canadian Business, among which is CIBC. “CIBC is especially proud to celebrate and recognize the winners of Canada’s Best Managed Companies in what has been a very challenging year,” said Dino Medves, Senior Vice President and Head, CIBC Commercial Banking. “The companies had to make tough decisions, adapt quickly to a new environment and most importantly, continue to innovate and invest for the future.” About Canada’s Best Managed Companies Canada’s Best Managed Companies continues to be the mark of excellence for privately held Canadian-owned and managed companies with revenues over $25 million. Every year since the launch of the program in 1993, hundreds of entrepreneurial companies have competed for this designation in a rigorous and independent process that evaluates their management skills and practices. For further information, visit http://www.bestmanagedcompanies.ca
mobileLIVE Named Canada’s Best Managed Companies for the Fifth Consecutive Year

Replace manual & scripted testing with automation Drastically reduce the cost of running multiple tests Test across multiple machines and interfaces Quickly detect system or product defects Reduce time while improving customer experience This is what the democratized future of QA and Software Testing looks with Model-Based Test Automation, and in this 30-minute video, you’ll discover not only how to accomplish the above, but why you’ll need to if you are still relying on traditional testing methods.
Model-Based Test Automation: Bigger, Better, & Faster QA

Service design has changed, and so have the men and women who practice it. That’s because they’ve had to adapt; they’ve had to evolve in order to overcome Bad Digital Experiences. Fortunately, we’ve assembled some heroes to discuss where this discipline is having the greatest impact on business and the changing needs of the people it serves. Judy Mellet - Director, Service Design & Strategy @ Telus Digital Uzair Sukhera - Sr. Director, Product & Design @ mobileLIVE Andrea Guertin - Vice President, Design Strategy @ Bridgeable Patrick Bach - Director, Service Design @ CIBC
Can Service Design Save the Day?!

The company is lending its digital expertise to help usher in the future of health care. Mississauga, On (March 11, 2021) – mobileLIVE is gifting Trillium Health Partners (THP) more than $100,000 to help create a new kind of health care for a healthier community. The gift includes $35,000 for the future redevelopment and expansion of Mississauga Hospital and $75,000 worth of professional IT services over the next five years. Increasingly, it has become the responsibility of enterprises to contribute to the reimagining and creation of a better world, and mobileLIVE believes that supporting our health care system and workers is integral to a thriving, resilient community. “There is a growing need in our community, especially among our most vulnerable,” says Jahan Ali, Founder & CEO of mobileLIVE. “Social responsibility is one of our cornerstones since inception, and the last year has only reignited our commitment to meet that need. With THP, in addition to making a financial contribution, we wanted to make a tangible impact by engaging our talented team to support THP with IT services.” THP already has an embedded culture of innovation. This partnership will accelerate and enable the advancing transformation through technology and expertise. “Now is the time to rethink health care and hospitals to create a more complete, equitable, inclusive and efficient system for our community of patients and their families. The opportunity to leverage the expertise of mobileLIVE is a way to accelerate success and we are so grateful for their partnership and support,” says Caroline Riseboro, President & CEO of Trillium Health Partners Foundation.
mobileLIVE donates $100,000 To Trillium Health Partners

Workshops and team collaboration have always been beneficial: View problems from different perspectives Get to the root of the problem Encourages creative problem solving and innovative thinking Keep teams focused on outcomes Increased accountability and investment Immediate, more tangible and actionable output There fun So how do we replicate all of that living in a predominantly virtual world? You’re about to find out. Learn how to reignite innovation, reconnect with your teams, and get from problem to solution faster, even when working remotely. Created to help enterprises overcome some of the challenges their teams are presently facing, this session will cover. The fundamentals of Remote Collaboration Why it’s critical for teams working remotely The best tools to connect and collaborate Strategies & Best Practices that drive participation The Future of Remote Collaboration And more
Virtual Tools & Strategies For Successful Remote Collaboration

Whether talking about native, mobile web, or hybrid applications and regardless if your project is iOS or Android, Appium is the most popular open-source framework for mobile application testing – and it’s easy to see why. And because of that, we’re going to talk about something else. Everyone knows that Appium is great, but what I’ve noticed is this common knowledge has resulted in more and more people turning to it in blind faith, without fully understanding how to get the results that made it so appealing in the first place. I want to fix that with these: Test using a Cloud Platform Device Selection & Fragmentation Using one script for both OSs Android and iOS If you are looking for efficient and cost-effective mobile automation, these not always followed best practices are critical. Those three best practices are what you have to do. Now, I’ll take you through how and why you should. Test Using a Cloud Platform – A Change in Mindset Most mobile application automation is done using a local setup where you have a mobile device connected to a laptop executing the tests, typically in an office where single or, multiple stations are set up as illustrated below. However, as everyone knows, typical is not what you would use to describe our current reality. And for many if not most predominantly working remotely, a new set of challenges arise: Setting up Appium can be tedious and time-consuming, especially for iOS. Devices cannot be maintained in a lab-style environment from home as devices need to be periodically reset. Loss of network connectivity or downtime within the office cause additional delay and hassle. Reliance on remote viewing of the devices can be slow and inefficient. The limited breadth of testing and coverage due to not being able to test on many different devices using the local machine. Testing bottlenecks – because you can’t execute everything on your laptop. Setting up parallel execution requires effort. And this was just off the top of my head! These challenges aren’t feasible given our current remote work environment. So what do you do? You write your scripts on your laptop and execute them without worrying about setup, bottlenecks, or limited breadth of testing. And to do that, you need cloud-hosted environments like Saucelabs, Experitest, Perfecto and others. Personally, I prefer Saucelabs and Exepritest. Here are a few reasons why: They offer a large cloud for continuous testing with the industry’s most comprehensive coverage for mobile devices. Highly scalable platform for increased parallel execution, decreased execution time, and elimination of bottlenecks. Provides complete transparency on your testing efficiency using videos, screenshots, logs and full analytics to determine where gaps may exist. Using an integrated development platform makes Appium automation even easier by directly executing Appium tests from Eclipse & IntelliJ, using embedded simple editors and detailed views. Offers hybrid support that connects to a local or remote device and uses the device’s reflection for instant visual feedback on device behaviour. Use Object Spy, object repository and XPath identifiers to automate complex scenarios. Modify tests and create a complete, robust automated mobile testing project (Experitest). Advanced automation capabilities to increase coverage. Test advanced use case scenarios such as barcode and check scanning, audio features, GPS simulation, 3rd party applications (Facebook, maps, e-commerce, etc.) TouchID, or customized elements such as sliders, pickers, tables, gestures, and more. While I am not a salesperson, this is usually the part of the conversion where the cost comes up for this setup. Local Setup vs Cloud Platforms Testing for 6 months on 12 real devices Local Setup costs are Device Cost (one time) – $800/device x 12 devices and 2-4 Laptops (2 Mac, 2 Windows) is equal to $12,600 and Cloud-Hosted Devices costs are License cost – $999 for (4 concurrent tests per month) for 6 months and One laptop is equal to $6,700 You can see that the cost for doing six months of testing on 12 real devices using a local setup is double the cloud’s cost. Why would you pay more to make your life more difficult? It’s clear that Appium automation on cloud platforms is the way as we advance. Choosing your devices for testing effectively While the abundance of device options is great for consumers, this fragmentation is a major headache for developers and testers. Currently, we have two main OSs for mobile phones, Android and iOS, which seems simple enough until you account for the different models, makes, and versions – especially for Android. It’s not feasible from a time and resource perspective to test all the combinations. This is why device selection is so critical, and here are some steps to help you narrow down your choices: 1. Visit the following https://gs.statcounter.com/ to get the latest mobile phone stats. 2. Get the mobile device market share, e.g for Canada: It means that in Canada 50% of people use Apple and the rest use Android devices. It also tells you which devices are mostly used. From the list, select the top 4 devices. 3. Android OS share. Android(10.0 10) 49.9% Android(9.0 Pie) 21.32% Android(8.0 Oreo) 9.05% Android(7.0 Nougat) 4.96% Android(7.1 Nougat) 3.81% Android(8.1 Oreo) 3.54% 4. IOS share iOS 13.6 34.24% iOS 13.1 26.17% iOS 12.4 9.52% iOS 14.0 8.78% iOS 13.5 5.32% iOS 13.3 3.03% 5. Resolution Share (1920x1080) 11.79% (1366x768) 8.17% (768x624) 6.73% (375x667) 5.91% (414x896) 5.72% (1440x900) 4.45%. Screen Resolution Stats in Canada - September 2020 Based on the information that is available, you can narrow down your list and create the best feasible combination of make, OS, and version. One Script / 2 OSs There are many ways to write efficient test scripts. Most engineers follow page models by default which is a good thing. But how do you create one automation script that will work on both Android and IOS? A properly developed application’s behaviour and logic are usually the same on both Android and IOS. There is no point in doubling the work by duplicating the business logic and developing two scripts, one for Android and one for iOS. Here is how you can tackle the problem at hand. The following screenshot shows an example of a unified Appium test to calculate restaurant bill. For a unified test to work on both Android and iOS, the following must be done. 1. The Appium tests need to instantiate the appropriate driver based on the configuration. 2. Use page factory methods to define elements for both OSs and for each page of the application. The annotations AndroidFindBy and iOSFIndBy will help pick the right element based on what OS the test is running automatically. 3. Create methods to implement the test steps. The following method will click on the button to calculate the tip. 4. Call the page methods from the test class to complete the test case. Take Away The world we live in has changed and the way we work and the way we test has to adapt. The key is to develop and perform testing with efficiency in the forefront, trying to avoid duplicate efforts and unnecessary costs – that is exactly what the above was intended to do. Hopefully, after this, you be more efficient, more effective, and better equipped to perform automated testing of mobile applications in whatever your new setting is and with the highest ROI possible.
3 Things Every Appium Developer Should Do For Mobile App Testing

In response to physical distancing, capacity restrictions, and unpleasant customer experiences, Stand-in is an app designed to regulate the flow of people going inside of a business, so there isn’t a line outside. Toronto: December 3, 2020 – Today, mobileLIVE has officially released Stand-in, an application designed to help businesses and customers navigate the new normal of physical distancing and capacity restrictions. Conceived after an unpleasant experience lined up outside of a big retailer and in anticipation for the cold winter ahead, Stand-in is a line-management system that ensures businesses can safely reach and maintain capacity restrictions inside without causing overcrowding or unsafe lines outside. “Not in my wildest dreams would I imagine having to wait in line to buy fruit at the grocery store, let alone 45 minutes,” says Hussain Qureshi, President of mobileLIVE. “But after that experience, seeing how inefficient and unenjoyable it was despite the increased staff, I knew we had to do something that would help these businesses operate safely. Nobody should be left out in the cold.” Stand-in offers a more comfortable and safer retail experience, focusing on helping businesses that have already suffered many recent hardships. After registering the business and its locations, customers can join a “virtual queue” from anywhere, providing them with their position in the queue and estimated wait time. When it’s their turn, they will be notified in advance and given the fastest route to get to the business. They will be automatically checked-in and out, all while providing real-time foot traffic data of customers to the business. Stand-in is entirely self-serve and requires no expensive hardware other than a smartphone. It can even work if people don’t have the application. Stand-in is free for both businesses and customers and is available now for iOS and Android devices.
Introducing Stand-in

Do you feel that your technology teams are not living up to the expectations for your Digital Transformation? Do you find technology to be a significant bottleneck in the rollout of your next-generation experiences? Does it take months to roll out new features and capabilities from concept to market? Do you believe that your API platforms fuel your business growth or create a hindrance in your vision for future growth? Can your cloud support the immediate demands of the market efficiently and effectively? Have you seen tangible results from your cloud transformation yet? If any of this sounds familiar and you’d rather it be a past problem and not a present one, then you’re in luck. Watch Uzair Sukhera (Director of Design & Innovation) and special guest Luca Marashi (VP of Engineering @ CTO.ai) as they discuss how to tackle these challenges and accelerate your digital transformation by simplifying your technology.
How to Simplify Technology & Accelerate Digital Transformation

Discover a framework that takes your ideas from Abstract to Concrete and into the hands of your users. One that gives you better design through collaboration and less risk by testing your business hypothesis with your users. Why would you want to create a product any other way?
Design Thinking: Taking you from Abstract to Concrete

There is undeniable value in a Design System; just look at what we titled this webinar. However, looking again at that title, you may notice something – the word Development. Despite how beloved Design Systems are by Designers, they are not the only recipient of its value. Implementing and benefiting from Design Systems hinges on the heavy lifting from Development teams. And in this webinar, you’ll learn not only how to mitigate challenges but: How Design Systems improve user experience, especially for multi-branded experiences The benefits of developing reusable UI blocks (hint: it’s time, effort and cost) How Design & Dev collaboration improves output & delivery Utilizing a common design language between Design & Dev Effective collaboration between Design, Dev, QA, and more! Quantifying the benefits over conventional development methods Setting & scaling your design system across the organization And more!
Design Systems: Better Development, Faster, and for Less

Theme Switcher is a Figma Plugin that allows designers to shift between multi-brand themes effortlessly. Intrigued? You should be. By designers, for designers, this plugin improves workflow and reduces the time spent on projects by 25%. Once downloaded, easily: Switch between multiple style sets Sync from Local Styles Apply Colour Themes With no external platform required, and all in less than three clicks. In this short demo video, you’ll discover what Theme Switcher offers; including, how to create naming conventions for brand themes, how to turn those into Local Styles, and more.
Theme Switcher Demo: How designers can use this workflow plugin

As an organization, as a team, and even just as a designer, how do you: Create productive & efficient workflows? Find the right talent with the rights skills? Grow & strengthen your design teams? Improve the value and quality of your work? The answer to all of the above is DesignOps. And if you have questions then this webinar and its expert panel will likely answer them all and more.
Demystifying DesignOps: From Theory to Practice

Today’s reality is one of accelerated product lifecycles, competitive pressure on a global scale, rapidly changing technology, and an ever-growing number of market segments all demanding their own unique experiences. That is, until tomorrow, when the demand shifts yet again. So how do you succeed in a world of constant change? In this session, you’ll discover how to: Organize a culture that drives meaningful outcomes Empower your people with autonomy Shift towards Human-Centred Delivery Manage the end-to-end value creation process Centralize services and self-serve platforms And more!
Delivering Value in the Age of Constant Change

Most major brands and product companies have already adopted Design Systems and for a good reason. Good design results from good design practices and few bring as much efficiency, consistency, and organizational value as a well-implemented and utilized Design System. This session was created to give a candid view of Design Systems in action, with a particular focus on small to mid-sized and legacy organizations. Addressing everything from design and developer collaboration to garnering stakeholder buy-in, and spanning the theoretical to the practical, you’ll discover not only the “Who, What, Why, and How” of Design Systems, but also our own unique and straightforward framework for successfully creating one. In this webinar, we answer: What is a Design System, and why you’d want one? How do you successfully build them, and who should be involved? What are their key components? How do you use and maintain one? Open Source vs Design System? And more!
Design Systems: Creation, Application, and Value

To better understand Microservices, you need the perspective of the developers who create them and the business side that drives them. You need men and women who haven’t just read about them, or work with them in isolation but have had their boots on the ground at a variety of client locations, on dozens and dozens of projects, that span multiple industries and verticals, and have driven successful outcomes. So we gathered those people up and recorded them!
An Open Discussion: “Who should own Microservices?”

The Accessibility for Ontarians with Disabilities Act (AODA) means that all public and private sector organizations with 50+ employees must make web content accessible to WCAG 2.0 AA standards. Failure to comply can result in fines of up to $100,000/day. But what does it mean or take to be AODA compliant? See for yourself in this webinar as we take you through: An overview of AODA regulations and requirements Give advice on accessibility testing techniques to ensure your website meets WCAG standards and is AODA compliant Tell you how you can make the business case for accessibility at your organization
AODA Regulations in 2021: Digital Accessibility and Compliance

Discover a solution adopted from large enterprises’ playbook and specially adapted for small to medium-sized businesses. Learn how to leverage the cloud to keep your teams communicating and collaborating anywhere, guaranteeing uninterrupted operations and service during a crisis while: Generating revenue Future-proofing your business Lowering operational expenditures Empowering remote work Scaling and growing with your business No segment has been harder hit by recent events like SMBs. That is why we would like to make ourselves available to answer any of your questions about the cloud, future-proofing your operations, or moving forward in our new post-pandemic reality. Request your FREE 1:1 consultation with one of our experts today to learn more.
How Small & Medium Sized Companies can Future-proof their Businesses

Watch as we discuss the possibilities and potential around the new business models and exciting experiences that 5G has the ability to create for consumers, for business, and society at large. Retail, entertainment, manufacturing, healthcare, telecommunications, and more; it’s no longer a matter of how 5G will revolutionize these industries, but when. And that is up to us. Stop imaging. Start doing.
5G Technology, Business Models, and Experiences of the Future

Recent events have shown all of us just how quickly the world can slip into chaos and confusion. But that “chaos” isn’t limited to a worldwide pandemic. It happens in varying degrees in our day to day lives. However, despite the chaos, whether global or professional, a business must keep moving forward. Customers still have problems that need to be solved, and your ideas still have the potential to solve them – that is if you can take them from concept to fruition. Watch and discover our framework for cutting through the chaos, and going from the problem space to rollout; getting your MVP where it belongs – in the hands of your customers.
Design Thinking: How To Shift Seamlessly From Chaos to Clarity

Discover HyperAutomation – the intersection of RPA, Test Automation, and AI – as we showcase how to successfully automate your E2E environment and drive ROI. This is a live recording featuring Jahan Ali, Founder and CEO of mobileLIVE, Noel Kirthiraj, CEO of UXPLORE, and Ragavan Balasubramaniam, Test Automaton Manager of mobileLIVE. It was hosted and moderated by Crina Bildea, Director of Sales.
HyperAutomation: Overcoming E2E Complexity

For your convenience, here is the full transcript of the Q&A between Naresh Babu – Director, Engagement Practice and Uzi Murad – Account Executive. Uzi Murad: Hello and welcome, I’m Uzi Murad and here with me today is Naresh Babu, head of strategy and architecture at mobileLIVE. Hey Naresh. Naresh Babu: Hi Uzi. Uzi: These days we see more and more enterprises adopting Multi-Cloud strategy. In fact, a recent survey by IBM showed that about 85% of executives are saying that they’re already running Multi-Cloud, or will be moving there within the next three years. So what we want to understand today is what’s driving organizations to the Multi-cloud strategy, and what are some of the challenges they are facing. But before we dive into the details there, Naresh, can you explain what we mean by Multi-Cloud? Naresh: Yeah. A Multi-Cloud strategy is just utilizing, I would say, two or more public or private clouds, for example, let’s say, you are utilizing AWS or GCP, or Azure and AWS, we can call it as a Multi-Cloud. Uzi: I see. And is that strategy a good fit for any type of enterprise? Naresh: So I would say Multi-Cloud strategy is a right fit for larger enterprises, because of the cost and complexity of running and maintaining it. For small to medium organizations, I would recommend Hybrid Cloud as the option. Uzi: And what does Hybrid Cloud mean? Naresh: Yeah. So, when you are running a local data center, and then you’re extending some services or a replication of that into a public cloud, you can call that as a Hybrid cloud. But there is terminology, something like Hybrid-Multi Cloud where there is a local data centre as well as more than two or three public clouds. So the combination of that is called Hybrid-Multi Cloud. Uzi: I see. So, definitely doesn’t sound trivial, I wonder what’s driving so many enterprises in that direction. I know many of them have the dual vendor strategy, they want increased competition, keep the cost down, but is that really what it’s all about? Naresh: Yeah. I would say yes. There are multiple drivers for the organizations and from my perspective, I would say it’s really the flexibility for picking the services, one versus the other. Let’s say for example, if you are in AWS and Azure, is AWS Lambda better versus Azure Functions? Or the second aspect I would say, is from the security aspect, where it’s very hard to bring down a Multi-Cloud environment using a denial-of-service-attack or DDOS attack, I would say. And the third aspect, I would say is data recovery or disaster recovery where you can create the most reliable architecture which can reduce a single point failure as well. Uzi: So I’m hearing: ability to do best of breed, improve the security, and finally disaster recovery and availability. Naresh: I would say, yes, yep. Uzi: So what are some of the top challenges that we are facing when implementing Multi-Cloud strategy? Naresh: Yes, so, when it comes to any new technologies, there are a lot of challenges. So when you talk about Multi-Cloud, i would say it’s still evolving, and organizations are already into it, but one of the key challenges is that there is no industry standard in terms of giving architecture guidelines or principles or best practices to be implemented. There are not many tools in the market that can help support or monitor the Multi-Cloud environment. And when it comes to provisioning, deploying and testing of it, you don’t see much tools as well. So from an application standpoint, I would say, one of the problems is identity brokering in the Multi-cloud environment, where each service provider might use their application to identify the request and response. Uzi: I see. So you mentioned identity brokering, what do you mean by that? Naresh: Yes. So let me give you an example. So when you are running an application for example in a local data centre, which has typically been authenticated by an active directory, and this has to contact or receive some information from your AWS file system, let’s say for example. AWS, on the other hand, uses IM service, which is identity management service to authenticate any request that is coming in. So how do you translate an AD token or AD authentication to automatically authenticate in AWS is called identity brokering. Uzi: I see. So what would be your recommendation to enterprises that are implementing the Multi-Cloud strategy? Naresh: Yeah. So I would say I can see in the industry there is a new adoption, it’s called infrastructure as code, which is one of the ways that you can convert doing admin tasks in terms of, from provisioning, to deploying, configuring, testing the virtual machines, creating containers, deploying containers, creating serviceless functions, deploying them: all of that can be considered as a code and this code can be run by anybody. Which typically what I’m trying to explain is an automated CI/CD pipeline spanned across a Multi-Cloud environment. Uzi: You mentioned tools, you said there are not too many tools out there. So are there any tools, and can they do the Multi-Cloud management? Naresh: Yeah, so, I’ve come across very few tools in terms of Multi-Cloud management, one would be Flexera, the other one would be Embotics, so I would say they are somewhere closer in terms of managing Multi-Cloud environments. And then there is another tool which again is being more famous is IBM Cloudpark, and people are mostly using it for data insights. And I’m thinking that if we can use, there is a tool called Terraform, if you can combine Terraform with Ensemble, which can act as a great IT automation tool, that can automate most of the IT tasks in terms of public as well as private cloud. I would say there is still a huge demand from enterprises to come up with a holistic platform that can allocate the workload strategy, at the same time managing the business containers in this hybrid Multi-Cloud environment. Still we have yet to see a unified tool that would act as a unified management platform. Uzi: So that unified infrastructure management tool, that’s what we really need? Naresh: I would say yes. Uzi: And do you see any of the major cloud providers coming out with this tool any time soon? Naresh: Yeah, why not right? I can see everyone is trying to get there, there’s a lot of third-party tools that are coming up. And definitely Azure and AWS have already implemented tools to have Hybrid Cloud management, and nothing is stopping from making a Multi-Cloud management platform, or unified infrastructure management platform. Uzi: Thank you Naresh and thanks everyone for joining us. Naresh: Thanks Uz
What’s Driving Large Enterprises to Multi-Cloud

Learn how to put your customers at the centre of everything you do. We can help you shift business-centric to human-centric through experience transformation.
Design Thinking: the Experience Transformation Journey Done Right

It’s an honour to announce we have earned the distinguished designation of “The Gold Standard” from Deloitte Canada. It is awarded to Canada’s Best Managed Companies who excel in Strategy, Capability, Commitment, and Growth for four years in a row.
The Gold Standard of IT Managed Companies: Canada’s Best Managed

What does the future hold? Few know with much certainty. The only certainty of the future is it guarantees change. What won’t change, however, is our commitment to helping you succeed in that future – no matter what it brings.
Past, Present, and Future: Using Cloud, Data, Innovation, & More

No matter the industry, and whatever the vertical, Test Automation is no longer optional for excellent customer experience – it’s mandatory. Discover how with our intuitive test automation services, great experiences and reduced OPEX don’t have to be mutually exclusive.
Intuitive Test Automation for Brilliant Customer Experiences

Richmond Hill, ON: The Ontario Minister of Research, Innovation and Science, Reza Moridi, paid a visit to mobileLIVE headquarters in Richmond Hill, to learn and discuss the company’s innovation and research practices. Jahan Ali, CEO of mobileLIVE, along with other members of the leadership team welcomed him to the office. During the tour of the office facilities, Minister Moridi was made familiar with the innovation practices and disruptive products in the areas of digital transformation and artificial intelligence such as UXPLORE that are being designed, built, modified, and marketed from mobileLIVE’s ready repository. To commemorate the Minister’s presence and etch a memory, the leadership team along with CEO, presented a plaque to thank him for his bold vision, leadership, and contribution in the field of research and innovation in Richmond Hill and Ontario.
Minister of Research, Innovation and Science visits mobileLIVE HQ

Richmond Hill, ON: Despite the stagnant economy of the country, mobileLIVE, a Richmond Hill based technology company, has earned several recognitions from the industry stalwarts for its fast growth, innovative solutions, high client retentive power and timely delivery of services. Deloitte recently recognised the fastest growing companies in Canada as well as North America in their Technology Fast 50™ and Technology Fast 500™ programs. These companies were identified for their disruptive innovations and potential for continuous growth. mobileLIVE ranked 13th as the Fastest Growing Technology Company in Canada on Deloitte Technology Fast 50™awards with a steady growth of 999 percent. The company also secured 119th position among the other Fastest Growing Companies in North America on Deloitte’s 2016 Technology Fast 500™. Also, interestingly, it is the 8th technology company from Ontario which had a steady growth despite the stagnant economy. Jahan Ali, the CEO of the company believes, “Our business is to ‘simplify everything’ for end-users through innovative solutions. This basically gives us the zeal to perform and deliver.” “Fast 50 companies are the cutting-edge innovators leading the technology industry in Canada,” said Anders McKenzie, Technology, Media and Telecommunications Managing Partner for Deloitte in Canada. “Their bold vision, unrivaled growth and true commitment to innovation allow them to not only improve today’s world, but also shape tomorrow’s.” mobileLIVE’s unmatched quality services, innovative technology solutions, helped the company to win the CAMSC “Supplier of the year” award. Ali dedicates the win to his people. “My people are my IP (Intellectual Property). It’s the team’s dedicated efforts that made us successful.” 83 percent of the CEOs in a Deloitte annual survey of Technology Fast 50 mentioned that an inclusive workplace is one of the top three strategic drivers of their company’s success.
Technology solutions firm wins accolades for remarkable growth

Richmond Hill, ON: mobileLIVE won the 13th position in the 19th annual Deloitte Technology Fast 50™awards for demonstrating bold innovation, dedicated leadership and strong growth. The Deloitte Technology Fast 50 program celebrates leaders in the Canadian technology industry and tracks the successful growth of Canadian-grown leaders. The program augments the broader Deloitte North American Technology Fast 500™ initiative with winners automatically eligible for this elite ranking. “Fast 50 companies are the cutting-edge innovators leading the technology industry in Canada,” said Anders McKenzie, Technology, Media and Telecommunications Managing Partner for Deloitte in Canada. “Their bold vision, unrivalled growth and true commitment to innovation allow them to not only improve today’s world, but also shape tomorrow’s.” To qualify for the Deloitte Technology Fast 50 ranking, companies must have been in business for at least four years, have revenues of at least $5 million, be headquartered in Canada, own proprietary technology, conduct research and development activities in Canada and invest a minimum of five percent of gross revenues in R&D.
mobileLIVE ranks 13th Fastest Growing Technology Company in Canada

Richmond Hill, ON: mobileLIVE ranked 119th on Deloitte’s Technology Fast 500™, a ranking of the 500 fastest growing technology, media, telecommunications, life sciences and energy tech companies in North America. “Today, when every organization can be a tech company, the most effective businesses not only foster the courage to explore change, but also encourage creativity in using and applying existing assets in new ways, as resourcefully as possible,” said Anders McKenzie, Technology, Media and Telecommunications Managing Partner for Deloitte in Canada “This ingenious approach to innovation calls for the encouragement of curiosity and collaboration both within and outside the office walls.” Overall, 2016 Technology Fast 500 companies achieved revenue growth ranging from 121 percent to 66,661 percent from 2012 to 2015, with an average growth rate of 290 percent.
mobileLIVE ranked number 119th Fastest Growing Company in North America

Richmond Hill, ON: The Mayor of Richmond Hill, His Worship Dave Barrow paid a visit to the mobileLIVE headquarters in Richmond Hill. The company CEO, Jahan Ali, along with the senior leadership team welcomed him and to the office. He was made familiar with the mobileLIVE office facilities as he toured along the office premises. The senior leadership team along with Jahan Ali, the CEO, handed him a plaque to commemorate the visit and thanking him for his vision, leadership, and commitment to making Richmond Hill a part of the largest technology cluster in Canada.
Mayor Dave Barrow visits mobileLIVE

Richmond Hill, ON: The Toronto Board of Trade has declared mobileLIVE as a finalist for their Business Excellence Award – “Emerging Entrepreneur”. This award recognizes a business that has seen rapid innovation-driven growth achieved by disrupting the status quo to spark and influence the industry transformation.
mobileLIVE gets nominated finalist for “Emerging Entrepreneur”

Richmond Hill, ON: mobileLIVE secured 16th position in PROFITGuide’s Startup 50 for its entrepreneurial achievements. PROFITGuide, over the last 29 years has been commonly known for acknowledging Canada’s top Fastest Growing Companies on their revenue growth. “These companies promise to transform Canada’s economy through innovation and determination,” says James Cowan, Editor-in-chief of PROFITguide and Canadian Business. “Their stories of early success are truly inspiring.” This feat of excellence synced mobileLIVE with the elite community of Canada’s most successful, vibrant, and important businesses.
mobileLIVE ranks 16th among “Canada’s Top New Growth Companies”

Richmond Hill, ON: mobileLIVE bagged the TechConnex Technology Leadership Award as the “Momentum Company of the Year” for continuous excellence in innovation and a commitment to the knowledge-based sector in the Greater Toronto Region. The award also recognized the zeal of the company in consistently reaching out to new customers or delivering new services within an existing customer framework, increasing revenues, adding employees, encouraging community involvement and embracing sound business fundamentals. TechConnex’s Technology Leadership Awards Gala & Showcase acknowledges the excellence amongst technology businesses and their achievement in one of five important categories of peers within the GTA Tech Ecosystem.
mobileLIVE wins the “Momentum Company of the Year” Award

Richmond Hill, ON: mobileLIVE won the prestigious 2015 Ontario Business Achievement Award (OBAA) in the “SME Excellence category.” This year, over 100 businesses submitted their applications for an OBAA award and out of them, mobileLIVE‘s achievements were recognized. Hosted by the Ontario Chamber of Commerce (OCC), the OBAA is a unique event that showcses some of the province’s most successful businesses and the positive impact they have made on Ontario’s economy. For 33 years, the OBAAs have acknowledged and celebrated Ontario’s best in business – awarding organizations that personify integrity, hard work, innovation, entrepreneurship, and export excellence. Jahan Ali, CEO of mobileLIVE accepted the award from the sponsors RBC. Commenting on the success, Ali says “I certainly owe a big thank you to the Ontario Chamber of Commerce for creating this wonderful opportunity and to my team who have made this possible. We are extremely proud of this recognition which will further fuel our quest for excellence.”
mobileLIVE won the prestigious “2015 Ontario Business Achievement Award”

Richmond Hill, ON : The Ontario Business Achievement Awards (OBAA) organized by Ontario Chamber of Commerce, recognized mobileLIVE for delivering Innovation, enhanced End User Experience and Service Excellence. The Ontario Business Achievement Awards (OBAA) organized by Ontario Chamber of Commerce, is the most prestigious awards gala in the province with a single focus on celebrating business success. For over 30 years, businesses have been awarded OBAAs for their achievements in areas including sustainability, innovation, market expansion, and exporting. Only two finalists were selected in each category from this year’s pool. mobileLIVE is honoured to be one of these finalists and is exceptionally proud of this significant achievement. It is a testament to the quality of work provided by the highly talented and experienced team working at mobileLIVE. The awards are scheduled for Wednesday November 25, 2015 at the Metro Toronto Convention Centre.
mobileLIVE is being recognized for delivering Innovation & Business Delivery Excellence

In the recently held, Ontario Business Achievement Awards (OBAA) organized by Ontario Chamber of Commerce, mobileLIVE received some excellent words of appreciation from the various business leaders of the region for its excellent business service delivery and innovation led practices. “It’s a well-known fact that SMEs are the backbone of Ontario’s economy and mobileLIVE is no exception. By centralizing operations here in the province, this organization is actively creating jobs and stimulating our economy from their hometown of Richmond Hill.” – Allan O’Dette, President and CEO of the Ontario Chamber of Commerce “By harnessing the unlimited potential of modern technology, mobileLIVE is making their customers’ products more relevant, effective and user-friendly with their innovative services in a highly competitive marketplace.” – Karl Baldauf, Vice President of Policy and Government Relations at the Ontario Chamber of Commerce “Finalists like mobileLIVE are setting the standard for innovation and creativity on the internet. Congratulations to mobileLIVE, proud member of the Richmond Hill Chamber of Commerce, on being a finalist for the Ontario Business Achievement Award’s SME Excellence Award.” – Hon. Bryon Wilfert, Chair of the Board at the Richmond Hill Chamber of Commerce mobileLIVE thanks Ontario Chamber of Commerce and the Ontario Business Achievement Awards Team for showering such inspiring words to the team. Jahan Ali, CEO, mobileLIVE concludes, “Create an experience beyond a product or a service and success will follow.”
What Ontario business leaders are saying about mobileLIVE

Richmond Hill, ON: Canadian Aboriginal and Minority Suppliers Council (CAMSC) presented mobileLIVE the 2016 Business Achievement Award, “Supplier of the year” for demonstrating growth in sales and employment; consistently providing high quality products and services at competitive pricing; offering innovative solutions; and significantly delivering greater benefits through growth and development to their community. On winning this award, mobileLIVE was offered a scholarship to participate in a Tuck MBE program sponsored by the General Motors. The company is proud to share the prestigious frame with other CASMC Business Achievement Award winners like E&Y (Ernst & Young), Triplewell Products, Sodexo, Stratus Plastics International, RBC (Royal Bank of Canada), and BMO (Bank of Montreal).
mobileLIVE wins “Supplier of the Year” Award

Richmond Hill, ON – mobileLIVE is sponsoring charity JDRF via TELUS’ third annual Telecom Networking Event, to be held on June 12, 2014 at the Metro Convention Center, South Building. Event Detail: Join TELUS for our third annual Telecom Networking Event: Talking Tech in Healthcare TELUS will be hosting its third Telecom Networking Event which is all about connecting with the telecommunications community and connecting with reputable charities. Various executives of the telecommunications sector including senior executives from TELUS (Sales, Consumer and Business Marketing, Procurement, Technology, and Channel Operations) have supported this cause and have regularly attended in past years. It’s a great opportunity to network and connect with a variety of senior executives, all while contributing to a great cause. Some of the attendees we’re expecting from TELUS this year are: Peter Green, President and SVP, TELUS Business Solutions Lloyd Switzer, SVP, Tech Strategy Joe Goodbaum, President, TELUS Channels Michael Guerriere, Chief Medical Officer, TELUS Health Tony Krueck, VP, Business Products & Services Jim Senko, VP, SBS and Mobility Phil Moore, VP, Large Complex Deals Eric Fergin, VP, Supply Chain and Procurement Drazen Lalovic, VP, Market Planning Alfred Baghouzian, VP, Devices and Applications Tickets are on sale now for $20, which include snacks and complimentary beverages. A cash bar will also be available. All proceeds will go to JDRF and United Way. With your help, we can make the event an even bigger and better success than previous years. Time & Place Date: June 12, 2014 Time: 5:30 – 8:30 PM Venue: Metro Toronto Convention Centre ; 222 Bremner Boulevard; South Building Price: $20
mobileLIVE sponsors charity JDRF via TELUS’ third annual Telecom Networking Event

Markham, ON : mobileLIVE has signed an agreement with TELUS to perform its HSPA Device Certification Testing for the next 3 years. mobileLIVE has one of the best 3rd party state-of-the-art lab in Canada for smartphones and IoT that can test in any service provider environment. “Our lab can simulate satellite and any cellular networks worldwide eliminating the need to travel to test roaming and location-based services. We can also simulate 100+ different types of male and female voices and accents, various interference, and noisy conditions delimiting the time to travel to different places to test voice quality and performance, all inside our lab,” explains Jahan Ali, CEO, mobilelIVE. Ali adds, “It’s a big business development for us. And we appreciate the trust and confidence that the market has on us.”
TELUS has selected mobileLIVE to perform its end-to-end HSPA device testing for next 3 years
Toronto: A recent report published by the Brookfield Institute for Innovation and Entrepreneurship says women in Canada are under-represented in the Canadian technological workforce. In light of recent International Women’s Day and its theme “Balance for Better,” Canadian tech service provider mobileLIVE decided to showcase how they’ve been working towards a more balanced workforce. “We are a team of 300+ technical and non-technical roles, working together to accelerate digital transformation for our clients. It is undoubtedly a proud moment for us to say that 31% of our total team is women, and it is a well planned strategic move to enhance the representation of the female force in our teams” explains Aftab Ali, Head of Human Resources at mobileLIVE. The Brookfield Institute for Innovation and Entrepreneurship explains women account for 20% of the tech workforce in comparison to their 80% male counterparts. Furthermore, the report also claims, “women participate at lower rates in tech, across all age groups.” In 2018, MaRS, Feminuity, and Fortay conducted a survey to examine diversity, inclusion and belonging in Toronto’s tech sector. Women in Toronto’s tech sector reported “lower levels of diversity, inclusion and belonging compared to men.” The report also highlighted that “women in Toronto’s tech sector also feel less engaged in decision-making processes at work.” “The average age of women at mobileLIVE is around 33, but we have a wide range,” affirms Aftab. “From GenZ to Millennials to Baby Boomers, with each excelling in their career trajectory. It is also worth noting that our leadership team comprises of 25% women, which sets a great balance within the organization.” At present, 28% of technical roles at mobileLIVE, including Software Developers, Business System Analysts, Data Scientists, Project Managers, Quality Assurance Engineers, Network Engineers, are held by women. On the other hand, 58% of the non-technical roles involving departments like Human Resources, Marketing, Finance, and Administration are held by women. From flexible work schedules, time off for childcare, exclusive shopping perks, health benefits, and a family-like culture, mobileLIVE continues to reaffirm their commitment in promoting equality and balance for women in the workplace and the world.
mobileLIVE surpasses the national average for women in tech

Toronto: For the third year in a row, mobileLIVE is being recognized for its overall business performance and sustained growth with the prestigious Canada’s Best Managed Companies designation. The 2019 Best Managed program award winners are amongst the best-in-class of Canadian-owned and managed companies demonstrating excellence in strategy, capability, and commitment to achieve sustainable growth. Entering its 26th year, Canada’s Best Managed Companies is one of the country’s leading business awards program recognizing Canadian-owned and managed companies for innovative, world-class business practices. Every year, hundreds of entrepreneurial companies compete for this designation in a rigorous and independent process that evaluates the calibre of their management abilities and practices. The “CIBC is pleased to congratulate mobileLIVE on being named one of Canada’s Best Managed Companies, recognizing its excellence in leadership, business performance and innovation,” said Dino Medves, Senior Vice President and Head, CIBC Commercial Banking. “As a sponsor of the Canada’s Best Managed Companies program for over 20 years, CIBC is proud to celebrate private companies like mobileLIVE as leaders in their industry.” “It is humbling every year to see the calibre of businesses that earned this designation,” says Jahan Ali, CEO and Founder of mobileLIVE. “Far from intimidating, we find it inspiring and use it as motivation to continue our streak into the fourth year.” Applicants are assessed on their sustained growth by a panel of independent judges against a predetermined set of attributes that include a clear strategy and vision, investment in capability and commitment to talent. “2018 was yet another big year for us,” exclaims Hussain Qureshi, President of mobileLIVE. “We grew our clientele, added industry verticals, and geographies, all while reaffirming our innovative spirit and solidifying our performance-driven culture. One of the biggest reasons we’ve been able to sustain this growth – and this designation – is the alignment between our business strategy and culture that acts as a framework for all our efforts.” “This year’s Best Managed winners are a testament to the success found when businesses invest in talent, innovate intentionally, and think long-term,” said Peter Brown, Partner, Deloitte Private and Co-Leader, Canada’s Best Managed Companies program. “These companies should be proud of this achievement, and their responsibility in acting as role models for other Canadian businesses.” 2019 winners of Canada’s Best Managed Companies award will be honoured at the annual Canada’s Best Managed Companies gala in Toronto on April 17, 2019. The Best Managed program is sponsored by Deloitte, CIBC, Canadian Business, Smith School of Business, TMX Group and MacKay CEO Forums.
mobileLIVE named one of Canada’s Best Managed Companies – for the third time

Richmond Hill, ON: mobileLIVE is honoured to be recognized as Growth 500 Employer of the Year among the list of Canada’s Fastest-Growing Companies. The Growth 500 Employer of the Year designation is reserved for a single Growth 500 company that has dramatically increased the size of its workforce in the past five years, creating net new jobs; that offers a diverse range of programs, benefits and services to attract, engage and retain employees; and demonstrates commitment from its leadership in creating a great workplace. Out of all the applications submitted by all 500 winners, the editorial team believed that mobileLIVE was the most deserving of this award because of its unique and innovative initiatives. “In 2017, we made a commitment to our employees, present and future, that by 2020 we would be one of the greatest places to work in Canada. And while we normally pride ourselves on our punctuality, we couldn’t be more thrilled to have arrived here a couple of years early. This award serves only to validate our efforts going forward as we remain committed to creating a launch pad for brilliant ideas, fulfilling careers, and a balanced life that has earned us this recognition.” This award acts as a benchmark moving forward, helping to guide cultural and administrative practices to ensure mobileLIVE remains one of the best places to work in Canada.
mobileLIVE recognized as Growth 500 Employer of the Year

Richmond Hill, ON: Canadian tech firm, mobileLIVE has earned a spot on the Growth 500 ranking for the second consecutive year. Canadian Business and Maclean’s announced today that mobileLIVE ranked 99th on the 30th annual Growth 500 – the definitive ranking of Canada’s Fastest-Growing Companies. mobileLIVE also ranked as the 39th Fastest-Growing Company in Toronto and 20th Fastest-Growing Software Companies in Canada. “The companies on the 2018 Growth 500 are truly remarkable. Demonstrating foresight, innovation and smart management, their stories serve as a primer for how to build a successful entrepreneurial business today,” says Deborah Aarts, Growth 500 Program Manager. “As we celebrate 30 years of the Canada’s Fastest-Growing Companies program, it’s encouraging to see that entrepreneurship is healthier than ever in this country. “ “Winning this award once is an achievement, however, being honoured for a second consecutive year is truly humbling,” says Jahan Ali, CEO and founder of mobileLIVE. “I can’t claim this award for myself; rather, it is the team we’ve built, their unyielding agility, adherence to scalability, and dedication to quality that has allowed us to maintain our growth trajectory.” Momentum has been building as this announcement comes on the heels of a number of growth initiatives from mobileLIVE, mainly, the addition of office locations across the country as well as adding some more depth and experience to their leadership team.
mobileLIVE ranks 99th among Canada’s Fastest-Growing 500 Companies

Richmond Hill, ON: mobileLIVE, the multi-award winning tech company just announced a new central office location, situated at 145 King St. W, in the heart of Toronto’s bustling Financial District. The new location is part of an overarching strategy intended to not only enhance accessibility to clients but to establish a central hub for all key initiatives and activities moving forward. This announcement comes on the heels of other recent news from mobileLIVE: the addition of two new members to their leadership team; Daniel Yinanc as VP of Innovation and Technology and Chris Chambers as VP of Sales (BFSI). The company confirmed that their new location in Toronto, coupled with an established presence in Richmond Hill and Montreal, is part of their growth strategy, both here and abroad, and includes the recent acquisition of ZSystems (Pvt.) Ltd. in Pakistan. The Lahore based tech company will help mobileLIVE provide a greater focus on international operations and expansion. “The market response and subsequent growth of mobileLIVE have been tremendous,” says Jahan Ali, CEO, mobileLIVE. “With Daniel and Chris joining the team and our stronger, more strategic presence in Canada and abroad, we are better poised to further accelerate the growth of not only ourselves but the clients we serve.”
mobileLIVE adds new offices as part of their strategic expansion

Richmond Hill, ON: mobileLIVE has won the prestigious title as one of Canada’s Best Managed Companies of 2017, leaving behind hundreds of other companies who apply to win this coveted title year after year. Companies which are fully Canadian-owned and managed were selected in the grounds of steadfast revenues along with demonstrating strategy, capability and commitment to achieve sustainable growth in the Canadian market and adding to the global economy. “This recognition affirms the company’s strong commitment in transforming client’s vision into reality, building a collaborative culture, and ensuring financial growth year over year,” said Jahan Ali, CEO of mobileLIVE in a statement. Ali, explains, “Our strengths in operational adaptability and scalability, enterprise grade solutions, end-user experience driven developments, modular and scalable approach, culture of robotic process and test automation, agile and lean structures along with collaborative working models to co-create, sets us apart.” Established in 1993, ‘Canada’s Best Managed Companies’ is one of the country’s leading business awards programs recognizing companies for their innovative, world-class business practices, distinctive culture and sustained growth. “It’s much more than just financial performance,” said Lorrie King, Partner, Deloitte and Co-Leader, Canada’s Best Managed Companies program. “Well-run companies are important to the economic health of our country. These companies serve as role models to help make all Canadian businesses better.” In 2016, mobileLIVE was conferred the Deloitte Technology Fast 50™ and Fast 500™ awards along with many other notable industry awards for fast growth, innovative approaches and entrepreneurial qualities. “Winning the Best Managed Companies title is a proud moment for us,” says the excited President, Hussain Qureshi. However, he believes winning is not the end in fact consistently living up to the title is equally important. “We will always go above and beyond in providing disruptive & innovative services to our clients, ensure unique and personalized experiences for end-users along with consistently investing in our team’s growth.” The best managed winners are an important engine of economic growth for being adaptable and sustainable in a global market. Applicants are evaluated by an independent judging panel made up of judges from Deloitte, CIBC, Canadian Business, Smith School of Business and MacKay CEO Forums. The Best Managed program is sponsored by Deloitte, CIBC, Canadian Business, Smith School of Business and MacKay CEO Forums. “CIBC is thrilled to congratulate mobileLIVE on being named one of Canada’s Best Managed Companies, recognizing its excellence in leadership, business performance and innovation,” said Jon Hountalas, Executive Vice President, Business and Corporate Banking, CIBC. “As a sponsor of Canada’s Best Managed Companies program for over 20 years, CIBC is proud to celebrate private companies like mobileLIVE as leaders in their industry.” 2017 winners of the Canada’s Best Managed Companies award will be honoured at the annual Canada’s Best Managed Companies gala in Toronto on April 19, 2017. On the same date, the Best Managed symposium will address leading-edge business issues that are key to the success of today’s business leaders.
mobileLIVE wins Best Managed Companies Title in Canada

Richmond Hill, ON: mobileLIVE is once again, recognized for its overall business performance and sustained growth with the prestigious Canada’s Best Managed Companies designation. The 2018 Best Managed program award winners are amongst the best-in-class of Canadian-owned and managed companies demonstrating excellence in strategy, capability, and commitment to achieve sustainable growth. Now in its 25th year, Canada’s Best Managed Companies is one of the country’s leading business awards programs recognizing Canadian-owned and managed companies for innovative, world-class business practices. Every year, hundreds of entrepreneurial companies compete for this designation in a rigorous and independent process that evaluates the calibre of their management abilities and practices. Jahan Ali, Founder and CEO mobileLIVE explains, “Winning Canada’s Best Managed for the second year is no easy task, nor is it one that a single person can take credit for. In fact, it takes everyone on the team staying true to our vision – to be the number one company in every every customer we serve. We are happy with the world taking notice.” Applicants are evaluated by an independent judging panel comprised of representatives from program sponsors in addition to special guest judges. 2018 Best Managed companies share commonalities that include a clear strategy and vision, investment in capability and commitment to talent. “We don’t believe in one-offs, random occurrences, or isolated incidents,” says Hussain Qureshi, President, mobileLIVE. “So, when we won Canada’s Best Managed in 2017, we knew exactly what we had to do in order to keep our coveted status. We differentiated ourselves, assembled teams and capabilities to drive innovation and productivity, stayed committed to our goals, created a distinct culture, engaged, invested, and rewarded teams with a long-term vision to achieve success for our clients.” “This year’s winners reinforce the significant impact that privately owned Canadian companies are making by pursuing innovation and maintaining a sharp focus on their clients,” says Dino Medves, Senior Vice President and Head, CIBC Commercial Banking, co sponsors of the program. He further adds, “CIBC proudly congratulates the 2018 winners of Canada’s Best Managed Companies, who exemplify business excellence and success.” 2018 winners of the Canada’s Best Managed Companies award will be honoured at the annual Canada’s Best Managed Companies gala in Toronto on April 11, 2018. On the same date, the Best Managed symposium will address leading-edge business issues that are key to the success of today’s business leaders. The Best Managed program is sponsored by Deloitte, CIBC, Canadian Business, Smith School of Business, TMX Group and MacKay CEO Forums.
mobileLIVE recognized as one of Canada’s Best Managed Companies again

Richmond Hill, ON: The Max Gala Foundation, declared Jahan Ali as the ‘Business Leader of the Year’, in their 2017 Annual Awards Gala. The Max foundation, progressively works to recognize, reward, motivate, and celebrate positive contributions as well as high achievement of Canadian Muslims towards the society. Jahan immigrated to Canada as a student and founded mobileLIVE, a company specialized in accelerating digital transformation for its clients along with robotic automation. Within six years of his entrepreneurial journey, Jahan has advanced the company to great heights, winning praiseworthy business titles year after year. Apart from his acumen as a businessman, Jahan is also known for his philanthropic activities in various roles. Be it a mentor or a coach supporting in the settlement of newcomers and immigrants to actively supporting various charities in building a better world.
Jahan Ali wins 2017 Max Gala Business Leader of the Year Award

Richmond Hill, ON: mobileLIVE ranked 219th in Deloitte’s Technology 500™, a ranking of the 500 fastest-growing technology, media, telecommunications, life sciences and energy tech companies in North America. On further breakdown of 500 companies, mobileLIVE is one of 70 companies with Headquarters in Canada. Out of these 70 companies, mobileLIVE ranked 16th among technology companies from Ontario, 22nd among software companies in Canada, and 30th among technology companies from Canada. “The Deloitte 2017 North America Technology Fast 500 winners underscore the impact of technological innovation and world class customer service in driving growth, in a fiercely competitive environment,” said Sandra Shirai, vice chairman, Deloitte Consulting LLP and U.S. technology, media and telecommunications leader. “These companies are on the cutting edge and are transforming the way we do business. We extend our sincere congratulations to all the winners for achieving remarkable growth while delivering new services and experiences for their customers.”
mobileLIVE ranked 219th among Fastest-Growing Companies in North America

Richmond Hill, ON: mobileLIVE today announced their ranking as 37th on Deloitte’s Technology Fast 50 program award due to its rapid growth, bold innovation and its entrepreneurial spirit. On further breakdown of the Fast 50™ companies, mobileLIVE ranked 11th among technology companies from GTA, 18th among technology companies from Ontario, and 23rd among software companies. Additionally, mobileLIVE has also been ranked 219th on Deloitte’s Technology Fast 500TM across North America and is one of 70 companies with Headquarters in Canada. On further breakdown of these 70 companies, mobileLIVE ranked 16th among technology companies from Ontario, 22nd among software companies in Canada, and 30th among technology companies from Canada. The Deloitte Technology Fast 50 program winners are made up of public and private companies in the technology sector that share common traits and strengths and have transformed the industry. Celebrating its 20th anniversary this year, the program augments the broader Deloitte North American Technology Fast 500™ initiative with winners automatically eligible for this elite ranking. mobileLIVE CEO, Jahan Ali says, “We are really proud of achieving this prestigious title 2nd year in a row.” he adds, ”Success is never by chance. You create it by obsessing over customer success, building a reliable team of innovators, and ensuring simplification for the end users.” “New technologies have disrupted various industries in ways that were unimaginable a few years ago,” said Erica Pretorius, Partner and National Leader for the Technology Fast 50™ program at Deloitte Canada. “Fast 50 winners have led the way and I can’t wait to see where they take us next.” Hussain Qureshi, President mobileLIVE says, “Winning the title again is very reassuring. We are very pleased with our technological advancement, path breaking innovative solutions, and world class customer service in accelerating digital transformation.” Sandra Shirai, vice chairman, Deloitte Consulting LLP and U.S. technology, media and telecommunications leader explains, “These companies are on the cutting edge and are transforming the way we do business. We extend our sincere congratulations to all the winners for achieving remarkable growth while delivering new services and experiences for their customers.” To qualify for the Deloitte Technology Fast 50 ranking, companies must have been in business for at least four years, have revenues of at least $5 million, be headquartered in Canada, own proprietary technology, conduct research and development activities in Canada and invest a minimum of five percent of gross revenues in R&D.
mobileLIVE Ranked 37th Fastest-Growing Company in Canada

Richmond Hill, ON: Canadian Business and PROFIT today ranked mobileLIVE 33rd on the 29th annual PROFIT 500, the definitive ranking of Canada’s Fastest-Growing Companies. The program ranks businesses based on their five-year revenue growth. On further categorization of the top Fastest-Growing Software Companies in Canada, mobileLIVE was ranked 13th among the 71 listed companies, and 10th Fastest-Growing Software Companies, based in Ontario, vis-a- vis the PROFIT 500 program. “It is never easy to earn a spot on the PROFIT 500, but this year’s applicant pool was the most competitive yet,” says Deborah Aarts, PROFIT 500 program manager. “This year’s winners demonstrate the resilience, innovation and sheer management smarts it takes to build a thriving business today. Canada—and the world—needs more entrepreneurial success stories like these.” For the past 29 years PROFIT 500 has been Canada’s most respectable and influential ranking of entrepreneurial achievement. mobileLIVE CEO Jahan Ali, says his company’s explosive growth recipe is in “Being end-user obsessed.” He continues, “We go to great lengths in understanding user requirements and use those insights in ideating, building, testing and delivering exceptional experiences.” “On securing 33rd position in the PROFIT 500 ranking we are delighted and feel honoured that our efforts are recognized by the industry and the markets we serve,” says the excited company President, Hussain Qureshi. “This achievement reflects on the performance reliability of our team and a promise to our clients of success and nothing less.”
mobileLIVE Ranks 33rd on the 2017 PROFIT 500

Richmond Hill, ON: Jahan Ali, Founder and CEO mobileLIVE, has been recently recognized by Ernst & Young (EY) as a finalist in their Entrepreneur Of The YearTM program, which distinguishes entrepreneurs who are bold and daring to take risks, challenges status-quos, dive into uncertainty, and overcome impediments with innovative solutions. The firm named 40 finalists across 10 categories in its acclaimed EY Entrepreneur Of The YearTM 2017 Ontario Awards program. “EY’s Entrepreneur Of The Year program celebrates the men and women who dare to dream big and build boldly,” says François Tellier, Region Program Director. “From coast to coast, our regional finalists are entrepreneurs who make the most of uncertainty, disrupt traditional business models and develop solutions to unforeseen problems. Just like this year’s EY World Entrepreneur Of The Year winner, Murad Al-Katib of AGT Food and Ingredients, they make us proud to be Canadian.” Jahan’s prowess in customer-driven approach and leading the company to achieve exceptional growth over the years, has been key in securing a place in the program.
mobileLIVE CEO named finalists of the EY Entrepreneur Of The Year™ program

Richmond Hill, ON: The Minister of International Trade, Ontario, Michael Chan, paid a visit to explore mobileLIVE’s Robotic Process and Test Automation factory. mobileLIVE team welcomed the Minister and offered him a tour of the office facilities. He was guided and explained about the various innovation led practices and products that the company offers. After meeting the diversified workforce of mobileLIVE, Minister Chan was also assured that the company values the principal of building more jobs and propelling the Canadian economy forward. As a vote of thanks for his bold vision and services around the Markham-Unionville region, the leadership team of mobileLIVE presented him a plaque.
Minister Michael Chan visits mobileLIVE Robotic factory

Richmond Hill, ON: Member of Parliament, Richmond Hill, Majid Jowhari visited mobileLIVE headquarters to learn how the company is progressing in the areas of Digital Transformation, IoT, Artificial Intelligence, Robotic Test and Process Automation. MP Jowhari, a Tech graduate from Toronto’s Ryerson University, along with a MBA from York University has an acumen for Technology Businesses, and has lead his own consulting firm for over seven years in a row. To commemorate the presence and etch a memory, the leadership team presented a plaque to thank MP Majid Jowhari for his bold vision, leadership, and contribution in Richmond Hill and Ontario.
MP Majid Jowhari visits mobileLIVE HQ

Richmond Hill, ON : mobileLIVE enhanced new features to its recently launched new automated testing tool, UXPLORE, designed for Smart communicating devices (mobile phones, PC’s) and Applications (mobile, web, and other IT apps). The first one permits testers to effectively schedule script runs on specific times/days as well as adding a recurrence to the runs. With this function, testers can now dedicate their working hours in developing/enhancing and validating new scripts, and run them during off-hours period to maximize their productivity. The second feature permits testers to update a library-based test case and effectively push the changes automatically to all the test suite utilizing that specific test case. This not only adds a high level of convenience but also permits a huge productivity gain in updating related test suites.
UXPLORE R1.1 offers additional features

Richmond Hill, ON: mobileLIVE is proud to announce the first release of the new UXPLORE automated testing tool designed for Smart communicating devices (mobile phones, PC’s) and Applications (mobile, web, and other IT apps). UXPLORE is the latest automation tool created by mobileLIVE that allows one tester to create a script and run it across Multiple Screens and Multiple Platforms with Real-time Reporting Capabilities from anywhere and at any time. UXPLORE’s web based GUI permits users to access the management portal with any browser supporting device. UXPLORE automation tool goes further than traditional testing tools with its unique capability of testing targeted screen equipped devices located at specific geographical area. UXPLORE is the only tool available today that will test a specific device sitting at a specific geographic location. With the simple drag and drop functionality, users can easily create test cases and suites without the need to have any previous coding knowledge. UXPLORE can automatically discover and report on issues and discrepancies that traditional automated testing software’s will miss such as: User Flows, Application Latency, Session Timeout, Health Checks, UI Discrepancies, Branding Issues, Spelling Mistakes, and Data Validation. UXPLORE can also read use information from an external source to be used to test live applications, such as login names, password, payment information and more.
Release 1 of UXPLORE

Richmond Hill, ON : mobileLIVE is proud to be certified as a supplier with Canadian Aboriginal and Minority Supplier Council (CAMSC). Being a Canadian owned and operated company, we look forward to working closely with prestigious CAMSC members. CAMSC operates as a private sector-led, non-profit membership organization governed by a board of Directors; comprised of major multinational corporations operating in Canada. The organization aims to boost economic development efforts and employment.
mobileLIVE wins Supplier Certification with CAMSC
Richmond Hill, ON : mobileLIVE is pleased to announce the launch of its latest app “MyThingsTracker”. With MyThingsTracker, users are able to capture and organize information of their expensive purchases or important documents in one central place and get reminded on when to take action or refer to them when needed.
mobileLIVE launches new app- MyThingsTracker

Richmond Hill, ON: mobileLIVE, under the ICT (Information Communications and Technology) industry, claimed 116th position among the Top 250 ICT companies awarded by the Branham Group, in its industry acclaimed Branham300 listing. “mobileLIVE is continuously gaining recognition as a leader in building custom mobility and IoT applications along with providing digital workforce for robotic process and test automation. We are focused on transforming our clients visions into reality, increasing their operational agility, and creating exceptional experiences for their customers.” said Jahan Ali, CEO mobileLIVE. Hussain Qureshi, President, mobileLIVE says, “Getting recognized by the Branham Group in their Branham300 list of top 250 ICT companies, is an accomplishment in itself. I am thankful to the organizers, as the Branham300 collectively builds the “Made in Canada” brand and accolades globally.” Wayne Gudbranson, CEO Branham Group adds, “The companies that comprise the Branham300 have a lot of reasons to be proud of. I am again impressed by the performance of Canada’s technology community. The sector has set another revenue record, as measured by our Top 250 ranking of Canadian companies, which are helping to build our innovation economy.” 2017 marks the 24th annual Branham300 ranking of public and private technology companies in Canada. The companies that made up the list of 2017 Branham300 has collaboratively set a new record of $105.3 billion, with a YOY increase of 9.6 percent; which is almost double the previous year.
mobileLIVE ranked among the Top 250 ICT companies

The AODA Readiness Checklist to use for Essential Accessibility

Designing for Accessibility: Our Framework and Best Practices

Tweaking Figma for Design/Dev Collaboration

Your Guide to Design Thinking Workshops
Bridging the Gap Between Design and Development

How Customer Experience Dominates in Today’s Digital Economy

PRO Gamification: The Retail Experience

A Guide To Adopting Test Automation For Better & Faster Results

Pursuit of optimal customer experience is driving digital transformation initiatives; with technology allowing customers to be in direct control of their interactions with businesses. From the ease of multi-channel digital connectivity to immediacy in service, the customers are demanding seamless and hyper-personalized experiences that embody simplicity, Do-it-Yourself, and social. Hyperconnectivity is growing at an unprecedented pace and there is a global urgency in embracing “digital-first” strategies. Benefits already being witnessed from digital transformation efforts include: increased market share by 41%, increased customer engagement in digital channels by 37%, more positive employee morale by 37%, greater web and mobile engagement by 32%, and increased customer revenue by 30%. However, growth in this highly competitive digital economy must be lead with a clear vision, in a collaborative culture of highly motivated departments, fueled with disruptive innovations in both business models and offerings. Ultimately, all efforts narrowing down into two strategic streams: Customer Value and Operational Agility In this paper, my colleagues and I share how customer experience is driving digital transformation initiatives. What are the key challenges and how they can be addressed to attract, win, and retain customers in this ever-increasing digital economy.
Customer Experience in the Digital Economy

You know it’s vital, I know it’s vital, so let’s move on and dive right into our recipe for success. True quality comes from quality minded people, and as such, we’ve subscribed to a different angle towards QA, one that differs from the traditional practices. Approach Traditional Quality Assurance often involves extensive work and coding before any testing is actually done. This results in finding more bugs in the software closer to the delivery date. At mobileLIVE, our QA involves Test Automation coupled with Continuous Integration from the start. This approach uncovers the majority of bugs at the beginning of the software development cycle and fixes them as the cycle progresses. The result is fewer bugs to reconcile at the end of the project, which in turn, allows for seamless and easy delivery. traditional QA has manual testing lots of bugs. mobileLIVE QA has test automation, continuous integration, not many bugs Whether you are working in an agile environment or taking a waterfall approach, the overall strategy for high-quality QA remains the same: QA best practices methodologies cycle: test strategy, test dev, test execution, defect management, delivery Best Practices Our approach to QA is what truly sets us apart in an already dense development landscape and we would like to share with you a comprehensive list of best practices that have proven effective time and time again: Focus on the User Experience: Testing at all levels of the project is crucial, but the most important thing to consider is the user experience. If the UX is bad, it inevitably means the quality is not at par. Although this will likely result in changes during earlier levels of development, the user experience must always be at the forefront. Automation and Continuous Integration: Automation is vital because it provides fast feedback, enabling continuous integration – a crucial component of the agile methodology. Automation is also key to reducing costs and improving the efficiency of your team; which is one of the main reasons why QA managers must educate themselves and be willing to implement automation practices. Test Coverage and Code Coverage: Many QA engineers talk a lot about “test coverage,” which gives a good general picture of the quality of the application. However, to achieve true quality, both test cases and code coverage analysis must be considered. For example, even if you achieve 100% test coverage, you need to still aim for at least 90% function code coverage to ensure the best results. The Shift-Left Approach: Typically, testing starts once the coding phase is complete. However, for optimal quality in an agile methodology, you need to shift the focus and begin monitoring and testing right from the inception of the project. This ensures that bugs are detected sooner, which not only saves time and money but also helps ensure a good relationship with developers on the team, accelerates the delivery of the product, and allows for greater test coverage. Smart Testing: Complete and comprehensive testing can sometimes present a challenge since many teams may not have the time or resources to go through every possible combination of cases. However, you should be smart in how and what you test. This means, communicating with the developer to find small test cases that will uncover the greatest number of bugs. Bug Prevention: QA engineers are trained to catch bugs; however, a resourceful QA engineer will also think about how to prevent them in the first place. Traditional QA starts testing at the UI level, but an agile method starts with unit and functional testing and then moves to the UI level. This approach prevents bugs from entering higher levels of development which can cause bigger problems later on and likely delay delivery. Quality Over Quantity: Focus on major critical bugs and glitches initially rather than several smaller ones. Agile Testing Process and Approach Agile is undoubtedly the preferred software development methodology for today’s developers. Agile testing uses the same principles to encompass all elements of software testing from unit to system testing. We recommend using The Four Quadrants of Agile Testing in order to not only meet but exceed quality standards in all aspects of a project. The Importance of Test Automation At mobileLIVE, we practice a culture of automation and thus believe that every development team should be automating all tests when possible. There is no excuse for not automating these tests, as in most cases, doing them manually will cause considerable trouble, lead to additional costs, and create untimely delays. Regardless of how thorough your manual testing is, human error will always be a factor, which is why automating all possible tests is the best way to ensure your results meet and exceed the quality standards you were hoping to achieve. The Value of Continuous Integration In addition to automating all possible tests, Quality Assurance managers must also ensure that all feedback is subject to continuous integration. One of the major benefits of automated QA is the fact that feedback is available immediately, which is why implementing that feedback and fixing bugs at all stages of the development cycle is imperative. Build Verification Tests (BVT), and Smoke Tests should be built into every stage of the project as they are the most comprehensive way to detect problems early on and prevent issues in future builds. The following diagram illustrates Continuous Integration flow from Code Check into Operational Readiness: Continuous Integration flow: sprint teams, git repo, jenkins, build, unit testing, int build, smoke API int testing, app e2e testing, release Key Takeaways Most would admit that agile development is the future; however, in order to exceed client expectations and improve the user experience, regardless of what method you choose, extensive QA isn’t a “nice to have,” it’s imperative. As the development landscape grows denser, our approach with its focus on automation, continuous integration, and the other best practices mentioned earlier will help you to maintain and surpass quality, ensure the highest satisfaction upon delivery, and provide the greatest experience for the user, as well as your development team, as possible. How do you approach QA? We would love to hear it!
Quality Assurance Approach and Best Practices

Let’s play a game. How many brands do you think I experience in a typical day? Shall we find out? It’s 6:55 AM and I’m awoken by the sounds of Lovely Day, by Bill Withers. A smile inevitably crosses my face as the tempo rises, that is, until I hear my girlfriend yell, “OK Google, STOP!” She obviously is not a morning person. Still half asleep, I wander into the kitchen to put on a pot of coffee and pour myself a bowl of cereal. As the aroma of the coffee diffuses throughout the house, it peaks the interest of my other half, who joins me for a cup. She mentions that the hardware store is having a sale on the bathroom tiles we liked and maybe “we” should pick some up after work. I tell her I’d be happy to as long as she promises to be ready by 7 PM for the show tonight. She agrees; I’m skeptical. After a long day of reviewing and editing content, making travel arrangements for a conference, and too much time with the accountant, I eventually make my way home. That is, only after a series of text messages caused my trip to the hardware store to also include the pharmacy, grocers, and courier. No matter, for when I pull in I get a little excited to see my girlfriends car in the drive and think she may, in fact, be ready. So you can imagine my disappointment when I saw her on the couch looking particularly comfy in a pair of sweats, a glass of wine in hand. I ask her about the tickets, putting a box of new bathroom tiles in front of her. She responds by handing me a beer and a book on bathroom renovations. Confused, and likely looking it, she then said, “The show is next week, but I picked up some grout, and we can get started on the bathroom tiles tonight ” Oh, a day in the life… So, how many did you count? There’s at least 15, but it probably wasn’t easy. However, if I were to put the words ”Kellogg’s,” “Samsung,” “Toyota,” “Home Depot,” and “Visa” in that story, it may become a bit more evident how often we experience brands, at least, the successful ones. That is because the successful ones lend themselves to our lives, adding value while not drawing attention to itself. This, in essence, is what the customer experience (CX) is all about, and is something that the most reputable brands in the country have perfected. And why shouldn’t they? After all, according to Gartner, CX is the new marketing battlefront, and in two years’ time, 81% of companies expect to be competing mostly or completely on the basis of the digital experience their customers get. This made me curious, so I decided to dive deep and compiled a list of 22 inspiring customer experience quotes and statements from 28 of the top brands in Canada by “sector” as reported by Leger. Enjoy! “It’s a world of multiple screens, smart displays, with tons of low-cost computing, with big sensors built into devices. At Google, we ask how to bring together something seamless and beautiful and intuitive across all these screens.” —Sundar Pichai, CEO, Google “The customer changes every day, so we need to remain keenly interested in the customer and evolve to remain relevant.” —Mike Motz, President, Shoppers Drug Mart “Our customers are at the heart of our company and our growth strategy. Understanding our customer better means we can create a more consistent experience and offer products, services and promotions that meet the specific and every day needs of our customers and create an incredible competitive advantage.” —Stephen Wetmore, President and CEO, Canadian Tire Corporation “If you see the name Sony on any product, content, or service, it symbolizes our promise to move you emotionally. Our products are designed to have a personal and individualized place in all of your lives.” —Kaz Hirai, President and CEO, Sony “This project (Bear Naked) was born out of a consumer need like most good innovation should be. The consumer need that we identified was what we call a ‘desire for taste exploration.” —Chris Tutor, VP of Strategy, Kellogg “Most people try to solve for what their internal problems are, or a pre-determined view of what they think the experience should be. We want to listen to our customers first, they tell us how they’d like to shop with us, and how they’d like to see us presented to them, and make those changes appropriately.” —Matt Carey, EVP CIO, The Home Depot “The way our customers operate their businesses and live their lives in today’s interactive digital world requires a shift to a hyper-personalized experience. Customers expect us to know them as individuals and provide them with access to more information and visibility. In turn, we have to empower them to take control. This focus has translated into a shift for FedEx in terms of how we approach our business and communicate to our customers. ” —Laurie Tucker, SVP of Corporate Marketing, FedEx “Our Vision at Visa, to be the best way to pay and be paid for everyone, everywhere, prioritizes consumer behaviour and drives every product innovation.” —Derek Colfer, Head of Technology & Digital Innovation, Visa Canada “We knew it was time to reimagine the core bookstore experience. As people and consumers, we are evolving. There are some people who will long for the old-fashioned dusty bookstore, but most people don’t. In the 21st century, people are “phygital”—that is, they do some things digital and some things physical.” —Heather Reisman, CEO & Chief Book Lover, Indigo Books “It is our strategic plan to improve every consumer touchpoint, beginning with the look and feel of the restaurant. Our new Fresh Forward design brings to life what we have always had—healthy, fresh vegetables. We are integrating new technology to make us more accessible to the consumer and leveraging all of this into a new image.” —Suzanne Greco, CEO, Subway “Through these channels, we can provide more details about the characters, unveil behind-the-scenes footage, create interactive discussions with our fans and, ultimately, engage with them to drive our collective imagination further down the road on its never-ending journey. Customer loyalty can only be achieved through sustained, entertaining, and engaging interactions with our fans.” —Patrick Corneau, VP of Sales and Marketing, Cirque du Soleil “I have learned, based on my experience, that everything is dominated by the market. So whenever we are struck by any obstacles or difficulties, I always say to myself: ‘Listen to the market, listen to the voice of the customer.’ That’s the fundamental essence of marketing. Always, we have to come back to the market, back to the customer. That is the Toyota way. So, whenever we’re stuck, we always go back to the basics. Because branding, image, or Lovemarks are determined by the customers, not us. We really cannot determine anything. The customer does that. That is the essence.” —Yoshio Ishizaka, Former President and Current Advisor, Toyota Motor Corporation “I often remind my team to keep our consumer purpose at the center of everything that we do. To me, our purpose centers on caring for people around the world by anticipating their needs, creating solutions and experiences that help them and those they care for live healthy, vibrant lives.” —Josh Ghaim, Ph.D, CTO, Johnson & Johnson “It is through digital transformation, coupled with our WestJetters’ caring touch, that we will be able to provide the ultimate guest-centric service.” —Gregg Saretsky, President and CEO, WestJet “…while the world is focusing on new and shiny disruptive technologies, we sometimes forget about the customer experience. If we start with the healthcare consumer in mind, the gaps in their experience, how it can be improved, and what the key problem statements are, only then will we be able to see how and which technologies are here to enable a transformation.” —Eugene Borukhovich, Global Head of Digital Health Incubation and Innovation, Bayer “Engaging and marketing to our customers in new ways is key to building shopper loyalty and encouraging repeat visits, and it is the foundation of our retail brand strategy.” —Pat Lizotte, Director of Marketing Strategies, Petro-Canada “In a culture where usage is the primary goal, the primary focus is on ensuring customers are unblocked and the product is constantly being simplified to make it easier and easier to use. This focus is so central to the work we do that it takes priority over adding new features.” —Brad Anderson, Corporate VP Enterprise Mobility & Security, Microsoft “There’s no one-size-fits-all audience.” —Magen Hanrahan, VP of Media and Marketing Services, Kraft Heinz Company “This new model will be powered by data, analytics and audience insights, providing creative solutions as we continue to connect with new generations of consumers.” —Yin Rani, VP of Integrated Marketing, Campbell Soup Company “I must say that if you’ve got good customer insight it’s an excellent starting point. However, I think it is a mixture of getting customer insight, understanding where you currently stand with certain metrics, and what you need to do to build on these metrics. All these put together contribute to building a customer culture within any business.” —Carol Sheppard, Customer Experience Research Manager, Molson Coors “The client experience is everything, end-to-end, from the point that you first establish interest and awareness and are sharing initial thoughts, to the long-term, sustained relationship where you are coming back and back because you want more and more services from the person offering it.” —Diana O’Brien, Global CMO, Deloitte “All that insight (data and analytics) allows us to understand the final clients of our clients a little better,” —Jérémiah Bousquet, Digital Transformation Leader, Airbus It is our hope that these quotes/statements from some of the brightest minds, behind some of the most prolific brands, will inspire you in your journey to create the most memorable customer experiences. Do you have any inspiring customer experience quotes? We’d love to hear it.
22 Quotes on Customer Experience from the Top Brands in Canada

Daniel Park is Head of Digital Experience for a large enterprise. Among his many ongoing projects, he has recently been tasked to launch a “mission-critical” venture that has the promise to change the way the organization interacts with their customers. However, before Daniel can begin, he needs to choose which vendor to partner with. While evaluating the vendor options, he notices that Vendor A has a history of performance inconsistency, delayed launches resulting in blown budgets, and have on more than one occasion produced products riddled with bugs and glitches – even after launch. However, the same could not be said for Vendor B. Time and time again they had proven their reliability, speed, and accuracy in project completion. They also had a track record of creating some of the most well received and engaging user experiences around – all delivered on time and on budget. Intrigued by the dramatic differences, he noticed a simple yet extremely valuable difference between the two. Vendor A employed manual testing in their development, while Vendor B opted for the automated approach. This made his decision much simpler in selecting Vendor B; after all, who would want to work with a team that invariably costs them time, money, and compromised customer experience. Today, I’m hoping to make the choice of adopting test automation that much easier for you. Test Automation – The What and the When Test automation is a method of software testing that utilizes tools and/or frameworks to control and monitor the execution of tests and compare real-life results with predicted or expected outcomes. Fortunately, the far-reaching implications and benefits of test automation supersede this definition. However, before I delve into why you need to adopt test automation in your organization, allow me to share what you should automate, when you should do it, and what is best left alone. Test Automation What and the When WHAT TO AUTOMATE. Test cases that are: Mission-Critical, Executed repeatedly, Tedious or difficult, Time consuming WHEN TO AUTOMATE. It’s best to automate test when. Customer experience matters, Time-to-market is critical, OPEX reduction is desirable, Repeatable accuracy is preferred WHAT NOT TO AUTOMATE. It is best NOT to automate: Subjective tests, Frequently changing requirements, Ad-hoc tests At mobileLIVE, test automation is a part of our DNA. Whether we are working across the complete mobility ecosystem, full product lifecycle, functional or non-functional 360° coverage, or even if just an evaluation across specialty domains, we test early and frequently knowing that defect prevention is preferred to defect detection. This mindset of test automation and continuous integration has served us very well. Although it is impossible to automate all tests (we know, we tried), the following framework helps us ensure the most optimal level of automation: Technology Facing Automated Unit Testing Automated unit/functional testing per check-in,Get quick feedback on your dev check-in (merge) Technology Facing Automated Non Functional Testing Performance testing, Load testing, Memory management, Security and maintainability, Interoperability and compatibility, Scalability and reliability Customer Facing Automated and manual Functional Testing Create test cases for stories, Verify stories and bug fixes, Write automation scripts for passed stories, Add automation scripts to test framework Customer Facing Automated and manual exploratory Testing Exploratory scenario testing, Usability testing, User acceptance testing, Customer experience testing Remember, when automating tests it’s important to determine exactly which test cases should be automated first. I recommend basing this on those that yield maximum ROI. Test Automation – The Why Talk of test automation is nothing new; however, it seems to be a growing trend among development teams large and small to opt for automated testing over manual testing. Which begs the question – why should you invest in a culture of test automation and continuous integration? Well, I can actually give you several reasons, none of which are “because it’s a trend.” ROI: Manual testing takes too long and becomes cost prohibitive when it comes to multiple agile releases/sprints, multiple platforms, OSs, screen sizes etc. Reliability: Automated testing is faster and more reliable when running repetitive standardized tests which cannot be skipped, but could result in an error when manually tested. Accuracy: Even the most careful tester will make mistakes during monotonous manual testing. Automated tests perform the same precise steps every time they are executed; all while recording detailed results. Coverage: Automated software testing can increase the depth and scope of tests to help improve software quality. Lengthy tests that are often avoided during manual testing can be run unattended. They can even run on multiple machines with different configurations. Continuous Integration: Tests can run automatically whenever code changes are checked in and notify the team or the developer if they fail. Features like these save developers time and increase their confidence. Morale Boost: Manual testing can be mundane and executing repetitive tasks with automated software testing gives your team time to spend on challenging and rewarding projects. Team members improve their skill set and confidence and, in turn, pass those gains on to their organization. The aforementioned are just a few of the benefits that test automation can provide a development team. However, it should be noted that not all test automation tools are created equal. The second most important decision after choosing to automate your testing is which platform to use; and if you are anything like us, that platform needs to be simple and intuitive, be able to test solutions across the digital ecosystem, and provide timely insights and real-time reports. For us, our preferred technology partner is UXPLORE. UXPLORE – Test Automation Done Right UXPLORE is an innovative Robotic Automation Platform that automates testing using bots (a digital workforce) to improve user experience and reduce operating expenses. The platform enables all users, both technical and non-technical, to easily create and deploy bots instantly, without a need for coding. All possible human actions to various digital interfaces (web, mobile, cloud, IoT) are pre-coded, and bots are trained by creating a sequence of these actions. UXPLORE bots work around the clock to automate testing; much faster, cheaper, and with higher accuracy than humans. If you are looking to deliver exceptional customer experiences , reduce time-to-market and operational expenses, improve accuracy and team productivity, then test automation is no longer a “nice to have,” rather, an imperative.
The What, When, and Why of Test Automation

Brandy, a Generation-Z consumer, comes across an Instagram “like” by her friend for a featured dress. She likes the garment and is interested in purchasing it in a different colour. She decides to go online and compare prices, and while browsing, she is prompted to download the retailers’ app, which would result in a 10% discount off her first purchase. However, after comparing prices, downloading the app, and moving the dress into her “shopping cart,” she abandons her purchase thinking the dress isn’t the one for her.Retailer App ExperienceA few days later, Brandy finds herself visiting the local mall in search of a new outfit for the Easter weekend. As she passes by the store location of the same retailer chain, she receives a notification on her smartphone offering her a “no obligation” discount subject to her visiting in-store to play an Easter Egg Hunt.using augmented reality she finds the Easter egg in store to earn the discountExcited to get in the Easter spirit and play the egg hunt in store, the retailers’ app on her smartphone intuitively prompts her to activate the “AR Buddy” mode so that she can begin the game, just as she would if she were playing Pokémon Go.As she browses the store through the lens of her smartphone, she excitingly finds and “cracks open” a virtual Easter egg that entitles her to an instant rebate of $20 towards a purchase within the next three days. At the same time, she also notices the blinking icon of the retailer’s online cart, which still has the dress she selected a few days earlier. While on the fence before, with the added discount she thinks that buying the dress now makes for a great deal that is difficult to pass up.virtual Easter eggHaving placed the order, she is then given the opportunity to like the same dress on Instagram, entitling her to an additional $10 off her next purchase. Thrilled with the bonus promotion, she earmarks another dress she has come across while searching the store for the Easter egg, thinking to herself, “I’ll get this dress next time with the extra discount.”PRO-Gamification And that is how Personalized-Retail-Omnichannel Gamification (PRO-Gamification) works. From the moment Brandy logged into the app, the retailer’s back-end services platform started tracking her shopping experience. The social network API, merchandising catalogue, analytics engine, and Business Intelligence services all worked in tandem to track her clickstream, cart abandonment, and in turn, were able to predict Next Best Actions (NBAs). The fact that she compared prices hinted at her sensitivity to product pricing, and as something the analytics engine could hone in on, it predicted a higher statistical likelihood that if offered a discount or promotion, she would convert.When Brandy passed by the retailer’s brick-and-mortar store, it gave the retailer an ideal opportunity to get her attention. Beacons placed at the store entrance helped the mobile app sense her proximity and signalled the retailer’s back-end services to deliver a targeted promotion as a push notification. Given the season, however, this was no ordinary promotion, which immediately caught Brandy’s attention. The egg hunt provided the perfect reward mechanism to convert her into a paying customer. The cart history with the dress she had selected earlier helped “firm up” the purchase by avoiding manual searches online or the need to ask a sales associate for help.Furthermore, beacons located strategically throughout the store helped her “find” her Easter egg in proximity to items she would likely prefer to buy – something determined by the analytics engine based on her prior search. Beacons also enabled the mobile app in helping her locate and earmark the new dress in the online catalogue. In fact, now she is almost tempted to purchase the other dress directly from the store’s Point-of-Sale (POS) as she can take advantage of the extra $10 promotion because it is her next purchase anyway.Brandy’s entire journey, from searching online, purchasing, and sharing her positive experience on social media not only triggered “impulse buys” in real-time, but it also turned her from a prospect into a repeat customer and brand advocate. And now that the retailer has established predictable behaviour markers, they can personalize her future shopping experiences.Quick links to key sections Gamification, Past and Present Gamification as a Unified Marketing Strategy Towards an “Everything Digital” Approach Identifying Customers Individually to Personalize Content Understanding Customer Sentiment in Omnichannel Melding Art and Technology to Create Memorable Experiences Bringing Experiences to Life via Storytelling The Value of PRO-Gamification in Retail Gamification, Past and Present Gamification in retail is not a novel concept; however, with consumers being more connected than ever before, the notion is quickly becoming an imperative. With the rapid increase in digital connections leading to increased speed and convenience across all aspects of life, the question now raised is how and where to deploy resources for digital initiatives effectively and efficiently and how to apply them towards gamification. Digital transformation itself has evolved into a priority stack comprising the Internet of Things (IoT), Design Thinking, and Artificial Intelligence, and retailers need to act accordingly.Simply put, gamification is the use of elements of play and reward to affect and influence user behaviour; and with this evolved stack, it is quickly becoming the new retail battleground to win and grow customer base.So why does it work? Well, at its most basic level, it can trigger positive emotions, mainly those associated with play and reward. And if you have followed our past article on customer experience, you know these emotions are fundamental in capturing user’s attention and commitment to a purchase transaction.Take me back to quick links Gamification as a Unified Marketing Strategy Although the gamification of shopping experiences is not yet mainstream in the retail paradigm, it can be applied towards any product or service, regardless of the stage in the customer journey. Not only that, but the process can be easily adjusted, regardless of requirements, and can be scaled to almost any budget as part of a strategy to lead potential customers towards the desired goal along their journey.At its core, the appeal of gamification is to provide the users with a sense of control. Similar to a game where participants get a reward – a new character or power-up for example – for completing a level, gamification taps into our brains inherent reward mechanism, thus helping to reinforce a specific habit or behaviour.For putting together a bundle of products or services, this technique has proven hugely successful.The modern consumer is short on time, especially when it comes to processing the volume of content required to select and purchase the right collection of products or services. By turning that identification into a gamified experience, the natural attention of the user is enhanced. This method also drives higher customer engagement and increased brand loyalty through the implementation of such customer-curated collections. This also has a positive impact when you are rewarding your customers with loyalty points for activities – such as store visits, product videos watched, products reviewed, or purchases made – and provides far more information on consumer habits and the shopping cycle across multiple channels, which can, in turn, drive future sales.According to a set of recent surveys on mobile POS and retail gamification, retailers plan to use enhanced gamification features, incentives, and loyalty program tactics in their mobile strategies. Furthermore, some studies suggest that a substantial number of retailers plan to identify customers when they walk in the store, and that customer experience and engagement are one of their top customer relationship management priorities. However, such undertaking cannot be effective or profitable without carefully implementing a gamification framework with the following key points in mind:Moving towards an “Everything Digital” Approach Identifying Customers Individually to Personalize Content Understanding Customer Sentiment in Omnichannel Melding Art and Technology to Create Memorable Experiences Bringing Experiences to Life via Storytelling Take me back to quick links Towards an “Everything Digital” Approach New ways to interact over digital channels give you new opportunities to engage with customers at an unprecedented level. For example, there was once only the need for call centres to handle remote purchases and support, but with the advent of smartphones, apps can now serve customers directly. This has also allowed for a significant shift in customer experience and expectations due to new devices like wearables, voice-based assistants, and even augmented and virtual realities. It is essential to appreciate that in a digital transformation (and, for that matter digital business) all contexts arising from functions, processes and interactions are in fact interconnected and should be treated thusly.Customers now expect interactive experiences on these new devices rather than relying on conventional methods of accessing content. With the help of big data analytical capabilities, retailers can turn enormous structured and unstructured data into actionable customer insights. “Big data” with the right analytics can enable retailers to develop enriched 360°customer profiles, establish customer-centric KPIs, and develop more targeted offers.Retail Presence in the Digital Domain Specificity of interactgital domainion is extremely important within digital experiences. For example, studies have found that the app conversion funnel is wider at every point of contact than conventional and mobile web. In particular, app users were found to browse four times as many products than those on mobile web; indicating that app users make for more loyal and dedicated customers. From that larger base, customers are almost twice as likely to add items to their basket in an app than in a mobile browser.Applications and targeted interactions not only convert a higher percentage of your customers, but they also bring in more revenue per transaction. Controlling this environment can allow you to engage customers through verbal responses, videos, images, reviews tailored to personalized elements such as buying history and browsing behaviour within mobile apps, on social media, as well as in direct interaction with you. In fact, each channel can yield multiple touch-points to track individual customer engagement and sentiment as shown below:browsing behaviour within mobile appsIn-APP Operation in Mobile/Web APP are Functionalities Used, In-Cart Abandons, Flows Completed, Daily/Monthly Activity and in Conversational Interfaces are Views/Verbal Queries, Emotions Exhibited, Topics Queried, Effort and Interest. Social Media Sentiment in Numerical Metrics are Followers and Fans, Number of Mentions, Inbound Links, Blog Subscribers, Retweets, Social Shares and in Engagement Metrics are Positive Sentiment, Negative Sentiment. Direct Communication in Brick-and-Mortar are In-Store Visits, In-Store Purchases, Web-Cart Conversions, Tie-ln with Campaigns, Location Data and in Call Centres/Support are Tickets Responded, Completed Survey. On top of that, IoT has made it possible for all connected devices and touchpoints to affect the customers daily life. It integrates data gathering sources, assembling data strategy and analytics for better-informed decisions; designing products, experiences, and businesses with a focused human-centred approach, all while identifying patterns and providing personalized experiences. Web and mobile are no longer the most significant source of data generation; rather, it is being generated by the apps we use and by the way we interact with smart devices including wearables, cars, cameras, and routers to name a few. According to recent studies digital businesses will be leveraging IoT for in-store experience in addition to mobile and web channels with less than 20 billion connected devices today to 30 billion in 2020 to 80 billion in 2025.Leveraging Mobile App-Centric Touchpoints According to a recent survey, mobile touchpoints remain relevant as the gap between, consuming analytics content on a desktop computer versus a mobile device, has all but vanished. This diminishing gap is even more apparent between smartphones and tablets. Traditional means of data delivery and presentation cannot be taken for granted. Instead, innovation is necessary for finding new ways to harness strategic data assets with cutting-edge tools for faster and better-informed decisions.Digital transformation does not change the value proposition for mobile innovation, in what I call the “Triple-A” of mobile analytics: Anywhere, Anyplace, Anytime. Via app Software Development Kits and Application Programming Interface (APIs), any data, whether structured or unstructured, big data or small data, on-premise or in the cloud, can be captured.Mobile App-Centric TouchpointsThe digital economy demands a mobile-first approach to maintain the strategic value in order to turn insights into action.Take me back to quick links Identifying Customers Individually to Personalize Content Personalization is a growing trend that enhances the customer experience, and its core is the ability to identify and remember the customer uniquely. This allows retailers to make interactions more accessible and more intuitive, as well as target the customer based on their specific behaviours. You must analyze and realize what the customer wants most – convenience.Limitations of Third-Party Analytics Tools Popular analytics tools (such as Google Analytics) help identify user behaviour through cookie-based tracking. However, one should note that cookies are site-specific, and therefore subdomain or cross-domain tracking needs additional effort. Since cookies are not shared cross-domains, every interaction of a single user across different devices is recorded as activities by unique users in the absence of user identification. For instance, a visitor researching a product on your website decides to subscribe to your newsletter a week later and purchases a product a month after that. All of these interactions count as the activities of three different users. Therefore, third-party analytic frameworks end up being completely ineffective in identifying unique customers who choose to use multiple devices or browsers across visits to a site.Generating Individually Identifiable Analytics Integrations between identity management solutions and Data Management Platforms (DMPs) or automation tools make it possible to link existing, anonymous consumer data to known user records once a user accesses a site via a registered session on-site. Using probabilistic models, the user’s identity data will be passed directly from the identity management platform to the DMP and attributed to the correct user based on the site ID match – even across devices and domains. A User-ID in Google Analytics is a unique set of alphanumeric characters that is assigned to a user to identify him/her across multiple devices uniquely.Considering the previous scenario after implementing User-ID verification, and the same visitor performing the same actions can now be recognized as a single unique user:User-ID makes it possible to implement cross-device tracking because it associates sessions across multiple devices to a single user instead of multiple unique users By setting up User-ID, you can gain access to cross-device reports in Google Analytics User-ID will help you understand the relationship between multiple devices and engagement between sessions, which is essential when developing new marketing campaigns and their gamification To track users across multiple devices, you need to assign custom User-IDs to site visitors by changing in the analytics tracking source code. However, you would also need to add code that would pull any session-specific (login) IDs from the authentication system and send to Google Analytics as the User-ID. Finally, to view and analyze data from sessions in which a User-ID is detected, new views can be created showing cross-device reports.track users across multiple devicesThese reports can provide much-needed insight into user engagement on multiple devices with multiple sessions. They can also be considered as a breakdown of the activities users participate in during each of their sessions, which can further enhance game and level design for retail experiences.Take me back to quick links Understanding Customer Sentiment in Omnichannel The interdependencies of all the channels available must be understood thoroughly because customers want consistency across channels. For instance, customers want to continue their shopping experience where they had left off whenever they switch between channels. In the retail scenario, brick-and-mortar stores are associated more with customer service. This face to face advantage obviously shifts when specialized cross-channel journeys are considered, such as searching online but purchasing in-store, and vice-versa. For instance, you may find that limited sales are occurring via social channels and wrongly conclude them as ineffective. But, when viewing the entire journey across channels, you may discover that social channels are in fact a critical influencer of sales.The result of appreciating such consumer behaviours have a profound impact on marketing strategies, especially when the customer is no longer viewed within a single channel. Rather, each channel must be considered a driver for conversion in a different channel, and loyalty or fulfillment in yet another – all as a part of an omnichannel (interdependent) journey.Multi Channel Vs Single ChannelThis creates a clear, single view of the consumer, which will enable you to interact across all available channels. Taking advantage of better customer information, delivering consistent quality of service, and personalizing the customer experience, you can evolve your customer-centric business plan-of-action and enable all your channels.Analytics for Decision Support The most prevalent method of data storage for business is in silos across a variety of new and legacy systems. This lack of consolidation makes gleaning meaningful and timely insights difficult, if not impossible. Moreover, the analytical approach used by most companies is channel-specific, hindering them from getting a complete picture of the end-to-end customer journey. Remember, consumers are constantly producing data about their likes and dislikes, channel preferences, product choices and more; and to capture it, you must be prepared to glean data from website visits, email opens, social interactions, forms completed, purchases and so much more.Choosing to view this data in channel-specific silos can be misleading. To reach customers with a level of relevance that grows conversions and loyalty, you must first understand your customers. Advanced analytics, though at the heart of this approach, is more than just a new name for business intelligence. With advanced data architectures, you can now store new types of data, retain that data longer, and join diverse datasets together to gain new insights, not only to describe and summarize results but also to create possible futures based on-time-sensitive decisions and to predict likely outcomes.Advanced analyticsDescriptive Analytics are used when Summarizing Results and tool used Data Aggregation and Data Mining. Predictive Analytics are used when Making Educated Guesses and tool used Statistical Modelling and Simulation Techniques. Prescriptive Analytics are used when Making Time-Sensitive Decisions and tool used Heuristic Models and Optimization Models Insights gained from big data analytics, improve the customer experience at every touchpoint through high-performance services, fast feedback and customized offerings. Today’s advanced big data analytics can allow you to unlock new insights in real-time, enabling you to proactively offer products and services to your customers at the exact time they are most likely to subscribe, buy, or respond. This will lead to a proactive retention approach through analyzing mobile/web interaction, social media sentiment as well as direct communication based on combining customer churn prediction and marketing action optimization.You can go beyond “actionable customer analytics” to automatically determine what marketing action should be taken for each at-risk customer to achieve the maximum degree of retention possible – and create a customer experience that is unparalleled in the industry.The Role of Machine Learning in Analyzing Customer Behaviour Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligenceare extremely useful in deciphering the data captured from each customer interaction and can be used to predict the likely outcome of each event several steps down the line. For example, outcomes may be customer satisfaction or dissatisfaction concerning a product sale or call centre incident. Based on the sum of these calculations for the customer, or the customer segment, the system will determine and recommend the highest probability actions to take for marketing, sales, or support scenarios.Machine Learning in Analyzing Customer BehaviourOne of the main applications of machine learning – to drive customer engagement – is in market segmentation. In the absence of labelled real-time data, a subset of these techniques (called unsupervised learning) is very useful in advertising, implementing strategies for customer engagement and so on. By intimately understanding the intricacies of measuring and analyzing the customer experience throughout the journey, you can apply advanced diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics that – when combined – provide additional insights into business-level problems. While unsupervised learning allows for a wide degree of applications in making sense of data without labels, it is only advised if some level of association can be made across customer data. The low-hanging fruit for a machine learning use-case is likely to spawn from historical and labelled data available to you.However, not all Machine Learning models are optimal for a given set of problems and associated data. For instance, supervised learning techniques constitute a different mechanism of deriving insight from existing and known (training) datasets. This can be thought of as a teacher supervising the learning process.When it comes to decision making, Machine Learning can not only provide insight into what actions to take but also into what actions that should be avoided. The value of Machine Learning, therefore, lies in spotting connections between channels that would otherwise go completely unnoticed and then surfacing those connections for you to take action. This can come in the form of automated recommendations and gamified experiences that increase the chances of consumers purchasing additional products, or as follow up marketing activities like an email offer for one of the associated items.Machine LearningAll of this data is ingested by several algorithms powered by statistical and Machine Learning techniques for suggestion and decision support. Approaches use both supervised learning (e.g. classification, regression) and unsupervised (e.g. dimensionality reduction through clustering or compression) machine learning techniques. For example, Netflix and Amazon Prime use similarity/proximity-based algorithms to generate recommendations based on (video-to-video views) in a “Because You Watched” section. A personalized video ranker algorithm, or PVR, selects the order of videos in genre rows, using an arbitrary subset of the Netflix catalogue. These short-term trends are powerful predictors of videos that Netflix customers watch for example, especially when combined with personalization.Occasion-Based Campaigns The use of occasion-based campaigns, be it for your catalogue or targeted and personalized advertising, can be a powerful tool for decision support as well as customer engagement and retention. At the individual customer level, NBA can be identified based on the offer acceptance rates of similar customer types and their willingness to convert during specific events or holiday seasons.Occasion-Based CampaignsWith each customers acceptance or rejection of an offer, the system can then update and adjust the NBA algorithm and predictive model. In essence, the ability to learn, adapt, and predict customer responses to your actions during specific events or occasions can significantly increase the likelihood of new customer acquisitions as well as retention of the existing customer base.Predictive NBAs and Branched Futures The customer journey in an omnichannel experience is considerably different than that of traditional multichannel. Studies have shown that almost 60 percent of online customers now expect retailers to approach them with value propositions ‘relevant’ to them – which would undoubtedly also be true if the same personalization experience were available to customers at bricks-and-mortar stores. Customers no longer want to review a generalized list of products and service offerings. Rather, they prefer insights into how features of those products and services will add more value to their day-to-day lives and why they should choose yours over a competitor. Knowledge transfer is best achieved through a gamified experience that is sensitive to choices made by the customer and the nuances that can be derived from the social setting in which those choices were made. Using this paradigm, “multiple-future” scenarios and storylines can be designed such that a set of choices, though not evident in their relationship between retail channels, can, in fact, be cross-linked.In the case of Brandy, her journey began online with social media, followed by a click-through to the mobile app. And though the order placement was still done online, her physical presence at the retail store acted as a catalyst. Similarly, a different scenario can also be mapped to a journey where the transaction occurs at the brick-and-mortar POS, but the catalyst is online searches and social media interactions. The ability to map and transition between journey points from channel to channel is at the heart of predictive NBAs, and the main driver behind interactive retail gamification.Take me back to quick links Melding Art and Technology to Create Memorable Experiences Omnichannel interactions can provide the customer with constant communications across their journey, one where the conversation history and context travels with them from channel to channel. But the context for omnichannel experience is non-trivial to maintain across many disconnected communication channels, from chat apps like Facebook Messenger, WeChat, and WhatsApp, to email, SMS, mobile and web chat. In the case of a Telecom Operator as an example, true omnichannel would mean giving the operator the ability to interact with the right customers, in the right places at the right times, all without having to sacrifice context. Omnichannel APIs can easily transfer the conversation from a chat app to in-app or web chat, from an email to SMS – or any other combination whether the customer is looking to upgrade a wireless device, change a plan, or request support. The operator can provide customers with a set of choices for where they would like to continue the conversation or get notified of a reply later on.AR/MR-based Interaction Perhaps the most significant opportunity for omnichannel marketing is the ability to create virtual versions of real products so consumers can enjoy an ultra-realistic shopping experience. While conversational interfaces are proving to be invaluable in engaging the user to intuitively access content and assist in decision making, such interfaces are limited to text- or voice-based chatbots. However, conversational interaction for Augmented and Mixed Reality (AR/MR) will be fundamentally different due to the enriched content rendered within an arbitrary 3D space. Free from the confines of a 2D “flatland,” the UX of the future will demand digital content to be more than what is currently accessed over the web. UX designers and developers will need to prepare content generation and digital assistants for verbal, as well as gestures, to interact with the users; not just by displaying audible or visual content, but by introducing key micro-interactions through evolutionary storyboarding that trigger the user’s active thought process.AR Vs MRIn AR, Real world remains central to digital experiences, enhanced by virtual details. In MR, Interaction with and manipulation of both the physical and virtual environment. It is estimated that approximately 67 percent of people who enter a fitting room in a store will likely make a purchase. Using technology to overcome this physical hurdle, Dressing Room apps use such technology that can allow people to virtually “try on” clothes, all without setting foot in store. After selecting a product on the virtual shelf, customers can select their size and the size of the garment to get a better idea of how the clothes will fit – which adds another dimension to gamification.Furthermore, the recent success of AR apps such as Pokémon Go has presented new possibilities in how such technology can be beneficial, especially if Brandy’s journey of the egg hunt is taken into consideration. Retailers can use similar tools to boost local customer engagement through AR mobile apps that encourage loyalty rewards.The Role of Proximity-Based Beacons and IoT Devices Beacons are battery-operated wireless devices that transmit Bluetooth signals to nearby smartphones. In the context of retail, beacons reach out to customers that have Bluetooth enabled and the right retail apps downloaded onto their phones. Beacon technology is a new way to engage with consumers and provide incentives for shoppers to enter a particular store, stay for a while, and make purchases. Their continued rise in popularity is expected to help reinvigorate brick-and-mortar retailers, offering customizable shopping experiences to customers that cannot be replicated online.Proximity-Based Beacons and IoT DevicesRetailers strategically place beacons around their store. The beacons connect to a customer’s Bluetooth enabled smartphone app. It sends a signal to the phone and the app is opened. The retailer can provide the customer with a wealth of information. Take me back to quick links Bringing Experiences to Life via Storytelling We are creatures of emotion. As such, naturally, the best gamification experience would create a sense of fun, happiness, and excitement for us. However, this is only possible with a quantitative measure of such sentiment, corresponding motivators and expectations, and the game mechanics that influence them. Analytics can be combined with customer data to predict behaviour and personalize gamified experiences in real-time. This can be achieved with a combination of:Your merchandise catalogue Potential customer’s presence proximity to your store Available inventory in that store The user’s past behaviour and current patterns These elements can provide insight into a customer’s needs and suggest possible products and services to address those needs in real-time. A text message, email or in-app notification could be pushed to the customer’s device (if known) with promotional offers to help them with their purchase.Establishing a Story Stories are fundamentally engaging and have grown into a safe harbour for us to experience loss, or more accurately, perceived loss. Based on the Freudian hypothesis of recovery and loss, such dramatizations enable the engaging power of stories and their application in gaming.Web and game developers have drawn on story-based strategies to enhance engagement with their audience. This strategy can draw on elements of game-play to optimize interaction with marketing and branding campaigns. Fundamentally, game-playing structures revolve around the theme of winning and losing, and create a perceptual “tension” of loss if a particular action is not taken. And this deep-rooted similarity to the very structure of emotional experiences is interpreted by the human brain as a potential risk that must be addressed by putting in the necessary effort. The outcome is automatically interpreted by the brain as an accomplishment.Building a Rewards Program We love being rewarded, whether in the form of discounts, points, or bragging rights. Rewards are naturally a part of retail because completing a purchase can already feel like we have walked out triumphant with a prize in hand. Building on customer engagement and brand loyalty by developing a tiered rewards program can further enhance this sense of reward, where customers can perform certain actions to inch their way towards a highly desired milestone.One style of a rewards program is to gain loyalty points. You can make use of such loyalty programs to encourage shoppers to make purchases. When a certain number of points are earned through purchases, they can be redeemed for discounts or virtual cash to spend at the store. At other times, such discounts could even be offered immediately to prospects just to get them “in the door.” However, the timing of the offer, the relevance of the reward, and the perceived value must be immediately obvious to the buyer, yet subtle enough, so it does not appear as forced.Making Games Relevant to Customers’ Locale and Timing Today’s customers rely heavily on social media to discover new products and brands and use mobile messaging apps to get feedback from friends about potential purchases. You can get customers to download your app by integrating social features and seamless sharing. For example, clickthrough and downloads can be achieved rather easily by deep-linking social sub-apps (e.g. messaging platforms) to the main app or its download location on the smartphone’s store. Once downloaded, the gamification of retail experiences can take shape rather organically. However, it should be noted that gamified promotions are only as good as the person they are offered to, the timing they are offered in, and the location they are offered at.Take me back to quick links The Value of PRO-Gamification in Retail While undoubtedly influential on Brandy’s behaviour, the “Easter egg hunt” should not be mistaken for gamification; instead, it was just a brief component within an elaborate and interactive implementation of PRO-Gamification. This gamification will lead you to a sustained stream of recurring sales, increased customer loyalty, and new and personalized customer engagement – precisely what consumers are demanding from their brands. The trick is in how you gain insights into customer behaviour, use location and timing cues to trigger customer engagement, and test new promotional strategies, while keeping the overall experience as relevant and meaningful to customers as possible.PRO-Gamification will empower you to generate more customer engagement across all channels, gain valuable insights into your behaviour, and bring more bodies into brick-and-mortar locations – but it does require careful planning and execution. That is unless you are the consumer, in which case, it is all just fun, happiness, and excitement.To win, you have to play. To implement the new retail imperative
PRO-Gamification: Defining the Future of Retail Experiences

I love technology; so much so, that I have made a career out of it. I see its potential, and I see it as the answer to many questions and problems that we as a society face. Technology is not meant to complicate our life; rather simplify it, streamline it, and enable us to do more. And it is these experiences with technology that are at the forefront of the consumer’s mind, not the complicated mechanisms behind it. It was Steve Matyas, CEO, Staples Canada, who once said “the customer doesn’t care what happens in the background,” and he couldn’t have been more right. Experiences define a brand; not products, services, or the technology that powers them. Essentials in designing experience Putting technology aside for a moment, at the forefront of any new idea or development should be the user experience. In order to do that accurately, you must go through the journey of these three essential aspects of design thinking: Empathy (with users to design human-centred experience) Ideation (generating ideas to best deliver on the user’s purpose) Experimentation (prototyping and refining with user feedback) These three essential aspects have far-reaching implications when it comes to developing new products and services because they help realign your development and design efforts with the true goal of technology – enabling the user. Instead, there seems to be a common thread in trying to integrate every last bit of technology into products and services; almost as if creating the tech equivalent to a Swiss Army knife. Except, much like the offerings of a Swiss Army knife, users don’t often find themselves in need of a mini saw, a corkscrew, and a Phillips head screwdriver all at the same time. The trick is in integrating technology so that it takes a backstage role; one that supports the requirements of the user, while propelling them forward, intuitively and seamlessly to their next step – not yours. Disruptive Technologies are artificial intelligence, machine learning, blockchain, augmented reality, virtual reality, internet of things When looking at some of the most elegant and memorable experiences provided by the Googles and Apples of the world, and you’ll begin to notice a commonality – simplicity. This simplicity isn’t found in the technology behind it, on the contrary, it is among the most complex and sophisticated to date. Instead, it is the experience for the user that is simple, which is why it’s so effective. Investing in the fundamental truth of humanity The customer experience needs to be viewed as an investment, one that will help ensure that your business can compete in not just future markets, but current ones. Here, however, we see many falling behind; and choosing to view the customer experience as a cost centre, rather than an investment in their success. And yet, time and time again we see the most successful brands prioritize experiences over technology. Why? Well, when was the last time your app wrote its own 5 star review or recommended itself to friends? Assuming that by now you have begun to realize the value and far-reaching implications of experience design, it is important to note that we are talking about a dynamic factor, one that invariably changes along with the people who experience it. To assume that your users are the same people that they were yesterday, would be a gross oversight. People evolve, and it should be this evolution that is at par with your technological development. What needs do your users have today, and what do you anticipate them to be tomorrow? By taking measures to understand their behaviour, preferences, and needs, it is paramount that you embrace a fundamental truth of humanity – we are always evolving. To stay relevant and consistently provide your customers with expected experiences, you need to be constantly defining and redefining what is important to users of every generation. Continuous Monitoring of the Evolving Behaviours, Preferences, and Needs You would be making a potentially devastating mistake by leaving something as powerful as user experience up to chance. After all, good or bad, your users will have an experience with your brand, so why not take the effort to ensure that you are providing your customers with the best one possible? As I mentioned, experiences are feelings, which then get stored as memories, and much like a hard drive, we have the ability to recall these memories, ultimately dictating the emotions we feel when we think about them. So let me ask you, are you confident that your customers are having a memorable experience or are they simply being asked to accept the one you are dictating?
Design Thinking – Technologies Come and Go but Experiences Last

Voice command technology has mostly been used in smartphones and computers in recent years, but today it’s becoming increasingly common for voice assistants to be incorporated into virtual and home assistant devices, consumer products, appliances, customer service offerings, e-commerce, and more. In fact, as the technologies required to operate voice assistants continue to improve, so too will it become increasingly common for consumers to expect this level of interaction from the brands they support. Most of us are already using voice commands on their smartphones, and it’s expected that this technology will be installed on over 7.5 billion devices by the year 2021. At the 2018 CES event in Las Vegas, there were numerous new prototypes and products that integrated voice assistant technology, proving that this trend is sticking around for good, especially in the world of e-commerce.Just look at recent news surrounding Amazon’s Alexa, whether she’s “losing her voice” for a Superbowl ad or the now infamous “laughing incident”, consumers are becoming more familiar and reliant on voice assistants. But as different brands and e-commerce companies find creative ways to implement voice assistants and more consumers become familiar with the technology, more companies are going to have to seriously consider how to integrate voice commands into their own customer products and experience, which is being revolutionized by this fun and interactive technology.The Current State of Voice Assistants: Web Searches, Questions, and Voice Command Calling We’re all familiar with the concept of voice assistants thanks to the voice command technology that modern smartphones are equipped with, such as Siri for Apple devices, Google Assistant, and Samsung’s S Voice. In fact, in 2017 the Pew Research Center polled internet users and found that 42 percent used virtual assistant technology via their smartphones, whether it’s to ask questions, set reminders, locate goods and services, or initiate calls.One of the major reasons why we use voice commands is the convenience that the technology provides, allowing us to multitask more effectively by allowing us to use our devices without having to type or look at the screen. The same Pew Research data showed that 80 percent of voice assistant users liked the idea of not having to touch their device. Talking is also more natural than writing, and significantly faster: whereas most people can only type 40 words per minute, they can say upwards of 175 words in the same amount of time. Nonetheless, the use of voice command devices is still largely limited to smartphones, computers, and home assistants. Moreover, there are only a few basic reasons why most of us use the technology, with common voice command examples including:Research dataTasks Canadians like to do with Digital Assistants are finding directions 58%, ordering food delivery 40%, making restaurant reservations 40%, making/managing shopping lists 36%. Technology Evolution and the Rise of Home Assistants In the last couple of years, tech companies like Amazon have been finding innovative ways to use voice technology, ultimately giving birth to the voice command home assistant. These virtual assistants include devices like Alexa by Amazon, Samsung’s Bixby, and Google Home, and we use them to find answers to questions, get weather or traffic updates, control various features around the house, order takeout, and much more. These devices have convenience as their number one goal, requiring only addressing the device to activate it, and then pose a question or initiate a command. For instance, a popular voice command for Alexa is “Alexa, show me my photos,” at which time the voice assistant will access the photos on your smartphone and display them.Popular Virtual Assistant Devices are Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant, and BixbyTechnological Developments are Expanding the Potential of Voice Assistants Voice command recognition algorithm technology is still in its nascent stages, and new developments are happening all the time that are making voice assistants more appealing and easier to use. Plus, these developments are also increasing the applications for the technology, which is why the use of voice assistants will only continue to grow in the coming years. For example, natural language processing has taken some major steps forward in recent years, and since 2012, Google alone has reduced its speech recognition error rate by over 30 percent. Another major development that’s making voice assistants more viable is the cloud because devices can use remote servers to process information and requests rather than a device’s own processor, and this makes the technology far more powerful. Finally, artificial intelligence and machine learning mean that voice assistants can improve themselves over time by learning from previous interactions, and this also means that devices will get better at remembering user preferences and histories.Voice command recognition algorithm technologyFactors that are improving voice assistants are development of cloud, artificial intelligence and machine learning, emergence of new developments and applications, reduced speech recognition error rate. Unlocking the Possibilities: How is Voice Command the Future of Customer Experience? Voice assistant technology isn’t limited to virtual assistants and mobile devices, and there are a number of applications where this technology is currently being implemented to enhance customer products and experiences. For example, voice command technology is a natural fit with home appliances, and companies like GE, Whirlpool, Samsung, LG, have already partnered with Amazon (Alexa), Bixby, as well as Google Home to manufacture microwaves, washing machines, cooking ranges, refrigerators, and other smart appliances that are voice activated and can provide consumers with interactive customer experiences. In fact, you can use your digital assistants to get your stocks up in the refrigerator, clean your dishes, do the laundry, and more using the smart connected appliances. However, this technology isn’t limited to in the home as we’ve seen from the insurance company Lemonade who is using voice assistants to provide incomparable customer service, and they’ve created an AI bot named Jim who can process claims and approve payments in record time. As more developments happen in this field in the coming months and years, voice-enabled devices, items, and customer service offerings will only continue to become more ubiquitous as well. Recent studies by MasterCard and Mercator found that 21 percent of voice assistant users in the US use the technology for more complex e-commerce and banking functions. The same study also found that users are becoming more trustworthy of the security and privacy settings of these devices, which will open more options for banking, telecom, and retail. Here at home, Google reported that 73 percent of Canadians would like to complete tasks by speaking to a digital assistant, and according to Tractica, by 2020 there will be over 1.6 billion digital assistant users. Although most voice assistant use still resides in the realm of smartphones and home, there will be newer ways to incorporate this technology into products and services. To stay relevant, we need to start incorporating the fastest growing consumer technology for 2018 or risk getting left behind. Looking to add some voice to your experience? Let’s Connect
Voice Assistants: Empowering e-Commerce Customers To Do More

Depending on which study you read, you’ll find failure rates for large IT projects range anywhere from 30 to 90 percent. Whatever the number, it is an astonishing figure considering the strategic importance of many IT initiatives in today’s world. Which begs the question – how can you improve project management and create a scalable framework by utilizing the best attributes of the Agile and Waterfall methodologies?Let’s take a look together.Agile and Waterfall—Preeminent Management Methodologies Project management is difficult, even under the best conditions, with software development projects potentially offering the greatest challenge. Neither business needs nor technology stop evolving, which means projects need to be managed in a highly fluid environment. That’s why it’s vital for your development teams to have a well-defined project methodology in place. By following a structured and scalable framework, project managers can effectively manage the complexity and variability of IT systems as well as the software application(s) being developed. This serves to drive benchmark success and reduce the risk of costly rework.Two of the most popular project management methodologies are Agile and Waterfall. Both of these are solid, mature methodologies and are popular for diverse reasons. When it comes to choosing between the two, neither is inherently better than the other; rather, it is the project itself and the team that is executing it, that should dictate which methodology is selected.In choosing between Agile and Waterfall, consider the situation, tactical goals, the composition of your team, and your culture. Even if your organization supports a particular model, there are usually opportunities to enhance your chosen method. You should tweak or blend the two methodologies to align with your unique needs, handle new challenges, and keep pace with the larger mandate.To clarify the opportunities and obstacles of both Agile and Waterfall, let’s begin with a deeper dive into each.The Agile Model Agile development uses an iterative, incremental approach that emphasizes the rapid delivery of an application in complete and functional components. If all planned work for the project cannot be completed in the current cycle, work is reprioritized, and the information is used for future iterations or “sprint” planning.Agile practices are best suited to projects that require constant improvements and need the flexibility to adapt to the varying requirements. As tasks are groomed, they can be evaluated by both your development team and the client in order to amend and meet the changing requirements. The multiple development cycles can be executed, with deliverables prioritized by business value.The objective of each cycle is to deliver a shippable product that can be demoed to provide feedback and shown as evidence of progress. Any recommendations are directed to future iterations. Agile offers the prospect of ongoing improvement and is highly flexible. In today’s fluid market, where software development needs to be fast and efficient, Agile offers an attractive option.Advantages Speed: Working software can be delivered quickly and at a consistent pace. Flexibility: The process adapts to changes as they occur, which allows for immediate client and end-user feedback that can be used in the next iteration. Predictability: Since every cycle is of a fixed-time period, project timelines are easier to predict. Value-focused: Development is often more value-focused, which helps fulfill specific end-user needs. Challenges Continuous testing: Testing is needed throughout the project, which can stretch resources and increase costs if not complemented by continuous integration and automation testing. Frequent collaboration: Active customer involvement can add to implementation time and expense if processes are not adapted across your organization. Scope definition complexity: The iterative nature of Agile development can create complications in defining the project scope if iteration goals are not defined properly. Self-organized team: Team members need to possess and exercise multiple skill sets to help each other and remove internal impediments as much as possible. The following visual demonstrates key recommendations to overcome the aforementioned challengeshow we mentor and remove impediments because we have1. Manageable Team size. 2. Single funnel and decision making. 3. automation and seamless integration. 4. collaboration. 5. self organising team. 6. time bound cycle. 7. tool. 8. quick daily update.The Waterfall Method Known as the traditional method of software development, the Waterfall approach is a fixed, linear methodology that comprises sequential Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) phases. Since each phase is sequential, after a step is completed, rework is typically required to enable your developers to revisit an earlier step to alter the project or its direction.The methods linear approach makes it simpler to manage and understand. Projects with established requirements to deliver new product(s) with multiple dependencies are good candidates for the Waterfall method.However, because of the Waterfall methods rigid structure and strict controls, there is little room for modification or error on the part of your team. Therefore, a project acceptance criterion and a detailed plan must be established from the start and followed carefully.Advantages Well-documented: Each phase calls for comprehensive documentation, which makes it easier to leverage code of previous projects and develop a solid base for upcoming projects. Firm deadlines: A defined starting point and a fixed evaluation process for each phase make it easier to estimate costs and meet timelines. Well-organized: Clearly defined projects with sequential workflows help simplify status updates to all your project stakeholders. Challenges Difficult to modify: Since testing and feedback don’t occur until late in the project, modifications and improvements can be complex and costly to implement. Lack of foresight: Since requirements are often unknown when a project is initiated, designers can’t always foresee problems that may arise out of the implementation process. Thus, Waterfall requires that key team members—and especially the project manager—have worked in similar circumstances. Delivery speed: Due to the sequential approach, your team can’t produce a shippable product until all project phases (SDLC) are completed. Evaluating Best-Fit Project Types With its linear model and clear specifications, it might seem that Waterfall may require less time with better control compared to Agile. This is accurate to some degree. However, with Agile and Automation Testing, products can be launched anytime, helping to accelerate time-to-market and revenue generation.In terms of evaluating between Agile and Waterfall, neither is intrinsically superior. Depending on the scope, structure and scale of your software project, you’ll usually find one methodology more relevant and useful than the other in specific scenarios. The characteristics of a project help determine which methodology will work best.Choose Agile when: Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is more pressing than product completeness. Clients have the opportunity to revise the project scope of future deliverables based on market condition and response. You have flexible and expert developers who can think independently. The product is planned for a market with rapidly evolving requirements or standards. Choose Waterfall when: The end product design and features are clearly defined and determined. Clients have a clear vision and are not expecting to modify the project scope drastically once it has commenced. Product completeness, rather than speed to market, is vital to success. Optimizing Your Return on Investment While the idea of following a designated methodology for completing a project makes sense, what happens when your unique project requires elements from both Agile and Waterfall? Simple, you take the best of both worlds and use a hybrid model. For example, we have used agile sprint-based development in Waterfall methodology and it has provided our team with the opportunity to review the outcome after every short cycle of development.Ultimately, understanding the opportunities and obstacles of these methods will make you and your team better equipped to implement a scalable framework to deliver complex IT systems that meet sustainable growth. Here at mobileLIVE, we’ve successfully delivered hundreds of projects using a combination of Iterative Waterfall, Scrum, and Kanban methodologies, all tailored to the clients’ unique needs.The above image clearly demonstrates the scalable approach by leveraging the three methodologies namely Iterative Waterfall, Scrum, and Kanban. At the time of backlog grooming, the stories are assessed, and right methodologies are chosen to develop the enablersRemember, while the method in which a project is executed is critical, ultimately what really matters is winning business and consistently delivering high-value software that meets end-user performance demands. Reach out to us today and learn how we’ve helped our clients streamline development without sacrificing on value for the end-user, all the while exceeding quality, one time, on budget – every time!Interested in learning which approach is right for you? Let’s Connect
Agile or Waterfall: Which Approach Is Right For You?

What makes an idea powerful? Simple. Ideas are powerful because they are living things, which have an ability to not only evolve and change but change the lives of those around it. mobileLIVE started as an idea, one that continues to evolve each and every day, but remains true to its vision of being a “Canadian Centre-of-Excellence” at the forefront of development, testing, and experience design services.mobileLIVE has achieved 100% customer retention and is recognized as one of Canada’s Best Managed Companies, Top Mobile Technology Company, and Fastest-Growing Company in North America. Consisting of nearly 300 diverse team members, we have successfully designed, developed, integrated, and tested 1000+ innovative digital transformation solutions for some of Canada’s most iconic brands. This is who we are and what we are known as today; however, the story of mobileLIVE has much more humble origins, and it began with just one man.The year was 1998; Microsoft just became the biggest company in the world, mobile phones resembled bricks, and a young electrical engineer, by the name of Jahan Ali, immigrated to Canada to pursue his Masters from the University of Toronto. Like many new immigrants, Jahan had his fair share of hardships, but he did not let new surroundings stand in the way of his dreams. In 2001, he not only graduated but landed himself a prestigious job working for Motorola. It seemed as though everything was coming together.A leader by nature, Jahan found himself growing restless in his role, despite having made significant contributions to not one, but two, major patents integral to Motorola’s success. It wasn’t a lack of money or recognition that was causing Jahan’s discontent, rather his unwavering vision; a dream of creating a Canadian Centre-of-Excellence and become the number one company for every customer it serves.In true form to dozens of entrepreneurs before him, Jahan left his successful career at Motorola and began mobileLIVE in the basement of his home. However, like most great ideas, its realization was easier said than done. From initial capital required to launch his company to competing against offshore trends for retaining market share in Canada, Jahan faced many challenges, but his innovative strategies and sheer determination kept mobileLIVE on an explosive growth trajectory.The Incredible Journey Stages in digital transformationStartup Phase Jahan had to find a way to distinguish mobileLIVE in an already dense digital realm. Noticing an industry pattern, primarily focused on OPEX and CAPEX reduction, Jahan saw an opportunity in certifying devices for telecom operators before launch and in response created Canada’s FIRST-EVER third party lab for smartphones and IoT (Internet of Things) certification. The lab was a huge success as it negated the need for telecoms to build their own sophisticated and expensive testing facilities. True to his nature and his vision for mobileLIVE, Jahan did not stop there.Service Expansion Jahan noticed an increasing trend in offshoring of software development to reduce costs. Disturbed by jobs being shipped out of a country that had given him so much, Jahan decided to further expand mobileLIVE services in the custom development of mobile and web apps while challenging the offshore model. mobileLIVE started offering reduced total-cost-of-ownership by building modular and reusable software frameworks, practicing user experience driven solutions, and developing iteratively with higher velocity. This was very well received and became the turning point in mobileLIVEs’ success and in moving jobs back to Canada.Product Development With a taste for success, Jahan wanted to further diversify the mobileLIVE portfolio in response to the growing importance of a digital workforce, artificial intelligence, customer experience, and process automation. At the same time, he realized that all the major automation products were being produced in the US and Europe, but none were being developed here at home, in Canada. This inspired him to align with Government of Canada’s innovation agenda and launch mobileLIVEs’ Robotic Software Factory, a product of 100% Canadian research and development. The robotic automation software is designed to emulate interactions of humans with a system interface to handle standardized, repetitious, and rule-based tasks. This not only proved valuable for testing user experience across ecosystem but also opened the door to process automation that could provide business with consistency across channels, lower operational costs, and improve team productivity. Within a year of launch, three major brands began to utilize this tool as an essential part of their automation strategy. This helped to solidify mobileLIVE culture as one of automation, with the end goals always being lower cost and enhanced customer experience.Accelerating Digital Transformation In the current phase, mobileLIVE has established itself as a tremendous force in accelerating digital transformation with specialization in experience design, web/mobile/cloud/IoT applications, analytics, artificial intelligence, and automation. The offerings of mobileLIVE have evolved alongside the digital landscape by providing solutions for customers and end-users designed to simplify, not complicate the experience. Each and every day our team renews their promise to our clients; of ensuring that their initiatives will go to market with an unprecedented focus on the end-user, exceeding quality, on time, on budget – every time!mobileLIVE Values From creating the FIRST-EVER third party testing lab for smartphones and IoT in Canada to helping pave the way for national pride in the area of robotics and system automation, mobileLIVE continues to evolve while remaining true to our vision. And despite how much we have changed over the years, we have always taken a customer-obsessed approach in everything we do, and that carries from our clients to their end-users. We do this by creating not only simple, intuitive, and enjoyable experiences for the end-users, but by developing modular, scalable, and adaptable frameworks, bolstered by a collaborative and unique delivery model, designed around building customer intimacy.As one of Canada’s Best Managed Companies, for the second consecutive year, we remain focused on our clients’ success by transforming their digital landscape, increasing their operational agility, and creating exceptional experiences for their customers.We are mobileLIVE, and our story has just begun.
A Digital Transformation Brand Developed & Integrated in Canada

It has been more than four weeks since the “FOR SALE” sign has been up on a house I drive by on my way to work. The house is in a well-known suburb within the western region of the Greater Toronto Area (GTA) where properties have been sold rather quickly in the past. It is priced on par with current market rates and does not suffer from any defects or design flaws. So why has it not been sold yet?Certainly, there are indications of a cooling trend in the Canadian real-estate market, but they are nowhere near alarming. This got me thinking whether there is something more at play than just a “downturn”. Real-estate is uniquely positioned because although it is consumer-driven, it constitutes a vital, highly expensive, and life-changing transaction. However, a paradigm shift in consumer trends to abandon bricks-and-mortar retail in favour of online shopping, as well as the onset of digital transformation, may also shed some light on a growing expectation not only for convenient and instantaneous access to rich and personalized information but also to land a “better deal” than in the past.Ultimately, can digital transformation of real-estate help current professionals and organizations differentiate themselves from the competition in these times of change?Why real-estate needs digital transformation? According to analysts, the salability of a property heavily depends on its Days on Market (DOM) index. Factors – such as seasonal variability, condition of the property, whether it was staged to sell, buyer’s availability to see a property, as well as seller’s lead time to allow in-person showing – can have a significant impact on DOM.digital transformationImmersive technologies such as Augmented and Virtual Realities (AR/VR) can drastically improve this index by providing convenience and enhanced experiences to buyers, agents and sellers alike, and making way for digital transformation. AR/VR can save considerable time and expenditure not only for potential renters or buyers, but also for sellers and realtors during times of potential downturn where buyer-to-seller and buyer-to-agent ratios drop significantly. Thanks to immersive tech like AR, MR, and VR, potential buyers can soon be able to move freely in their future residence or office virtually, just by putting on a VR headset or by watching an AR representation of it on their smartphones or tablets. And perhaps this technology that combines VR and AR might just be the key to harnessing immediate success in the real-estate market in today’s highly volatile environment.What are immersive technologies? Since its inception by Laurence Manning in his late 1930’s science fiction stories, VR (and its close cousin AR) has only recently gained massive popularity. Technological progress and digital transformation has allowed the improvement of immersive User Experiences (UX) and reduction in costs, thus favouring their democratization – but the UX for AR and VR can be considerably different.VR is a three-dimensional, computer- generated environment which can be explored and interacted with by a user. A range of devices (e.g. headsets) can be used to stimulate vision, hearing, and touch in order to create the illusion of a virtual reality that is created using a computer. AR, on the other hand, is an enhanced version of reality to add digital information on top of a captured image or video. AR is typically available in mobile apps that use a smartphone camera to capture videos of the real world, and then superimpose a layer of information on it, including text, images, and virtual 3D objects. But recent advancements have been able to combine the characteristics of VR and AR to give rise to immersive Mixed Reality (MR) experiences such as those possible with the Microsoft Hololens.How does VR or AR concretely fit into the digital transformation of the process of sale or leasing of residential or commercial real-estate? The experience for potential clients wanting to visit a property could be of two types: Either remotely (by visiting the real-estate broker’s website,) or in-person with or without a real-estate professional to guide these virtual tours. To simplify the visit process, visitation developers can leverage AR and VR experiences by capturing 360 Videos of a property being offered, as well as creating its virtual model at a small fraction of the cost of physical staging and refinishing. Such modeled spaces can then be imported onto 2D media for AR experiences or presented as VR content using virtual headsets.Enhanced customer experience through virtual visits and staging 90% of households today begin their real estate search on the Internet, with more than 50% of searches made on mobile devices. To enhance the user experience on the realtor’s website, a virtual presence of the property through VR and AR can highlight Points of Interest (POIs) that allow potential buyers a better understanding of the property. However, unproductive physical visits despite appealing POIs can result in the added cost of sale if buyers are unable to correlate their “imagined” property compared to how it really looks in real life.While these technologies cannot offer the guarantees of a sale, they can undoubtedly allow customers to refine their search. This reduces the number of unproductive visits to the benefit of generating and following more serious leads by realtors. Customers can also make more educated selections from a realtor website using technologies that create immersive experiences, as they provide a spatially richer experience than mere photos or videos. Potential buyers can then decide much more easily whether specific properties are “worth the visit” for them.Analysis has shown that around 50% of potential buyers can request on-demand (or same day) access to a property for viewing in a “buyer’s market”. While some mobile apps today have enabled on-demand availability of real-estate professionals, the actual viewing availability of the property can drastically impact the potential sale. By leveraging immersive technologies, realtors could at least generate interest for a deferred visit by offering an instant VR experience without the need for immediate physical access to the property. This also benefits real estate professionals, who will no longer be required to organize visits just to generate interest in a property. Instead, they can offer potential buyers with an immersive virtual experience of the property visit.Furthermore, market trends in some areas in the last five years suggest that 1% to 3% of investment in home staging can bring an 8% to 10% increase in sale price for a residential property. This means that for staging a typical property (e.g. a residence in a suburb of Toronto, Canada) valued at $800,000 CAD, an upfront staging cost of up to $24,000 CAD may be incurred in some cases. And there is an inherent risk of the staging not being on par with the buyer’s expectation or tastes. Such upfront costs could be eliminated (or reduced to a fraction) by the use of virtual remodelling and staging of a given property until the buyer interest can be assessed. Potential savings could also be passed onto buyers where little to no physical staging being required, and this may incentivize them just enough to close the deal.In fact, builders and realtors will need to start leveraging storytelling techniques to communicate “the art of possible” during virtual and in-person showings with these technologies. Storytelling can allow seasoned stagers or graphic artists to work remotely with realtors to virtually “stage” a property based on potential client feedback in real-time, which may further help in making the sale.Why Real-Estate needs digital transformation?For instance, potential buyers looking for a “fixer-upper” may wish to visualize the property with the appropriate refinishing. Those looking to purchase a new home based on a design by the builder may want to visualize the finished home through a 3D immersive experience. And those adamant on specific looks of the property – for instance, wanting a wooden floor with oak finish instead of porcelain tiles currently offered with the “base model” – could gain enough confidence to make the purchase with the upgrade. Similar experiences can be offered using virtual staging objects, such as curtains, furniture, and lighting to facilitate purchases from partnering hardware and upholstery providers.Better analytics to drive decision support Analytics is also an important aspect of using immersive technologies since they allow realtors to gauge the client’s interest in a property, as well as that of the personalized experience. Popular analytics providers are able to offer some web-page related KPIs, such as pageviews, sessions, and exits. However, these technologies and experiences can provide realtors with deeper insight into specific aspects or features that are requested by potential buyers. For instance, a customer requests to see what a living room might look like with maple hardwood floor along with crown molding on ceilings can be captured digitally and provide useful data for prediction and next best actions.Analytics from within VR and AR environments could also shed direct insight into nuanced buyer behaviors. For instance, the mere fact that buyers spend more time viewing a particular property within the virtual tour could indicate their interest in this and similar properties. The time spent within specific virtual sections could indicate potential problems with the property that need to be resolved in order to make a sale. This data, however, can be segmented not only at the demographic level, but also from geographic, seasonal, and behavioural points of view to better drive decision-making.Putting it together VR and AR technologies can help realtors make a stellar first impression on both homebuyers and sellers. These technologies can solve common communication and timing challenges with the prospects and lead to a digital transformation in the field of real estate. As we observed, VR and AR can help realtors and support professionals spend their time effectively and efficiently allowing targeted and personalized experiences. They can also substantially reduce unneeded staging and scheduling expenditures, and opportunity costs due to unproductive showings which can be directly passed to the consumer, thereby incentivising them to close. By helping customers visualize what is possible through VR or AR, eliminating non-productive viewings, and reducing overall costs of preparing a property for sale, the real-estate industry has a real opportunity to revitalise itself using immersive technologies and digital transformation.While some software companies have started exploring this market, adoption of their solutions and products are not mainstream yet. However, we believe in the next 3-7 years, AR and VR experiences will change our lives in the same way that the web has done in the last 3 decades. And the time is now for real-estate stakeholders to give serious thought to these technologies. In order to stand out from the competition and better meet the expectations of buyers, current market players will have to adapt quickly. Investment in the adoption of 3D modelling, VR demonstration, and AR staging tools is therefore of tremendous value for builders, real estate agencies, and sellers alike. However, the end prize just might go to those who take the first step and differentiate themselves by transforming their digital engagement and experience.
Is AR and VR bringing about Digital Transformation in Real Estate
Digitization is sweeping across many industries, creating an unparalleled demand for companies to innovate, experiment and deliver capabilities faster. Increasing speed and agility isn’t just a desire—it’s imperative for survival. You need to adopt a more flexible and efficient approach to software delivery—one that eliminates the barriers and exploits the dependencies between development and operations. And for that, you can adopt a DevOps culture.In a DevOps environment, your entire team is responsible for delivering both new features and stability. Instead of simply creating code and turning it over to an operations team to put into production, responsibilities are balanced more equally, with procedures in place to make sure both teams have insight and visibility into application performance.Not surprisingly, DevOps practices continue to gain in popularity. According to data from DevOps.com, the adoption rate increased substantially from 2015 to 2016, from 66 percent to 74 percent.What’s driving the shift? Long lead times to get software into production make it difficult for companies to provide cutting-edge services and enhance the customer experience. To keep pace with the market demands, IT teams must build, deploy, test, and release software in ever-faster cycles.DevOps cycle. build, deploy, test, releaseHere are six reasons why you should consider adopting a DevOps culture:1. Accelerate innovation With an integrated operations and development team, applications can be developed and deployed much more rapidly. This is vital, since business success today hinges largely on an organization’s ability to innovate faster than the competition. Since change sets are smaller, problems tend to be less complex. DevOps engineers can take advantage of real-time performance data to quickly grasp the impact of application changes. And software fixes are faster because team members only need to check the latest code changes for errors.2. Improve collaboration Rather than attempting to eliminate the difference between the two disciplines, a successful DevOps environment promises to build a bridge to make them work better together. The software development culture then, continuously focusses on combined achievement rather than individual goals. When your software and operations teams trust each other, they can experiment, research, and innovate more effectively. It’s no longer a matter of tossing application code over the wall and hoping for the best. Your development environment becomes progressively more seamless as all team members work toward shared goals.3. Increase efficiency Automated tools and standardized production platforms are key elements of DevOps best practices which help make deployments more predictable and free your IT staff from tedious repetitive tasks. With automated testing and integration, developers need not fritter away their time relying on code integration processes to complete.Acceleration and development platforms offer additional opportunities for improving efficiency:Scalable infrastructure, such as cloud-based solutions, help speed testing and deployment processes by increasing access to hardware resources. Compilation and development tools help shorten development cycles and speed product delivery. Continuous delivery workflows can help produce faster and more frequent software release. 4. Reduce failures The shorter development cycles associated with a strong DevOps approach promotes more frequent code releases. With these more modular implementations, your teams can expose problems in configuration, application code, and infrastructure earlier. DevOps also keeps team members engaged throughout the life cycle of a feature or application, resulting in higher quality code. Fewer fixes are required because developers look for and eliminate potential problems as they write code. According to a recent State of DevOps report, organizations that adopt a DevOps culture have 60 times fewer failures than those not implementing a DevOps approach.5. Accelerate recovery time Because DevOps deployments are more targeted and isolated, bugs are easier to spot and in turn, fixes are often faster and easier to implement. Your team will mostly need to check the latest code changes to be able to resolve an issue. Resolution times are inherently faster because the responsibility for troubleshooting and fixes remains contained within a single team. In fact, research shows that high-performing DevOps teams recover from failures 168 times faster than lower performing peers.6. Enhance job satisfaction Rather than rule-based or power-based culture, DevOps promotes a more performance-based company environment. This reduces the bureaucratic obstacles and fosters sharing of risks. The result is a more contented and productive workforce, which helps boost your business performance. Developers and operations engineers generally prefer a DevOps environment because they can work more efficiently and wear more than one hat. They gain a better understanding of where their role fits into the larger scope of IT and within the business as a whole. This makes them more marketable and more valuable.Fast software delivery is crucial in today’s digital age and a DevOps culture is the driver of this process. It enables your business to accelerate go-to-market services and roll out new features quickly and efficiently. While adopting DevOps is not a simple process, when done correctly the investment will pay dividends far beyond the initial effort. With greater speed, security, and stability, a DevOps culture could be just the transformative shift you need to gain an important performance advantage.Let’s Connect to help you gain the DevOps advantage!
6 Reasons Why You Should Adopt a DevOps Culture in Your Business

Pursuit of optimal customer experience is driving digital transformation initiatives across all industries because technology is allowing customers to be in direct control of their interactions with us. From the ease of multi-channel digital connectivity to immediacy in service, customers expect frictionless and hyper-personalized customer experiences that embody simplicity, Do-it-Yourself, and social. Likes of Amazon, Apple, Google, and Facebook are also not making it any easier by setting standards that customers expect every business to match.Without a doubt, the importance of Customer Experience has grown to become equal, if not more than products and services offered. Brands who focus on improving customer experience by mapping the evolving customer behaviors and preferences, applying human-centered approach, innovating collaboratively, and executing with agility – easily differentiate themselves and excel onto a path of greater success.But let’s be clear, customer experience does not belong to any one department. In fact, it requires intense collaboration from the entire organization. Everyone working “together” towards a common purpose for the sake of the customer, who only recognizes us as – one. From a customer’s perspective, it primarily involves customer-facing functions and touchpoints, however, there is a myriad of business challenges that we need to manage in an effort to achieve the desired customer experience.To bring it all together, below is an infographic capturing shared – customer expectations and business challenges – in a digital economy.Customer Expectations & Business Challenges in a Digital Economy is a graphical representation that depicts the unique Customer Expectations and the associated Business Challenges faced in trying to meet them.From the structure of the organization (People, Culture, Processes) to the disruptive technologies (AI, Machine Learning, AR/VR, IoT, Conversational Commerce) involved, we need to sync up with evolving customer behaviours and deliver beyond their expectations. It’s not going to be simple, but we must, in order to attract, win, and retain customers in this ever-increasing digital economy.
Creating the Optimal Customer Experience via Digital Transformation

His name is David…not Tom, not John, and definitely not Donald! He is in his early forties, a technophile, practical in nature, and employed as a Senior Manager. He enjoys buying new gadgets, but being a homebody doesn’t eat out, nor travel for vacations. Yet, his shopping app kept sending him options on where to dine out today and where to take his next vacation.After patiently ignoring it for a month, he finally uninstalled the app and now goes around sharing his negative sentiments on how poor his experience was. The irony – app creators convinced David enough to get him to download the app, but either missed gathering enough information about him during registration, or never bothered analyzing his behavioural data. Result – a lost opportunity for loyalty and advocacy because they failed to recognize him as an individual and personalize his experience and customer journey to suit his needs and preferences.Let’s be honest, David is not the only one out there who seems to be getting frustrated. Even you and I expect to be recognized as individuals. Even more so, when there is enough proof advocating benefits of personalized marketing – it’s critical for current and future success; it improves brand loyalty and customer experience; it influences what customers purchase and drives revenue; it raises conversions; it has a higher click-through rate than traditional ads and so on…yet, many brands are failing to prioritize it.Thanks to AI-driven automation platforms, many of us are progressing well into achieving personalization through UX and UI. I carefully used the words “progressing well into achieving personalization” because personalization is clearly – a continuous process – and not just a one-time effort.Trying not to sell you a platform here, in a nutshell, automation platforms take signals from multiple data sources including location, demographic, psychographic, behaviour, lifestyle, interests, device, and browser information etc. Analyze customer patterns, do the segmentation, evaluate intent, and trigger next best recommendation based on an individual’s needs, preferences, and expectation from the customer journey.How does automation help in personalization?But collecting information from these data sources and analyzing them is the heavy lifting intelligent algorithms will do for us. What should we be doing to ensure success in the personalization process to create an unforgettable customer journey?Here’s my list of quick reminders Data Sources It all starts with understanding the evolving needs, lifestyle, social, and behavioural patterns of our customers throughout their journey. So, let’s ensure all data sources are integrated, to achieve a unified view. This sets the foundation for segmentation exercises and mapping of customer journeys, and without it, we won’t get far.Micro Segmentation This is a crucial exercise, where we define users in segments such as demographics, geography, behaviour, lifestyle and then feed our personalization platform. Here on, with the help of the platform, we will drill down these segments into micro-segments for e.g., behaviour (usage patterns, price sensitivity, etc.). We’ll have greater success if our one-to-one marketing and UX or UI efforts are based on the value and relevance of these micro-segments.Customer Journey Mapping customer journeys is only the beginning. We have to keep working our way towards optimizing and improving customer experience in real-time, throughout the journey. Remember, we need to win all stages and ultimately reward our efforts by achieving loyalty and advocacy.Key Moments Like they say, “we live in the moment” …be ready to catch that key moment in real-time. As soon as our customer sends out a signal of their intent, our library of content should be ready to match the context and trigger right away for best results.Mobile Experience Prioritize mobile-first experience. Customers expect always-on, frictionless digital experience across touchpoints and if we’re still struggling to create an intuitive, contextual & DIY mobile experience, then we are surely missing out…big time!Addressable Name Depending on the channel of engagement, start personalizing by name, it’s the very basic step. Generic greetings just don’t do it, especially when we are attempting to create personalized experiences. Let’s build an emotional connection right off the bat.Messaging Whatever the medium, a hint of customer knowledge in the message does improve engagement. We surely want customers to know, that we have recognized them as individuals. Be personable, but don’t scare them by displaying too much personal information. That’s still creepy.Timing Timing is key. Simple steps in understanding customers time zone, the best time of responsiveness, or behavioural pattern, will make a huge difference in response and message effectiveness. Our objective here is in reaching out when customers will respond most favourably.Team Assemble a strong dedicated team to manage personalization. It’s integral to the process. Create a team of creatives, digital marketers, and IT. Empower them with tools and decision-making authority, so that they can maintain the required agility in this process.And last, but not the least…Continuity As pointed out earlier, personalization is a continuous process of learning, improving, and achieving. Don’t be shy in evaluating response, refining, and attempting again to achieve the desired results. Start small, measure, improve, and keep growing!What’s on your list for achieving personalization?Let’s Connect if you want to set up/improve your personalized experiences.
How Can We Ensure Success in Personalized Experiences

“Machines will take over nearly half of all the work done by humans”, claims an Oxford university research. Another prediction says, “90 percent of the world’s population will soon be jobless owing to the fast development in the field of Artificial Intelligence, machine learning, deep learning, analytics, and robotics.” The panic that robots taking over our jobs is going viral!Bill Gates, founder of Microsoft, in a recent interview anticipated that, robots will replace a lot of workers and therefore they should be taxed to bring in funds to socially support displaced workers. Some governments across the globe are also working to facilitate the Universal Basic Income (UBI) scheme to support people who are distraught by automation. While it’s true that robots are all around us these days, considering them as a threat, is fairly incorrect.Way back in 1964, Westminster in Colorado got its first automated gas delivering robot. John Roscoe, short stop convenience store owner, bought an electric box that would let a clerk inside the shop activate any of the pumps outside. It was not before the 1970s when self-serve pumps started gaining momentum. Pump makers eventually added automation systems to let customers pay at the pump. By 2000’s, task specific robots took over the gas attendants role in pumps all across.Automation changed outlook With self-serve pumps in actions, the cost of overall fuel dropped down because you’re not paying for the gas attendant’s salary. People, in turn, started investing their savings in learning and inculcating various other soft skills and value addition roles.Also, if statistics are to be believed, in the 1970s, 14 percent of men held four-year college degrees and 8 percent of women in Colorado. However, by 2015, it was up by 32 percent of men and women. So automation, in a way helped to transform a pool of people whose mindset was fast cheap labour jobs to professionally skilled jobs.While pump attendant jobs went away, new jobs like software coders, engineers, sales staff, and project managers propped up. The pump owners too utilised their savings in building small convenience stores and marts in the pump vicinity. This in turn, employed some others to work as clerks, sales staff, and cashiers in these small shops.Even today, despite the number of jobs that technology is fast eating over, it is creating better avenues of income as well.New doors open up with automation A new study from Redwood Software and the Centre for Economic and Business Research (CEBR) explored the trends in robotic automation in 23 countries over the past 20 years to quantify their impact on GDP per capita and labour productivity. The analysis revealed that, robotics now adds more value to the economy in comparison to the traditional industries, therefore, fuelling job growth.Interestingly, history has also shown us that factories that have used automation in their manufacturing or production phases have cut down prices of the overall product, making it more affordable in the market, and increasing demand for more production. While some others generated more profit to pay higher wages, bringing in more employment and quality in production.Amazon is a brilliant case in point of this phenomena. Over the past few years, the company has invested heavily in automation, from 1400 robots to the present over 45,000 robots working in its warehouses. The new hire rates have also not changed, during the same period of time. But the company has been able to provide unique customer experience all across its business touch points.Have you heard about brand influencers? US based company Influential One, which partnered with IBM Watson, analyses and understands the integrity that people have with various brands via their social media interactions. The company then connects people and brands to earn money by being “brand influencer”, a new category of job aided by AI understanding.With automated apps and IoT led devices, taking over our lives, new avenues will surely open up to bring in new dimensions to the workforce. Jobs in various categories like VR/AR personalised entertainment, Nanotechnology, E-marketing, Space Economy, Senior Care, Sharing Economy like AirBnB, Uber, etc., Renewable energies, Coaching, Organic Data Analysis, Chamberlains and Stewards, jobs that demand human contacts like Nurses, Counsellors, Psychologists, etc., Genetic Engineering and more such positions will eventually prop up.Just being modern Luddites, afraid of losing work and place in a society led by robots is not a good sign. Automation will always bear a symbiotic relationship between Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Human Intelligence (HI). Therefore, let’s keep the evolution of human history in mind and keep working towards a brighter future!
Are Our Jobs at Risk with Automation?

While we were still working on mastering Social, Mobile, Analytics, and Cloud (SMAC), Digital Transformation aka (DX) itself has evolved into DX 2.0 representing the priority stack – Internet of Things, Data, Design Thinking, and Artificial Intelligence (IDDA).It’s all happening – thinking Internet of Things with all possible connected devices and touchpoints in our daily lives; integrating data gathering sources, assembling data strategy and analytics for better informed decisions; designing products, experiences, and businesses with a focused human-centered approach; and making artificial intelligence predict patterns, automate and personalize experiences.Let’s take a deeper dive…The new chief of data generation Mobile itself, or for that matter mobile and web, are no longer the chief of data generation – its Internet of Things (IoT). Data is not only being generated by the apps we use but our interaction with almost every smart device including; wearables, cars, cameras, routers, places, social, etc. representing the enormous universe of opportunities and tons of yummy data all around us. With less than 20 billion connected devices today to 30 billion in 2020 to 80 billion in 2025, digital businesses will be leveraging IoT and not limiting themselves to mobile and web only.Data is king, big or small Data, big or small, remains to be the king in DX economy. Data is the most valuable currency; our gateway to growth. Data is being generated at a phenomenal pace and by 2025, Digital Universe is estimated to create 180 Zettabytes of data in the world annually. Unfortunately, many businesses are still managing data poorly – leaving it scattered, unclean and unfit to use. Imagine the opportunities being lost here. We need to declare an urgency in hiring employees or partners who master data, can help implement data strategy and analytics to fuel growth.The human centricity The Design Thinking approach of empathizing, defining, ideating, prototyping, and testing is centred around humans. Thanks to 918,202 UX Designers all over the world, not only the quality of products has just not improved dramatically but the incredible design thinking approach is being applied to almost everything – even business operations. Realizing that businesses are run by humans (employees – or at least till robots take over) design thinking approach is being used to enhance team collaborations, processes, innovations, performance, and satisfaction. This in return is benefiting customer satisfaction and business growth.Magic of artificial intelligence Artificial Intelligence is the magic wand in achieving automation and personalization. Implementing robotic process and test automations along with bots socializing and assisting, AI is not only saving time and cost but increasing agility and accuracy as well. At the same time, AI is working through basic segmentation, to prediction and personalization based on customer preferences and behavior patterns, all the way to unbelievable autonomous vehicles. By 2029 Artificial Intelligence will actually read at human levels, understand language and be able to communicate at human levels, at a vast scale.Digital transformation is a journey; not a destination and we at mobileLIVE believe, DX stack has evolved into IDDA from SMAC. However, it’s not one or the other rather both stacks – SMAC & IDDA – need to be conquered to continue growth in this ever-increasing digital economy.What do you think?Join the conversation @mobileLIVEInc #DX2.0
DX 2.0 – Core Digital Transformation Stack has Evolved

It’s 1975, a customer walks into a Nordstrom store in Anchorage, Alaska to return a set of tires. The clerk, saw the price on the side of the tires, reached into the cash register, and handed the man $145.It did not matter that Nordstrom had never sold tires.Nordstrom was and continues to be an upscale clothing store. The customer had bought the tires at the store that occupied the same retail space prior to Nordstrom moving in. But in those 2 seconds while making a decision, Nordstorm’s philosophy kicked in and the staff did what they were trained to do – “Ensure that the customer experience was optimal”.Times change, mediums of communication change, but legendary stories such as this one have become the cornerstone of CX philosophy of many a companies, including ours. Apple, Nordstorm, Lululemon have all continuously shown us that the magic unleashed when the entire organization is collectively able to optimize every touchpoint with the customer – telling the same story, creating personalized, focussed, and iconic experiences.Challenges make way for opportunities The challenges and opportunities are now amplified with the boundary between digital and physical getting blurred. Managing and improving this phy-gital (physical-digital) customer experience delivers real benefits to companies that successfully execute customer-centric strategies. McKinsey predicts that companies with great digital experience will have 30-50% increase in measures such as likelihood to renew or to buy another product, making the case for investment even more compelling.Revolutionary, multi-sensory initiatives To adapt and change, companies have to embrace a design thinking approach anchored not on technology but on ease, effectiveness, and emotion. CX is becoming not only omnichannel but more multi-sensory, complex to design and immersive (AR/VR). It’s heralding us into a new era.Take this example from the retail industry; a 100 year back when someone walked into a store more often than not the shopkeeper knew the customer, their choices, socio-economic status and based on it made recommendations.Fast forward to 2017 and it would be hard to find a service agent in a big box retailer to save someone’s life; let alone talk about a product. Here Big data and IoT is being used to recreate the experience from a century back. Providing customers relevant, targeted, and focussed recommendations based on their buying pattern of the last few trips and using IoT as the last mile. Its essentially providing the customer the required information to help influence their decision-making paradigm in the 2 seconds when they are making it.Beacons help track customers in the aisle and while they stand pondering on the type of noodles they need to buy – in real time based on inventory and promotions a recommendation is pushed to the end customer’s phone. Revolutionary!But it’s only the beginning. Imagine two friends go shopping for a tent. Spotting one they like, they both crawl inside to check the capacity. But there’s something unusual about this scenario: One is in Toronto, the other in London. And neither is anywhere near a sporting goods store. Virtual reality, along with its first-cousin augmented reality, offers retailers the opportunity to transform how people shop! Mobile Apps and Websites, will soon become “so third quarter 2016”.Transformatory DX will empower CX Customers, stoked by these transformatory digital experiences are going to ask for more and organizations will have to deliver. Incumbents across all sectors from retail, mining, telecom, finance, healthcare, and others will continuously need to redesign and transform significantly. This transformation does not need to be radical each time if their current operating model puts the customer’s needs and wants at the center of a digital transformation strategy; enabled by redesigned customer journeys and agile delivery of insights and services.
Future Proofing Your Customer’s Digital Experiences for Growth

Believe it or not, Gen-Y (also known as Millennials) is already the largest generation in the Canadian workforce and I’m sure so is the case in most countries. They were being ignored for their lack of income and spending power. However, it has become glaringly obvious that Gen-Y is a gigantic population, holding significantly powerful positions in the industry, and growing their spending power.But wait, it doesn’t end there. The first wave of Gen-Z has graduated and already entered the workforce. Dubbed as the first digital-native generation, extremely tech-savvy, masters of multitasking, risk-takers, and truly global, are already contributing significantly in the digital economy.By 2020, both these generations will collectively account for the largest prime target customers. While past decades have been built on the axiom of “better, faster, cheaper”, Gen-Y and Gen-Z take stock in other values.So let’s take a look at what these generations want.They want immediacy Immediacy is key with them. The era of “better, faster, cheaper” has evolved into an expectation of “NOW!”. They have short attention spans and it should come as no surprise, if you lose these generations due to lack of convenient access to your offerings, slow content loading, slow response time, or poor user experience on any touch point. They know they can demand immediacy because of the multitude of options out there, while multi-tasking comfortably through several screens at one time.They want mobile-first experience With immediacy comes mobility. Growing up with digital devices, these generations are natural with technology. While Gen-Y adopt new technology a lot more quickly compared to previous generations, Gen-Z is born among digital devices and have no intentions of denying their device addiction. It is therefore critical for businesses to design platform relevant, intuitive, and contextual mobile-first experiences. Trust me, their mobile device is always at an arm’s length if not already in the palm of their hand.They want hyper-personalized experiences The biggest differentiator of Gen-Y and Gen-Z compared to previous generations is their craving for hyper-personalized experiences. Individuality is big with them and they want personalization from all brands. They want to be recognized, valued, and provided custom solutions to suit their individual needs. Start empathizing with them and build their trust. With integration of social listening, advanced analytics, design thinking, and machine learning – every business should be able to offer hyper-personalized content and experiences.As compared to their predecessors, Gen-Y and Gen-Z’ers are reshaping customer experience management at a much faster pace. Already a gigantic population, true digital-natives, holding significantly powerful positions, and growing spending power – these generations should be at the heart of every business transformation to compete in this ever-increasing digital economy
Who is Reshaping Customer Experience?

I still remember how each generation of mobile network provided something different, something new, and caused us (myself included) to wonder what was around the corner.1G first generation of wireless cellular technology for voice calls1G or the first generation of mobile networks were analog technology; characterized by vast energy consumption. Sure, we could make voice calls, but the quality was terrible, security was non-existent, and given its speed, there really wasn’t much else we could hope to do with it.2G network was slower, but shift from analog to digital2G was undoubtedly a massive upgrade from 1G as it was the shift from analog to digital – an effort that was spearheaded to ensure a more reliable and secure communication channel. Not only that but 2G gave way to features like text messaging, conference calls, and roaming.3G network technology enabled calls, texts and access the internet3G is responsible for most of the features we all come to expect from our mobile networks and are common today across the globe. Web browsing, email, data sharing, instant messaging and more all became a global phenomenon. This generation also saw a rise in streaming services.4G fastest connection to mobile Internet experience4G brought with it fundamentally new technology, not unlike the leap from 1G to 2G. Suddenly we had high speed, high capacity, and enhanced security that was able to deliver diverse applications like cloud computing, 3D entertainment, telephony, mobile payments, and a plethora of others, all without compromise.However, we are on the cusp of a new era of mobile networks. Heralded as one of the most exciting breakthroughs of the century, we are at the dawn of something magical that will change the way we travel, the way we communicate, what we do for entertainment and the way we do business.5G promising next generation technology, future of connected word5G technology promises to be more than just the next generation but a new point in history; one that will enable a future of a connected world, unlike anything we could have imagined.Curious as to what that will look like, I’ve gathered some incredible use cases and capability displays. The video below proves how 5G speed is superior to 4G in terms of latency. Here’s a hint, 19 milliseconds can change everything! But what about business? Let’s take a look at how this superior network promises to enable enterprises large and small to create new services, deliver new and innovative products, and allow for efficiencies and possibilities in such areas as Connected Automotive, Smart Manufacturing, Connected Energy, Wireless eHealth, Smart Cities and more. The possibilities seem limitless, ushering us into a world that was once thought only possible in the movies. But this isn’t fiction; this is our fast-approaching reality. Cloud virtual reality and augmented reality are poised to disrupt the world of entertainment, but to what extent is still hard to imagine.You would be wrong to think that only the world of entertainment will benefit from this leap forward. Let’s look at how one of the key players in this technology envisions making the 5G network a commercial reality. We have travelled down the rabbit hole and are looking into what is seemingly an alternate universe, one where the impossible is becoming harder and harder to find. We are only skimming the surface of what this amazing technology can do, and as it stands right now. The only limitation moving forward will be our collective imagination. I think 5G is the magic wand we all have been waiting for.
5G Future: A New Generation of Possibilities With 5G Technology

What do Uber, Airbnb, Instagram, and even the iPhone have in common? Aside from being groundbreaking, disruptive, and wildly successful services and products, they all share a respective point of origin – they all began as an MVP.MVP or Minimum Viable Product is a concept publicized in Eric Ries’ Lean Startup that emphasizes learning in new product development. It can be defined as a version of a new product that carries “just enough” features to engage and satisfy early adopters, from which feedback can be gathered and learned from for future development.airbnb, instagram and uber MVPsTypically, any new product development is a costly endeavour – that is, until enterprises started to borrow from the startup playbook. Now, and through the utilization of MVP, organizations can develop quickly, reduce their new product development costs, de-risk their investment, test the concept in the field, learn from their users, and iteratively add new features.Today, you are not only going to learn how to develop and plan an MVP but how to do so with the help of the Design Thinking process to put an unprecedented focus on what matters most – the user.Why Design Thinking? When it came to new product development, typically, resources were allocated towards projects that “sound like a great idea” and because of that, were given time, people, and budget to explore. Sadly, and as I am sure many can relate to, this has time and time again proven to be an inefficient waste of valuable resources.Fortunately, there is a new school of thought, one that doesn’t say “that sounds like a good idea,” or at least, doesn’t until the question “where’s the proof that this is a good opportunity to spend resources on” is answered. This is where Design Thinking comes in to play on the innovation lifecycle.design thinking in innovation lifecycle. explore problem, test problem solution and execute product/market fitDesign Thinking plays a crucial role in the initial part of the innovation lifecycle by helping find the “customer/problem” fit: what’s the right problem to be solved for the target customer segment? In this phase, the goal is to “invent the future” by discovering the unmet needs of the users and the unsolved problems he/she wants to be solved.But how exactly does Design Thinking help with defining and planning an MVP? It first helps by exploring the customer/problem fit in order to find the right problem and “do the right thing.” And that is done by empathizing, defining, ideating, prototyping, and testing.Design Thinking for MVP Validation1. Identifying & Understanding Business Needs Everything begins as a small idea for something new or innovative. But how do you know the idea is valid or worth investment? In other words, how do you know your business value proposition is, in fact, valuable?One of the hallmark characteristics of Design Thinking is its emphasis on collaboration, specifically, involving everyone related to the business, from designers to developers and from business owners to the market at large. By inviting them to work together, it provides diverse perspectives on the concept being proposed and can help identify the market and business needs behind the idea to determine long-term goals of the product, solidify a shared vision, affirm the reasoning behind the project, and define success criteria.Through this collaboration, organizations can leverage the unique knowledge of different stakeholders and customers to discover the most valuable opportunities and to create a sense of support and ownership for the project that will not only accelerate its implementation but minimize the risk of failure while improving the potential for innovation.2. Identify Users & Discover Opportunities Aligned with your business value proposition, identifying users and their unique needs is mission critical. After all, it is bad business to build something that nobody wants. So how do you make sure there will be users for your potential solution? How do you identify them? What are their needs?User and Business GoalsDesign Thinking is also known as human-centred design and as such, requires working with clients, stakeholders, and customers to bring real user outcomes. With this user-centred approach, it emphasizes on not only understanding the user but identifying their current experience, goals, and needs in order to help determine what the real problem(s) is/are. This is achieved through a combination of quantitative and qualitative user-research methods specifically designed to answer the key questions about user behaviours, preferences, habits, and value proposition. The value of this approach is that it prevents the False-Consensus Effect, which is a bias in which people tend to overestimate the extent to which their opinions, beliefs, preferences, values, and habits are normal and typical of those of others. While hard to admit, it is prudent to remember that “you are not the user,” and it is worth investing time and effort in understanding the context of ‘real-users.’3. Decide what Features to Build By now, you should have identified your users, their unique needs, and your business value proposition. However, you may have also noticed something else happening in tandem – your idea has started to turn into something a lot more tangible. When that happens, you know it is time to visualize and begin designing the core features.Collaboration during the brainstorming process is vital to finalizing the list of core features to be developed. This list should be based on collected opportunity statements, a detailed product roadmap based on a breakdown of the proposed features, and finally a matrix that prioritizes them. Keeping the end-goals in mind of both the user and the business, reviewing the product from different points of view, and utilize the diverse expertise available to you will all aid in you not only making the right decision but “doing the right things.”Design Thinking Workshops specifically employ tools, methods and techniques to bring out the best ideas through a collaborative way. They are quite different from typical meetings and discussion sessions where power-distance relationships, personality types, and organizational culture often gets in the way of collaboration.4. Build a Prototype, Test, Learn & Iterate Building a quick prototype is the best way to allow users to test the concept and provides valuable information to designers, developers, and product managers on how the users will interact with it. Once done, you then iterate on that prototype accordingly to user feedback before building your actual MVP. This has proven to be the fastest, most cost-effective way to build and validate the product concept before spending a lot of time, money, and effort to build and launch it.It is stated by IDEO, “If a picture is worth a thousand words, a prototype is worth a thousand meetings!”Explore customer problems and design thinkingexplore a customer problem with design thinking methodEmpathize. Identify and understand users and business needs. Define. Identify user’s goals, pain/gains and discover opportunities. Ideate. Decide what feature to build. Prototype. Build a prototype, test, learn and iterate.While the MVP consists of core features, it is essential to remain nimble. Products must evolve based on the market and user’s needs down the road. It is through tests and feedback that you will learn if assumptions about your product idea are indeed valid. However, sometimes (and in some cases, often) it will turn out your assumptions are not validated based on the feedback, or they may just be in fact, wrong. But don’t worry – this isn’t a bad thing. You want to fail early and fail cheap on your way to building a better product.Design Thinking for MVP & Beyond Digital products and the ecosystems they call home are dynamic, constantly evolving – much like the users, their needs, and expectations. And it is in this environment that we see the unparalleled value of the design thinking methodology and its user-centred approaches, early user engagement, and collaborative nature flourish. By utilizing design thinking to address the real needs of the users and in turn, “do the right things,” this practice will make all the difference in not only delivering innovation and value to the market but has the power to transform an organization and its people.By now, you know how to create an MVP utilizing Design Thinking, but that is only half of the equation. After you establish what you want to test with your MVP, you then must choose which MVP validation method will provide you with the most reliable and actionable data from real-life users; techniques, that we will cover in an upcoming article.
Design Thinking: Turning Minimum Viable to Most Valuable Product

Chances are, you’ve already heard of the Future Workforce or the Intelligent Digital Workforce, which essentially is a newer way of referring to Robotic Process Automation (RPA). For the sake of clarity, let’s quickly define it and move on to why you need to adopt this disruptive approach.RPA is a practice of automating existing repetitive, high-volume, and complex tasks with the help of software “bots.” The bots emulate human-like interaction with multiple systems without changing the current IT landscape.Another way to look at it is, while humans focus on creating the intellectual value for you; the bots carry out the mundane work much more efficiently and cost-effectively. The best part, you’re always in control of scaling this digital workforce up and down as and when required.When first introduced, process automation was met with resistance, however, since then it has proven itself to be industry agnostic, and the initial cost of setup is typically dwarfed by internal cost reductions and the significant ROI.As one of the first steps in digitizing your business, automation will bring control, efficiency, and profitability across operations while you focus on implementing other growth strategies. Keeping the above in mind, let’s get into some RPA success stories that were implemented by UXPLORE; one of our preferred partners in automation.Case Study 1: Trade Spend Analysis & Sales Insights A leading CPG distributor serving all major retailers in Canada used to gather weekly sales data at a store level manually. The data was then cleansed and mapped to product SKUs. Trade spend analysis were performed and shared with stakeholders.On average, it took 2-3 days to perform this process manually.manual process vs robotic processManual Process.Log into retailer portal to download raw sales data. Repeat for all retailers. Check for data validity and escalate to retailer if any issues. If raw data is valid, clean and transform data. Map data to item code / SKU. Aggregate sales data by SKU. Perform Analysis by SKU. Generate Reports company / brand partner. Share Trade Spend Analysis with each company. “This manual process takes me 2 – 3 days to finish the whole process”.And now the software bot does it in a few hours or on the same day!automated robotic process for automationAfter implementing Process Automation.Bot gathers sales data per schedule. Bot automatically repeats for all retailers. Apply data validation rules to accept/reject files and auto-escalate. Automatically clean and transform RAW data. Map retailer code to standard item code for each row. Aggregate data at item level. Perform Analysis by SKU. Auto-generate PDF reports for each company. Distribute weekly Trade Spend Analysis and Sales Insights to each company. “Well, with Automated Process give me same day or overnight for that”.Distributor’s success:A fully automated workflow except for escalation management 100% accuracy and a 50% reduction in the time cycle Increased bandwidth of Financial Analysts Case Study 2: Purchase Order Management A telecom operator with more than 200+ suppliers and 1000s of active POs to manage daily needed to ensure that all orders were coordinated, acknowledged, and accurately tracked.On average, it took 8 hours to perform this process manually.manual process time spanManual Process.Log into Email. Check if any new emails from any suppliers. Save attached PDF. Process the PDF. Lookup PO In SAP. Update PO status with details from supplier. Check for any anomalies. Escalate to Procurement Manager for follow-up. “This manual process takes me 8 hours to finish the whole process”.And now the bot does it in less than an hour!robotic process time spanAfter implementing Process Automation.Bot monitors incoming emails. All received emails are handled. PDF attachments are stored automatically. PDF attachments are processed. Relevant POs are automatically retrieved in SAP. PO details and status updated per information received. PO is audited per predefined rules post update. Trigger escalation if applicable. “Well with Automated Process, I can do it in less than an hour”.Company’s success:Near real-time processing of POs, improving handling time by 90%+ Same day escalation when required 100% accurate and up-to-date PO status in SAP Case Study 3: Hiring – Offer Generation, Onboarding, and New Hire Integration A fast-growing talent recruitment firm that regularly hires a large number of employees and contractors needed a way to streamline the process once the hiring decision was made.On average, it took 2.5 hours to perform this process manually.Manual Process.Hiring Decision. Generate Offer. Email Offer to New Hire. Receive Offer Acceptance. Notify New Hires Manager. Background Check. Setup New Hire in HRIS. Email Account Setup. Setup Payroll. Request Access Cards. Send Welcome Email to New Hire. New Hire Day 1. “This manual process takes me 2.5 hours to finish the whole process”.And now the bot does it in 8 minutes!After Implementation Process AutomationAfter implementing Process Automation.Generate Timesheet Report – First Audit. Apply Rules and Filters. Identify Employees with Timesheets Pending. Individually Email Employee a Reminder. Repeat Same Steps for Second Audit. Generate Timesheet Report – Escalation. Identify Employees with Timesheets Pending. Escalate to Manager of Each Employee. Check Timesheet Approval Status. Followup with Managers who are yet to Approve. “Well with Automated Process, takes less than an hour”.Recruitment firm’s success:Increased team capacity by replacing 80% of the manual process 100% accuracy of employee master data Significantly improved new hire experience through response time Case Study 4: Time & Attendance Record Tracking & Validation A leading technology-services provider (this is us actually; mobileLIVE) delivering hundreds of enterprise-grade projects needed to find a way to manage their resources efficiently; more specifically, they needed to accurately track the time spent on projects to ensure revenue and margin assurance.On average, it took 6 hours to perform this process manually.Manual Process.Generate Timesheet Report – First Audit. Apply Rules and Filters. Identify Employees with Timesheets Pending. Individually Email Employee a Reminder. Repeat Same Steps for Second Audit. Generate Timesheet Report – Escalation. Identify Employees with Timesheets Pending. Escalate to Manager of Each Employee. Check Timesheet Approval Status. Followup with Managers who are yet to Approve. “This manual process takes me 6 hours to finish the whole process”.And now the bot does it in less than an hour for us!After implementing Process Automation.Generate Timesheet Report – First Audit. Apply Rules and Filters. Identify Employees with Timesheets Pending. Individually Email Employee a Reminder. Repeat Same Steps for Second Audit. Generate Timesheet Report – Escalation. Identify Employees with Timesheets Pending. Escalate to Manager of Each Employee. Check Timesheet Approval Status. Followup with Managers who are yet to Approve. “Well with Automated Process, I can do it in less than an hour”.Our success:Fully automated workflow with no manual effort or intervention 100% follow-up rate with all notifications sent within minutes and multiple times when required Significantly increased HR capacity to focus on more value-added initiatives Small Step – Higher ROI While you may view process automation as a means to increased profitability and efficiency, in reality, it does much more than that. By teaming humans and bots together, you are relieved of time-consuming, repetitive, but essential tasks. Instead, you will find more energy to focus on implementing growth strategies and business-critical decisions.
Robotic Process Automation: Bots Team Up With Humans

Software development is saturated with frameworks, methodologies, and processes; most of which come with the promise of better development. Just ask any developer, and they will likely only be too happy to share their favourites or suggest which method you should use. Are you looking to implement a large project successfully? They could suggest a method. Are you trying to avoid discrepancy between design documents and what is actually implemented? They know a framework that’s perfect for that. And if you wanted to ensure your project has minimal regression and is maintainable over time, then they certainly know what process you should follow. But what happens when the complexity of your projects grow and faithfulness to just one method doesn’t provide the benefits and value your project (and the user) deserve? As we learned from the hybrid cloud , very often the best solution to a complex problem is a combination of several.Today, I am going to share with you how to tackle difficult and complex development in the agile space using not one method, but a hybrid combination of three specific ones.The 3 Methodologies The promise of better development through a hybrid solution of multiple methods works – but you can’t utilize just any three. They need to be complimentary, they need to pick up where another falls short, and they all need to provide their unique value that assures predictable and productive outcomes. In short – the perfect combination is TDD, DDD, and BDD.Test Driven DevelopmentTest Driven Development, or TDD, is a process of developing software where a test is written prior to writing code. Once that is done, developers will work towards writing just enough code to pass the test, and then begin refactoring.Domain Driven DesignDomain Driven Design, or DDD, is an approach to development that connects the implementation to an evolving model; placing the focus of the project on the core domain (sphere of knowledge), the logic behind it, and forces collaboration between technical and nontechnical parties to improve the model.Behavioural Driven DevelopmentBehavioural Driven Development, or BDD, is a refinement of TDD and DDD that aims to streamline development through narrowing communication gaps, creating a better understanding of the customer, and allowing for continuous communication. Simply put, BDD is a way of combining business requirements with code and allows you to understand the behaviour of the system from a business/end-user perspective.While those above are all standalone and beneficial frameworks in their own right, as I mentioned earlier, the demand for more complex development is and has proven itself too much for any single one – but not all three.A Hybrid Practice the intersection of TDD,DDD and BDD provide a hybrid approach to development which assures predictable and productive outcomesCombining methodologies in order to reach the desired outcome seems like a great idea – especially in theory. However, it isn’t enough to just combine these methods and hope for the best. Aside from having organizational buy-in and a shared understanding of these concepts singularly amongst your teams and its members, the most crucial step is to understand when and where to utilize these frameworks to ensure maximum output.So where do we begin?Well, knowing that the first step to solving any problem is to truly understand the problem you are trying to solve, the only logical place to begin from is the outside in.Thinking Outside In (BDD) Before a single line of code is written (or even thought of, for that matter), you need to begin by understanding the problem you are trying to solve, how the problem was created in the first place, and perhaps most importantly, what value you project the solution to have. In this discovery phase, it is best to make use of open-ended questions to determine what specific pain point you are trying to alleviate, who and how will they benefit from it, and what impact will it have on the organization.At this point and if done correctly, you should have a good understanding of why this development is beneficial and a clear vision of what to build. So far it has been BDD taking us to this point, now it is time for DDD to take over.Thinking Big Picture (DDD) What is the best way to tackle a large development project? You break it down into smaller, more manageable segments, or in the case of DDD – domains. When you split the project into smaller domains, you can have segregated teams handle the functionality of that domain end-to-end. And to best understand those domains, you enlist the help of domain experts; someone that understands the problem and that realm of knowledge more than anyone else.Typically, the domain expert is not the one who is responsible for developing the solution, rather, DDD collectively is used to help bridge the knowledge gap that usually exists between these experts and the solution that is trying to be realized. Through models, context, and ubiquitous language, all parties involved should have a clear understanding of what the particular problems are and how the ensuing build will be structured.Thinking Inside Out (TDD) I know what you are thinking, “at what point do we start writing code?” Well, the answer is now, but before you do – you need to write a test.As previously discussed, TDD is a practice where you write the initially failing test first that defines a function, and then you go back and try and write the minimum amount of code for the test to pass; followed by refactoring to ensure acceptable standards.But why did we wait so long to write code? We are still talking about development, aren’t we? Yes, of course, we are still talking about development, but we are talking about quality development, and that means bug-free development. In broad terms, there are two types of bugs:The ones that cause your system to crash The ones that show the wrong results By taking the above-mentioned hybrid approach to development, you will find that TDD helps you mitigate and avoid the first type of bugs; with BDD and DDD helping you avoid the latter – which also happen to be the most expensive to fix.Moving Forward As the complexity of your projects grow, the only way to maintain the viability of your build and ensure success is to have your development practices grow with it. While the individual practices of TDD, DDD, and BDD are all valuable in their own right, it is the point in which they intersect that will provide the real value moving into the future.Now, if you are faced with a large project that demands zero discrepancies between design document and implementation, requires minimal regression, and is maintainable over time, you can suggest an approach to that; more specifically, a hybrid approach that utilizes these three methods.
The Value at the Intersection of TDD, DDD, and BDD.

If I was to be writing about the benefits of test automation, rest assured you would be reading all about the enhanced reliability it provides, its laser-like accuracy, and far-reaching coverage. And of course, I would certainly make sure to stress how it can drastically improve product quality, reduce time-to-market, and perhaps most valuable of all, bring with it a high return on investment.However, I am not writing about the benefits of test automation, although they are indeed impressive when all laid out like that. Instead, I have chosen to write about something that is arguably much more valuable than the benefits of test automation to your business – and that is how to achieve them. And just like most things done well, it requires the right procedures, the right strategies, and of course, the “right” best practices.Today, we are going to dive into what those best practices are so you can not only get the most out of your testing efforts but deliver the highest ROI.which test cases to automateDetermine which test cases to automate First off, you need to accept that it is impossible to automate all testing. We know, we tried. But in knowing this, it makes selecting which test cases to automate all that more important.In essence, the real value of test automation comes from how many times any given test can be repeated. If a test is only to be performed a couple of times, it is better left to test manually. As a rule of thumb, test cases that run frequently and require large data sets to perform the same action are ideal candidates for automation.Here are some perfect examples of the types of tests that can benefit drastically from automation:Tests prone to human error Repetitive tests that run across multiple builds Tests that require numerous or diverse data sets Tests that are effort or time intensive when done manually Tests that run across different hardware, software platforms, and configurations Tests that are simply impossible or not feasible to run manually Test Automation ProcessDivide your efforts based on skill level While it is nice to think that everybody is at the same skill level on your QA team, the reality is that it is seldom the case. Considering this and the fact that test creation is at the crux of test automation, it is vital to divide your efforts accordingly based on the skill level of your team and the tool selected. Allow me to elaborate.If you have chosen to use an open source tool, then your automation engineer must have adequate coding skills to utilize it fully, or even at all. However, that isn’t to say that junior engineers can’t use test automation. Depending on which tool you select, such as certain proprietary ones, then QA engineers of all skill levels have the ability to create test scripts with minimal training or guidance.Another route for filling any skills gap or lacking infrastructure that may exist is outsourcing certain aspects of the process to a skilled and experienced partner. This can include everything from strategy, proof of concept, script development, infrastructure setup, and even workshops and hands-on training.choosing the right test automation toolChoosing the right test automation tool Some would say that selecting an automated testing tool is essential for test automation. We’d argue that it is selecting the right tool that makes the real difference. However, a quick Google search will show you that the market abounds with hundreds of different test automation tools to choose from.So where do you begin?Here are some basic guidelines to consider when selecting which tool is right for you:Flexibility: It is unlikely that your team is all at the same skill level which is why you need to select a tool that can be utilized by everyone. For example, if you lack the expertise to write automated test scripts, you will want to make sure that the tool provides an alternative, like the ability to perform keyword testing.Supportability: Tools available are usually platform and technology dogmatic, meaning that you will not often come across a tool that will support multiple platforms and technologies. Determine what you are testing and across what operating systems and then determine which tool best supports your efforts.Reusability: One of the most significant benefits of test automation is its ability to reuse tests which is why you need to choose a tool that can do just that. Does it allow you to create tests that are not only reusable, but maintainable, and even more important, resistant to UI changes in the application?your data quality mattersIf you want good tests, you need good data Perhaps one of the most boring and time-consuming aspects of test automation is the creation of test data. Sadly, the fact that it is boring does nothing to diminish the importance of it.Creating test data, more specifically, well-structured test data is an undertaking that is undoubtedly worth your time and effort. When you set a baseline of good quality test data, it becomes much easier to write automated tests through the entire development lifecycle.When it comes to your test data, one of the best practices you can implement is to use external data sources. The reason behind this is that by using external data, it makes your tests not only easier to maintain but more importantly, reusable. When this is done, you can easily add various testing scenarios with the data file being extended through new data, all without any edits to the original automated test.Test Automation ProcessShift-Left for maximum results In order to maximize your test automation efforts, you need to begin your testing as early as possible and as often as is required; or, as many know it, you need to Shift-Left.The Shift-Left movement is one that is seeing testers and developers begin their testing efforts much earlier than was historically done. The reason being is that when testing begins earlier in the project lifecycle, the more bugs and glitches can be found. Tests like automated unit testing can even begin on the first day of development and used to gradually build your test suite. It doesn’t require an extensive or complicated explanation to realize that when bugs and glitches are detected earlier, it is much faster and cheaper to fix them than in the ensuing production or heaven forbid, deployment.If you are looking to produce higher quality products, reduce your time-to-market, and garner a higher ROI, then I wouldn’t hesitate to suggest test automation as the solution. However, the solution of test automation is only of value when it is implemented correctly and utilized using best practices. And while not every business is the same, nor are their uses for test automation, the aforementioned best practices can all be easily adapted to help you maximize your automated testing efforts.
“The Best” of the Best Practices for A Test Automation

My daughter recently asked me if I would take her to the toy store. I had just come home from the office after a long day, and all I wanted to do was relax on the couch and watch TV. I told her I couldn’t, the reason being that I was “too tired” but I would gladly take her tomorrow. She, reluctantly, accepted my answer and went about her business, likely to pose the same question to my wife.This is an example of an excuse, masquerading as a reason. I had no real reason preventing me from taking her; I just used me being tired as justification. Fortunately, the consequences of my excuse were virtually non-existent; my daughter only had to wait a day before she got what she wanted. Sadly, the same cannot be said for many of the excuses we make, especially in business, where most opportunities aren’t as persistent as my daughter.Today, we are going to look at some of the most common excuses companies make for why they have not already implemented test automation. And while many of these excuses may sound familiar, or have been echoed within your own organization’s walls, the main takeaway from this is not the excuses themselves, but the benefits of test automation that you’re missing out on by making these excuses.test automation too costly“The cost of test automation is just too high!”In business, the number one excuse I hear for not doing something is the expense. However, interestingly enough, not incurring said expense usually comes at its own cost; often, a much higher one.In the case of test automation, I usually hear test managers claim that the cost of implementation is just too high. This is understandable, after all, at first glance investing in automation or in an automation testing company may seem cost prohibitive – especially for smaller organizations. However, when implemented properly and utilized correctly, test automation will typically pay for itself through decreased labour, reduced time-to-market, and by allowing your teams to focus on more critical initiatives like customer needs and product functionality and improvement.Test automation best practices“I don’t really have a need for test automation.”Perhaps the cost of test automation isn’t an issue for you. Maybe, you believe that your business simply wouldn’t benefit from such an initiative or by looking into the possibility of hiring an automation testing company – which is a fair point. Why would you want to incur any cost if there wasn’t a sufficient need to justify it?Test Automation ProcessBut let me ask you, does customer experience and the perception they have of your brand matter to you? Would your organization benefit if it was able to not only produce better products but bring them to market much faster? What if you were able to reduce the operating expenses of your business, without sacrificing growth and profitability? How about ensuring that you can repeatedly and accurately run tests that help to ensure the highest quality products?If you answered yes to even one of the above questions, then you certainly do have a need for test automation, one that won’t only delight your customers but improve your operational agility.test automation not for us“I don’t think test automation will work in my industry.”Of all the excuses I have been given as to why an organization is reluctant to adopt test automation or hire a test automation company, “I don’t think it will work in my industry” is undoubtedly the easiest to refute.The truth when it comes to test automation is that it is, in fact, industry agnostic. That means test automation can be successfully implemented in any repetitive and predictable test environment, regardless of the industry. I personally have been involved in successful test automation implementations in Telecoms, Banks, as well as Healthcare, however, from Manufacturing, Insurance and other Financial Services, Media, Entertainment, and Automotive, examples of successful and profitable test automation implementation abound.prefer manual testing“Manual testing is better.”In my experience, it is a bad practice to have a dogmatic allegiance to any one method of doing anything, especially when, if the circumstance is right, a better alternative presents itself.In truth, when it comes to testing, there simply is “no better than the other,” just different, in both approach and application. Manual testing undoubtedly has its place, like for one-off tests or ones that require human observation, however, when it comes to time-consuming, tedious, repetitive, or missional critical tests; test automation can not only help brands develop quality software faster, but it also allows them to do so at scale and a fraction of the cost. Typically, the best testing strategy is one that utilizes both manual and automated testing and finds a happy medium that is uniquely tailored to your business.Test AutomationI told my daughter the reason I couldn’t take her to the toy store was that I was tired, and that was my excuse parading as a reason. And the rationale behind doing it was that there were no significant consequences. However, by now, it should be clear that many of the excuses for not adopting test automation are not so consequence-free, and the sooner you start to accept them for what they are, excuses, not reasons, the sooner you will be able to make an accurate assessment as to whether test automation is right for you.
The High-Cost Excuses Preventing Test Automation

“Imperative” is not a word to be thrown around lightly. It stresses upon the vitally important, the critical, and perhaps the unavoidable. At the same time, imperatives needn’t be intimidating for they help shape the world around us as we know it. Likewise, Digital Transformation isn’t a choice anymore for any business. It’s imperative because the economy demands people, technology, and business to be unified; to pursue innovative and agile operating models; find newer ways of accelerating growth and profitability. But then, like anything worth achieving, this transformation also requires the right approach and the mastery of three critical outcomes: Experiences, Productivity, and Empowerment.Experiences Despite popular belief; it isn’t only about products and processes, but experiences. Why? Because experiences define the brand, its reputation, its ability to stick, and its possible recommendation. Emotions remain long with us even after the screen has dimmed, and the power turned off. So good or bad, customers and employees will have an experience with your brand, why not make all the effort in turning them into your competitive advantage.Productivity Everyone wants to achieve more; which is why it’s not about choosing to be productive, but how. It’s about how to free men and women from the shackles of repetitive and mundane tasks. It’s about how to reach new levels of speed, accuracy, and cost-efficiency; all while liberating talented minds to focus on what matters most. Adopting intelligent and scalable approaches ensure not only enhanced productivity and reduced time-to-market, but also a more meaningful employee experience.Empowerment To achieve something you never have, you have to do what you’ve never done. The future will demand a lot of firsts and if you are not prepared to learn, to innovate, and to take your ideas to the next level – then be prepared to be left behind. It shouldn’t be about living in the future, but inventing it. So, invest in yourself, your empowerment, and most importantly – your future.Success in this transformation isn’t complicated. It’s a choice. A choice to be better than yesterday; a choice to perfect experiences; a choice to be more productive; and a choice to empower your future.
Digital Transformation: How We Approach Tomorrow, Today

One evening I was having drinks with some colleagues after work and, as should come as no surprise, the topic made its way to Scrum – more specifically, what was the best advice we’d ever heard on the subject.“If your team looks good, you look good,” said Oscar looking around the circle for approval. We all nodded in unison as it became Lin’s turn to chime in.“Always experiment with your process- nothing is permanent.” Another piece of sage advice we collectively agreed with, as Phil tried to flag down the waitress. It was my turn.“Never confuse movement with action,” I solemnly said. It didn’t get the same quick reception as the others; however, slowly, the group began to nod in unmistakeable agreement.“Yes,” exclaimed Lin, “that is brilliant! Where did you hear that gem of Scrum advice?”I looked around the circle of my peers and with a smile said, “Ernest Hemingway.”Putting aside the source of this counsel, including the fact that it was never intended for Scrum and that the person who penned it never even used a computer, I have yet to come across more sound advice. That is because confusing movement with action is the same as confusing output with outcome; two valuable measures in the Agile methodology.Output can be considered the story of what you produced, such as velocity and volume. However, where output falls short is in addressing the value of what was produced. For that, we have outcome, which is arguably a more appropriate measure for development as it helps to quantify the actual performance and success of the processes we put in place. Sadly, we see Sprint Reports, Burndown, Burnups, and Velocity Charts all relating to output, likely because outcome is harder to interpret. Which begs the question – how do we ensure we work, and more importantly, deliver, on both?While the four Scrum events admittedly seem to showcase output over outcome, the latter is still present and teeming with value – that is, if you know how to find it. Today, we’ll show you how to do just that by extracting what output should be gathered from each event as well as the often overlooked, but no less valuable, outcome.Daily Scrum Daily ScrumAt the heart of the Agile framework is the Daily Scrum or Daily Standup. These short, 15-minutes meetings are designed to improve communication, with all members arriving prepared, punctual, and ready to answer some variation of the “three questions” we’re all too familiar with.In the Daily Scrum, the output can be considered:Looking for anything that is stopping the team’s current effort and reporting these impediments back to the team Once established, it is imperative to devise an action plan to deal and ultimately remove these impediments What stories are completed and what will the team be working on that day The outcome, on the other hand, should be:An updated sprint backlog. This should be done by keeping it in front of you during the Daily Scrum, so you can determine how impediments will affect it and adjust accordingly Improvised plan to meet the sprint goal that is based on the team’s updates It is imperative that each sprint has a sprint goal that can act as a catalyst for inspiration and instil a sense of achievement in the team. When trying to achieve value and not just velocity, you’ll likely find that teams function better and work with an increased sense of collaboration.Sprint Planning How is Sprint Planning done?The Sprint Planning event is one that focuses on two main questions:What needs to be and can be delivered in the Sprint? How will the work needed for the execution of the Sprint be achieved? Answers to the above are derived from the Product Backlog, past product increments, projected capacity, and past performance. However, when dealing with output and outcome, it is usually the Product Backlog that yields that most information in the Sprint Planning phase.The output from Product Backlog includes:A shared understanding of the items to be taken into the next Sprint Ensure that definition of ready is met for all the stories Concerning outcome, the Product Backlog yields:That stories in the Sprint are fully understood by the team, increasing the probability of achieving true value The team becomes clear on the value and acceptance criteria of the stories, including the rationale behind it The team clearly defines ask and have prerequisites ready to estimate the story, sorting out all assumptions before development Items are more refined and prioritized based on customer impact and business justification By the end of the Sprint Planning, the team should be able to explicitly state the desired outputs and outcomes to the Product Owner and Scrum Master, as well as how they intend to accomplish them in the upcoming increment.Sprint Review Sprint reviewDuring everybody’s favourite Sprint Review, the efforts of the team are assessed against the sprint goal. The team will showcase what they have accomplished; however, this shouldn’t be limited to merely output.Typically, a Sprint Review takes the form of a demo, with the team ideally having completed each Product Backlog item. Generally speaking, the success of these meetings is based on the simple output of:The Product Owner reviews and accepts the delivered product increment or provides feedback Seems a little sparse if you ask me, but when you dive into the outcome of the session, you start to see some real value brought to light. These outcomes include:A strengthened partnership between stakeholders and the development team. The focus should be on the experience, not the demo Feedback on the increment produced in the sprint with a particular emphasis on the stakeholder’s needs in the backlog and how the feedback will be incorporated into the stories A team-wide agreement on changes to scope based on feedback, along with the timeline of the planned release, with a focus on how it will impact the vision of the project At the end of the Sprint Review, not only should the team have a revised Product Backlog that helps define the next sprint, but it should also act to clarify that valued outcomes are on par with output.Sprint Retrospective Sprint retrospectiveOften the most misunderstood of all Scrum events is the Sprint Retrospective. This is designed to afford teams the opportunity to inspect themselves and create a plan of action for improvements moving into the next Sprint. It is also an excellent opportunity to review and assess output and outcomes.The output from the Sprint Retrospective include:What issues arose in the last sprint Develop an action plan to fix them Develop a proactive approach to prevent them from happening The most important and yet, usually overlooked outcome of this event is one that can be found in a core Agile principle – to at regular intervals, reflect on how to become more effective, and then fine-tune and change behaviour accordingly. In other words, Continuous Improvement. This includes looking for technical debts to upgrade the code base and working with Product Owners to clean and maintain the Backlog.If asked what sounds more compelling, a company that increased its velocity by 300% or increased its share price by 30%, the answer is obvious – 300%. However, this point beautifully illustrates the importance of asking the right question, because while 300% is more compelling, an increase in 30% share price is by far more valuable. When working in Scrum, it is essential to ask the right questions to not only get a more accurate picture of the development but to determine if you are confusing “movement with action.”
Scrum Methodology: Why Focus Needs to Shift from Output to Outcome

Time and time again, the strategy that is delivering great customer experience, driving business, and seeing some of the most significant returns is personalization, and in the digital world, smart personalization. Gartner predicts that e-commerce businesses that personalize their customer experience successfully could see profits rise by up to 15% by 2020. Apart from the vision, strategy, and talent, you need the right tools; and much like a carpenter is crippled without a hammer, our modern business landscape is growing ever reliant on personalization engines.The goal of smart personalization is to make decisions easier and experiences more enjoyable, so I thought I’d do the same by compiling a synopsis of 21 smart personalization tools, all in one convenient location. While many of the features presented may overlap, each offers its own unique value, a value I’d encourage you to discover if you also wish to deliver an excellent customer experience. Just read below to uncover which personalization engine is the best fit for you.ppersonalization tool- attraqt behavioural targetingCapitalizing on the fact that humans are visual creatures, this software takes a more visual approach to behavioural targeting, focusing on product sequencing to analyze – and ultimately optimize – what customers are looking at in order to increase the conversion rate tangibly. It also offers search services in over 40 languages, making it one of the few to have such broad, global implications and is an obvious choice for companies looking to expand their market internationally.Barilliance Customer ExperienceThis software is set on improving the customer experience by analyzing and personalizing shopping not just while the actual shopping occurs, but even when it doesn’t work out. Leaving the website without a purchase or even cart abandonment where items don’t go all the way to a transaction, are part of this data gathering process. This coupled with retargeting emails, product recommendations, and real-time website personalization make Barilliance a great option to up your personalization efforts.baynote omnichannel experienceModern commerce is all about omnichannel, which is part of the reason that Baynotes cross-device personalization engine is so appealing. Their solution works with existing systems and utilizes powerful algorithms to not only identify shopping behaviour patterns, but collect that data, analyze it, and in turn, deliver highly targeted responses. The behaviour data that is collected then helps brands gain a single view of their customer, like, where they came from and why; irrespective of the device the journey started from.bouncex marketing stackBased on the simple principle that it is impossible to market to your visitors if you don’t know who they are, BounceX offers a full segmentation stack comprised of sophisticated cohort rules that hyper-targets each unique visitor into strategic segments. It then couples the visitor’s data with their behaviour on-site, enabling for precise and targeted campaigns.Product recomendation engine Bunting“You can sell more by getting personal” is the stance that Bunting takes, and given the plethora of features in their cloud-based personalization tool, I’d have to agree. Built for marketers, by marketers, Bunting offers Product Recommendations that can be tested to determine which is most efficient, Personalized Content, Urgency and Social Proof, and Cart Abandonment targeting that can help you increase your conversions.Episerver Digital Experience Cloud This is another comprehensive package that integrates not just with catalogue and purchasing aspects of a website but also works with third-party systems for search, PIM, and more. It uses machine learning to improve its efforts over time, ever increasing the degree of personalization. This truly omnichannel platform is designed for the modern consumer, and with its new expandable add-ons, brands can further customize this tool to their specific needs.Everage Real time personalization platformThe dream of every marketer is to achieve 1:1 customer engagement; and Everage promises to do just that. Combining customer data with advanced machine learning and in-depth behavioural analytics, Everage for E-Commerce Optimization allows you to systematically understand and interact with each visitor to your site or app; one at a time, in real-time, and at scale.Email personalization software exit intelligencePower and price are two of the most significant selling factors when it comes to Exit Intelligence, a marketing tool that is primarily used to catch visitors before they leave your site. With their expertly managed pop-up software, this mobile-first tool provides gorgeous designs, reduced bounce and abandonment, split testing and targeting, and is easy to install. All this makes it particularly useful for design thinking experts, developers, and other stakeholders in the team to create a highly personalized customer experience. Plus it comes with an ROI tracker, so you’ll always know how your investment is paying off.Revenue optimization software granifyWhen it comes to personalization, the more granular that you can go, the better. Granify, a machine learning powered platform allows business to get specific with the data they are after. From in-depth shopping behaviour right down to “mouse hesitation,” Granify tracks over 400 specific micro-behaviours to give business a truly unique view of their customers.Limespot personalization toolA powerful combination of linguistic analysis technology and machine learning, LimeSpot is designed to not only target content but to understand it. Personalizer is their AI-powered option that helps to deliver personalized recommendations, upsell, and cross-sell, while, Approach, is a customized email campaign engine design to increase sales by targeting recipients with the products they are most likely to buy.monetate personalization softwareWhile the goal of business is to make things as easy and effortless for customers, that isn’t to say that important and valuable efforts like personalization need to be complicated. Monetate brings more than a decade of experience and over 300 brands in their portfolio to back up their platform that boasts 1:1 personalization, product recommendations, and an easy, customizable segmentation engine that builds and runs tests to ensure your automated messages are the type your audience is looking for.Optimization and personalization tool omnicinvertBefore you can optimize your marketing efforts for your buyers, you first need to understand them. With Omniconvert, you can do both at the same time. They claim to be the only tool that allows brands to survey, test, message, and segment all in one place, however, while that is undetermined, their premium support, 5-minute installation, top-notch security, and 30 day money back guarantee all make this tool a great option.online reatrgeting software optimonkBringing surgical like precision to e-commerce personalization, OptiMonk utilizes onsite retargeting technology that presents targeted popup overlays to your visitors. Not only that, but it also includes the ability to capture contact information like email as well as segment visitors based on a variety of categories like Cart-Contents, Engagement, and Page Stay Duration and then automatically provide personalized, relevant content.Omnichannel personalization tool personyzePersonyze uses the power of AI and powerful targeting to create tailored experiences for your audience. Giving the user the ability to set their target audience based on a list of 70 “out-of-the-box” characteristics as well as custom-defined ones, Personyze goes beyond just website personalization, offering recommendation engine, email personalization, targeted banners and pop-ups, as well as A/B testing features.personalized ecommerce software PureClarity Anyone should be a little hesitant when a company claims to be able to increase online revenue, especially by a specific number like 26%, however, given the features of PureClarity’s platform, it may not be too far off. Combining AI and Big Data, this tool provides personalized site searches, personalized merchandising, personalized email marketing, and analytics; all in one platform that is packed with hundreds of segment variables.Richrelevance personalization cloudA global leader when it comes to omnichannel personalization, RichRelevance is a highly acclaimed tool utilized by more than 200 multinational companies, all of whom trust it to deliver relevant and innovative customer experiences across web and mobile. Using machine learning and 125+ pre-built algorithms, this tool can learn and respond in real-time to customer behaviour and activity in order to provide them with the most relevant recommendations and content.Ad personalization software softcubeFew people in business can argue the power of video when it comes to customer engagement, and it is this fact that Softcube hopes to capitalize on. Powered by AI, Softcube boasts the ability to create videos showcasing your products in use automatically. Using an expansive video library and advanced neural networks, videos are effortlessly produced and can be showcased across a variety of platforms.Steelhouse personalization tool review This software gathers first-party data in real-time, looking at search terms, purchase patterns, location, and other useful metrics to create an image of the customer. Not stopping there, SteelHouse also offers users the opportunity to create unlimited target segments; opening a new realm of possibilities for targeting. Users of DemandWare are also now able to enjoy increased integration with SteelHouse software thanks to a strategic partnership between the two companies, further adding to the power of the platform.Perosnalization software for product discovery unbxdWhile many of the entries on this list offer a specific tool for enhanced personalization, UNBXD boasts a complete “product discovery suite.” This includes an impressive commerce search feature that provides enhanced product discovery and recommendations, all while subtly guiding customers in the direction you want. Perhaps the most unique offering by this tool is the ability to provide recommendations at the shopping cart, which can dramatically increase upselling and cross-selling.Content personalization software webengageOne-to-one marketing just got easier thanks to WebEngage and their personalization module that comes integrated with a complete multi-channel marketing suite. So what does it include? More like what doesn’t it include, for it provides journey mapping and user profile creation, cross-device segmentations, geo-fencing and more, all working towards a single customer view. It also offers real-time user tracking with attribution so you can utilize those channels that yield the best results.machine learning based personalization tool yuspA personalization tool is only as effective as the features it has in proportion to the needs a business has. In regards to Yusp, you’d be hard pressed to find a feature it doesn’t have. This personalization engine boasts Product Recommendation, On-Site Personalization, Search Personalization, Mobile Personalization, Email Marketing Personalization, Personalized Couponing, Cart Abandonment Email, Social Personalization, Online Ad Retargeting Personalization; and if you can believe, more.Personalization, in all of its proven glory, is not to be considered “an effort for next quarter,” “an idea we’ll review next month,” or “something our customers just aren’t interested in yet.” Instead, it needs to be celebrated, much like the customers it is geared towards. With the possibility of providing tailored, unique, and personalized experiences, the question isn’t going to be when will it happen, but why hasn’t it already?P.S. while my list is extensive, I’d encourage you to search out options I may have missed and also share it with me.
21 Smart Personalization Tools to Improve Customer Experience

Business innovation and the opportunities they create is how enterprises distinguish themselves from one another. It is how they do things better, how they create value, and ultimately, how they pass that value over to the customer. Business innovation isn’t a box you can check off and forget about, rather, it is a continuous effort that is empowered by technologies and methodologies that are available at any given moment. Today, that technology is artificial intelligence.Many of you are likely familiar with the AI enablers to follow; some having worked with them first hand. Others are likely familiar with the applications, however, may not have known that artificial intelligence is playing an important role in the background. Regardless, my point is to inspire you to think differently about AI and how it can impact your business. Like many new technologies, the full potential of AI is being realized slowly, and it only takes someone exploring the possibilities around them to discover something new.Enablers of Innovation Big Data Here is the thing about Big Data – it’s big. I’m talking massive. Big Data has to be so in order to reveal patterns and associations, and predict trends accurately. However, while humans do have the capacity to discover patterns and predict trends, it is an impossibility at the scale in which modern enterprise demands. For AI, on the other hand, it is impressively suited to glean through large data sets in order to quickly and most of all accurately derive actionable insights.Internet of Things The Internet of Things was bred out of convenience and personalization, which only stands to reason why AI will only help to continue its widespread adoption. Building internet connectivity into a wide variety of devices is one thing, however, allowing those devices to communicate with us and coordinate with each other will only lead to greater shopping, home, entertainment, and professional experiences.Enablers of InnovationDeep Learning When talking about artificial intelligence, the word that stands out most is intelligence, and a hallmark of that is the ability to learn. Deep learning does just that, by utilizing artificial neural networks to act as a human brain would, analyzing and learning all without the aid of a computer programmer. This ability to “think” on its own is a driving force behind such innovations as autonomous vehicles, which is great, as keeping a computer programmer in the trunk of your car isn’t a feasible option.Reinforcement Learning Reinforcement Learning (RL) is an important type of Machine Learning where “machines” learn how to behave in an environment by performing actions and seeing the results; not unlike students in a classroom. This behaviour can be learnt based on a reward mechanism, once and indefinitely, or keep on adapting as time goes by. RL algorithms can converge to establish an ideal behaviour baseline, especially for robotics, autonomous driving, and process control.Probabilistic Programming One of the fascinating things to rise out of AI is the feasibility of probabilistic programming. In simple terms, this programming allows for problems to be solved in nonlinear time. What does that mean? Well, traditional simulations used for problem-solving only arrive at the results at the end; however, the probabilistic programming can look at the conclusion first and determine how those results can be achieved “going backwards.” This has far-reaching implications, from customer service to financial forecasting.The above are the enablers that bring the latest and most advanced business applications to light. However, what’s arguably more important are the opportunities that AI can bring to your business, and here are some of the most exciting ones.Applications & Opportunities Autonomous Vehicles The automobile market is enormous, however, despite what you may think, it is still a limited market. That is because while anybody can buy a car, not everyone can drive one. That is, they couldn’t before Artificial Intelligence came along. People who are blind or suffer from certain physical limitations will soon have the ability to go anywhere thanks to this new technology. The use of these Self-Driving Vehicles (SDVs) in logistics is another innovative application and this tech is already being tested with prodigious results.Robotic Process Automation While we hope everyone loves what they do for a living, the reality is that even the best “dream jobs” have their periods of boring and monotonous work. In fact, some jobs seem to be exclusively filled with such processes. But it doesn’t have to be. AI fueled Robotic Process Automation (RPA) currently replicate basic rule-based tasks, much faster, accurate, and cost-effective than humans, and will eventually constitute the epitome of an Intelligent Digital Workforce.how Artificial Intelligence can help your businessLogistics & Delivery A product is only of value if it reaches the hands of the customer, and this principle is why logistics and delivery is so crucial to business success. Integrating AI in your supply chain management can unify your data; analyzing and providing insights across the organization as well as streamline the customs brokerage process. However, it is in predictive analytics that we see the most significant value, through its demand prediction, route optimization, and network management.Customer Service Whether they have made a purchase or not, and regardless of how far along in the buyer’s journey, any good enterprise needs to ensure that the customer’s demands are met. However, given the multitude of touchpoints on that journey, this can be difficult. For AI, however, it can act as a “gatekeeper” throughout the experience handling simple questions like inventory, availability, or straightforward exchanges and refunds, which frees up staff to focus on more complex and sensitive issues.Chatbots Thanks to AI, chatbots have grown more sophisticated, and in many ways, are almost indistinguishable from humans. In fact, chatbots are often a better alternative than using traditional CSR. Instant response to inquiries, reduced service time, fewer errors, increased customer engagement, the ability to handle simple transactions, and proactive customer interactions are all within the grasp of these bots. And if you can think of a scenario that wouldn’t be improved with AI, then you have just found an instance for a human CSR to take the lead.Customer Relationship Management CRM systems were in and of themselves a considerable business innovation, one that continues to yield results for sales teams. However, given the less than stellar success rates of such implementations, AI is poised to do what sales teams and CRM alone can’t. From transcribing and analyzing calls to qualifying, engaging, nurturing, and following up with leads via email, AI is positioned to not only do more for the enterprise but the customers they serve.Payment Services Life is filled with some certainties that go beyond death and taxes. For example, if your house is anything like mine, you regularly need milk, fruit, toilet paper, and a variety of other “staples.” AI, as your own personal “butler,” can make those authorized payments and arrange for shipping to your home when your supply is getting low. Anyone with kids will quickly see the value of always having the essentials on hand.Translation Whether you are a business traveller or looking to branch out into new international markets, one of the most significant barriers to not only business but people is language. However, thanks to AI, more and more companies are expanding into new markets, no longer encumbered by language. And while technology has made the world a smaller place, I believe it is AI that will help empower true universal communication.Behaviour Prediction Anyone in business knows that the customer is the most important thing, which is why perhaps so much time is spent trying to guess what they’ll do next. Thanks to Artificial Intelligence, however, these predictions have gone from guesswork to a science. AI and its ability to analyze massive data sets give the enterprise the ability to learn more about their customers, such as their shopping habits, preferences, and even churn rate, so that they will not only be able to foresee what the customer will do but can ideally influence it.How can Artificial Intelligence help my business growDecision Making When asked the key to their success, it isn’t uncommon to hear powerful men and women give credit to “trusting their gut.” And while this may be your best option in certain situations, the modern business landscape is unlikely to be one of them. Artificial Intelligence has given enterprise the ability to weigh the variables, judge potential outcomes, and make the best decision based on the relevant data. And while not as sexy as “trusting your gut,” AI-powered decision making is likely to be a lot more accurate and yield better results.Intrusion Detection While technology has enabled us to do more, it has also caused us to be more conscious and aware, especially when all our new capabilities can potentially leave us vulnerable to digital intrusion. Current defence against cyber attacks are generally of a responsive nature; however, with AI’s help, this can be switched to proactive. With AI, an enterprise can set a baseline of normal activity on their network, and as a result, more accurately recognize potential threats if they deviate from typical behaviour.Content Creation Content isn’t just a way for an enterprise to get their message to the customer, it is a way to provide that customer with value. However, AI is increasing the efficiency in how we do that by allowing us to deliver personalized content to the user and by helping inform our strategy through insightful data analysis like which type of content will perform best. Creation aside, AI already does aid in the distribution of content, allowing for more efficient and documented campaigns.HR & Recruitment HR and recruitment are by nature a very “people” laden vertical; however, that should be no indication that AI integration isn’t applicable. HR is filled with numerous rule-based tasks that could be done much better by AI and RPA. Let us take onboarding for example. Typical onboarding would take an HR associate 2.5 hours to complete from hiring decision to sending the welcome email, while an AI-fuelled substitute could accomplish the same in just 8 minutes.Digital Marketing Marketing is usually only effective when the right message gets to the right audience, more specifically, on the right channel. Thanks to AI, with its ability to analyze large data sets and to automate processes like distribution of marketing materials, targeted messaging across channels is becoming easier and more effective than ever. This will help ensure that marketing dollars are spent in more effective ways and can also help to tailor messages that are appropriate for whatever stage of the buyer journey the customer finds themselves.Manufacturing Robots are already par for the course in many industrial sectors, however, that is for their physical capabilities, but today, AI and its ability to reason, theorize and forecast is what has the manufacturing world excited. From improving predictive maintenance, reducing supply chain forecasting errors, and reducing energy costs through demand forecast, the benefits of AI in manufacturing directly impact the bottom line.Few moments in history are marked by the presence of a technology that is so adaptable, has such widespread potential, and that can impact as many verticals across as many industries, as AI. With businesses investing more each year and with jobs like Data Scientist topping the list of “Best Job” three years in a row, the relevance of AI should be clear. However, while the intelligence behind AI is artificial, its applications and use are as real as they get, and there will be nothing fake about the business innovations yet to come from this important technology.
15 Business Opportunities Enabled by Artificial Intelligence

Words can be funny; more specifically, how the same word can have incredibly different meanings for different people. Take the word scrum for example. For 95% of the population, that word either elicits thoughts of people in jerseys all huddled together about to restart a game, or holds no meaning at all. However, when you change the ‘s’ to a capital, to us, the word Scrum takes on a whole new meaning.Scrum is on the mind of many engineers, managers, and especially software developers; however, with any widely spread practice, it is usually only a matter of time before misconceptions, misinformation, and myths begin to infiltrate. What’s worse, is that for many, we don’t even realize it is happening.To separate fact from fiction and in hopes of empowering us all to practice Scrum in its purest form, I have taken the liberty of compiling five of the biggest Scrum myths that many of you may be familiar with but might not know them to be false.Myth: Scrum Master Leads the Daily Scrum Myth: Scrum Master Leads the Daily ScrumOne of the biggest myths that I have come across happens at the Daily Scrum; and if you have been around as long as I have and attended as many Daily Scrums as myself, you’ve likely seen it too.Let me know if any or all of these sound familiar:You attend a Daily Scrum, and the entire team is giving their updates to the Scrum Master The Scrum Master gives his or her input and suggestions, trying to micromanage the efforts of the team The main focus of the Daily Scrum is on the Scrum Master The meeting lasts for more than 15 minutes If you answered yes to any of the above, then first off, allow us to tell you that what you witnessed is NOT a Scrum Master leading a Daily Scrum; at least, not how it should be.The goal of the Scrum Master is not to lead the team, nor do they have any such authority. In fact, the presence of the Scrum Master isn’t even mandatory for the meeting. According to the Scrum Guide, the daily scrum is entirely owned by the Development Team; however, the Scrum Master is responsible that the meeting takes place. This includes sending calendar invitations, choosing the time that works best for everyone, instituting soft penalties for being late, and ensuring all impediments are noted so that they can be resolved later. Remember, the goal of the Daily Scrum is merely a chance for the team to all get on the same page and agree upon a strategy for the following 24 hours. Ideally; within 15 minutes, all the work from the previous day is discussed and analyzed while the work to follow is plotted.Myth: The Scrum Master Must Resolve Every Problem Myth-Scrum Master Must Resolve Every ProblemDifficulties, problems, issues, complications, hurdles, setbacks, and snags are just par for the course when you are in the midst of development. Actually, that’s just life, but I’ll leave that conversation for another day.The Scrum Guide, which should be considered holy text for development teams practicing Scrum methodologies, clearly outlines all the various duties that a Scrum Master is expected to fulfil. And one of those is to remove impediments to the Development Team’s progress. I know what your thinking, “Doesn’t that statement seem to validate the myth?” I agree, it looks that way, but the key thing to remember here is the word “impediment,” which many developers assume to be any and all problems that come there way during a sprint.An impediment, when taken in a Scrum context, should be considered problems that are interfering with a Development Team’s progress that lie OUTSIDE of their capability to resolve. This notion is closely related to one of the most fundamental concepts of Scrum: self-organization.Development is an often precarious, usually unpredictable, and almost definitely a complex undertaking; however, the use of a teams expertise to collectively solve problems is crucial. Some examples of issues that may arise that deserve the attention of a Scrum Master includes:Team member falls ill Hardware issues Absent Product Owner Bugs and glitches in the production environment Problems with the development environment Internal conflict between team members Remember, the capacity of a Scrum Master is to solve problems that the Development Team cannot. So if you’re unhappy with your lunch order, you missed your train into the office, or your significant other is giving you a hard time, it is best to save those problems for someone else.Myth: Velocity Equals Value Scrum velocity and valueThe short answer; no. However, as that wouldn’t make for good reading, I feel I should elaborate. But first, let us make sure that we all have a clear understanding of what is meant by Velocity and Value.According to Scrum.org glossary (because where else would you go for all things Scrum), Velocity is defined as “an optional, but often used, indication of the average amount of Product Backlog turned into an Increment of product during a Sprint by a Scrum Team, tracked by the Development Team for use within the Scrum Team.” As such, velocity can be an incredibly useful metric for predicting the volume of items that can be delivered in a Sprint, or comparatively, how many Sprints will be required to reach release.Value, on the other hand, as defined by the Oxford Dictionary is “the regard that something is held to deserve; the importance, worth, or usefulness of something.” Now, when most people think of value, their minds normally turn to money, so for the sake of this point, let us use it as a proxy and a valuable product as being able to increase revenue or decrease cost. In the context of Scrum, value is only created when the product or increment reaches the customer; they find it useful, and they start benefiting from it.Now that we have two clear definitions of velocity and value it should be clear that they are very different things and one is not indicative of the other. One (velocity) is a tool that a Scrum Team can utilize to self-manage during the development process, and the other (value) is simply a means of the customer assessing the usefulness of the product.Myth: Sprint Review is a Demo Scrum Myth-Sprint Review is a DemoDevelopment is by no means the easiest of work, which is why the opportunity to showcase and demo your increments to Stakeholders can be so rewarding. However is the Sprint Review really the time to do it?Do any of these sound familiar:You gather for the Sprint Review, and the Stakeholders are on one side and the Development team on the other; not unlike a middle school dance There is very little input from Stakeholders (often because they weren’t invited to) The mouse and keyboard never actually make it into the hand of a Stakeholder None of the Stakeholders present are actually going to use the product The Sprint Review gets referred to as a ‘Demo’ If you answer yes to any of the above, then there is a good chance your definition of a Sprint Review may is bit askew. But rather than tell you why all of the above is wrong, let us draw a comparison to how a Sprint Review should look:Development team and Stakeholders should appear indistinguishable to an outsider The Product Backlog holds a distinguished spot and is continuously adjusted as new insights are uncovered Participants are invited to offer up their ideas, feedback, and suggestions actively The Increment is presented not just by the Development Team, but by the entire Scrum Team – including Product Owner The Product Owner assesses the Product Backlog and discusses progress and expected completion dates If you think the latter sounds more productive than the former, you’d be right – and the Scrum Guide would agree with you. For it emphasizes that Scrum Team and Stakeholders must collaborate about what was accomplished in the sprint and based on any changes in the Product Backlog, discuss next best actions to optimize value.Myth: In Scrum, There is no Planning Scrum Planning MythFor some Scrum Teams, the word “Plan” or “Planning” is considered taboo. Certain Scrum Masters may refuse to let their team look past the current Sprint. And from the outside, many seem to believe that Scrum Teams are aimlessly working away trying to create products without a sense of direction or overarching aim. However, despite popular opinion from the outside and some misguided souls within, planning is, in fact, a crucial part to Scrum – and there is no better way to prove it than by the numbers.The Scrum Guide mentions the word ‘Planning’ a whopping 19 times! And the word ‘Plan’ a still impressive 9. And in case you were wondering, use of those words at no point are preceded by the words “You shall not.”So what are some examples of planning in Scrum?During Sprint Planning (see the word ‘Planning’) Scrum Teams work together to plan (see, again) what will be performed during the Sprint. This plan is then captured in an albeit flexible Sprint Backlog that is aligned with an overarching Sprint Goal in order to provide direction and focus The Daily Scrum is about planning what the Development Team will do for the next 24 hours During the Sprint Review, the Sprint Team and Stakeholders inspect the work completed and based off of it, plan what can be done next to optimize value The above are just a couple of examples of planning that are imperative to the success of any Scrum endeavour. And while flexibility in approach is undoubtedly of great appeal and one of the most valuable aspects of Scrum, it should never be thought that Scrum Team efforts are lacking specific intent.While earlier I made the distinction between scrum and Scrum, in reality, they have a lot in common. Both involve groups of people in what often looks like an unorganized mess; however, they are all ultimately working towards a shared goal, passing the ‘ball’ backwards and forwards while the team marches ahead. And although it is unlikely that the Scrum we are all familiar with will result in us wearing matching jerseys, it is always important to understand that you are a part of a team and to succeed and win at the game; you need to understand the rules.
5 Myths about Scrum Methodology, and the Scrum Master, Busted

The challenge with the customer experience is that it is ever-evolving, and all too often we are seeing the seemingly infinite demands of the customers met with the finite limitations of people. So how can brands meet these demands? When you take into account Gartner’s statement that “By 2020, customers will manage 85% of their relationship with the enterprise without interacting with a human,” the answer becomes simple – technology. And there are none that exist that are so perfectly poised to improve nearly every facet of the customer experience like artificial intelligence.So how is AI changing the landscape of the customer experience? Simple, it is empowering more personalized, self-serve, and scalable experiences.Personalization using AIShopping Experiences Have you ever gone to a restaurant where the food was so-so, but the service was unparalleled? The type of place where you are always greeted by name when you walk in; they know what table you liked to sit at, and usually have your drinks on the table shortly after sitting down. It is this familiarity and personal touch that keeps people coming back, and it is this same feeling that is driving customers to specific brands. The only difference is that it is AI powering this experience rather than a waitress.In our lifetimes, each of us will generate thousands of gigabytes of data, which seems impressive; however, it is only valuable if analyzed. Sadly, this is where our human limitations come in, along with our ingenuity, since just because we can’t actually do it, doesn’t mean it can’t be done. AI and machine learning are being used to comb through big data to provide the customer with an unrivalled level of personalization. This includes product recommendations based on previous purchases to websites changing their appearance in real-time to adapt to a customers browsing habits – even going as granular as adjusting to their reading level. When AI-powered personalization is implemented, not only is the customer experience improved but so is the conversion to purchase, driving new and repeat business.Behaviour Prediction through Artificial Intelligence Human beings are brilliant, mainly in part to our brains, which is the most complex structure in the known universe. With it, we cannot only absorb the information around us, but for the most part, we can take that information and process it, put it in context, and use it to realize patterns and make predictions. This has proven incredibly useful not only in our survival as species but in business, as the ability to predict what the customer wants and will do next can often mean the difference between success and failure. It is here again, however, we find ourselves faced with our limitations, as the ability to analyze, process, establish patterns and make customer predictions at the scale that modern business demands are simply an impossibility. Fortunately, what we can’t, AI can.The only thing better than giving the customer what they want is being able to predict that want before it is expressed, and AI can do just that. Analyzing behavioural patterns, trends in the market, and user experience across multiple channels through Artificial Intelligence can lead to not only accurate predictions, but instills a feeling of value and of being understood by the brand, all of which help to develop loyalty and retention, as well as being a natural pathway to upselling and cross-selling.Product Discovery Few would argue that the most desired action a customer can take is to make a purchase; after all, sales are the driving force of business. Still, there is a lot that goes on before that action can take place, and looking at it from a logical perspective, the next most crucial step to making a purchase is discovering what exactly you want to purchase – sometimes without even knowing you want it.Does this sound familiar: you walk into a store “just to browse,” however, after an interaction with a skilled sales associate, you end up walking out with a bag full of things you didn’t know you wanted but are ultimately happy you purchased? Well, replace that sales associate with AI, and you’ll get a pretty good sense of the capabilities of this technology. AI can hone in on the wants and needs of the customer by analyzing their previous purchases and search history, and make recommendations accordingly. With time and relevance being perhaps the hottest commodities in the life of the consumer, AI-powered product discovery can not only streamline the process and lead to upsells and cross-sells, but also garners goodwill with the customer who now only sees products and services that have been predetermined to be relevant to them.self service using AIImage Credit: Amazon Go The New Standard When discussing the notion of customer experience, the conversation should always begin and end with the preferences of the customer. There was a time not long ago when these preferences included a very hands-on approach from brands and their representatives, whether it was in product discovery, sales assistance, or customer service. However, today, we have seen a dramatic shift, one that considers the customer opting for a more self-service experience – an experience ultimately powered by AI.There is a growing belief that a phone call is not the best way to resolve a customer service issue – and I’d have to agree. That, of course, isn’t to say customers don’t still have issues; instead, these new, tech-savvy generations prefer to solve their own problems, turning to online forums, FAQs, chat, and bot services. To adapt, brands need to recognize this new, self-reliant customer and offer them a human-free, digital-only experience. Failure to do so will not only result in a negative CX but will invariably impact the businesses bottom line.Rise of Chatbots The goal of every brand should be to try and provide value to their customers through the experiences they have with them. However, this poses a problem with humans limited capabilities and customers seemly limitless demands. One solution to this problem, if you couldn’t have guessed by now, is AI, more specifically, the use of AI-based chatbots to act as assistants to your customers.First of all, chatbots inherently enhance the customer experience through their timelines and efficiency. Natural Language Processing (NLP) allows chatbots to understand customer questions and respond to them with precise answers, all without having to dial-in to a call centre or wait in a queue. Not only that, but they can also make personalized recommendations in real-time based on historical data. Finally, chatbots ensure a consistent level of service, a fact that cannot be guaranteed when you have a human being on the end of the line or chat.Customer Service Roles It is truly awe-inspiring to imagine all the capabilities of AI and how much it can do for us, especially in the world of business. However, that should never wholly discount the roles humans play in the customer experience, more specifically, customer service. Today, we see these roles have evolved, but they most certainly have not been eliminated.The use of AI in customer service is gaining prevalence, specifically, with AI-based chatbots and virtual assistants that result in an automated, fast, and ultimately hassle-free experience when it comes to lower tiers of service issues. This has not only proven profitable and more efficient for an enterprise but also tailors to the preferences of the customer who demand immediate solutions. As a result and despite people’s fears, the consensus is not seeing the elimination of customer service representative jobs, rather, their evolution, one that is seeing them handle more complicated, difficult, and comprehensive support issues, giving the customer more time and attention if that is what they want, or their issue deserves. Ultimately, delegating more straightforward tasks to AI means premium human customer support can handle the more valuable and elaborate matters; ensuring the customer experience is a pleasant one.Customer Touchpoints A customer touchpoint is any point of contact between a brand and a customer where they engage to exchange information, provide a service, or handle a transaction. While this definition seems pretty straightforward, it starts to become a little complicated when you account for our modern marketplace that sees an ever-increasing amount of ways for brands to interact with their customers. However, this is where AI really shines, for the implementation of AI can help lead to a unified experience, regardless of the touchpoint chosen by the customer.Thanks to AI, whether a customer has an issue at 2pm or 2am; if they are reaching out from their cell-phone or desktop, or whether they are located in Toronto or Munich, the ability to provide a seamless and holistic experience for them is within the grasp of enterprises.Continued Learning Among the many advantages of AI is the fact that it is always on. It is on to assist customers in their product discovery, it is there to help them make a purchase, and it is present if and when an issue arises that requires brand support. However, as a complementary feature of always being on, by nature, that also means that AI is continuously learning, improving, and making itself better, which in turn, facilities a better customer experience.With AI in place, from the moment a customer, potential or current, logs on to your site, browses your catalogue or interacts with your app, it is watching, learning, and recording what happens. As a result, the next time a customer logs on, things will look different, more personalized, more specific to that unique customer. This allows for more concise and targeted marketing efforts which save time and money on the brand side and exponentially increase the customer experience by only providing tailored and relevant information.How to scale services using AIInventory Management One of the fastest ways to hinder your customer experience is through poor inventory management. Can you imagine the frustration of going through all the effort of finding what you are looking for – and even after it is clearly displayed – you discover that your choices are out of stock?Inventory management, interestingly enough, exists on a single contradiction – keeping enough stock to ensure orders are met and business keeps moving, but not enough that it impacts cash reserves. This is where AI comes in to automatically monitor the stock, uses machine learning to analyze bulk data and forecast demand within the supply chain, and in some cases, even implement robotic automation in the procurement process. After all, the key to a happy customer and a superlative CX rests in the ability of the customer to get what they want when they want it.Cost Effective The aim of every business is to ultimately build and expand; however, doing so is not without its cost. For a company to successfully grow, they must have an infrastructure in place that can handle the increasing volume of sales, inventory management, and customer service issues. Typically, that would require the hiring of more staff; that is unless you have the power of AI in your corner.AI empowers businesses to scale up their customer service at the push of a button (or several, but you get the idea). Imagine, you launch a new product, and at the same time, you release a new and interactive FAQs that can solve thousands of customer concerns. Then you switch one server to another and now have a mighty fleet of chatbots who are ready to respond to the onslaught of customer inquiries instantaneously. Couple this with the ability of AI to continuously learn and you can now easily branch out into new geographic markets, no longer encumbered by language barriers. And the best part – you only have to train them once.By now it should be clear that technology such as AI has already begun to revolutionize and change the landscape of the customer experience – as it should. Customers today are by no means the same customers of yesterday, and as such, the same level of attention, service, and accommodation is just not on par. The truth of the matter is that customer demand is ever-increasing; which is all the more reason for AI to fulfill those needs.The future isn’t about AI replacing humans; instead, it is about AI empowering humans to do more, and the sooner you realize it, the happier your customers will be.
10 reasons why your CX (Customer Experience)needed AI starting yesterday

Have you ever driven down a road that was incredibly uneven or bumpy? Did you ever get frustrated trying to install a piece of software on your computer? Have you ever eaten at a restaurant and had lousy food and even worse service? If you said yes, then you have been a victim of poor user experiences that you haven’t forgotten. While UX is a crucial element in both the digital and physical world, it is in digital that we see the value of UX skyrocket, and that is for one reason – choice.People will often drive down a bumpy road because it is faster or will eat at a restaurant with bad service because it is the only one in town; however, they won’t settle for a subpar digital experience. Why? Simple – quick and easy access to your competition. The internet and technology have torn down limitations and empowered the user to find what they want. What does this mean? Well, if you cannot provide your user with the experience they are looking for, rest assured, somebody else can and will.So what’s trending in User Experience? That was my question, and fortunately, I am lucky enough to work with a room full of UX designers, creatives, and researchers who could help me find my answers. Here’s our pick of 17 UX trends.User Journey Simplification Although trends in UX are ever evolving, a constant that will never fall out of fashion is simplicity. When users interact with an app or site, they typically have a goal in mind that they’d like to accomplish, and if any aspects of the design impede, hinder, or delay achieving that goal will only lend to a bad experience. Simplifying the journey isn’t just about making the next steps from point A to point B easier, but it is about making those steps more intuitive, and where possible, minimizing them. This is why linear flows, with their clear beginning, middle, and end, and progressive disclosure, making information visible when needed, have gained such popularity.Simplifying the journeyImage Credit: Uber In-App Gesture Paired with Animation Today’s market is seeing more devices being introduced that are gesture reliant, which sounds ideal, but not without its hurdles, mainly, the lack of physical interaction, such as a “button click” that indicates input. For this reason, developers have started relying on animation to provide the user with feedback and guide them through a smooth, memorable, and “natural” experience.In-App Gesture Paired with AnimationImage Credit: Dribbble| Full-Screen Experiences Modern devices are not only devoting much more real estate to screens, but those screens are among the highest quality available. So what does that mean for developers? Simple – more space to play with. However, the fact that these devices are capable of so much visually will also work against you if your media is not up to par. Images and videos that appear pixelated will only serve to lower the expectations and the experience of the user.Full-Screen ExperiencesEmotional Experiences Brands have long known that the most effective way to interact and create memorable experiences with users is through emotions. However, this year we see emotional intelligence actually being integrated into the mobile experience to make it not only more enjoyable but more engaging. This technology allows users to better express emotion, provides them with a natural way to interact with a UI, and can even mimic emotions in UI feedback. Today, we are seeing technology becoming an expressive extension of our personalities.Emotional Experiences in AppsImage Credit: Apple Biometric Authentication The ideal UX is always a near perfect blend of form and function; however, in our world today, the coupled considerations of security and privacy cannot be ignored. Fortunately, this has provided the perfect opportunity to not only enhance security but also do away with one of the most cumbersome parts of personal devices – passwords, and the solution is biometric authentication. The technology behind biometric authentication is not new; however, we see more widespread adoption along with the evolution of the technology, with touch ID being replaced with facial recognition.Biometric Authentication in app development Image Credit: Biometric Updates ; Dermalog Conversational Design Few things are more natural for a person to do than converse using their voice and as technology has made it possible, we see a rise in conversational design and interfaces. However, while conversational interfaces are unlikely to replace GUI completely, we see an integration of the two. For example, chatbots are regularly integrated as assistants into messaging platforms, and progression in natural language processing is giving way to completely voice-based interfaces to develop conversational design. As a byproduct, the need for copywriting for this type of interface has never been more important, as the words and exchanges between device and user need to be selected carefully. After all, the difference between a memorable bot and an ineffective one is personality, and that is what UX designers and other stakeholders can achieve through conversational design.conversational designAdvanced Personalization There was a time when the bar for personalization was when a piece of correspondence included the recipient’s name; however, as the user has evolved alongside technologies like conversational design, that simply won’t cut it anymore. One of the most exciting uses of personalization is utilizing the fact that people carry their mobile devices when travelling and providing them with useful and relevant information that corresponds to their location. Technology is also allowing the personalization to go one step further by actually adapting the UI to the user’s requirements, such as language, poor eyesight, or colour blindness.Advanced Personalization in app developmentAugmented Reality While conversational design has the potential to change the way we interact with our devices and applications, augmented reality, or AR, has the potential to change the way we view the world – through those devices. For many, their first exposure to AR was in the form of a game, Pokémon Go; however, thanks to Apple and Google releasing AR frameworks, we are seeing a surge of these applications. From immersive games that allow us to turn our devices into a lens through which to view (and play in) the world to solving real-life problems, like being able to measure the size of objects without using a traditional physical measuring tape, AR is poised to be a helpful and engaging trend.Augmented Reality in UX3D Effects Developers have long understood that the greater depth and more immersive the experience, the more memorable it becomes. That is why many are opting to shed their 2D habits and push technological and processing limits by creating more 3D effects. However, it is important to remember that just because you can, doesn’t mean you should. Accessibility needs to be accounted for on par with the user experience, and thus, in order to implement this trend correctly, it will likely require a delicate balancing act of form and function, but the excitement of adding another dimension to how we design in digital is hard to ignore.3D effectsImage Credit: WebDesign Trends ; 3D websites Expressive Typography The goal of a brand is to engage and communicate a message to its customers; however, all too often, one of the most fundamental ways of communication, words, or rather, the style in which the words are written, is often overlooked. Thankfully, that is looking like it is changing as more and more designers are embracing typography. Large, unique, and in many cases, hand-drawn fonts are quickly becoming the norm, as typography is becoming a more sought-after aspect of design and development. Utilizing this practice can allow brands to distinguish themselves further, ultimately enabling the typeface to become an expressive element of the message, especially when combined with animation, as well as encourage prolonged reading for the user.Expressive Typography in appsBright and Vivid Colours Looking to influence people? By now you probably know that emotion is the route to get there; however, what you may not have known is that colour, much more than words and images, can help facilitate whether a person has a positive or negative user experience. Fortunately, the onset and ready availability of display technology such as 4K have made it even easier for designers to implement a dynamic and much more impactful colour range. And almost symbolically, the direction is towards bright and vivid colours, almost as if to cut through the bland and dim designs of years past.Colour usage in appsImage Credit: awwwards Creative Menus Anything other than the most basic user experiences will all have one thing in common – options; however, it is the way in which those options are presented that can make a huge difference and possibly pay huge dividends on user-interaction. And while depending on who you ask, this couldn’t come soon enough, it seems the classic, yet dated, hamburger menu is on the way out in favour of more inspired, experimental, and design-driven alternatives. We are seeing more and more designers embrace horizontal menus, progressive disclosure menus, and utilizing unusual typography.Creative Menus Image Credit: Shiny Demos ; Charlotte Wood Design Usability Engineering Have you ever heard of the human-computer interface or HCI? You should, as that is the way in which users interact with technology; which at its core, is a cornerstone of user-experience. However, in today’s fiercely competitive market, more developers are turning their focus to usability engineering, which is a discipline that blends a firm knowledge of computer science and psychology to approach the development process. Usability engineering is done hand-in-hand with users to ensure a deeper understanding of functionality and design requirements, such as utility, learn-ability, efficiency, retain-ability, errors, and customer satisfaction. Given the direction of the market with AI, AR, VR, IoT, and voice, this more in-depth understanding of what resonates with the user through Usability Engineering has never been more valuable.Usability Engineering Image Credit: Fuzzy Math Content Focused Experiences There has begun a shift recently that is seeing UX turn away from design elements that are intended to merely impress and solely relying on UX designers, and instead, focus on what is arguably more important – the content. Utilization of flat design and minimalism are all meant to remove the distraction and help shape a more content-focused experience for the user. In this situation, UX designers take the role of ensuring that nothing impedes a user experience of the content. To follow this trend, UX designers must implement a distinct visual hierarchy, designed to ease content comprehension; utilize functional minimalism by removing unnecessary elements for more precise focus; and whitespace, which gives the content “more room to breathe” and improves the user experienceDevice-Agnostic UX Design There was a time not that long ago when everything was designed for desktop, with mobile seemingly an afterthought. However, today we see a progression towards more mobile centred design, and yet, that still doesn’t do enough in our ever-changing digital landscape. With the rise of the Internet of Things, we are shifting from mobile-first experiences towards multi-device experiences. At its core, this trend is all about creating a continuous interaction and digital experience, regardless of the device. For the user, they have a task in mind, and the way in which that task is accomplished should solely be based on the most convenient and relevant medium on hand, be it a phone, computer, smart speaker, or car. In order to achieve true user experience, it needs to be device agnostic.Device-Agnostic UX DesignAccessible and Inclusive Design No matter the industry you work, there is a global shift underway in which is seeing people becoming more socially aware, and this is causing a push towards more inclusive and accessible designs. And while yes, admittedly it is a fool’s errand to try and design something that is truly universal and is equally enjoyable to use for everyone, it is still no excuse to utilize all existing technologies and practices to make someone’s life easier. This includes reframing from using triggering or inconvenient elements for the sake of design, accepting that your users aren’t cookie-cutter and diversity is the norm, that you test using users from a variety of backgrounds, and utilize a diverse set of designers. Remember, inclusion and accessibility isn’t a barrier to innovation, rather a stepping stone to universal design.Image Credit: CAL Design Collaboration in Design To think that UX designers are the only players in the UX game would be a gross oversight. That is because marketers, product managers, designers, developers, copywriters, and even the user, all play a role in shaping memorable user experiences. By collaborating through the process and practicing design thinking, not only is empathy and experimentation added to the process but all of the aforementioned can give one another feedback and work towards establishing a collective understanding. The result is not only better experiences being crafted but does so with such intent and diversity that the previous point, accessibility and inclusive design, almost definitely becomes a byproduct of such collaboration. By identifying shared goals, continuously opening the lines of communication, and being open to new perspectives and constructive feedback, the world of UX promises only to become more lucid as time progresses.Collaboration in Design Image Credit: Stormid Considerations For UX Designers Going Forward Experiences are surely evolving alongside the technology that empowers them. As is clear from some of the trends mentioned above, we do not only see a global shift in UX but one of global citizenship that is purposely taking into account the diversity of the user through design thinking, like through conversational design or usability engineering. And while impossible to predict the future, we do know one thing about the direction of UX – it will continue to have a direct impact on the top and bottom line of your brand.
17 Trends for UX Designers to Create Unforgettable User Journeys

Socrates was an ardent critic of the written word and his most famous pupil Plato once wrote that “If men learn this, it will implant forgetfulness in their souls; they will cease to exercise memory because they rely on that which is written.”Daryl Zanuck, CEO of 20th Century Fox in 1946 once predicted that “Television won’t be able to hold on to any market it captures after the first six months. People will soon get tired of staring at a plywood box every night.”And Thomas J. Watson, CEO and Chairman of IBM in 1943 once infamously said: “There is a world market for about five computers.” We know how that turned out.What do the above examples show us? That very often some of the most important, transformative, and disruptive innovations can have an uphill battle from their inception; usually associated with false assumptions, and sometimes from unlikely places. And while the above examples are from a time past, our present day is not immune to misconceptions, misinformation, and false beliefs. Case in point – Robotic Process Automation or RPA.Simply put, RPA is the practice of taking routine, repetitive, and rule-based tasks and automating them with software “bots” to perform just as a human would. This can include automating processes in financial operations, human resources, IT, procurement, and data and analytics to name a few. While robots have long been used on the factory floor, they have evolved, and now software bots have infiltrated offices across the globe through RPA tools. However, much like the written word, the television, and the computer, there are still many who are yet to embrace this technology due to false claims and myths that abound on the subject.Today, I am going to dispel those myths once and for all.RPA Is Just Physical Upon hearing anything with the word “robotic” in it, most of us will turn to metal machinery, perhaps a long mechanical arm or a powerful torch fusing together two pieces of metal. This isn’t surprising, especially when those specific uses have been implemented in the automotive industry for decades. However, that is a very limited view of RPA, for the key word to note is “process,” and as you should all know, business is filled with repetitive tasks and processes that can’t be done through a solely physical output.Myths about Robotic Process AutomationWhile the applications are many, one such area that organizations are seeing real value by implementing RPA is in the hiring process. For example, UXPLORE has automated everything from the Offer, Onboarding, and Integration process for their clients. Normally, it would take 2.5 hours for an HR associate to onboard a new hire; from hiring decision to a welcome email. However, by automating the process, that time has been incredibly reduced to just 8 minutes.Robots Will Replace Humans One of the most popular misconceptions about RPA is that we humans, or at least, a good number of us, would eventually be out of a job. Well, that is only partially right.RPA isn't about the loss of jobs but the creation of an industryAs with every emerging technology, this is both true and untrue. There’s no denying that something like the automobile put wheelwrights and blacksmiths out of business. However, it also created a new industry for auto repair and manufacture. Also, the creation of the internet created a whole new suite of jobs and skill sets for the jobs it may have made redundant, such as video rental store clerk. RPA is a new change that will affect some occupations while at the same time creating new opportunities, the same as every other emerging technology before has done.RPA Only Reduces Cost Unquestionably, one of the greatest appeals of RPA is the potential for vast cost savings. After all, bots don’t get paid, don’t get sick, and can work 24/7. However, yet again we see this misconception being caused by a narrow scope of RPA.Time, accuracy, and in some cases physical safety can all be substantially improved upon with RPA. And this value not only supports business operations, but the effect can be felt right down to the customer experience. RPA improves accuracy, process quality, and response time, which means a greater experience for the customer. Not only that but by capturing data for analysis, they are able to provide a more tailored experience for the user. By handling simple, frequent questions, it can leave the humans free to deal with more complex, challenging customer support issues that require comprehensive, sophisticated, and empathetic responses. It also doesn’t hurt that bots can be scaled up or down, making it ideal for seasonal operations or periods of high-traffic.rpa process for accuracyRPA Is Just a Trend Technology, like fashion and music, can be full of trends that are wildly popular one moment and fall to the wayward, however, that in and of itself is one of the hallmark characteristics of a trend – they are short-lived. RPA, on the other hand, has been used for decades as a physical technology, and in recent years, as a software solution. Needless to say, it is only picking up steam.Let’s take a look at the once-popular customer service model of offshoring. This was done to save cost as labour was typically much cheaper overseas. However, that fact doesn’t hold true anymore, and as the cost of labour rises, companies have been scrambling to find a better way. And the better way for an ever-growing number of companies is RPA, and the benefits and savings are as real as the satisfied customers. According to the National Association of Software and Services Companies (NASSCOM), RPA can yield companies a “cost reduction of 35-65% for onshore process operations and 10-30% in offshore delivery…[and] an investment recovery period as short as 3 months…” So tell me, if something is more efficient and saves you money, why would you stop doing it?RPA Is Expensive and Not Worth the Cost of Investment RPA is a business initiative and one that should ultimately be sought out to not only cut cost but improve efficiency. However, like any initiative, RPA is not immune to initial upfront investment for implementation.cost of RPAFrom the build phase which includes the provisioning of IT infrastructures such as physical/virtual machines and databases to consultancy costs and partnerships, an RPA initiative undoubtedly comes with a price tag; however, that is taking a very narrow perspective. That is because typically, the initial cost is usually dwarfed by the rapid internal cost reductions and significant ROI. When you think about it, implementing RPA is essentially tripling your capacity, as bots don’t begin at 9 and end at 5. Due to this fact alone, I have seen organizations yield a 50-100% and higher ROI within the first few months of implementation.RPA Won’t Work in My Industry While the idea of using RPA to lighten workloads, improve efficiency, and reduce cost should be appealing to anyone in business, many are still uninformed of the real potential this once burgeoning technology has now that it has made its way into the mainstream.Let’s take insurance, for example, an industry that is continually trying to balance and mitigate risks and reduce costs in order to turn a profit. However, with today’s customers demanding faster, more personalized service, the old system of doing things wasn’t cutting it. The same can be said for the banking industry.Healthcare is another, with RPA quickly taking over patient scheduling, claims processing, billing, and data entry. Of course, let us not forget telecommunications, manufacturing, distribution, and utilities. In the last decade, RPA has made huge leaps in providing real value across industries, and as the technology grows and improves, its uses will only evolve and become more commonplace.RPA Is Only for Large Organizations There was a time when I would have said yes, RPA is only for large organizations, and that primarily had to do with the upfront costs such as purchasing a “boxed” solution or hiring the appropriate IT support. However, thanks to cloud technology RPA is now a viable option for businesses of all sizes.RPA is now a viable option for businesses of all sizesTypically, if your organization, from HR to customer service, is faced with repetitive and rule-based tasks, there is likely a place for RPA. According to Energias Market Research, the global RPA market is expected to reach over USD 2.8 billion by 2023, which translates to a compound annual growth rate of 33.3%. While certainly an impressive figure, I believe that it will only be realized by the steady adoption of RPA by small and medium-sized businesses driven by inexpensive implementation costs and high ROI. Keep in mind though, that in order to adopt RPA effectively, you need to assess its viability and ensure you have the right tools and alignment in place.Office Work Can Be Completely Done With RPA Across the globe, organizations of all sizes are utilizing RPA to increase accuracy, save time, and reduce cost; and while RPA is literally built to do just that, it does have its limitations. RPA is ideal when dealing with repetitive and rule-based tasks; however, when you start to use it for more complicated and non-standardized processes, it becomes a much more challenging process.Even processes that pass the feasibility of RPA may not be an ideal candidate to automate; specifically, if the process itself is not efficient. When you automate an inefficient process, all you will be successful in is speeding up your inefficiency. The best approach is to redesign your process prior to automating or change it accordingly during the design phase of delivery.A Truth Worth Remembering Robotic Process Automation has come a long way from its inception and use on factory floors. Today, it is being utilized for more “white collar” tasks, and as the technology further develops, we are seeing it transcend industry and provide real value to not only business but to the customer. However, before you can utilize RPA in your strategy, you first need to understand what this technology can and can’t do, and in order to do that, you need to stop believing the myths and realize what RPA really is – the future.
Robotic Process Automation: 8 Myths Debunked

Hi there, it’s me, your customer. The one you spend millions of dollars – on mobile apps development and otherwise – trying to connect with during the waking hours? Ya, that one. Well, guess what? I am connected. But perhaps the term “connected” is misleading. I prefer to view myself as “empowered.” And if you want to connect with me, you first need to understand what this empowerment is, and I won’t lie, it borders on superpowers!Don’t believe me?What else would you call my ability to add items to my partner’s shopping list while sitting in a meeting? Or delighting my family by booking a long overdue family vacation while waiting for my train (which was late, as usual)? What about paying bills while waiting for my kids to perform at their school concert, only to capture photos and videos and then instantly sharing with friends and family all around the globe?How about streaming music on long drives, and even changing the destination at the drop of a hat, all while never getting lost? I don’t ever really need to know where I am going. Instead, I can figure out both the journey and the destination along the way. My life is an adventure, one where I can simultaneously order toilet paper, crush candies, and reply to emails whether I am in the office or Switzerland.Being able to accomplish anything from anywhere at any time is pretty incredible, isn’t it!? The digital experience I get through my mobile takes me far and beyond. From the moment I wake up to the moment I fall asleep, whether I am in the bathroom or the boardroom, I am connected.But am I connected to you?Please don’t mistake my empowerment for entitlement, and it doesn’t matter if you agree with my level of screen time or not. You only have two choices; you can either judge it or learn from it, and if engaging with me is important to you, I suggest the latter.So what do you need to learn from these digital experiences?Well, for starters you need to learn the tools I use, for, after all, it is my device that keeps me connected. But you need to go deeper than that if you want to truly connect with me. You need to know how I prefer to learn, discover, and how I make decisions. What I like and don’t like. What I want from my digital experience. You need to unearth what is important to me and what values drive my decision making. How do I like to be engaged? What keeps me loyal? And what a sucker I am for speed, comfort and convenience! That is my expectation from my digital experience.Think I am asking a lot? Don’t.I know you are collecting data on me as you work towards bettering the mobile apps development you’re tasked with, and I don’t mind it, as long as you use it to improve my life – my experiences. You should already know where I live, where I shop, what I buy, and maybe even what I do for a living. You probably know when my birthday is, how many kids I have, what new car I am interested in buying… so do something extraordinary with it!I have given you the keys to the kingdom, a direct line to me. Stop viewing mobile as one of your marketing strategy channels and start viewing it as the KEY to your marketing strategy. Mobile has given me the convenience, the personalization, the value, the power, and the digital experience I prefer; and that won’t change because I am not willing to give it up.But like Brad Jakeman, the marketing guru behind such illustrious brands as Macy’s, Citigroup, and currently Pepsi, says “The irony is that while there have never been more ways to reach consumers, it’s never been harder to connect with consumers.”Thanks, Jake, you nailed it.We consumers will continue to be connected, the only question is, will we connect to you?
I’m Connected but am I Connected to You?

If millions of years of human evolution have taught us anything, it is that people have always preferred the use of voice to interact. However, for decades it was agreed that the technology “wasn’t quite there yet” to be used with machines. In the interim, nose-to-the-phone model of personal computing became the defacto standard, and no one really questioned it. Things have really begun to change in the past few years as Apple Siri, Amazon Echo, and Google Talk gained momentum and their QoE is a welcome relief.The pleasant-sounding demeanour of voice assistants being used beautifully masks the complexity of the underlying technology and is exactly what was needed for mass market adoption. Now we finally have a relatively inexpensive purchase which has an iconic experience and the ability to increase commerce. I am told, Amazon Prime Echo users have a propensity to spend $200-300 more per annum than their Prime counterparts not leveraging these devices. Secondly, conversational commerce – the intersection of messaging apps (WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, Echo) and shopping, is finally getting critical mass. For the first time ever, more than 50% of the 10+ trillion digital messages in 2016 were anchored on these conversational messaging platforms vis-à-vis email.My son and I adore our Amazon Echo, and Alexa has become the 5th family member in the house! We find it anchoring us to the home base, more like a throwback to the 1950’s when the house started becoming rearranged and anchored to where the radio or TV was. We have moved our echo from the kitchen to my son’s bedroom to the basement and now back to the kitchen, where we believe it really belongs. As it stands, a report from PwC states that 59% of people between the ages of 18-24 interacted with a voice assistant at least once a day; compared to 65% of 25-49 year-olds. Based on my personal experience and the rapid rise in fan-base of these devices I am estimating that by 2025, nearly 60-70% of all interactions with machines would have transformed significantly from where it stands today- mind reading, gesture control, and voice interaction would be the name of the game. What we are seeing is the 1st phase of the proliferation of these devices and the ubiquity of them will really depend on how quickly the following 4-5 things can be addressed by the OEM’s:Make them conversational Today, my son and I nearly bark at Alexa rather than converse with it. The “Alexa Voice” feels like it needs to be “used” as opposed to just “conversed” with. Nobody wants to feel like they are scolding someone to try and find out what the weather is.Less of an assistant, more of an advisor Wouldn’t it be great if these devices proactively spoke to me, as opposed to waiting for me to start an interaction? “Sachin don’t have that ice cream” or “Sachin time to call a cab” etc. Ideally, the future of voice assistants would be laden with proactive features.Continuity Have the ability to leverage AI and ML to give context to a conversation and ensure it is continuing from where it left off as opposed to starting from scratch every time. These two fields are expanding daily, and voice assistant technology needs to be utilizing these developments as quickly as they are had.Secure and Private Ensure that there is some form of KYC as these personal devices are exposed to larger audiences. The dichotomy of near field and far field needs to be sorted and quickly.Ability to understand emotions and react Have the ability to understand and emote, as well. As they always say, it’s not what you say but how you make me feel that really counts.Never the less, we have come a long way from 1956 when a 16-year-old Victor Scheinman first invented a speech to text transcription device. We could have reached where we are today, a lot earlier but finally, we have the right business reasons and motivation to continue evolving it and growing it! With Amazon Echo, Echo dot, Echo look, Echo show…the list is going to grow very very quickly as access to the software becomes universal and less elitist!!!Can’t wait for it to be omnipresent!
Voice Assisted Commerce: The Gateway Drug for CX Designers & OEMs
In the relatively short time that human beings have been on this planet, we have seen a lot of things fall to the wayward and into extinction. In some cases, it was animals like the Dodo bird, the Caspian tiger, or the Baiji dolphin; in others, it was our creations that became outdated like dial-up internet, 8-track cassettes, or what’s even more relevant today, the Single-Channel experience.Anyone in the world of tech, retail, sales, marketing, or digital business is familiar with the buzzwords Multi-Channel and Omni-Channel experiences, except, these should no longer be considered as buzzwords. Yes, both of these strategies have stood the test of time and have proven their value in improving revenues and customer experience, especially in comparison to the ones who are still hanging on to a Single-Channel strategy.But perhaps I am getting ahead of myself. First, allow me to establish what exactly these two strategies are because I have entered many discussions where differentiation of both is completely misunderstood.Two Strategies – One Customer A Multi-Channel strategy is what the vast majority of companies today are practicing. Much like the name suggests (multi, or “more than one”), it means employing catalogue, social, online, marketplace, and retail, ultimately providing the consumer with a choice of multiple channels to engage with a brand. In this scenario, each channel operates independently, with its own native goals and tactics, to drive the customers’ journey.Multichannel strategy: online store, social, catalogue, retail, marketplaceOn the other hand, Omni-Channel strategy (where omni represents “all”) also utilizes multiple channels to interact with customers just like multi-channel; however, it is here that the similarities end. An omni-channel experience is one that “unifies” all channels to provide a continuous experience for the customer.Unlike multi-channel, which is very channel based in its individual efforts and strategy, omni-channel is more cohesive in nature, with the ultimate goal of providing a seamless experience, no matter where or when the customer chooses to engage and/or convert in their journey.Omnichannel strategy: online store, social, catalogue, retail, marketplaceSo now that I’ve established what both multi-channel and omni-channel strategies are, let’s see them in action.Mark’s Multi-Channel Journey While out for drinks one night, Mark notices his friends’ watch and is quite taken by it. So much so that he decides to take out his phone and look at the manufacturer’s website. While scrolling through their product line, he is met with a pop-up that offers him a 10% discount on his first purchase if he subscribes to their mailing list. He enters his email, and even goes as far as selecting a watch to purchase, however, realizing he is at a bar with friends and it may not be the best time to buy, he abandons his cart and puts his phone away.The next day Mark receives a welcome email from the manufacturer with links to their social pages and product catalogue. He decides to visit their Facebook page, and upon arrival, he is greeted with another offer for 10% off his purchase through the Facebook Shop if he “Likes” their page. As he scrolls through he finds the same watch he likes and again, puts it in his shopping cart. However, still a little groggy from the night before, Mark isn’t quite ready to commit, so he closes his computer and decides to get on with his day.multichannel buyer journey: mobile, web, retailA few days later Mark is walking through the local mall when he comes across a retail location of the watch manufacturer. To his surprise, he notices the front of the store is covered in signage indicating that there is a sale and all watches are 20% off. Taking this sale and his unexpected arrival at the physical store as a sign, Mark decides to enter the store and buys a watch.By the time Mark gets home, he receives a “Thank You” email from the manufacturer on his recent purchase. A few days after that, and still very happy with his new timepiece, Mark is a little disappointed to see his social media feeds continuing to be retargeted with ads for the same watch he just purchased.As you can see, Mark’s Multi-Channel journey took him across different opportunities to not only interact with the brand but to purchase from whichever channel he felt most comfortable with. For Mark and his journey, it was all about choice, one that was ultimately his to make as to when and how he would purchase. Unfortunately, some of the other channel teams never received the data about Mark, and thus, valuable resources were wasted trying to retarget him.Mark’s Omni-Channel Journey Now let’s take a look at what that journey would have looked like if it was through an omni-channel strategy, and I’ll start right after he puts his phone away at the bar.The next morning Mark is awakened with a welcome email from the watch manufacturer. The email reminds him that his 10% discount offer is still valid and also provides a quick link to his abandoned cart if he wishes to complete the purchase right away. However, he chooses to ignore this email and gets on with his day.Omnichannel buyer journey: web, social, call centre, mobile, email, retail, catalogue, direct mailAfter a few days of Mark’s inactivity, the manufacturer’s preset tactics switch gears. Instead of sending Mark the same discount offer that he seems to be ignoring, they display a mix of retargeting ads and customer testimonials on his Facebook feed, a tactic they hope may give him more confidence in making a purchase.Three days later and still unmoved, the offer gets amped up. They send Mark a personalized email invitation to experience the watches first-hand and take advantage of the special 20% discount at one of their retail locations. He accepts the invitation, visits the store, and ends up making a purchase.By the time Mark goes home with his new watch, there is a “Thank You” email waiting for him. Soon after, the manufacturer reaches out to Mark on social media, requesting a product review, which he responds to positively. In the meantime, ads across all social media for the watch have stopped; only to be replaced by watch accessories made by the same manufacturer.What’s the crucial difference between Multi-Channel and Omni-Channel? Omni ensures a continuous and seamless progression throughout the journey.How Do You Decide Which Strategy is Right for You? Before choosing between multi-channel and omni-channel, it is important to acknowledge a couple of things. First, and as should be clear by now, they are not the same. Secondly; and this one may come across as a bit abrupt, but, omni-channel is a superior experience.Reason being, that omni-channel strategy provides the customer with a consistent, intuitive, and personalized experience that they expect but (with a capital “B”), choosing an omni-channel experience also means – investing heavily in your organization’s capabilities. What does that look like? Well, for starters you’ll need a deeper understanding of your customers, an enhanced technical infrastructure, advanced employee skillset, and most of all, a shared vision to not only kick off the initiative but to fully realize its potential.In a multi-channel initiative, all channels work independently of one another, allowing for modular implementation and upkeep. This can allow organizations to get their feet wet first, so to speak, and prepare them for an eventual shift to omni-channel. The major downside with multi-channel is that consistent branding and communication can prove difficult with so many disconnects between channels; often leaving customers feeling unhappy through conflicting experiences.While both have their benefits and challenges, it is up to you and your objectives to determine which strategy is right, and in some cases, even feasible, to implement. Remember, a non-functioning or disjointed omni-channel strategy is essentially the same as having no strategy at all. So if you are looking to make the leap towards omni-channel, ask yourself:Do we have the vision and team alignment to make this successful? Do we have the required talent, skillsets, and compensation model? Have we identified the right mix of tools to support our transition and implementation? Do we understand the implications of data integration? What to Remember The channel strategies have evolved alongside customer expectations. Today, customers are empowered to do more, and as such, expect more from their brands in the channels and avenues they can interact with them. In the journey of digital transformation, we already know that the future lays in experiences; however, the only question left is how seamless, intuitive, and memorable will yours be?
Multi-Channel or Omni-Channel Experiences: Which is Right For You?
Most people are familiar with the term hybrid; although it is usually in relation to cars. Fortunately for the sake of my point, it will do just fine. Now, by definition, a hybrid is the result of something new being made by combining two different elements, and in the case of hybrid cars, it is an electric and gasoline-powered engine. This provides the user with the fuel efficiency of an electric motor with the power and convenience of a gasoline one. However, it isn’t only cars that are enjoying the benefits of combining two different elements to create something new and better, for the world of IT has constantly been melding together concepts, principles, and methodologies in order to have the best of both worlds. Today, we are going to dive into one of those combinations known aptly as the Hybrid Cloud.What is a Hybrid Cloud Strategy? According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology, a hybrid cloud infrastructure is a composition of two or more clouds (private, community, or public) that remain unique entities but are bound together by standardized or proprietary technology that enables data and application portability. Inferring from this definition, a hybrid cloud strategy is the use of these multiple infrastructures, including an organizations’ own on-premise IT and data centres, to achieve IT goals. When you allow workloads to transition between public and private clouds as needs and costs change, a hybrid cloud model can empower organizations with enhanced flexibility and more data deployment options. So whereas a cloud-first strategy prioritizes the cloud for all IT functions, a hybrid strategy uses a combination of infrastructures to provide an organization with the benefits of each without limiting themselves through adherence to one.Benefits of a Hybrid Cloud Strategy Gartner estimates that 90 percent of organizations will have adopted a hybrid strategy by 2020, and when you look at the benefits, it is easy to see why. Both public and on-premise deployment boast their own unique advantages; however, they also come with their own drawbacks. That is until you combine them.Simply put, a hybrid cloud strategy is ideal for organizations of all sizes who prioritize security, are positioned for growth, and who have high data demands, mainly because it addresses all these factors and more. Here are a few of the advantages of a hybrid cloud business strategy:Benefits of a Hybrid Cloud Strategy10 advantages of hybrid cloud.flexibility, scalability, cost-effective, enhanced security, network performance/reduced latency, backup and disaster recovery, more opportunity for innovation, agility, speed to market, risk management.A hybrid cloud strategy is also incredibly useful for organizations who work with dynamic or changing workloads. Take for example an order entry system, one that sees a spike in demand around the holiday season. This situation would be a prime candidate for a hybrid approach as they could have the application running in a private cloud, but can utilize cloud bursting from a public cloud during times of peak demand.How to Build a Hybrid Cloud Strategy One of the greatest benefits of adopting a hybrid cloud strategy is that you can customize it to the needs, present and future, of your organization. In other words, there isn’t just one type of hybrid cloud; rather, there are multiple approaches and combinations. However, in order to establish a hybrid cloud strategy, the following requirements must be available:A public Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) platform Creation of a private cloud, either on-premise or via a hosted private cloud provider Sufficient Wide Area Network (WAN) connectivity between environments Private clouds must be properly architected to attain compatibility with public cloud Now that I’ve established the prerequisites for hybrid implementation, it begs the question as to what exactly it would look like – and there isn’t one answer. One option is an organization could invest in cloud management software, providing them with a single platform from which to manage public cloud applications and on-premise infrastructure. Another option is the vendor-native hybrid cloud strategy, where you take your on-premises infrastructure or data centre and connect it to the public cloud in order to leverage its benefits.Regardless of your approach, the beauty of a hybrid strategy is that it allows organizations to tailor their infrastructure to meet their specific needs. However, like most things in life, there are steps you can take to help ensure your hybrid cloud initiative gets off to a good start:Integrate new cloud services with existing on-premise infrastructure so you can have access to all necessary applications Implement security measures to control and restrict the flow of vital data Use a virtualization layer, or hypervisor, to deploy existing applications in such a way that it works seamlessly on-premise and on the cloud platform. This will provide an easier approach to lift and shift between cloud and on-premise infrastructures When possible, develop future applications using container technology tools which can reduce dependence on cloud platform vendors and allow you to use on-premise and different cloud platforms in unison Automate tasks whenever and wherever possible, especially repetitive manual ones Develop and monitor KPIs (deployment frequency and speed, failure rate, time-to-recovery) so as to ensure a winning strategy using the hybrid cloud model The key to constructing a successful hybrid cloud is found in the selection of hypervisor and cloud software layers that are uniquely compatible with your desired public cloud. This allows for proper interoperability with said public clouds API and promotes seamless migration between the two.Hybrid Cloud Implementation: Challenges and Solutions As is true when implementing any new strategy or practice, challenges can often arise. However, being informed, and more so prepared, for these occurrences is the best way to ensure a smooth transition to utilizing a hybrid model. Here are some common hurdles and helpful tips to work through them:Security Risks – Data in a private cloud is secured, however, a hybrid cloud may require different security platforms to safeguard sensitive data. By selecting the right platform, developing a deep understanding of the data requirements, and with the right partnership in integrating your network solution, security risks can be minimized. Integration and Maintenance Cost – Integration of public cloud with private cloud, on-premise infrastructure, or integration with various cloud providers can prove challenging. It adds a greater complexity from not only the management and implementation point of view, but it can also make tracking resources and computing power across multiple environments difficult. Technology and DevOps Process – A hybrid cloud strategy requires greater prudence in selecting technology and solutions which can work across a variety of environments. When this isn’t accounted for, all too often I see lifecycle management and deployment slow down. However, turning to an expert in your rollout can help provide the best possible solutions and technologies such as containerization using Docker/Kubernetes/Openshift and automate application build and deployments by ensuring proper CI/CD process is implemented. Among the most popular technologies in the field right now include Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, HPE OneSphere, and Amazon Web Services through their recent partnership with VMware software. Hybrid cloud strategy is the way of the future for any organization that’s looking for flexibility, affordability, enhanced security, improved access and communication, and customizable solutions for IT needs. However, like any new strategy, this can be intimidating when experience is lacking. Don’t hesitate in reaching out to an expert to help develop and implement a hybrid cloud solution that isn’t only tailored to your specific requirements, but is designed to drive your business forward.
The What, Why, and How of Hybrid Cloud Strategy

I had the pleasure of being invited by Genesys to be a part of the Toronto Tech Summit’s panel discussion on “How AI is Shaping Society,” late last week. I thoroughly enjoyed the conversation along with my awesome fellow panelists (from IBM, Element.AI, Inegrate.AI and RBC) and the crowd was extremely engaged! In case you missed it, here are some of my answers to the questions posed:Q: How will Artificial Intelligence change the way we interact with each other? Now that we’ve seen the new Google Duplex (and Microsoft Xiaoice) and its ability to interact with humans, what does this mean for the future of human-to-human conversation and interaction? Are we going to see this technology as a proxy for talking to people?“Technopanic” is not a very new concept. When cars were first introduced, people claimed it would lead to the destruction of the concept of “families.” When telephones came in, it was the destruction of “civil conversations,” and with calculators, it was the end of “memorizing.” None of that has really happened. We have evolved our lives and made them more productive if anything else.Our tech fortune tellers generally have the habit of going overboard with the extremes. With AI transformation, I honestly believe some things will change dramatically, and some will evolve slowly. The drudgery of making phone calls to dispute charges from Telcos, banks or to set up appointments will be a thing of the past with AI technology.Human-to-human interaction will go from being one dimensional, as we know it today, to a hybrid one where assistive technologies would optimize outcomes. For example, I could very well see Chris (the moderator) using one of the futuristic devices in a crowded fish market in Mumbai haggling over the price of shrimp in the local dialect. I was in the UK a few months back, where one of the billboards read the tagline of a company, “when your heart stops beating we keep tweeting.” Human interaction is going to definitely change, but for the better. It will be more efficient and more productive when you want it, and stays the same when you don’t.benefits of Artificial IntelligenceQ: Why does AI have to be explainable or auditable?There are software companies who create applications that help to better understand if inmates from jails are ready to be paroled. Based on their scores, judges chose to parole them or put them back behind bars. However, as data science and analytics is not completely foolproof a bad decision, however unintentional, could very well equate to years of additional jail time! From what we hear, people of colour are 77% less likely to get bail than others. Just one single KPI, independent of the type of crime they might have committed. Now, this inherent bias has made it to algorithms, and we clearly hope that software is explainable and auditable to essentially undo cases such as these.Q: What is the longer-term impact of assistive AI technologies?I have a tendency to look for historical similarities when things happen, and with AI, given the potential magnitude of sweeping changes, we only have a handful of inventions which come close. The direct outcome of assistive tech is that due to higher efficiency and productivity of the bots and AI-powered contraptions, a lot of jobs will be lost. Fortunately, a lot more will be created, and most importantly every job will change. However, the secondary changes are far more difficult to predict. For, eg. When you look at the transition from “Horses” to “Cars” in the early 1920’s, there were three important secondary outcomes, which no one really could have envisioned:impact of assitive AI technologiesSince cars went by billboards a lot faster than horses; companies started using logos rather than their full names. A new stream of advertising started, more centred around brand recognition Cars were more expensive than typical consumer products, and hence people had to take credit from banks; which had never really happened until then. A new stream of banking called “Consumer Credit” was born Globally, 25% of total agriculture land was used to produce hay; used to feed horses. When the population of horses started to reduce, people started growing wheat, leading to a surplus of wheat and a subsequent dramatic drop in prices. As the downstream value chain of farming wheat was highly inelastic – a lot of farmers went bankrupt, and so did the rural banks they were associated with. As rural banks began to collapse, it caused a cascading effect which led to urban banks going out of business and accelerated the slide of the stock market – already in recession – which lead to the Great Depression For me, the most important point is that we have to be agile, adapt, and evolve. Over 40-years, all goes well, but over the short term, we will have to pivot and pivot quickly when needed, to continue existing and thriving.Q: Will AI foster cross-cultural relationships that are unencumbered by language barriers or will AI take the world in a darker direction?Absolutely. We are going to be spoilt for choices of tools to break through language and cultural barriers. We are hopefully going to find ways to verbalize what’s in front of the visually impaired, and we are going to find means to fight cancer or diagnose it at a much earlier stage and solve the problem. Life is going to get a lot easier in a lot of different ways, and it will also lead to a bunch of different paradoxes fuelled by AI.paradoxes fuelled by AIWe are going to get lazier but healthier…get dumber but more productive…hyper-capable but helpless…and there are murmurs of the world going into darker spaces too. I wouldn’t say that’s not outside the realm of possibility. However, it’s not as extreme as they make it out to be in The Terminator series or other such sci-fi movies. If you have to take it to an extreme and talk about what would happen when one creates super intelligent machines beyond general AI, then it’s possible that they would think of us as we think of ants today. We don’t want to harm them, in fact when we see them, we try and avoid them by sidestepping them. However, when their objectives and goals are not aligned with ours, we don’t think twice before annihilating them. That is definitely a possibility, but I believe we will never get there, and this is why.In years from now, what do you think will happen even if there are rumours of a company from the bay area coming close to cracking the code on super-intelligent AI. How do you think other superpowers would retaliate? This is a scenario where winner takes all. A six months lead equates to possibly 500,000 times more productivity in this domain, once the end product is ready. Could it lead to the 3rd World War? Perhaps.Q: What is the most promising application of AI recently that has the potential to positively impact society? It could be on a business, individual, or social level?In the 1600’s Louis XVth apparently loved his food. So much so that he had 500 people source vegetables and fruits from around the world. Fast forward to the 21st century and “commoners” like you and I have access to a better variety and quality of food items from Loblaws and other grocery stores. All this thanks to Louis XVth himself; not to mention globalization, better supply chain, etc.Likewise, today we have to be geographically located in a developed country to get access to the best doctors in the world. However, because of AI and mobile devices, the democratization of the best healthcare diagnosis and medical assistance to remote communities will happen over the next 2-3 decades; something that 30-40% of the world doesn’t have today. It’s going to have a far-reaching beneficial impact on millions of lives!Q: Name one type of AI application which will fail?Well, great companies with bad management fail, and sometimes vice versa happens too. Its hard to put a finger on what will succeed and what may not; however, Cambridge Analytics did go out of business, so there you go.Wondering if your business is a candidate for an AI acceleration? Let’s Connect and discover the possibilities of how AI can transform your business.
How Artificial Intelligence and AI Transformation Shapes Society

Have you ever had one of those unforgettable travel experiences that you just couldn’t help but talk about upon your return? Glad I’m not the only one; however, today I would like to share a particular experience with you, one that may not be what you’d expect. I say that because my excitement wasn’t caused by the country we travelled to, the city we explored, or the attractions we visited. Rather, it was the hotel my family and I stayed at that left such a lasting impression and quickly became an attraction in and of itself. Perhaps I should explain.Over the years I have stayed at many hotels; however, this particular experience quickly became unique from the moment I completed the reservation. Like most people nowadays, I make my travel arrangements online, and while receiving a confirmation email is nothing new, in this instance, I also received a link to download the hotels’ app; an action which entitled us to a discount. Never one to pass up a deal, I downloaded the app, received my discount, and patiently awaited my departure – but things got interesting way before that.A week prior to my departure, the app sent me a series of photos of local attractions that I scrolled through and either liked or disliked. After just a few short moments, it started suggesting personalized activities that my family and I might enjoy, even giving us the option to purchase tickets. The following day I was sent a list of popular restaurants located near the hotel and was given the opportunity to easily make reservations. The day after that, I received a long-range weather forecast for our destination, one that included the weather the day of our arrival and continued for the duration of our trip. It even suggested that we packed sunscreen and may want to consider bringing something warm as the temperature was expected to drop in the evenings. Finally, the day before my departure I received another alert that included a suggested packing checklist to help ensure that nothing was forgotten. Thinking to myself that this was already a distinct travel experience, I was nowhere prepared for what happened upon my arrival at the hotel.The moment my family and I stepped through the front entrance, we were greeted by a welcome notification on my smartphone. In a highly intuitive fashion, the hotel app guided us through the check-in process; one that we could easily complete ourselves. How easy? Well, let me put it this way; instead of a concierge guiding us to our room, my daughter took us there by interacting with a virtual assistant (in the form of a teddy bear no less) that walked along the walls of the hotel corridors. We didn’t even need a key to unlock our room. Imagine arriving, checking in, and walking into your hotel room all without having to speak with hotel staff.It wasn’t the check-in experience alone that captivated us, rather, the experience continued on to our room itself. It allowed us to personalize our surroundings via the app, including the art on the walls, the temperature of the room, and even the curtains. We could request toiletries, order room service, control the television, and arrange for a wakeup call, all from my smartphone. It gave us the wonderful feeling that whoever designed the hotel had us in mind. The experience left my family and I feeling empowered as if we were in complete control of what, when, and how we wanted things to be. And that wonderful feeling is just one of the many benefits that come along when your process is driven by Design Thinking and Innovation.Design Thinking: What is it? The definition of design thinking, simply put, is an iterative approach to problem-solving, one that intentionally takes into account and utilizes different perspectives, knowledge, experiences, and skills to create practical solutions and drive innovation. While this may sound like a rather haphazard approach to design, in reality, it is very process driven and like any process, involves a sequence of steps to be carried out in order to achieve a goal:Design Thinking Process1. Empathize.We understand the people who we are designing for, We are solving problems for them not for us – so we avoid assumptions, We conduct interviews, observe, and listen in context, We map the end to end journey.2. DEFINE.We transform our empathy findings into INSIGHTS to define the need, We stay away from an “everything to everybody” mindset, We then come up with Problem Statement – Point of View (POV), We turn problem into opportunity by How-Might-We questions (HMW).3. IDEATE.We brainstorm a range of crazy and creative ideas along and in teams, We learn from each others ideas and go beyond obvious solutions, We transform abstract ideas into concrete solutions, We storyboard each concrete idea into homogenous and lucid stories.4. PROTOTYPE.We create prototypes to test number of ideas quickly, We test rapidly rather than deciding on the direction too early, We enable audience to imagine what their experience would be like, If fail, we fail quickly and cheaply, and lean from people’s reaction.5. TEST.We use prototyping to test and validate our understanding of the problem, We prototype as if we know we are right and test as if we know we are wrong, We only show and do not tell, letting users explain to get the feedback, We revisit assumptions based on raw feedback from users, and.6. ITERATION.At its core, this human-centred approach to innovation looks to align the needs of the people (Desirability), the possibilities and potential of technology (Feasibility), and finally, the requirements for business success (Viability). Aside from the innovative and disruptive products and services that can be created via Design Thinking frameworks, what is truly beautiful about the process is that it is not limited to any specific industry or area of expertise.Design Thinking in Hospitality: Intercontinental Hotels, USA Travel for business is almost as old as business itself; however, ask anyone who has done so and they will likely tell you that working out of an often cramped hotel room is less than ideal. So how would a hotel go about providing a better working environment for those travelling for work while not alienating those that are travelling for pleasure? This is exactly the problem faced by Intercontinental Hotels Group, however, before they could solve it, they first needed to understand the needs of their guests.Younger workers are tech-savvy, independent, entrepreneurial, and most of all, demanding. And as a result of research, sensory data, surveys, and interviews with potential customers, it was found that what the hotel chain lacked was informal, flexible experiences; energizing and uplifting spaces; peer-style customer service; personalized choices; and intuitive and integrated technology to control it all.The result was Ignition, a new meeting and working experience located in the lobby of Crowne Plaza hotels. Some of the more notable amenities include workspaces ranging from single person pods to a 10-person “apartment” that can be booked by the hour, food and beverage on demand – that even come on a specialized design square plate to fit perfectly next to a laptop – and a brand new “Host” role within the organization to help business travellers in a variety of capacities, including delivering food, sourcing restaurants for meetings, and more. Ignition was designed to keep travellers in a state of heightened productivity, all part of the brands promise of “Making Business Travel Work.”Design Thinking in Banking: Commonwealth Bank of Australia, Australia Taking a simplistic view, one could say that a banks’ customers fall into one of two categories; business and personal. So how would a bank go about creating richer, more exciting experiences between those two, more specifically, the merchant and the customer? Easy – you find the place where these two meet.Commonwealth Bank of Australia wanted to help customers and businesses build stronger connections and they believed that the best way to do that would be an innovative and different form of payment. After conducting research in Australia, Germany, and the UK, they learned a number of things that would impact their design moving forward. First, they saw that the ideal platform should support the full spectrum of human behaviour around payment. Second, the platform should add value by bettering relationships between banks, merchants, and customers. Lastly, they learned that the payment experience should be customizable, working one way in a luxury retailer and another in a gas station. The results were Pi, a new retail business platform, and Albert, a portable payment device.Pi can easily be implemented by larger merchants into their existing network, while smaller merchants can grow their business using some of the powerful tools provided. Albert offers a large and intuitive touchscreen that not only can handle current card methods of payment but can also adapt to future methods, even eliminating the need to swivel a screen from cashier to customer.Design Thinking in Telecom: ETB, Colombia How does a 130-year-old telecom stay relevant in the 21st century, all without alienating its loyal customers but still appealing to the new, tech-savvy generation? Simple, they practiced a design thinking mindset.ETB, Colombia’s oldest telecom, decided to leverage their already highly recognizable brand and created a blueprint for a complete overhaul of their retail spaces, one that would appeal to a new generation without neglecting their current customer base. However, in order to do that, they needed to transform and design their public spaces (stores) and give them a more personal feel. This included new warm and bright retail outlets, self-service kiosks that eliminated waiting in line, as well as a facelift of the brand with a new colour palette and brand guide.The result was a complete and scalable blueprint for the next generation of stores, services, and roles within the organization.Design Thinking in Retail: Burberry, England How does one of the most iconic fashion labels in existence increase an abysmal growth of 2% per year? A difficult question, until you apply the design thinking process, at which point it becomes quite clear – you need to connect with the new generation (Millennials) of consumers, and do so in a way that appeals to them. That is the “what,” but now comes the “how.”In order to grow revenue, the company understood it needed to connect with the “digital demographic,” one that reaches for their phone any time a want or need arises. Innovating off the brands’ core heritage, they crafted a marketing strategy that connected the values of a younger customer base, that was “cool and innovative,” and one that would convince a new generation to become loyal customers. As such, the label created personalized campaigns, invested in their social media presence, and was the first of any luxury brand to reach 1 million followers on Facebook.The result was an increase in revenue to $3 billion annually and a transformation into one of the most digitally innovative fashion brands in the market today. All of this came from simply empathizing with their end users and taking a human-centred approach to their marketing efforts to directly relate and reach their desired demographic; digitally – which is exactly where they’d be.Design Thinking, Agile, and Lean: Complementary or Conflicting? All too often we see organizations blindly following frameworks and methodologies because they have a problem they can’t solve. And most often, in doing so, they will negate themselves from other viable solutions, simply because they are adhering to a single approach. It is here that the problem lays.The idea of a particular right way of doing things is slowly being disregarded as more and more people realize that there is nothing to be gained from dogmatic adherence to any one method. So instead of asking lean or agile or design thinking, it needs to be understood that these processes aren’t mutually exclusive, and perhaps a better statement would be agile and lean and design thinking. A recent presentation by Nordstrom Innovation Lab very neatly combines the core principles of Design Thinking, Lean Startup, and Agile Execution into a unified strategy.The lean mindset is what drives business to continuously learn through experimentation until they discover the right answers. It helps dictate what to build, all while improving the work that delivers the greatest value. Agile, on the other hand, is all about achieving the best outcome through technology. It is about how IT and development teams can continuously deliver value, adapt to changing needs, and produce the highest quality of work. Lastly, design thinking helps to tie it all together by understanding limitations, recognizing and capitalizing on the opportunity, and exploring all the possibilities from a human-centred point of view. When applied in unison, these methodologies can help any team create solutions that deliver the desired outcomes; as long as iteration is continuous.
Design Thinking Opportunities: Turning Challenges into Opportunities

Very few, if any, are truly self-sufficient these days. That is to say, we don’t typically build or produce things for ourselves; rather, we rely on a network of producers and service providers to help us get through our day to day lives and perform many critical tasks and functions. Another name for this reliance is a dependency, and much like we have come to rely on certain services to achieve the outcomes we desire, similar types of dependencies exist in the software engineering world, and those dependencies have to be made available by some mechanism generally called Dependency Injection, and that is what I’d like to discuss today.What is Dependency Injection? Dependency Injection or DI is generally thought to be a very complex topic, but in truth, it’s quite simple and easy to understand, even if you’re five, as this example illustrates:How to explain dependency injection to a 5-year-old?When you go and get things out of the refrigerator for yourself, you can cause problems. You might leave the door open, you might get something Mommy or Daddy doesn’t want you to have. You might even be looking for something we don’t even have or which has expired.What you should be doing is stating a need, “I need something to drink with lunch,” and then we will make sure you have something when you sit down to eat.Source: StackOverflowDI is a technique under the Inversion of Control (IoC) principle/pattern. In this mechanism, a centralized object is made responsible for providing all the services or things on which our application blocks depend. The application blocks define the list of services or items they need, and they don’t have to worry about how to construct or instantiate those services and how to dispose of them if they’re no longer required.Angular’s Implementation of DI In the Angular framework, DI is one of the core mechanisms, taking care of instantiating and loading dependencies for all components, directives, and services.Angular automatically creates a centralized Injector that is loaded when the application bootstraps. The injector looks for all defined dependencies and maintains instances that can be reused, inside a container, generally referred to as DI Container.But how does the injector know how to load or create an instance of a dependency? Angular has something called Provider, which “provides” that information to the injector. When you require a dependency, be it a service, function, or value in your application, you have to register a provider in the application injector. The injector will then use that registered information to instantiate and load the dependency whenever it is required.A component that depends on a service named `AppService` Considering the constructor here, as soon as code reaches a point to instantiate this component class, it informs Angular about the dependency. The Angular process checks if the injector has an existing instance of the dependency. The injector looks for an existing instance in its container and creates one if not, and finally returns the instance to Angular by keeping a reference in the container.Note: The type of dependency is NOT optional, you have to tell Angular about the object type so it can create its instance when needed. In this example it’s the AppService type.In this example, we have only one dependency, whereas, in practice, it can be more. When Angular finally receives the instances of all the dependencies from the injector, it then calls the constructor with those service instances as arguments, of course, in the same sequence.There is a small caveat in this example; we provided the service reference to Angular using the component’s providers’ collection. If we use this approach, we are telling Angular to get a new instance of the AppService for each instance of the component. But that probably isn’t what we needed, right?Hierarchical Injector The Angular’s root or centralized injector is a hierarchical injector, which is one of its most exciting features.It means if we provide a service for one module or component, the instance of that service will be available to all the descendants of that module or component. In an Angular application, there are multiple places where we can “provide” a service:AppModule: If we provide a service at this level, it will act as a Singleton service, i.e., one instance for the whole application, unless we override this for a sub-module or component.AnyOtherSubModule: If we provide services at this level, Angular will create a child injector automatically, which will inherit from the parent injector. This child injector will be responsible for maintaining instances of the services provided for this module and all its children (modules, components, directives, services, etc.) unless we override this in a sub-module or component.AppComponent: Providing a service at this level means one instance of service is available for AppComponent and all its children, but not other services or AppModule. Angular will again create a child injector inherited from parent injector to maintain instances of services at the AppComponent level.AnyOtherSubComponent: As in the example above, one instance of service will be available for one set of instances of this component and it’s children (if they exist). This will also be handled by an automatically created child injector for each instance of the component.Note: None of these patterns are wrong. It will vary depending on the application needs and whether you want one Singleton instance of a service or you want separate instances of the service for each component and its descendants.In real-world applications, most of them will have child injectors being created by Angular to manage service instances and provide them whenever needed. Since Angular creates these child injectors automatically, Angular handles all the clean up as well when those child injectors are no longer required.The @Injectable Decorator We’ve talked about injecting services into components, directives, and pipes, etc., but haven’t talked about injecting services into services. Look at the example below and guess if it has an error:LoggingService: A simple class that maintains a collection of log itemsCounterService: Another class with a few methods, and depends on the LoggingService classAppModule: @NgModule with both services declared above listed in the ‘provider’s’ collection There is a problem in the example above and Angular will report an error similar to the one below:The class ‘CounterService’ cannot be created via dependency injection, as it does not have an Angular decorator. This will result in an error at runtime.Either add the @Injectable() decorator to ‘CounterService’, or configure a different provider (such as a provider with ‘useFactory’).This is a very common misconception about the @Injectable decorator. Since the CounterService depends on the LoggingService, we have to tell Angular that CounterService is “injectable”, which means it depends on some other service and that other service will be injected “into” this service. So we have to add the @Injectable decorator before the CounterService declaration like below.The important thing to note here is that no error was reported for LoggingService because it doesn’t depend on anything for instantiation.For the sake of performance, consistency, and avoiding any future errors, it’s a best practice to add @Injectable decorator to all service classes. For instance, if we decide to inject some dependency in the LoggingService in the future and forget the @Injectable decorator, Angular will throw the same error.To fix the above error, simply add the @Injectable decorator to the CounterService class.CounterService with @Injectable decorator The Super Power of the @Injectable Decorator The amazing @Injectable decorator has another fascinating usage. We can use it to provide a service at the root injector level, which makes this service globally accessible to all modules, services, components, pipes, etc. No matter where your service resides in the code, you can make it globally accessible by passing in a special object to the @Injectable decorator like below:@Injectable decorator with config to provide service for root injector Voila! Our service is now globally accessible and can be injected into other modules, services, and components without providing it anywhere else. And one very important benefit that we get here is that our service is now fully tree-shakable.By default, Angular CLI generates services with this pattern and recommends having @Injectable decorator being added to all the services. As mentioned earlier, it’s a best practice to have it with all service classes, but it is up to the application requirements and use cases to choose for other available options and patterns.As of Angular 9, the Angular team introduced two more value options for the `providedIn` property, listed below:‘platform’: Since we can have multiple Angular applications running on one page, for instance, if you have a micro frontend architecture, you can share services across applications using this value.‘any’: Use this value to instruct Angular to create a global instance of this service for all eagerly loaded modules, and a separate instance of this service for all lazy loaded modules that inject it.Take Away In this article, we saw how Dependency Injection works in an Angular application and how we can utilize the injectors and providers to get instances of our services based on our requirements. However, this topic is broad and I have only skimmed the surface. But I hope that my simplistic approach was able to provide you with a broad understanding of Angular DI and inspired you to consider it for your next development.
Angular Dependency Injection and the function of Injectors & Providers
Data visualization was always an important, albeit niche subject that only the most diligent number and statistically driven businesses and technology practitioners cared about. And then suddenly, the tragic and globe-spanning events of 2020 have made data visualization a mainstream staple. Across the world, eyes are glued to screens, watching bar graphs, line charts, and geographic maps with close intent. Now more than ever, it’s essential to skillfully understand data visualization from the perspectives of both a reader and creator and to be able to understand the various narratives that visualizations can convey.What is Data Visualization? Data visualization is defined as the graphical display of data and information, primarily for the purposes of data exploration, communication, or sense-making. This critical distinction separates data visualization from just being graphic design and aesthetics. That’s because it’s also about constructing the right relationship, context, and indicators to communicate to your audience effectively. Data visualization is just as much about usability as it is about being visually appealing. While a typical audience might be more familiar with charts, graphs, and maps, data visualization also includes infographics, gauges, and other forms of visual expression such as iconography and illustration.Why Visualization? It Makes Biological Sense Organizations that can gather and act quickly on their data will have a competitive edge in the marketplace due to the speed at which they can make informed decisions. Typically, when encountering data, people use the slow and inefficient cerebral cortex in the front of the brain, responsible for logical thinking and cognition. Choosing to visualize the data shifts the balance towards the fast, automatic, and unconscious processing performed by the visual cortex. With increased efficiency and speed comes increased knowledge, as it becomes easier to isolate new and emerging trends, find patterns, or identify outliers in a data set.Why Today? Today, we have more data circulating than ever before, with publications referring to the modern era as the age of ‘Big Data.’ Forbes estimates that we create 2.5 quintillion bytes of data every day, which is only increasing. There is an ever-growing amount of business, technological, and user data captured every day, and it presents compelling opportunities for organizations to interpret and make practical use of it through visualization.Data visualization’s biggest strength, the ability to create a coherent and human narrative out of hard numbers, is increasingly evident in the age of the 2020 global pandemic. Epidemiologists are encouraging everyone to ‘flatten the curve,’ turning a simple line chart into an artifact that embodies our hopes, fears, predictions, and the responses of the entire world: not bad for a few lines and dots! Understanding data visualization during this unique time will provide you with exciting use-cases and examples to study from, as organizations across the world are utilizing various visualizations to convey different narratives.How to Start Visualizing 1. Understand Your Audience: The first step in visualizing your data is to determine and define the audience that will be consuming your visualization. Whether your audience understands the subject at hand will determine the granularity of visuals and the specificity of labels.It can help you think about what decisions you’d like to drive in your audience through your data visualization. Is it an infrequent and significant decision, like purchasing a house, where detailed comparisons are necessary? Or is it more tactical, like a weekly sales performance review that only requires a few metrics? Determining this will inform the visualization elements, such as thresholds for target metrics, or colours, to indicate urgency.2. Choose the Right Visual: There are an incredible amount of visualizations, variations, and types to choose from: bar graphs, line graphs, pie charts, are just the tip of the iceberg. To determine the correct type, consider the relationship between the items in the original data-set.bar graphs, line graphs, pie chartsA temporal visualization like a line or area chart may be the best fit if it’s data captured over a period of time. A geospatial visualization such as a heatmap or tree graph will communicate more effectively if it relates to a location. Periscope features a handy flow-chart that can help you get started in selecting the right visualization for your needs.3. Provide Context: Visualizations without context can be challenging to interpret, so titles, labels, and text can help provide your audience with a functional understanding of the visualization.functional understanding of the visualizationEnsure that labels have the proper weighting, that the title should be the most prominent, that the axis labels should be legible and balanced, and that bolding should be used sparingly for emphasis.In addition, a legend or annotation can go a long way in improving the usability of your data visualization.4. Ensure Accessibility: Ensure accessibility with your visualization so that it’s usable and understandable by everyone in your audience. Don’t use colour as the only visual cue; instead, combine both text, colour, and patterns with helping communication.Play around with shapes and sizes that don’t directly represent what’s being conveyed, such as different line styles and text sizes. In addition, always label the data directly, as adding data explanations in labels makes it harder to see, and adds cognitive load to the reader.Visualization Best Practices Clarity and Data Accuracy: Data visualization appeals to our unconscious and intuitive visual perception. However, the data represented should still hold up under critical scrutiny. Points of data should retain their original values: it can be far too easy to manipulate data with a visualization that skews itself towards a particular narrative or exaggerates a comparison. Since visualization is meant to be a resource for analysis and sense-making, this should be avoided, and the integrity of the data should always be preserved.Visual Encoding: Part of the visualization process involves encoding the data points into a visual form through the use of shape, colour, angle, size, and various other visual attributes. By modifying these, you can make distinctions in the data and present it in a more complex format. For example, colour can be utilized to indicate focus, quantity, categories, or even add additional layers of meaning to your visualization, such as red for a negative value. The best data visualizations make creative use of visual attributes to add further context for understanding and analysis.Labels and Axis: The above principles also apply to the labelling and text that accompany a visualization. For clarity and accuracy, any axis in a bar graph should start at a baseline of 0 to keep the integrity of the data presented. Labels should not be rotated as to ensure their legibility and clarity.Data Visualization Future Trends: An emerging trend in data visualization, powered by digital technology, is user interaction and control. A few examples are outlined in Google’s ‘Material Design,’ such as progressive disclosure: the ability of the user to reveal pieces of information that they select or interact with. In addition to this, direct manipulation of a visualization through panning, zooming, and scrolling is also finding frequent use today. These controls are often accompanied by filters or toggles that manipulate the data visualization for analysis purposes. Implementing these controls can be an incredibly effective way of allowing your audience to interpret further and make sense of your visualization.An exciting take on this involves turning visualization interaction into a curated experience or interactive game. The New York Times featured an interactive visualization that allows the user to guess the trends in causes of death and match their results to the real data. The Washington Post features a simulation and modelling of various virus outbreak scenarios, where the users can even re-run each simulation and compare the resulting curves and graphs accordingly. The interactions here provide an additional layer of understanding by letting the user examine their biases and assumptions and tackle complicated and unwieldy topics by ‘humanizing’ large numbers.Take Away Never before has data visualization been so relevant. While it may be more mainstream now, it still follows the same principle that has guided data visualization since its inception: turning hard numbers and vast amounts of data into a narrative that is actionable, comprehensible, and human. As long as organizations follow best practices, understand the data, and preserve its integrity, they’ll be able to leverage visualization far into our data-filled future.
Understanding the Story of Data Visualization

“For people without disabilities, technology makes things convenient. For people with disabilities, accessibility makes things possible.” – Judith Heumann, U.S. Department of Education’s Assistant Secretary of the Office of Special Education and Rehabilitative Services.The above statement was made back in 2012. That would suggest that for the better part of a decade, experts have been highlighting the importance of accessibility. However, you need only look around the web and at a few applications to see that it hasn’t been generally adopted.For example, eCommerce would typically identify the target user while developing their web store. This list should include people with special needs, but how often does it? Implementing good governance around web accessibility ensures that people with specific disabilities can access your web store, walk through the product catalogue, and ideally, make a purchase.If eCommerce companies lower trade barriers and enforce accessibility, their growth rate and trade percentage will undoubtedly increase. Following accessibility standards in web applications has been shown to help increase market growth 10x faster than without following the accessibility standards. The graph below shows the web Accessibility compliance for the period of 2008-2020.ai companiesWeb Accessibility AdaptabilityThe below map highlights one of the biggest challenges to web accessibility: one-third of countries don’t have standards or guidelines in place. For example, most of Europe has taken a proactive approach to accessibility, helping them adapt much faster than most. However, other parts of the world are a little slow in following the trend, lacking a defined and enforceable law to develop accessibility features in all new web applications development.ai technologyCountries, including the USA, Canada, and the EU, have already passed legislation to ensure digital accessibility on certain web applications. Here’s a high-level breakdown of what that looks like:USA – Federal, state, and local government websites are committed to fulfilling WCAG AA level compliance of accessibility standards. CANADA (Ontario) – Private or non-profit organizations with more than 50 employees and all public sector organizations must meet AA level by January 2021. EU – Is enforcing accessibility standards for any new website development since 2019 and is planning to make accessibility standards mandatory on public sector web applications from 2021. Consideration on Web AccessibilityThere are some important considerations that must be taken into account when developing a web application to enhance its accessibility standards:Web applications should always be keyboard friendly All the images should have “alt text” in the app Contents in the app should be easily accessible for all users with or without disabilities It’s a myth that making eCommerce websites accessible needs a lot of development effort, expert knowledge, or a substantial financial investment. In reality, it only requires new ways of thinking and some extra effort on top of your current development. Plus, there are many free tools, guidelines, and assets available for the development community on how to implement and follow accessibility standards in web applications.A Few of the Benefits of AccessibilityOrganizations and brands are always searching for new and better ways to connect with their customers and expand their business. And when they create products and applications that help and accommodate users with disabilities, it gives this marginalized group a feeling of being part of society and that they haven’t been overlooked. By keeping accessibility standards in mind throughout the process, from development to testing, we can build accessible applications for people with diverse disabilities and eventually result in the following:Avoiding legal complications: In many countries, it is mandatory to follow accessibility prerequisites and develop a product that follows accessibility standards before launching it for end-users. Also, testing is compulsory to meet accessibility compliance. Potential growth in the business: According to research , 23% of people with a disability never go online, versus 8% without disability. Thus, designing and developing applications that follow accessibility standards will help in potential revenue and market growth. Accurate search results (Improving SEO): If developed to AA standards, web applications should have rich content and excellent user experience. This will help it not only become discovered more easily and quickly but will inherently improve your SEO. Better User Experience (Improves usability for all types of visitors): Increasing the accessibility standards of our eCommerce stores will be beneficial to any user who uses the application. Following the accessibility standards make eCommerce web applications more user-friendly – it’s that simple. Writing higher-quality code: Websites that are developed WITHaccessibility standards as a top priority are more valuable to the developer and client as they tend to contain a higher-quality of code. Accessibility should be a part of the project discussions at the very initial stages. Accessibility implementation should be considered mandatory for every element/component from the start of development; that way, developers will know what they need to include and how to build it.Not following this practice will lead to more work at later stages of the lifecycle, which not only increases cost but impacts the deadlines.Common Accessibility Mistakes made by Developers and DesignersAccessibility is an essential factor for application developers and designers to produce high-quality web stores that can provide real value to its users, including those with special needs. Web stores or applications must follow these sets of accessibility standards .While developing a web application, designers and developers will often encounter varying sets of mistakes, a few of which may include:Missing alternative text for images and any other non-textual content Not marking up headers and lists in HTML (and then using CSS for designing) Developing a web application that’s dependent on mouse/cursor to explore the site (rather than making the functionality accessible through the keyboard) Missing captions and/or transcripts for audio/video like broadcasts Missing proper colour contrast; an integral part of making a site accessible Developing a website that meets the accessibility standards without having enough knowledge of accessibility guidelines results in wasted of effort Take AwayIf eCommerce businesses tear down accessibility barriers and design their web stores while considering the users/customers that have a disability (permanent or temporary), they will likely notice something – their business begins to grow. Not only that, but they will also be providing a long-overdue right to a very marginalized group of people. In short, web accessibility benefits us all. And while there may be moments in your journey to becoming accessible that prove challenging, in the long run, following this practice is not only good business, but it makes you a good person.
The Impact of Web Accessibility and ADA Compliance on eCommerce

The job of the developer is, in many ways, a tireless one. Few could argue the importance of their work, its tangible impact on business initiatives, and how widespread their involvement can be across an organization. Yes, a developer has the potential to do a lot of great things for a company, its staff, and customers – that is, assuming you have a good one.You need only ask someone who has been involved in development work to know that not all developers are created equal. Which begs the question – what does a great developer look like? Today, I hope to paint you a clearer picture of the ideal developer as I share the 7 essential qualities every developer must-have.1. They pick the right tools Much like a carpenter wouldn’t use a screwdriver to hammer in a nail, choosing the right tools matters for developers. This applies to not only what you want as an application’s stack, but what you use to implement the solution and track issues when they arise. Make the right choice, and having sound knowledge of these tools can make a tremendous impact on how a developer performs.web development toolsLet’s look at a use case. Choosing an inferior debugging tool at the start would result in a developer having to spend an enormous amount of time and effort tracking and debugging issues. Hence, before jumping headfirst into development, take a step back and explore all the tools available to you. Your selection should complement your technology stack, reduce manual efforts, and substantially improve development performance.2. They keep their code clean The term “Clean Code” is a familiar one among developers and their peer circles. There are books written on the topic emphasizing the importance of various clean code approaches and illustrating how to bring these methods into practice. In a nutshell, the Clean Code philosophy states that the developers should write code that’s self-explanatory, easy to maintain, and easily understandable. Poorly written code is a nightmare to manage but can even result in total project failure and redo from scratch.The Clean Code philosophy dictates that code should be as concise as possible. It makes optimizations easier as well as results in smaller executable build size. Therefore, from naming conventions to the right number of code comments, bringing Clean Code principles into practice increases the developer’s productivity, contributing directly to project success.3. They are problem-solvers, with a can-do attitude Every developer should possess a good set of problem-solving skills. That’s because it’s commonplace for developers to come across multiple programming problems while building just about any solution (site, app, design).programming issues bugs & problemsThe software system development cycle faces a wide variety of challenges to keep the system’s performance, design, and user experience up to the required standards. But with the right tools, algorithms, and excellent analytical skills, a developer can come up with innovative solutions for any complication they face. Having excellent problem-solving skills, confidence to achieve, and a can-do attitude towards any challenge make that developer a valued resource in any organization.4. They are willing to adapt The world of technology is growing and changing rapidly, with the introduction of new and the evaluation of existing technology happening every day. For example, JavaScript was mostly unchanged until a few years back, but now it’s evolving at a fast pace after and becoming a crucial tool for digital application development. This need of the hour resulted in an overwhelming demand to modernize the language to match the standards of others in the software industry. That’s the reason not only JavaScript has transformed, but a lot of new frameworks and libraries have been introduced.This change in technology demanded JavaScript developers to be more adaptable to keep pace with advancements. A flexible personality can easily adjust to the evolution of technology or processes. Adaptable resources are the key to any organization’s success as its culture keeps evolving to meet the rapidly changing demand of the technical market. That’s why developers need to keep up to date with the latest technologies and vary their role according to the needs of the day, and in some cases, the hour.5. They are efficient through optimization Writing optimized code is a rare skill, but not an impossible one. It’s something that usually comes with experience, practice, and exposure. This method has a significant impact on the performance of your application. Therefore, if an application is taking time to load, then the developer likely needs to optimize.After the performance, things like SQL query optimization, caching, response optimization, SEO, accessibility, user experience, etc., comes into consideration, which also profoundly impacts the success or failure of an application. If a user finds it hard to land on the website or face challenges to navigate what they want to do, it means your business might lose a client or customer. That’s why, while developing a software system, developers must consider optimization parameters and design the application in a way that best serves its users.6. Aim for success at the start What sort of a developer do you wish to be? While I can’t answer that accurately, I can say with confidence that it isn’t a bad one. Do you see yourself as reckless but fast, or an individual who believes in planning with proper architecture in place and delivers quality work by being slow and steady?software development processSure, from a shallow perspective, immediacy might seem more attractive than a slow approach. But it will result in a product that is buggy and difficult to maintain. Considering the cost, it is a better option to move ahead with a plan in place, follow standards and software development patterns, and develop a sturdy application. Remember that the end goal is to deliver an application that meets the client’s aspirations and serves the purpose to its users.It is an excellent approach to take some time at the start, plan the things, choose the right architecture and design pattern, set the standards to be followed in the code, and think over your solution and algorithms then implement it.7. Self-evaluate along the way Once there was an architect who designed a library that was praised by all for its magnificence. The structure started to crumble because the architect did not consider the books’ weight soon after opening the library. The same is valid with software development, as a developer needs to take into account the most basic details and evaluate the application on all fronts.A developer needs to test code, discover issues, and fix them with the development of every feature of the software. Self-evaluation of the developed feature results in less technical debt and fewer bugs in the later stages of the development life cycle. Make sure not to release code that is buggy or, in the words of our metaphor, always take into account the weight of books.Take away By now, I hope you have some clarity on what makes a great developer. And whether you are looking to hire a developer, or are one and find yourself looking to improve your skills, consider what you read today. And just as Rome was not built in a day, one can not bring these habits into practice overnight. Quality takes time, whether you are talking about software development or professional development.
7 Essential Qualities A Developer Should Have For Web Development

Salesforce Commerce Cloud(formerly Demandware) is a user-friendly and seamless eCommerce platform that offers a suite of features intended to transform the experience of how brands connect with their customers at every step of their journey. Salesforce B2C Commerce plays a considerable role in the worldwide market. In 2017 alone, 540 million unique shoppers made a purchase online through a Salesforce Commerce Cloud-powered website, and those sales equalled $21B. Impressive!But what makes this platform so widely adopted and heavily used? Today, we will dive into exactly what makes Salesforce Commerce Cloud so great, and many argue it has caused a B2C commerce revolution. Enjoy.Key Features of Salesforce Commerce Cloud Key Features of Salesforce Commerce CloudCommerce Storefront: The B2C Commerce Storefront is an eCommerce module where brands can customize the user experience. The Storefront Reference Architecture (SFRA) is based on mobile-first best practices helping brands to build and launch sites quickly and easily so they can get their products in front of their customers.Merchandising and Marketing: Thanks to Artificial Intelligence, Salesforce Commerce Cloud has immense power, giving merchandisers a broader scope and capability to craft and provide their customers with the best-personalized experience. These capabilities help brands fuel eCommerce growth with features that empower product pricing, catalogue management, promotion management, and site search.Multi-Site Management and Localization: Brands that have an international presence need localized sites for greater success in specific areas. Salesforce Commerce Cloud offers a powerful internalization feature that helps brands to develop geo-specific sites or add features to existing websites according to the local cultures, currencies, and languages. Having localized websites also benefits regional marketing efforts. They can quickly build and launch websites with the help of a global reference storefront.B2C Commerce Extensions: Through B2C Commerce APIs, brands can integrate with different third-party applications and social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter to enhance and bolster the marketing efforts of the eCommerce store. Commerce extensions help brands introduce their business to new and diverse markets that might have otherwise been inaccessible.Benefits of Salesforce Commerce Cloud Benefits of Salesforce Commerce CloudPersonalized Experience Boost – Salesforce Einstein AI: To improve usability, Salesforce Commerce Cloud has its own built-in Einstein, which utilizes artificial intelligence to help quickly create better experiences for your users. It does so through predictive analysis of available data to give users better search results from the available product catalogue. For most, this uncompromisable as it’s generally accepted that only the best-personalized experiences earn your business more customers.Mature Marketing Process: Marketing is a crucial element when it comes to eCommerce. Within the boundaries of the Commerce Cloud, merchants can manage and share product information, images, and promotional content across various social media platforms. The Salesforce Marketing Cloud can also be used to customize user search criteria based on different merchant policies.Enhanced Mobile Experience: Today’s consumer world is all about smartphones and all the things they can empower us to do. The list of things you can do is quickly overshadowing what you can’t do on mobile. That’s why the eCommerce industry introduced mobile storefront to give customers easy access to do online shopping, where they want to shop. At present, we’d say Salesforce Commerce Cloud brings the world the best option for a mobile-friendly eCommerce store. It lays great emphasis on the mobile-first approach, providing optimal shopping experience to users.Internationalization: Due to multi-site management features, Salesforce made internationalization incredibly robust and easy. It allows organizations to manage multiple storefronts for multiple locations across the globe from a single back-end platform. By having an excellent technical grip over Salesforce Commerce Cloud attributes and features, one can effortlessly manage multi-currency, multi-language, and multiple eCommerce processes.Scalability: This requirement comes up in any eCommerce or enterprise-level website when the business wants/needs to expand and extend its scope to more markets worldwide. Salesforce solves this problem by providing you with the scalable instance associated with your storefront from which you can easily upgrade your system without impacting user experience.Single platform: Salesforce Commerce Cloud has one feature that it is extremely proud of and makes a point to emphasize, and it’s empowering merchants to run their business across multiple channels from a single platform. Salesforces Omni Channel Module allows merchants to perform many operations such as order management, inventory management, sales, and marketing campaigns as a single SaaS solution.The Advantages Salesforce has over its Competitors There are few competitors in the eCommerce industry that could challenge the power and prestige of Salesforce Commerce Cloud. A few notable mentions include Magento, Bigcommerce, Weebly, and Virto Commerce. Having said that, there is still a great divide between Salesforce and the rest, as it seems Salesforces already have the solution its customers and the development community need, while its competitors are still trying to figure it out.Salesforce Commerce CloudThe capabilities of Salesforce Commerce Cloud are extensive enough to give the development community unprecedented control over creating a web store. You could develop one using Salesforce Commerce Cloud, without having to wrap your head around the in-depth technical aspects of the platform, such as databases or networks. Salesforce Commerce Cloud offers multiple features (as should be clear now) that stand out from the competition, such as multi-store management, channel management, shopping carts, and inventory management. Another significant thing about Salesforce Commerce Cloud is that it is a SaaS platform, meaning the development community won’t need to worry about maintaining its infrastructure. This platform is an easily manageable and user-friendly tool with outstanding customer support and community behind it.Take Away It should be clear that Salesforce Commerce Cloud is a powerful, mature, and a scalable platform with amazing features for merchandisers. From having multiple storefronts to an unprecedented level of scalability, and a lot more, there is much the eCommerce industry should be thankful to Salesforce for. And as the world continues to shift to and react to the current situations, the need for such a platform will only grow, much like we’ll all retailers will have to do. Fortunately, Salesforce will likely grow right alongside them.
Salesforce Commerce Cloud – A Revolution in B2C Commerce

Your digital identity is arguably more valuable than cash and is used by online operators for ordering products and completing the transaction in a buy flow system. While convenient, on the flip side, the online availability of personal information isn’t without risks. Hacks, breaches, and even full-blown identity thefts are still quite common, and it’s even more imperative to mitigate such risks during an era of digital transformation.The concept of Digital Identity Verification is a byproduct of the internet, digital transformation, and, in its simplest terms, is when companies verify the identity of the online customers and clients they do business with. This can be done through digital identity verification software tools available in the market, such as Onfido, Jumio, IDology, and Acuant that can authenticate scanned copies of documents like passports, driver’s licenses, and other nationally issued ID from authoritative sources or proprietary government data.Today, I hope to give you all, especially companies undergoing digital transformation, a buy flow centric crash course on Digital Identity Verification, including what it is, what it looks like, why you need it, and some of the challenges and benefits associated with verifying your digital identity.Enjoy!What makes up a Digital Identity? All the information about someone’s digital identity can be categorized into two groups with a few examples provided:A person’s digital attributes:Birth date Email addresses Bank details Biometrics (fingerprints, eye scan, 3D face map) A person’s digital activities:Search queries Purchase history Comments, likes, and shares on social media Forum posts The Digital Identity Verification journey The Digital Identity Verification journey starts with the creation of a user’s identity and its distribution over the network, preceding the following steps:The verification of identity to ensure all identity traits are correct. The use of identity with: The authentication to check a person’s ownership of some assets. The authorization of role/access rights based on identity. The authentication attributes get shared with multiple parties. The last step in this journey is to revoke identity from the system when digital identity information needs to be removed/ deleted.Why is Digital Identity Verification necessary? Almost all businesses are going through digital transformation in one way or another and moving to digital, e.g. banks, retail, telco, and more. Companies are now using digital infrastructure to carry out their online operations to get people connected with what they want. Still, many companies are continuing to physically use identity checks, such as when one needs an in-person verification to open a bank account, get a new phone number, or notarize a document. In today’s rapidly growing online era, this is not a scalable solution; slowing and limiting digitization. Digital Identity Verification can speed up all these processes and helps remove issues such as remote location access and geographical boundaries.Digital Identity Verification for Buy Flow Buy Flow or Shopping Flow refers to online shopping, where users must complete some steps to buy their desired products directly from a website.Digital verification systems are a must-have technology in the buy flow process as most eCommerce businesses are moving towards digitalization.However, like with anything worth doing, there are some challenges associated with relying on digital identification, but by the end of this piece, I think you’ll agree, they are dwarfed by the benefits it brings.Challenges of Digital Identity Verification in Buy Flow Challenges of Digital Identity VerificationData availability and management Issues: Tracing a customer’s identity is an integral part of the digital verification process. It requires data to be cross-checked and matched for accuracy, including the collection of personally identifiable information (PII). The data is necessary, but can often leave customers feeling uneasy. Giving out your necessary credentials and personal data on something like a credit history can open up security risks, exposing personal data to a genuine threat of digital malice.For not only service standards but adequate security to be achieved, companies need to adopt security solutions for storing customer’s data online. All the personal data and documents should be cross-checked with the official databases provided by applicable authorities. In the absence of such sources, it will be challenging to perform verification checks for authentication or, for that matter, to refuse access. Ensuring the best possible security and handling risk management will require identity expertise in multiple data collection methods for online ID verification. It’s paramount that users have control over the data collection methods and should know how their personal identity traits will be used for online validations.Obstacles in determining the accuracy of Digital Identity Verification: To create, maintain, and grow your customer base, it’s crucial to have accurate, efficient, and customer-friendly verification in place. This helps to ensure your brand comes off as a trusted service provider. To achieve this, you need a dynamic identity verification system that can handle large audiences while performing verification repeatedly. Applying Know Your Customer (KYC) processes to prevent frauds are also very important in this regard. To handle all these things, you also need tangible resource investments at the back-end to maintain secure platforms.Enhancing digital trust and customer experience: Your customers have been exposed to and likely already have several online identity verification systems that they use. However, having complex and suspicious data collection methods, risky transactions, and unfriendly user interfaces can put off new and existing customers alike very quickly. Establishing trust is vital for achieving long term success in the digital world. You must always be providing the right solutions for the right users and should be willing to extend a helping hand if required quickly. To achieve success, your selection of online identity verification tools must provide usability in the following aspects:Providing users with ownership and data security Perform regular verifications for the consistency Safeguard the clients against potential cybersecurity threats Risk and compliance management for business growth Catering to data protection and privacy regulations: With an increase in the usage of identity verification applications, there are also continuous changes in regulatory requirements associated with them. Customers are more concerned about how their personal data is collected, screened, and stored. This means that firms providing the Digital Identity Verifications need to keep up to date with changing regulations and policies. International standards and regulations are being formed to stay on of advancements and technological changes. As such, security standards must be updated and compliant with the latest data protection policies rolled out by the regulatory authorities.Benefits of Digital Identity Verification in Buy Flow Benefits of Digital Identity VerificatioProtects your business against criminal activity: Hacking and identity fraud are commonplace in the digital world, which is why businesses need to protect their customers and themselves. One of the key advantages of Digital Identity Verification is that it helps keep your online business safe against such malice by identifying your users’ personal digital traits to ensure that their transactions are legitimate. Identity verification provides a better user experience with a sense of safety against all online threats, which will eventually result in better customer experience and loyalty.Helps businesses comply with AML and KYC rules: Online businesses need to be AML (Anti-Money Laundering) and KYC (Know Your Customer) compliant to prevent the flow of dirty money within their systems, not to mention avoiding the risk of a hefty fine and damaging their reputation. A practical and straightforward way for businesses to prevent this from happening is to have a sound, reliable system in place to verify their customers’ digital identities.Improves customer experience and signup rates: Digital Identity Verification helps to improve the overall user experience, leading to an increase in signup rates. Digital identity verification is a real-time process, so it makes the processes quicker and smooth for customers. If you have a sound digital identity verification system in place, it can verify users within seconds. That means customers are no longer required to submit the hard copies of passports or driver’s licence for a signup process, which takes days if not weeks in some cases. Instead, customers can get their identity verified right there and then.Reduces operational costs: A significant advantage of using Digital Identity Verification is that it saves operational costs for the business. This goes on to further protect not only the business but the customer as well.Take Away Much like I promised at the beginning, by now, you should have a reasonably solid understanding of not only Digital Identity Verification, but what it is, why you need it, and some of the challenges you can expect on your way to the benefits it surely brings. However, as the world is shifting undeniably towards digital, the sooner enterprises start to make this transition, the better off not only they will be, but their customers. Because, as should be clear, Digital Identity Verification does much more than provide good customer experience, it gives a sense of security for both the company and its customers – and that’s just good business.
Impact of Digital Identity Verification on Buy Flow

A Customer-First Experience sounds great, and really has a nice ring to it, but how do you design your application to be UX first? Now traditionally, web applications were tied to the features and roadmap of a single monolith solution. In order to change that, we need to not only shift that paradigm, but we needed to reverse roles; and for that, the concept of Decoupled Architecture was introduced.Decoupled Architecture is a type of computing architecture that enables computing components or layers to execute independently while still interacting with each other through well-defined protocols.So what’s unique about it? Well, in Decoupled Architecture, every component is an independent business unit that consists of its own logic and data and performs its tasks independently of the others. Most of the time, we use Decoupled Architecture for complex applications to allow layers and components to be completely sovereign from each other. This architecture enables developers to develop, test, and deploy application modules independently.3 Design Principles for a Well-Architected Decoupled Solution1. API-First in Decoupled Architecture: What is API First? It is on-demand, stateless services that your frontend application can call to retrieve content or perform a specific transaction. The API is designed to meet the expectation of the customer. However, with legacy solutions, these same APIs were designed based upon a journey. For example, Perform Step 1 before 2 and Step 2 before 3 etc. What if you wanted to start at step 3? That would not have been possible before. But with API first, the services are broken down into modules facilitating the ability to adjust and decouple itself from the service journey to animate the user experience.2. BFF in Decoupled Architecture: Nope, not Best Friends Forever; BFF means Backend For Frontend in this context. Imagine this is your computer and orchestration service layer for your web application. From time to market perspective, this allows the frontend team to develop the user experience in parallel with the backend team who become the underwriters with the service contract owner being the user. Consequently, that outcome becomes reusable and trustworthy because it’s consistent regardless of which form or mutation it undertakes. Allow your frontend application to focus on enriching your user experience and decouple itself from the management of the complex business rules.3. SaaS in Decoupled Architecture: Decoupled Architecture also allows the Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) strategy. In this scenario, we move everything to the cloud, so the data is accessible from anywhere. Even some of the companies move their data and services to different geographical locations. So they are available from a nearby data center to achieve efficiency. This pattern aims to provide scalability, availability, and concurrency of data and services.Decoupled Architecture and its Benefits Decoupled Architecture and its BenefitsBelow are a few of the developmental advantages an organization can achieve by following decoupled architecture as a core development principle:Independent UI component framework Decoupled architecture is one of the best solutions to build diverse experiences Independent Deployments: Deployments are faster and smaller Deploy faster with segmentation without risking functionality Scale your web applications and improve your maintainability Improve online rendering performance Reduce negative experiences with fail and hide independent handling Decoupled Architecture and its Challenges Before deciding if Decoupled Architecture is right for your organization, consider the following that could pose some challenges:Performance is a challenge and usually, overall response deteriorates. In the case of distributed components and layers, latency increases as compared to in-memory architecture. It needs an extensive thought process to design a network layer: Since everything is now in independent modules, components, or layers, so you must careful while handling communication requests between each element. In such scenarios, developers have to write extra code in the network layers to avoid barriers. Redundant code in decoupling can result in code duplication in different modules. Testing is very complex in a decoupled environment. decoupled environment.No one could argue of the shift we are seeing towards Customer-First Experiences; however, achieving them is easier said than done. Fortunately, with Decoupled Architecture, you can make your code more manageable, scalable, and consistent, all while curtailing the total cost of ownership to get your product to your user faster and with confidence.
Decoupled Architecture: UX Designers Making Customer-First Design

Today, technology has advanced to such an extent that we can deliver True Personalization by providing value to the customer while yielding profit to the business.But what is True Personalization?When a customer purchases something, you would typically send a follow-up email, thanking them, and the journey would stop there. But it doesn’t have to.Let’s say, after a few days of that initial follow-up email, you send them tips on how to use the product in different ways, along with some of its associated benefits. After all, what customer wouldn’t want to learn about their recent purchase and how to maximize the use, benefits, and enjoyment? But you aren’t done yet.After a week or two, you send another message with a special offer on a different product that compliments the customer’s previous purchase. This data-activated approach to marketing significantly increases online sales while reducing marketing spend and effort across various channels.And that is what poses one of the biggest business problems today – how do we provide personalized offers and experiences that provide value but don’t come across as intrusive?A diagram depicting the combination of segmentation and automation in personalizationType of Personalization Product Personalization is showing relevant products based on the demographics, infographics, and psychographics of the customer. Product Listing Personalization is determining the order of products shown to the user, based on a perceived value from previous purchases. Search Personalization is the ability to customize the search results of a particular query. It also can achieve instant keyword and product recommendations, and personalized search page ordering. Content Personalization is the presenting of personalized, onscreen content based on specific data gathered about the visitor, on-page, subpage or widget on any page, e.g., most relevant content determined by the user interests. Marketing Personalization is the sending of the most relevant offers in your marketing communications. If we are to believe the research published by McKinsey & Company, then the value of True Personalization will be in the trillions. In fact, just adding up, Retail, Banking, Insurance, and Telecom is estimated to be $2T+.A graph showing the combined value of the retail, banking, and telecommunication industry at two trillion dollarsAlthough there are multiple tools for Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Marketing Resource Management (MRM), there is not much orchestration of data happening across channels as these systems typically work in silos.The time has come for businesses to start asking themself if they are giving the customer what they want when they want it, which can be seen in not only their offers and related content but how it is tailored to their customer.Only a few companies have deployed True Personalization, which can provide massive opportunities. It can even be deployed in a systematic way beyond digitals channels. Tools like Augmented Reality/ Mixed Reality can improve product and service experiences in different environments, enhancing in-store visits.The customer’s view on personalization Today, 89% of companies compete primarily on the basis of customer experience. This is interesting when you consider that Forbes says 80% of businesses believe they provide excellent customer experience, but only 8% of the customers do agree with it.This is all that matters – do customers see your personalization efforts as annoying, or do they understand and feel the value? But before you answer that, you first must understand the customer’s expectations on personalization:To remind me of things: A particular item your customer is looking for may be out of stock, and they want to be notified when it is available again. To know me better no matter where I am: When a customer is using a navigation app, it can suggest the location of the nearest McDonald’s and offers to order it, so it is ready when you arrive, even account for traffic and travel time. However, to achieve this, you must unsilo teams and use your data effectively. To only have relevant recommendations: When a customer abandons a purchase, it is common practice to retarget them with ads and messaging. This can quickly get annoying, so it is better to use advanced technology and algorithms to determine complementary products based on past purchases and interests to dictate marketing spend, and not just an abandoned shopping cart. How to achieve True Personalization Personalizing a customer journey based on a single data point is simply not adequate. In order to provide True Personalization, you need to look at the consolidation of multiple data points to gain a better understanding and define the customer journey holistically.However, it is essential not to confuse personalization with segmentation. If you know that a customer has made a particular purchase and group them with others who bought a similar product, you will undoubtedly gain very little, if any, insight. True Personalization will be achieved when the data from different channels and touchpoints come together and allow you to form a solid understanding of the customer’s interest. But how do you do it?Let’s start by forming a deeper relationship with your customer to provide them with a more personalized experience. I would start with developing a Customer Data Platform (CDP) that would help keep you organized and understand a complete view of the customer from different channels.A circle diagram with four sections, labelled data, decisioning, design, and distributionMost organizations have already implemented a CRM and CDP tool but they are often owned by different stakeholders, essentially siloing the data. To counter, this is what I would recommend:Step 1: Establish your CDP in a way where meaningful data collected is kept in a unified model that can be used by data scientists to create ML /AI personalization models around. This can be targeted and personalized to these customers using a microsegment approach focused on a smaller customer segment with similar interests.Complementing the CDP with an IRP (Identity Resolution Platform) enhances the data by matching the anonymous IDs of the customer from different platforms. Collecting data from various channels the customer frequents will provide greater insight into your customers.Aside from the CDP and IRP, the Data Management Platform plays a significant role in enhancing the data. The DMP helps in synchronizing with third party data to understand and create other micro-segments. It also helps utilize the larger pool of data to target more substantial prospects with the same characteristics.Step 2: Micro-Segment the data and use it for decisioning. The decision engine plays a significant role when it comes to targeting the customer with more personalized communication as it requires sophisticated ML and AI engines to discern patterns.Step 3: Validate the content and offers. Since there would be a lot of micro-segments, it can be challenging to validate content. I would recommend trying an approach with different forms of art, photos, content, and tagging and storing the artifacts. Critical digital asset management can be adapted to store and retrieve them effectively.There should be a plan around the classification of content and offers to account for a wide range of factors. All of this can be stored in the offers table, and a decision engine can run to optimize and validate.Step 4: Orchestration of the customer data is essential to understand customer behaviour in all channels and react accordingly. The hardest part is connecting all the systems to the marketing platform to target the customer and microsegments. If possible, collect purchase data in real-time and send it to the DMP to educate and evolve the system.A diagram depicting personalization towards various digital channelsTake away Companies will often focus on the upsell, cross-sell, next-sell transactions that are a byproduct of personalization; however, they will often overlook the more critical one-on-one, loyalty and brand building relationships they have the potential to create. The approach companies need is one that facilitates the creation of deeper relationships with customers, one that provides education and value long after the cash register has closed on that first purchase.While organizations are becoming better at managing and tailoring their data, the opportunity is abundant in activating the right tools and making them actionable. The potential and possibilities are near limitless. So moving forward, let us not segment personalization and marketing, the time has come that neither can be mutually exclusive.
Product Personalization & Modern Marketing: The Ideal Mix for CX

“Working From Home” sounds much less charming and appealing nowadays, which was impossible to imagine just a few months ago. This is likely a result of the fact that few of us have a choice in the matter.As of March 17, nearly 90% of organizations have encouraged/required employees to work from home, according to Gartner.However, despite our new reality, the work must go on. And this has caused us to come up with new ways to innovate, new ways to collaborate, and new ways to get stuff done while working from home. And perhaps one of the greatest virtual tools in our arsenal is the Remote Workshop.In truth, we have been conducting remote workshops long before we started working from home to better work with our global offices and clients. However, with this being the new normal, we are taking advantage of the opportunity and turning our meetings into remote workshops for more effective collaboration – and a lot more fun if you work with the right virtual workshop tool.Utilizing Mural, a virtual workshop whiteboard tool, and a variety of video conferencing applications and other virtual tools, we have successfully broken down the boundary between reality and the virtual world, overcoming the distances between us to focus on the project at hand even while working from home. That is why we decided to share our experience of using virtual tools with you in hopes that you too will find success in your new remote reality of working from home.Table of Contents Simply click and start reading what you want!Why Remote Workshops The Challenges of Remote Workshops Limitations in Facilities Lack of In-person Contact Less Control because of Limited Visibility Stress of Staying Focused How to Conduct a Remote Workshop Planning for a workshop Preparing for a workshop Running a workshop After a workshop Take away Why Remote Workshops? Remote WorkshopsBridging workshop facilitators and participants from physical space to online experience, Remote Workshops have emerged as a de facto way of working from home. Most of us are drowning in countless emails, phone calls, and video conferences, increasing stress and fatigue. A remote workshop conducted with the right virtual workshop tool could fill your day with some fun and playful activities while bringing a sense of achievement with visible outcomes from a collaborative brainstorming session.In a remote workshop, a digital whiteboard is used to accommodate all types of media, i.e. images, mockups, presentation slides, GIFs, and even videos, which you easily drag-drop to share with your participants. As a facilitator, you can also define the viewport of your audiences by presetting the frame of each scene and their viewing sequence.Thanks to keyboards, you won’t face the awkwardness of being unable to recognize someone’s handwriting. Plus, there is no need for tearing down or whipping off your sketch on the whiteboard after every session, giving you sufficient time and materials for cluster and stratified workshop outcomes.Furthermore, a digital platform and a virtual workshop tool empowers you to create and publish reusable frameworks for different workshop types and/or activities. Frankly speaking, we love this feature of the virtual workshop tool as we no longer have to draw the empathy or prioritization map on blank sheets of paper before every workshop – phew! The time we saved has allowed us to focus more on our workshop planning and preparing.The Challenges of Remote Workshop Challenges of Remote WorkshopEven though there is no shortage of reasons, why conducting a remote workshop can pose some challenges. This likely spawns from our collective inexperience in the transition from offline to online; however, these challenges are nothing that can’t be overcome while working from home.Limitations in Facilities: In most physical workshops, we typically lock ourselves in a room with a huge screen to run the agenda and supporting slides, along with as many as whiteboards and unlimited Post-its for the collision and fusion of ideas. Whereas in an online environment, you’ll likely only have a laptop alongside your cup of coffee. That’s it! Although the boundaryless virtual whiteboard sounds cool, you are still limited by screen size. And while physical interaction and activity do have a direct correlation with creativity, it can be overcome with more creative activities incorporated in the remote workshops using virtual tools.You could also find yourself in a nightmare if the network quality at home fluctuates or fails to support consistent communication between you, your colleagues and/or clients. Fortunately, Mural is a virtual workshop tool that gives you features like the ability to follow along, which helps solve this problem nicely.Lack of In-person Contact: Human beings are social by nature. But social distancing and working from home is preventing much of the essential non-verbal communication we rely on, and perhaps none more than eye contact. We speak volumes through our eyes and can read a lot from looking at someone else’s. Sadly, you might have noticed in your recent video calls that there was hardly any direct eye contact, which could make you feel uncertain or lack confidence.social distancing and working from homeYou might have also noticed the awkward silence when facilitating virtual meetings through virtual tools recently. Does this sound familiar: you try to keep your doubt and anxiety to a minimum, wondering whether the audience is following you, all while trying not to sound nervous. If so, don’t worry, you aren’t alone.Less Control because of Limited Visibility: In a physical workshop, it’s easy for a facilitator to carefully observe participant’s reactions, while in a remote workshop, the facilitator is mostly interacting with people through a conference call or another virtual workshop tool (with potentially frustrating video quality no less ).Many times an experienced facilitator can be clever on activity schedules and timeframes by judging participant reactions. This used to be the “killer skill” for a facilitator – to identify participant needs and make decisions quickly. However, these little signals become much more subtle through a screen while everyone is working from home. You may end up struggling to drive the conversation or control the timeline through the virtual tools you’re using.Stress of Staying Focused: Physical workshops can run all day with a lunch break and a few short pauses throughout. On top of that, participants usually have some opportunities to shuttle between their seats and the whiteboard. These activities, although mundane, serve to keep participants’ bodies moving and necks stretched.Now, the reality is everything is concentrated into a remote session where you and your participants are glued to your chairs and immersed in your laptop screens for 2 hours straight. It can be quite stressful to focus on a computer for long periods, not to mention the occasional distraction from kids or four-legged friends. Not to mention checking emails and messages at every opportunity.Experts agree that the longer we’re in this remote working from home environment, the better we will adapt. So let us speed up that adaptation and show you how to overcome these challenges by conducting a productive remote workshop of your very own, using the right virtual tools for your team.How to Conduct a Remote Workshop? Conduct a Remote WorkshopOur workshop process can be broken down into four stages – Planning for a workshop, Preparing for a workshop, Running a workshop, and After a workshop.Below is a checklist we follow to ensure we have a successful workshop with productive and actionable outcomes:A table of checklist showing the stages, tasks, and tools, for running a remote workshop. for further information read the content below* The selection of communication tools is depending on the number of screens you use in the workshop. See details in the “Running Remote Workshop” section.Now let us walk you through the process step by step:Planning for a workshop: Typically, we will receive a notification from a member of our sales team or client, requesting a collaborative session to solve a particular issue or problem. We treat them as the owners of the workshop, and they serve as our go-to person for any clarification regarding the topic, desired outcome, or essential participants. The workshop plan must be signed off by the owner.Planning for a workshopIt’s necessary to know who you are speaking to in a workshop. You need to have a fair amount of knowledge about your participants, decision-makers, and their roles in their business. You also need a comprehensive understanding of the workshop’s purpose to plan out relevant activities. Ask the owner for a short description of the goals, expected outcomes and success criteria, and any specific requirements about the workshop.To help with the planning we created a workshop brief, based on the NN Group template. The best practice is to book a 1-hour call with the workshop owner on his/her calendar and dedicate time to this task. We encourage you to craft the brief with the owner to align on the meeting intention and expected outcomes. Alternatively, it’s also acceptable if the owner prefers to work on his/her own, and come back to you for a consensus.Preparing for a workshop: The number of participants is what you need to confirm with the workshop owner at this stage. This can have a significant impact on the types of activities you can plan, keeping in mind that smaller numbers work better for remote workshops.Preparing for a workshopThe next step is to select which video conferencing tool you will use. Ensure that it adheres to corporate IT policies and/or any restrictions of team members, in the event of cross-company collaboration.Like a physical workshop, use a spreadsheet to outline the activities. We usually use a Google Sheets template. Your plan should cover these fields – Step, Section, Duration, Group/Individual, Activity, and Details. As opposed to a physical workshop, we don’t need the Prop/Materials column.physical workshop rolesThe real fun begins when you finally get to open the virtual whiteboard to create visual frameworks for the activities you just planned out. If this is the first remote workshop for most of your participants, we highly recommend you to create an onboarding activity with instructions and tool tips. Send it out to your participants 3 days ahead of the scheduled workshop and ask them to practice and get familiar with the tool.onboarding activityThis will save you not only onboarding time, but you also get to test out the access from your participants’ side and troubleshoot before the actual workshop.If this pre-workshop onboarding activity is not possible, we highly recommend budgeting time for an ice-breaker onboarding activity at the start of the workshop. Mural has several templates you can use.Now that your activities are planned out, and everything looks great, we’d recommend booking another hour to walk the workshop owner through your plan. This is to cross-check if your workshop design is aligned with the objectives the owner had in mind. Don’t be afraid to be questioned: build trust by listening to his/her point of view, and explain your thought process behind designing it.Your final workshop agenda must be signed off by the owner before the workshop.Last but not least, we suggest you send out a welcome email to all participants, in which you introduce yourself as the facilitator and possibly your co-facilitator, explain the purpose and agenda of the session. You can also include the onboarding activity link you created for your remote tool and the workshop brief(preferably with the signature of the workshop owner).Running a workshop: It’s workshop day! Jump on the video call 10 minutes early, so you have sufficient time to set things up and to greet participants who come early.Running a workshopThe first thing is to share the virtual whiteboard link with all participants. We usually copy-paste the link into the chat window, ask everyone to open up the link in another tab, keep the window handy, and then return to the call window.Talk as clear as you can and try to look at the webcam while talking. This helps establish eye contact with your participants to feel like they are talking face to face with you. This makes you look more professional, sound confident, and appear well-prepared.Stay in the video conference view for a couple of minutes at the beginning of the workshop. This allows the participants to see each other and have some quick huddles while waiting for others to join the bridge. Start talking warmly with your participants, and ask if they had a chance to go through the brief. You can reduce the time spent on explaining the workshop purpose and goal if you find that most of your participants have read the brief and are clear about the objectives.The opening should not go beyond 5 minutes. Introduce the rules of the workshop, such as following the facilitator’s instructions, respecting timelines, and not judging others. Remote workshops must avoid free talk or call outs, as we all know what it sounds like when more than two people are talking at the same time. Guide the participants on how to signal you when they feel the need for a conversation.In our workshop rules, we have a sub-section named Best Practice for Digital Sticky Notes, which is slightly different from sticky notes requirements in real life. For instance, we don’t need all-cap writings to be more recognizable in a digital format. We encourage the participants to type in more detailed inputs, rather than being overly-generic (see the example below).workshop rulesYou’re all set! Now it’s time to invite the participants to move to the virtual workspace window and start the activities. You should advise your participants to have both video calls, and workspace windows opened at the same time, so you get to see each other while working on the whiteboard. Our experience for single-screen users is to use 1/4 of the left side for video call view and the rest for the workspace on the right (see the example below). Interchange the two windows if you are left-handed.remote meetingsWe recommend an upgraded setup for facilitators who practice remote workshops more regularly. It’s a dual-screen arrangement that you can also recommend to the participants who have a spare monitor at home. An extra screen could provide relief to overloaded browser windows and help you observe the participants and comprehend their signals in time.A second screen is also helpful when you need to communicate with your co-facilitator on some quick fixes on the plan but don’t want the participants to be aware. If you are not using a separate screen, set up a mobile channel with the co-facilitator on an instant messaging platform. Don’t forget to mute your cellphone or set it to vibration.communicate with your co-facilitatorYou should allow a short break every 1 or 1.5 hours, based on our experience. 5 min break for grabbing a drink or deal with emails, and another 5 min for a quick neck/back/eye exercise, which you will find tons of videos on YouTube.Time flies in remote sessions, trust me. Work closely with the co-facilitator on holding the timeline tightly for each activity, by announcing the time left – by 1 minute, 30 seconds, respectively – and also ask if more time is needed when only 10 seconds left.Always keep an eye on the time left in your workshop. You might end up tweaking the time-spent for several activities, so it is normal if there are still some tasks left with only 10 minutes left. At this point, remind your co-facilitator to speed up on the current activity and wrap it up within 2 minutes. You can spend another 2 minutes explaining that the time left doesn’t allow the rest of the activities and ask the participants whether they want to book another session or complete them individually after the workshop. Let them know the virtual workspace is accessible as long as the participants have the link.The last 5 min will be given to the workshop owner to conclude the key takeaways from the session and the next steps. Wrap up the workshop by appreciating the participants for their valuable inputs and close the session on the video call.After a workshop: Congratulations! You have just completed a remote workshop. Take a quick break, and then schedule a touchpoint with your co-facilitator to go over the findings and share insights while they are fresh. You can organize the insights and cluster results in a report (we usually use Google Slides for this). Don’t forget to export the entire workspace as a PDF file and attach it at the end of the report.Send the report to all participants, along with a post-workshop survey, to collect feedback. These should ideally be sent out within a week to make sure the participants don’t wait too long for the report, and you get quality feedback while they still having a clear impression of the workshop.Take away Today’s reality is that most of us don’t have a choice when it comes to working from home; however, that doesn’t mean we can’t make the most of it. With organizations Square and Twitter announcing that they will permanently allow their employees to work from home, it is likely remote working will stick around and become the new norm. We need to reconsider remote workshops as a regular way of working and this guide has hopefully made you that much more prepared to become early adopters and to best deal with this shift.
Using Virtual Tools To Conduct a Workshop While Working From Home

As a story writerI can write better storiesso that everyone has a better understanding of the productThere are different approaches to writing user stories depending on the project and what best suits it. And no matter what method you choose, the above Who, What, and Why structure will undoubtedly be a part of it – and for a good reason. This hallowed method has proven to help capture the critical details about your user. And the better you can do that, the better off you’ll be.The benefits of writing good user stories are undeniable – better collaboration between the web developer, designer, and stakeholders brings the user closer to the project, shared understanding, and so much more – but how do you achieve them? Or better still, how do you write not only good stories but great ones?You are in luck because here are 5 incredibly useful techniques and tips to consider if you want to elevate your user stories to the best they’ve ever been.1. Stories: Independent Testable Units Independent Testable UnitsStep one of refining user stories is to make them as independent as possible, helping to minimize dependency on a web developer or others during the development and testing phase. To achieve this, continuously break the requirements into tiny separate pieces until they become independent – a method adopted by any successful web development company. But how do you know that the stories on your list are, in fact, self-sufficient and independent? You can check by asking yourself a simple question: can we develop, test, and push it into production without relying on any other stories? If the answer is yes, you’ve had success.As a result of this approach, it’s not uncommon for a web development company to see improvements in the team’s productivity levels. Moreover, small and independent stories are great for supporting continuous integration and continuous delivery, having deliverables at the end of the defined estimated time. Writing a story as a task or covering all use cases of an interactive web page in a single user story won’t be a productive approach for Agile or Kanban Methodology but can prove somewhat useful for the Waterfall model.2. Remember, the User comes first User InterfaceWhile writing user stories, one should only focus on how the user will be interacting with the system. Your thoughts on the process, time, budget, feasibility, or technical limitations should be reserved for another time. Proceeding with given restrictions and conditions will be a decision taken by administrative and technical teams. By bringing a bigger picture from a user perspective to story writing, you will help the web developer, team members and stakeholders understand the requirements better and have a deeper grasp of the user flows. One way that a web developer or other stakeholders in the team can do this is by capturing user needs, points of view, and pain points while interacting with the application.3. Write your stories collaboratively Web Development CoordinationUndoubtedly, one of the most productive (and most enjoyable) practices of story writing, as any web developer would tell you, is to do so collaboratively. Converting requirements to user stories and defining every possible use case is a task that requires a plentiful amount of brainstorming. And considering all the perspectives of application usage must be an essential part of that brainstorming session. Collaborating and getting different points of view contributing to a common goal can help bring up many use cases that would have gone unexplored by just one person. A successful web development company is one that focuses on collaborative efforts, because they yield positive results in the latter stages of the project when each member involved has a better understanding of the requirements and can contribute much more efficiently towards their part of the project.4. Follow the 3 S’s – Simple, Straightforward, and Self-explanatory Behavior Driven Development“If your story makes complete sense to a layman, you are on a good path of story writing.”The simpler and easier it is to understand a user story, the more value it can bring to the person reading it. To do this, a web developer should write stories in the most straightforward way that will provide a clear user entry and exit point. Incorporating the 3 S’s rule helps you avoid tiresome back and forth requirement clarification within your team. Having your user stories more understandable and with a focus on achieving the desired function will help your teams avoid misinterpretation and degrees of reshaping.One common approach to story writing, Behavior Driven Development, works primarily around the 3 S’s rule and a mixture of a few others. This methodology focuses on ways to minimize gaps and supports the most straightforward and simplified method for story writing.Take the following user story as an example, which focuses on the end user’s goal and has a precise entry and exit strategy.Feature: Search Images on Google Images Scenario: Search for entered query, Given user has landed on Google Images, When user inputs a query to search, And clicks search, Then results matching the entered query should be displayed 5. Refine until nearly perfectAny web development company or expert will tell you that defining user stories and acceptance criteria until they are nearly perfect is paramount to success. Acceptance criteria are an essential part of the story and must be reflective of the client’s expectations. In addition to having all functionalities listed, an ideal case would be one with little or no ambiguity and no partial success or failure statements. It should have just one of two results – success or failure.Another aspect of proper acceptance criteria is how quickly it can be verified. Verifying more functionality in a short duration of time will invariably help the testers, web developer, and clients crosscheck features more efficiently. Add in another round of quick collaboration with team members that can act as a final polish and you’ll be putting the finishing touches to your user story in no time, as any successful web development company would.And there you have it – 5 tips and techniques to help any web developer on the way to writing the best stories yet. And once you get in the habit of writing better stories, it won’t be long until that effort translates into a value that is passed on to the user – every time.
5 Techniques for Writing Better User Stories

You have likely heard of GraphQL but may not be quite sure how and if it’s different from REST. Well, you’re in luck! Today, we are going to go through some essentials on how GraphQL is benefiting the developing community over REST.A Look at GraphQL Most people think that GraphQL a database technology, but this isn’t accurate. GraphQL is a query language API, and as many of you likely know, most of the applications today have their data hosted on a remote server in a database. The API only has to give an interface to put-away information that meets application requirements.GraphQL is an alternate option to build APIs in REST. Facebook developed it as an internal technology for their versatile applications, and later, publicly released it as open-source. Since then, the software development community has utilized it as one of the favourite technology stacks for developing web services.As a query language, GraphQL defines specifications of how a client application can request the needed data from a remote server. As a result, the server application returns a response to the requested client query. The exciting thing to notice here is that the client application can also query exactly what it needs, without relying on the server-side application to define a query.Let’s dive deeper and analyze the core differences between REST and GraphQL.GraphQL architecture is client-driven and Rest is server-driven. GraphQL organized in terms of schema and type system and Rest is endpoints. GraphQL operations are Query mutation subscription and Rest are create, read, update, delete. GraphQL data fetching specific data with a single API call and Rest fixed data with multiple API calls. GraphQL community is growing and Rest are Large. GraphQL performance is fast and Rest are multiple network calls take up more time. GraphQL development speed is rapid and Rest are slower. GraphQL learning curve is difficult and Rest are moderate. GraphQL self-documenting exist and Rest are not. GraphQL file uploading not-exist and Rest are exist. GraphQL web caching exists via libraries built on top and Rest are exists. GraphQL stability are less error prone, automatic validation and type checking and Rest are better choice for complex queries. GraphQL use cases are multiple microservices, mobile apps and Rest are simple apps, resource-driven apps. Fetching Remote Data Assume that a mobile or web app wants to access data from a server that displays the blog author information. The app is supposed to display the author’s name, the blog posts written by the author, and the three most recent blog topics written by him/her. Let’s give an abstract level review on how to fetch this data in REST vs GraphQL.Here is the pictorial representation of REST vs GraphQL API:REST Request In REST, an API endpoint is called to request the data that the client app needs and the server returns the response based on the requested query. When someone uses REST API, they would first have an endpoint which could be https://www.mobilelive.ca/blog/author/, this endpoint would fetch the author’s information. Now another REST endpoint is needed to access the blog posts https://www.mobilelive.ca/blog/author//posts, and finally, you would need yet another endpoint to get the blog topics https://www.mobilelive.ca/blog/author//topics. Now here, you will notice two issues:Problem 1: Multiple roundtrips with RESTAs you would have noticed, there are multiple roundtrips that one should make while utilizing REST to get the information that a client application needs. One has to add additional endpoints if the information is extended.Problem 2: Over-fetching and Under-fetching Problems with RESTFrequently with REST, one will wind up with unnecessary information at a specific stage. For instance, when calling the blog/author/ endpoint, the client application will get all the information related to the author’s profile. It could even get back other information like date created, date updated, age, and gender. But what the client application required was the only author name. It’s a case of over-fetching in REST. On account of under-getting, one can see here that the call to blog/author/ was not adequate to recover what the client app was searching for. The client app needed to make a separate call to another endpoint blog/author//posts to get the last three posts composed by the author.GraphQL Query Request Now let’s think about what happens in GraphQL. You think of a query to request what you need, and you get back precisely the data you asked for. There are no full circle trips to remote servers to bring information to GraphQL.We only go for the fields that we need from the server to the client app.Look again at the above example, where we were searching for the author’s information through a specific ID, the blog posts written by the author, and the three most recent blog topics. The requested query in GraphQL is organized to get the information precisely.The server will provide a JSON response that has been specifically requested. It has returned the author’s name, the posts composed by them, and the previous three topics created by the author – that’s it. There were no multiple round trips to the server, no over-fetching, and no under-fetching of data. Let’s have a quick look at the graphical representation of the differences between the two.Quick Product Development on the Frontend During the consumption of REST APIs, frontend development groups have to wait a certain amount of time for the backend group to finish writing these APIs for the client app to fetch and post the data. Often the frontend team is the ones who become the victim for this slowness in the development lifecycle because their hands are tied until the backend developers finish developing the REST APIs. The overall development process is solely reliant on the REST API development and delivery time. The GraphQL lifecycle provides a very different and more efficient approach where both frontend and backend developers can work in parallel without obstructing the overall development process.Is GraphQL an Underrated Query Language? If someone is new to GraphQL, it will be challenging for them to set it up as its ecosystem and processes are still advancing and maturing. But once one has a good understanding of GraphQL, they can send simple string queries from the client application to fetch data from remote server-side applications to do the required job. On top of that, libraries such as Apollo, give ease to caching and API development. It handles the scenarios about caching on its own, without a need for custom code to enable it. On the other hand, file or image uploading in GraphQL is still not tremendously evolved, and one needs a REST API to better perform this job.Takeaway Both GraphQL and REST API development lifecycle approaches are useful depending on the need, and both have their advantages and disadvantages. GraphQL is exponentially gaining popularity, mainly because of its “no over and under-fetching” ability. It provides more efficient collaboration mechanisms for the client-side and is proving to be a great and powerful tool, especially as the software industry is adopting an agile framework. In short, GraphQL is a tool to achieve specific query oriented goals; however, it’s not a solution for all the API related challenges and certainly not a replacement for REST.
GraphQL vs. REST: What You Didn’t Know

In essence, Behaviour Driven Development (BDD) improves communication between the project stakeholders to avoid missing requirements, having more bugs, delaying timelines, and failing the product. Much has been written around BDD methodology, but in this blog, I’m going to share how it makes life easier for each stakeholder.How BDD makes the job easier for Product Owners: i'm the product ownerAs a Product Owner, you’ll be responsible for the overall success of the product, and you would want to think in every possible way a user would think to make sure all edge cases are covered. BDD will help you in merely writing out those edge cases or any potential cases in the form of scenarios in plain English text. This feature of BDD will help in higher collaboration from the team towards the product as every member of the team would have a better understanding of the product. Also, product owners are the ones who have proper clarity on exact needs. They can have multiple scenarios listed to make sure everyone in the team does not deviate from the original requirements path.Moreover, BDD feature files will act as executable documentation of the product, which will have an automation set up between feature files and test scenarios. Therefore, any minor or significant change request in a feature has to go through test scenarios that would fail unless a code is changed. This automation will help to maintain a sync up between requirements and development.How BDD increases the efficiency of Designers: i'm the designer “Usually, the software is designed and built without giving much consideration about its usage and support ecosystem.”As a Designer, you want to build the best mock-ups for any organization you work in. BDD will help by providing a user-centered design approach where every single bit of deliverable functionality focuses on the intentions and patterns of the user. Collaboration with the team and getting to know each possible variation would help you to have UX designs ready, considering all aspects of the user journey. Moreover, having such clarity at the beginning of the project can help you evolve your design thinking to new levels. Designers and developers must consider the needs of the user; it is one of the most critical concepts in BDD and is the key to user-centered design. By analyzing the behaviours of users that will use the system, we continuously explore various options to choose an alternative that would best meet the needs. In doing so, the process of design thinking and implementation will continue to evolve and get better at every stage of the software development cycle.How BDD is a game-changer for Developers: i'm the developerAs a Developer, you want to have a clear set of requirements so you can confidently build what business has asked. You don’t want to go out to business professionals now and then to get clarity on needs when you have it already covered in multiple scenarios under feature files and that too in Plain English. It cannot get any better than this! There are tools available for testing, which are just a wrapper over the existing testing libraries (namely jest-cucumber for Javascript). So adopting the BDD approach won’t let you stay limited only to feature files but also leverage testing and that too, making sure each part of the requirement has a corresponding test case against it. Features written in plain language can be easily automated.To start with, feed an example to an automation tool (such as Cucumber or Spec Flow), which will result in the automated specification. Developers can use the result to do the application development. Moreover, BDD involves collaborating with stakeholders and other members of the team, which will help you gain confidence in the product you are going to build.How BDD decreases the gap between Testers and other Stakeholders: i'm the testerAs a Tester, you want to successfully run acceptance testing and make sure software works as intended by the business. Another advantage of BDD is it favours system testability. The original concept behind BDD is driving the product based on behaviour, which makes it vital to have a check that things don’t go south. Unlike TDD, BDD focuses more on testing products as a whole instead of testing small parts of the code. Making sure a person gets from point A to point B is what BDD is concerned about, giving little or no importance to the path taken. Tools like Gherkin offer flexibility to implement a connection layer between the test specification and system, which is a part of automated test steps. Also, during the collaborative phase, Testers can pair with developers and designers to have a better understanding of features to be tested.A practical BDD use case: Product Owner to Developerproduct owner to developer. “Here is a new feature we just thought of. I have updated the feature story with this scenario on Jira. Can you please process this request and push required code changes?BDD Approach.Developer makes needed code changes and pastes the Feature File from Jira onto the codebase. BDD will force the developer to write test cases for the newly added scenario, i.e. behaviour testing has to be done. All’s well that ends well.Traditional Approach.Developer does a fantastic job by making required changes, and pushes the updated code and new updated tests onto the environment. Uh Oh! We Forgot Behaviour Testing!. A newly added scenario had a corresponding unit test, which made sure code was working fine, but behavioural testing was not done. Let’s adopt BDD next time.The above diagram showcases benefits BDD can provide as compared to the Traditional Software development approach in terms of scalability and maintainability. Making sure newly added scenarios don’t disrupt behavioural implementation is what smooths the process for releasing change requests and is well covered by adopting BDD. An extra step towards writing multiple scripts and any possible cases using BDD will pay off soon by making it easy for the product to manage and scale. Also, a proper implementation of BDD will secure behavioural testing of the product, which is most likely to result in other approaches becoming available.
How BDD is making Product Design & Product Development easier

“Any application that can be written in JavaScript, will eventually be written in JavaScript.” – Atwood’s Lawately, JavaScript is becoming one of the most powerful languages because of its performance and universal acceptance. According to the latest survey, JavaScript remains the most popular programming language for more than half of all developers. The main reason is that it’s a light-weighted programming language that can easily be integrated with other frameworks/languages. Moreover, open-source JavaScript has played a significant role in digital transformation by creating interactive web pages using frontend development frameworks. Another key feature is that all the top web browsers, including Google Chrome, Internet Explorer, Firefox, Edge, Safari, and Opera, all support JavaScript.On the other side, most startups use JavaScript to develop backend services with the help of the Node.js framework.programming languages popularityA Huge Leap in Backend Technologies The use of Node.js is poised to continue to grow over the next several years. To be clear – it will not supplant all core backend technologies as many large firm backends are composed of multiple technologies and not just a single one.The primary reason is quite simple – application development in JavaScript on the frontend and backend are generally considered to be more cost-effective to build and easier to maintain. If one is exceptionally proficient in JavaScript, which already accounts for many components of the web, using it on the backend allows them to make changes more quickly. Companies like eBay, NASA, Uber, Walmart, Netflix, and LinkedIn have all spoken openly about moving towards or making heavy use of Node.js, which confirms the opinion mentioned above.Node.js developmentMachine Learning and Data Analysis through JavaScript Building and training machine-learning models using a web-scripting language might seem ambitious, but in 2020, it is entirely feasible. TensorFlow.js, Google’s open-source library, is helping to make machine learning possible in the browser. It also has the potential to tap into other cutting edge technology spaces such as Data Analysis, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Internet of Things (IoT), where Python still rules the game.Growing in Mobile Development Popularity Hybrid applications are going to become more and more critical in the future.It does not make sense to learn Java or hire Java developer for developing Android apps and to learn Objective-C / Swift to develop IOS applications and learn C# or hire a C# developer to develop Windows 10 phone applications.mobile applications developmentBenefits of Using React Native for Hybrid Application Development It is incredibly cost-effective for companies to use and build multiple platform applications with just a single code base like Ionic or React Native. It will significantly decrease the cost and time the company spends to hire new developers.JavaScript has a Future in Desktop Application Electron is taking over the desktop application space. It is designed as an open-source framework and utilizes web technologies, such as JavaScript at its core, along with HTML and CSS. The main benefit of this framework is to take care of the difficult parts (e.g. automatic updates, crash reporting) so that developers won’t be distracted by unimportant aspects of development. It is compatible with popular operating systems such as Mac, Windows, and Linux. It is compatible with popular operating systems such as Mac, Windows, and Linux, and has been used to build out such famous desktop applications as Slack, WhatsApp, and Pexels.V8: Helping Overcome Performance Problems V8, Google’s open-source JavaScript engine, provides high-performance for JavaScript applications by Just-in-time (JIT) compilation. With the introduction of V8, the many concerns about performance are taken care of for JavaScript-based applications. It optimizes the JavaScript code at the maximum level by converting it into machine code for the CPU to execute.JavaScript Performance Issues Popular Frameworks and Libraries There are many dynamic JavaScript frameworks and libraries that allow you to build highly interactive enterprise-grade applications with ease and efficiency. The popular JavaScript frameworks for frontend are React, Angular, Vue, and Ember, while on the Backend, we have Node, Express, Hapi, and Fastify.Advantages of Frameworks It is more about “What” than “How,” meaning development, on the whole, is moving towards imperative programming, rather than declarative. This trait allows developers to focus on quality application development without worrying about the underlying high performant code.Here are some reasons why one should consider using a JavaScript framework, a JavaScript Developer, or a Javascript Development company for the next app development:Support from a vast community: JavaScript has one of the most mature ecosystems. Its vast community base makes entry easier for those who are new. A JavaScript engine is available to run the code as soon as someone opens the console on any browser. This feature has made the life of a Javascript Developer easy and simple to work with such a complicated programming language, whereas previously, developers had to do everything by themselves. On top, npm and Yarn package systems help in many aspects, such as creating random strings, handling streams, and buffers.Guards against vulnerability: the robust security measures built into top JavaScript frameworks make applications resilient to vulnerable attacks.Quick to market: well-structured patterns and functions allow complex projects to be delivered quickly and efficiently rather than investing time in writing thousands of lines of code.Less development and it’s cost-free: to use open-source frameworks, open-source Javascript empowers developers to create custom solutions quickly.Conclusion To remain competitive, JavaScript requires a strategy to evolve in scripting and native development. First, to capture a more significant piece of the pie in cutting-edge technologies such as Machine Learning, AI, IoT, and Data Analysis by keeping pace with Python. On the other hand, Kotlin is challenging others in the mobile application development space. As such, they require lots of effort to remain and further grow in native app development.Having said this, the community should not become complacent and stop innovating in Frontend and Backend frameworks. Otherwise, there is a high chance that some other framework, like Flutter, would take over.For your Reference and Convenience Standard Governance Body:ECMA-262 TC39 community leads to JavaScript standards.ECMAScript releases every year a new standard of JavaScript. Developers can request to add new features to the language.
How JavaScript is Quickly Becoming the Market Leader

Microservice architecture provides a framework to develop a software system into small independent manageable components to deploy and operate independently.In practice, microservices deal only with the smallest area of the domain as possible, so it does only things that are required to fulfill its specified function in the stack. For example, the first feature for a mortgage firm software system is providing access to loan terms at the time of login. That means it is ideal for moving loan term out into a separate microservice, e.g. “Loan Terms Service.”Besides, when people speak about microservices, they indirectly talk about services that need to communicate remotely with each other. Usually, microservices are deployed on distinct systems, and most often operating in locations far from each other. It is common to create such services to use REST or some form of RPC protocol to communicate over the network. It sounds pretty straightforward to wrap a feature from the whole set of the domain into some REST API and will start communicating with each other over the network seamlessly.So now that you know what microservices are, how about what it isn’t? Here are five myths and misconceptions parading as “truths” that you may come across or hear people say.1. Microservice architecture makes things simple Although microservices can offer advantages over monolith architecture, it does not always simplify the things. While microservices look better than monolith architecture, one has to avoid making claims that it is devoid of complexities. For example, making several HTTPS requests between multiple services, causing a high latency for the client. Microservices are more flexible than monolithic, but there are challenges associated with it. It has its infrastructure, which requires ongoing integration, which requires rational planning to handle the complexity.It is never easy to define the details of a domain, particularly in startups that still fine-tune the governing processes. Sometimes a single feature needs to collect data about other features/functions to do its job correctly. In this process, often transfers the obligation to write data outside its domain. In such scenarios, architects came across the challenges of distributed transactions, such as calling remote services in parallel or series for a given request. Or how to manage the possible errors that might affect the demand? Every distributed transaction needs its method to handle potential failures, which can produce a great deal of work.2. Microservices and Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) are the same Most people confuse SOA with microservices, and they think both architectures are the same. They use both terms interchangeably, but it’s not true. As opposed to monolithic architecture, each service in both microservice architecture and SOA architectures has a specific responsibility. In Microservice architecture, services are deployed and operated independently; therefore, it is easier to deploy a new service on demand and thus scale the application accordingly. Fault tolerance is another area that differentiates the two architectures. Enterprise service bus (ESB) is a single point of failure in SOA. In contrast, it is not the case in microservices; it uses lightweight HTTP protocol or RPC calls to communicate with each other or with the gateway. The whole system will not be affected if any service goes down.Another fundamental difference is, in SOA, all services share the same data storage, unlike in a microservice architecture, each service has its own independent data storage. Every approach has its advantages and disadvantages, e.g. when services use data among them, bring dependency due to tight coupling. Another main difference is microservice architecture is somewhat smaller in size and scope then SOA. SOA can be monolithic or can comprise of multiple microservices.3. Microservices are better for scalability Service packaging and deployment become easy with Docker. It is an excellent way to achieve horizontal scaling efficiently and effectively, but this approach is not limited to microservices. Any monolith application as a whole or its smaller components can be scaled independently by creating logical clusters that handle a particular subset of the traffic.Microservices deliver plenty of benefits, but before going ahead with adapting this architecture, one needs to understand the domain and requirements of the targeted application. Microservices could be the right choice provided one has a solid understanding of the boundaries and the dependencies. However, if you’re not clear what you are trying to achieve using microservices could do more harm than good.4. Microservices are simple for Engineers It seems simple to have smaller teams focused on a subset of a big solution, but it often leads to many other challenges. Thus, minimize the gains one is expecting while adopting this approach. In microservices architecture, testing and debugging of the application is never easy. Developers have to run all the services in their local environment to check a feature or make any change. Moreover, to write a proper set of integrations tests means require an understanding of all the services in the system. It is necessary because a given use case might invoke multiple services for capturing all the possible error cases. That’s the reason it takes extra time, effort, and resources.Finally, it also creates social problems between teams working on the same project. Bugs that span across multiple services, require different teams to work together and synchronize their efforts on fixing things. It can also create a situation where resources become irresponsible and push the issues onto other teams.5. Microservices are for all applications Not all applications in an enterprise environment is a good fit for a microservice architecture. It should be applied based on the systems needs and long term strategies. People think that a microservice architecture fits for all types of applications, which is the biggest misconception.A system should be evaluated carefully before applying microservice architecture to avoid going overboard. If not enough thoughts are given upfront, then there is a high risk of creating complexity, which would be costly at the end. There needs to be a balance in choosing the microservice architecture vs monolithic.So, when should you use Microservices? The most critical and workable approach towards microservices is knowing the domain in which you are operating. Microservices can do more harm than benefit if you have a vague understanding of the domain. Selecting microservice architecture is the best choice when having a firm grip on requirements, system domain, software limitation and dependencies.Workflows are another essential thing; having a good understanding specifically about how workflows contribute to the concept of a distributed transaction is vital. A distributed model can be framed best if you know the paths that each data request can make through the system. On top of that, you need a deep understanding of failure paths and potential causes of breakdown. Once enough knowledge is developed of workflows, then monitoring it comes as next. You may need a lot of data about different parts of your systems at your disposal to analyze the reason behind underperformance and exceptions.Finally, once the organization has a robust engineering governance process and demonstrated the value proposition, then think of implementing microservices, helping to grow and scale the applications. The bottom line is that avoid trying new things without gaining insight. Otherwise, organizations will be struggling to stay in business and forget about growth.
5 Misconceptions about Microservices
The word “innovation” is synonymous with advances in technology. However, at its core, innovation boils down to the ability to adapt and discover new opportunities that enable new ways of working, building competitive advantages, and improving people’s lives.For startups, disrupting hallowed industries and transforming entrenched business models is the culture that helps them innovate and act differently from the rest. Realizing the importance of quickly responding to rapidly changing market dynamics; larger, more well-established businesses are embracing the startup mindset and a culture of continuous innovation.In this article, I’m going to share what I’ve learned about designing and nurturing Innovation as a Culture.Designing an Innovation Culture What does innovation mean in the context of your business? Is it about new products and customers’ experience? Processes and speed-to-market? Excelling at the existing business or radically transforming into new business lines and models? Establishing this should be your starting point. From here, you can begin to evaluate your culture and what’s needed to achieve the desired results.Whether you are looking to optimize your current culture or lay the foundation for a new one, I’ve found the Design Thinking methodology extremely effective. Design Thinking helps in assessing and determining what barriers are preventing innovation, identifying what enablers are needed to bring your teams to their future state, and what accelerators need to be introduced to enhance efficiency.An abstract image, a person is looking at the light bulb and the light bulb symbolizes the culture of InnovationSeveral creative techniques of Design Thinking come into play to achieve all this, but then, that’s another article for another day. For now, let’s focus on the toughest part; getting started and keeping the culture alive and thriving.Keeping it innovative is easier said than done First and foremost, the innovation process must balance accountability and creativity for your people. End of the day, it has to be guided by the organization’s objectives, key focus areas, core capabilities, and commitments to stakeholders, while not choking creative thinkers with restrictive budgets and deadlines. You must remove the fear and create trust; otherwise, you will kill the ideas that fuel innovation before they ever get off the ground.It’s much easier said than done, so here’s my pick of four best practices that will keep your culture (and innovation) on track.Find the best and quickly: A culture of innovation cannot exist without its fundamental component – people. The race is on to hire those with varied skillsets, able to lend themselves to a variety of projects. To source, attract, and retain this new breed of talent, you need to augment your approach. From hiring and interview techniques to where you find them, you must embrace unorthodox methods. You are looking for people who won’t just lend a hand, instead, who WANT to solve problems. I’d even suggest forming a team with diverse backgrounds and interests so that you have a healthy balance to challenge one another.Create an innovation playground: The difference between creativity and innovation can be summed up in one word – focus. In leading the charge of creating a culture of innovation, you must provide a safe place for ideas to be unleashed; however, that space must exist within the borders of organizational objectives. Think of it as a fenced-in playground. One where team members can let their creativity run free, all the while being kept in check by the confines and parameters of the business – hence, the focus. Too rigid an emphasis on things like budget and deadlines will only serve to hinder innovation – extinguishing the creative spark before it has a chance to shine. Once teams understand and trust the realm they can operate in – one rich in the freedom to pursue new ideas while still being accountable for practical and profitable development – you’ve begun fostering an innovation culture.Stepping stones, not roadblocks: To further reinforce your innovation culture and maximize the output of your “playground,” it is essential to breakdown the hierarchal barriers. The goal is to provide your innovation with stepping stones, not roadblocks. Creativity rarely leads to innovation when it’s bottlenecked, and innovation can’t take flight when it has to find an opening in three executives’ schedules just to get the green light. To counter this, you need to allow for ideas to not only flow freely but have the required resources, time, and support when they happen and begin to take shape, not when you have an opening in your schedule.image shows people pushing large objectsPush the boundaries of what’s possible: The practice of brainstorming is not new. It’s an opportunity where employees are encouraged to share their thoughts under the umbrella that no idea brought to the table is a bad one. But those ideas are, for the most part, reasonable and fall under the realm of possibility. But what about the seemingly impossible? Because it is only when people dare to do what has never been done before that true innovation takes shape. If it wasn’t for people pursuing what was once deemed as unreasonable, we’d all still be riding the horse and buggy around. The unreasonable and impossible are just that – until they aren’t.Getting started is the hardest part The reality is, everything’s changing at an accelerated rate. Uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity are the new norms of this modern world. To combat this, we need to remain creative, agile, and be able to embrace a state of constant innovation.It’s best to start small, pick your focus, create an optimal cross-functional team around the mission, and let them experiment. This approach ensures ownership, collaboration, and provides opportunities for course-correction through continuous evaluation of the results of lean change experiments. Keep the best practices in play; eventually, you will create bigger and better disruptions.
How to Design, Nurture, and Maintain Innovation as A Culture

When asked what I do, I usually have an answer queued up and ready to go: I develop and design digital products, services, and experiences for our clients that are rooted in a deep understanding of the user and business goals. Next, they follow up with, “what does it take to design an experience?” and that’s where it gets interesting.Today, I’m going to take you through mobileLIVE’s design process, one which has evolved through many trials and several iterations. In it are best practices for different design workflows and it’s proven flexible enough to support software projects across any industry.Our Design Process Phase 1 – Discovery Discovery phase of UX design processWe start with the understanding of users, their context, and challenges. For enterprises, it’s equally important to understand the stakeholders and business processes. It’s essential to understand the lay of the land – how is the experience delivered to the end-users? What are the roles that each stakeholder plays in delivering the experience?Stakeholder Discovery Stakeholder Discovery is always the first step. In this phase, it is essential to align the entire project team around goals for the project. The biggest goal of a UX Strategist at this phase is to give each stakeholder a chance to communicate their needs and wishes.The UX Strategist plays a key role in translating the information from stakeholders to the design team and frame it in the context of customers’ goals.Team Roles: Business, UX Strategists, Developers and MarketingData Data tells about customer behaviours – what are they doing? Where is the experience falling short? Which areas need most attention? Where do we see the most friction? But getting these answers isn’t easy! Bringing cross-functional team members together is a must to transform the messy and unstructured data into actionable insights, and facilitate and enhance its analysis.Insights are also collected through competition research, expert evaluations and UX tear-downs.Team Roles: Business, UX Strategists, Developers and AnalyticsUser Research Research at this phase allows the team to ensure everyone is tackling the right problem. Sometimes, the business assumes that the information they provided is enough for the Design team. In our experience, this is rarely the case.Data analysis helps us focus the user-research on the right problems; however, for new products or services, existing data may not be sufficient, and UX strategists must work with product managers to understand the context. Sometimes quick tests, surveys also help collect information or validate assumptions.The designers involved at this stage must be able to drive the conversation towards understanding the end customer. That’s the reason that User Research is an essential ingredient of the Discovery Phase, so the whole team will share a defined problem and be better equipped to work on the solution in the next steps.Team Roles: Product Manager, Business, UX Strategists and ResearchersPhase 2 – Define Define phase of UX Design ProcessDefine is the next phase in the UX process, where we analyze all the information gathered to establish a clear view of the problem, with an opportunity to redefine the problem we are solving.Understand the user In the Define stage, the team will synthesize observations about the user gathered from the previous phase. We dig deeper to understand the users by creating user personas, journey maps, and different use-cases. These activities help us develop new hypotheses to test, uncover hidden problems, learn from our previous experience as well as that of others in adjacent problem spaces in the industry.Team Roles: Business, UX Strategists, Interaction Designer, Researchers and UX WriterRedefine the problem Synthesizing is the right action at this point – piecing the puzzle together to form whole ideas. The team should be organizing and interpreting the data gathered to create an accurate and encompassing problem statement.Another essential part of this process is storytelling through visual and mixed media formats. Explaining complex ideas and vague concepts through storytelling helps bring everyone on the same page.Team Roles: Business, UX Strategist, UX Writer and DevelopersPhase 3 – Ideate Ideate Phase of the UX design processOnce you have clearly defined what problem you are trying to solve and have ample background knowledge, the time has come to get creative. In this phase, the intent is to challenge assumptions and create solutions to the problem at hand.Workshops User experience is all about finding creative solutions to real-world problems. Although it may sound simple, good ideas don’t just happen. It’s part of the process to actively facilitate innovation.Creating an environment where the team will be able to generate a broad set of ideas, with no judgement or evaluation, is the aim. In simple terms, a design workshop is a dedicated session for coming up with new ideas. The main goal is sparking innovation by bringing people from diverse backgrounds. Inviting business, design, and technology teams in these workshops ensure that our ideas solve the right problems and are implementableTeam Roles: Business, Product Manager, Solution Architects, UX Strategists, UX Writer and Interaction DesignerCreation Different concepts and solutions explored in workshops and other activities in the define phase are documented. All stakeholders must understand all the concepts that are being generated and all the artifacts that are crafted.Team Roles: Business, Interaction Designer, Information Architect, Creative Director, UI Designer and UX WriterEvaluate All design explorations and explorations are reviewed with stakeholders. Alignment in all the actions is fundamental for the success of any product or service.Team Roles: Business and UX StrategistsPhase 4 – Prototype Prototype for UX Design Process“A prototype is worth a thousand meetings”Prototyping is the most exciting phase of the design process. The goal is to make the shortlisted ideas and solutions tangible. The main objective of prototyping is to build and test your ideas, embracing mistakes quickly to reach success faster.Paper Prototype Looking for insights but working on a tight budget? You’ll be hard-pressed to find a better method than paper prototypes. Producing an early and scaled-down version of the product will help you reveal any problems with the current design.A low-fidelity prototype, although incomplete, will utilize some of the features that will be available in the final product, thus providing good insight.Team Roles: UX Strategist, Researchers, Interaction Designer and Creative DirectorWireframe When looking at wireframes, we are essentially talking about the “skeleton” and flows of your user experience design. Centred on structure, the wireframes help you to focus more on functionality and less on the details – especially visual. Wireframes show you ‘how will the experience roughly work.’Team Roles: UX Strategists, Researchers, Creative Director, UI Designer and Interaction DesignerHigh-Fidelity As we work our way up the levels of fidelity, we evolve the functional wireframes with visual elements and components. A high-fidelity prototype is usually clickable, therefore more compelling and engaging for everyone involved, clearly showing the interactions.Team Roles: UX Strategists, Researchers, Creative Director, UI Designer, Interaction Designer, Animators, Brand Designer and UX WriterEvaluate Before taking any further steps, we highly recommend that all the material documented is brought back to the stakeholders to be discussed and evaluated. An open conversation will be able to cut down on discrepancies and realign all teams involved in the same direction.Team Roles: UX Strategists, Developers, QA and AccessibilityPhase 5 – Evaluate Evaluate your UX Design ProcessBy this phase, you should have the makings for a relatively complete product, one that is a solution to the previously defined problem. But how do you know it works? You don’t – until you test it.Usability tests At this point, you should have your final designs (or at least what you and your team considered to be the final one) and ready for testing them in the real world. We recommend a full user test cycle as soon as possible to mitigate the impact of a total crash.The primary purpose of usability testing is to identify usability problems within the design so they can be fixed before going live.It should be noted that usability testing is an iterative process. It is only through repetition that you’ll be able to map the issues, understand what works, and improve the design.A test report should be created every time you perform usability testing. This way, you’ll be able to keep the documentation updated and stored.Team Roles: Business, UX Strategists, Researchers, Analytics and DevelopersSynthesis After the analysis process is done, it is time to create a coherent summary of all the data gathered so far. This will help the understanding of what worked and what needs to be improved.Team Roles: Business, UX Strategists, Researchers, Analytics and DevelopersWhile most processes have a clearly defined beginning and end, when it comes to design for experiences, the process is truly ongoing. If innovation is your mandate, then ideas need to be continuously discussed, evaluated, improved, and evolved.I hope this framework serves you well and acts as a guiding light to you and your teams. With it, not only will you engage the right resources throughout the process, but improve on communication, all while discovering that good experiences, like any product, can be crafted – you just need to know how.
How To Avoid a Lousy User Experience Through Your Design Process

Banks have always taken a customer-centric approach to how they operate – an approach, that for the last 30 years has become more and more fueled by technology.From ATMs that allowed customers to avoid lineups for simple transactions to the internet that brought banking home, and the smartphone that brought banking anywhere – we have seen a constant trend of the customer being empowered to do more.The industry, on the whole, is collectively focused on the future and what will best serve the customer. However, I’d argue that you need only take a look around at present and see what some of the more forward-thinking financial institutions are already doing to get inspiration on what your customers will not only want but soon demand.The technologies that enable transformation – and superior customer experiences – have never been more readily available, viable, or robust. Today, I’ll take you through what will soon be the industry standard as we visit what the digital banks are doing to ensure customer expectations are surpassed on their path to maturity.Omni Channel User Experience What was once a nice-to-have has quickly become essential in the age of customer convenience. No matter the device, be it a smart TV, tablet, phone, watch, car, or desktop, customers want to be able to bank when and where they want to. While technology has made this increasingly more feasible, it has also created new challenges like maintaining UX and the user journey across these channels. Digital banks are keeping this user experience simple, engaging, continuous, and omni channel.User Experience It is impossible to talk customer-centricity without touching on user experience. And UX, more specifically, seamless and pleasant UX has become the expectation for customers going forward. Unfortunately, this is not without its challenges. Banks cater to diverse customer segments, each with their own needs and wants. This requires nuanced worked; however, through intuitive and conversational design, banks are simplifying the journey while keeping customers engaged.Cardless Banking person holding a mobile and tapping on the ATM machine to withdraw cash, image shows Cardless BankingThere was a time when nobody thought we’d see a shift to a cashless world, and yet, here we are. And today, we are on the dawn of another shift, one towards cardless banking, and this shift is one that nobody is doubting. The natural evolution of the ATM; many forward-thinking banks are offering the same experience but without the physical card. Instead, a simple scan of a QR code or a tap of a phone or other smart device is all that is required to withdraw cash without the use of debit or credit cards.P2P Payments Person to person payments or P2P is one area of FinTech that is booming and shows no signs of letting up. These payments allow the transfer of funds between two parties utilizing their individual bank accounts or credit cards through an online platform or mobile app. Used for a multitude of things, from splitting a $27 lunch bill between friends to paying rent, P2P payments are adding value and keeping the customers engaged.AI & Analytics Banks possess one of the most potent advantages in business – data. In fact, banks sit on vast pools of customer data; data that can be used to better understand customers and manage their experience. Utilizing AI and advanced analytics, banks are leveraging the data they already possess and use it to proactively showcase the right products to the right customers, not only saving vast sums on marketing dollars but upselling and cross selling to existing customers through timely and relevant promotions.Internet of Things Imagine checking the balance of your account, simply by asking – while driving down the highway. Or opening the fridge and discovering you’re out of milk, only to place an order for it immediately from the screen on your fridge. When talking about the internet of things, the possibilities are seemingly endless, with 5G network around the corner and the growth of connected devices in cars, homes, appliances, wearables, and more; banks are presented with an ideal opportunity to add a new level of convenience to their customers.Augmented & Virtual Reality image shows a person looking into his mobile device, mobile screen showing the way to his destination using AR, use of augmented reality and virtual reality in bankingAs banks shift their attention to attracting and retaining the next generation of customers, they must begin to utilize the technology that appeals to them most. And for future – and present – generations, that technology is AR and VR. Imagine using augmented reality to guide your customers to the nearest ATM or virtual reality to help showcase investment products and their returns in dazzling, engaging visuals. Paired with mobile devices, AR and VR technology is empowering customers in ways never before possible and soon a reality with 5G network.Chatbots Chatbots are already commonplace in many industries, including BFSI; however, the technology that powers them is continuously evolving, and their capabilities are growing to new and exciting levels. AI and NLP based tools are empowering customers to transfer funds, check their balances, pay their bills, find the best credit card rate or apply for a mortgage; all with an air of ease like never before.Open Banking Open Banking is a practice of using APIs that allow third-party developers to build applications and services around a financial institution; like a bank, and the financial data of its customers. This has the potential to open the doors to countless new products, services, tools and partnerships that were once thought a regulatory impossibility. The implementation of PSD2 in Europe has already signaled that the market is ready to adopt open banking and FinTech is leveraging it, leaving North America to decide if they are willing to act quickly to keep their customers engaged and ensure their banking needs are met, not only today but for years to come.Few could argue that banks are already investing heavily in technology; however, what is critical not to overlook is why they are doing it in the first place. Technology is excellent, but not for technology’s sake. Instead of imagining what you could do, begin assessing and investing in what you must do, and it starts by putting the customer and their expectations first.Today’s customers may even switch banks based on their digital experience. The need to focus on the whole customer journey rather than selling a single banking product or service is imperative. Speed and efficiency are important to customers and so is their comfort level in engaging with a digital bank. They must believe that their needs and preferences are met and that there is a level of personalization tailored to their day to day banking needs. The technologies that will power the customer experience for years to come are here, and they are only waiting for you to take advantage of them.
How Digital Banks Create an Omni Channel User Experience

Ready to launch a new product? A new app perhaps? Do you know if there is a need for it in the market?In this day and age, it has become extremely easy to take an idea and invest in getting it developed. But then, not every idea is a good idea. You need validation before money and time are invested, and that’s where an MVP comes in.You’ve probably heard the term in almost every national sport but the MVP I want to discuss is a bit more important to your business. So, what is an MVP? Simply put, MVP (Most Viable Product) is the first version of the product that lets you validate and capture the attention of early adopters with the least amount of time and money invested. The two most important points when planning your MVP are; determining and prioritizing your features for the release.This infographic will help guide your MVP planning phase and what to do after.How to Plan Your MVP Infographic is a step-by-step guide that is your go-to reference point for quickly and effectively determining features on the journey to creating your Minimum Viable Product.
How to Plan Your MVP to Ensure Success in Product Development

Are you happy with how efficiently your operations run? Do you want to become more profitable? Would you like to work on new growth opportunities? If you answered yes, you aren’t alone. In fact, these challenges are felt across the board and “Going Digital” aims to alleviate them. However, like anything worth doing, there is a process involved that can not only help you get there but maximize your Return on Investment.The 3-tiered approach When going digital, my recommended approach is 3-tiered.Intelligent Automationautomation for business digitizationThe first step to Digital Maturity is to bring efficiency and OPEX reduction to your business through automation. You should begin by focusing your efforts on existing business process, including but not limited to supply chain systems, inventory control, and order processing. The goal of automation is to enhance your control over your operations while increasing efficiency through the speed, reliability, and accuracy that only technology can provide.Improved-Decision Makingbusiness intelligenceOnce automation is in place, you may begin to notice something – you have more time. While many executives and business owners would argue that there is no such thing when it comes to operating a business, in reality, you will find yourself able to pivot your focus from the aspects of the daily operations to see more of the “big picture.” The goal of this stage is to empower yourself and your leadership team with a Business Intelligence System that allow better, more informed and timely decisions.Opening New Markets and Opportunitiesnew markets and recognizing opportunities for business digitizationNow that you have empowered your business with Operational Efficiency and Intelligent Decisioning Systems, you should start prioritizing towards new growth opportunities. You should begin exploring new markets and recognizing opportunities, but in tandem, and to enable the aforementioned, it is important to start investing in enabling technologies. This investment is critical to the continued performance of your business and should be inseparable from your strategy moving forward. This can include things like e-commerce platforms, mobile and web apps, and digital marketing activities that allow for local and global expansion.The above paints a beautiful picture; one of a lean, agile, and market-ready organization that is not only efficient but poised for growth. However, there is one critical component that empowers all of it; a facet of digital that is necessary for success and cannot be separated from any successful transformation – Data!In the remaining part of this article, I will expand around the what, why, and how of data management, data storage, and big data framework.The Foundation of Data importance of dataSo why is Data important?Data hides business insights & insights have business value!A bold statement, especially when you consider what insight and how much business value is a matter of details; however, the principle is generally applicable. What this principle doesn’t allude to is where to begin with Data Management, and when talking about data, the only place to start is at the source.Data Sources data sourceIf you want to harness the power of data, first, and arguably most important step is determining and identifying your data sources. And broadly speaking, these can be identified into two categories; internal and external.Internal data refers to the data you already possess (or should) and consists of data collected in such domains as sales, finance, marketing, human resources, supply chain, along with a subset usually classified as CRM data, which contains your customer profiles and their behaviour. However, when talking about data sources, it is always wise to rely on more than one.The other type of valuable data is external data, which can often be just as relevant. External data comes from the market, including customers and competitors, and is usually statistical in nature being derived from questionnaires, research, and consumer feedback.Data Collection Pipes & Big Data Framework Big data framework for business digitizationAfter you have determined what data you are looking for and where it will come from, the next step is determining how you will collect and process it, and this is done through your data pipeline and processing framework.Typically, these frameworks are built around the open-source Hadoop technologies, with a variety of tools available in the ecosystem. If you are looking to utilize data to create a more actionable and valuable business strategy, investment in this is crucial.The Power of Proximity the power of ProximityUtilizing a big data platform is critical, especially if you are working with vast amounts of data; however, one of the other benefits is that you are able to bring all your data to a collective location where it can be holistically processed. This allows you to correlate data from various sources to provide you with a more complete picture.While it is advantageous to bring your data together for collective analysis, it is important to note the value of preserving data in its raw form. Following such practice will add shelf life to your data because by keeping it intact, you are able to safeguard the hidden insights which can be utilized as use cases are identified.Creating Balance With Use Cases use cases for business digitizationWhen an organization embarks on a big data strategy with plans of creating a big data framework, the focus will inevitably be on data collection. However, this approach is often met with hesitation as data collection requires capital expenditure but holds no benefit until the business value is extracted.To combat this and garner internal buy-in, your optimal strategy should include identifying business use cases as organizational data collection occurs. When done, this will not only provide immediate value for your investment but works as a confidence-building measure between business and technology.Machine Learning importance of machine learningKnowing that business value comes from business insights, the question that needs to be addressed next is how to derive those insights from your data. In order to do that, you need machine learning.Machine learning techniques can be applied to big data frameworks in order to extract actionable insights. However, as mentioned in the previous point, the identification of business use cases is the key to identifying which modelling approach will prove most effective. Sadly, there is a wide variety of techniques available, all of which require a thorough understanding and expertise, which brings us to our next point – how do you bridge the skills gap in order to derive and make use of these hidden insights.Bridging the Skills Gap bridging skills gap for business digitizationWhen it comes to big data, machine learning, and implementing and utilizing a data strategy, perhaps the biggest hurdles faced by an organization is found in the scarcity of skilled and experienced professionals. Thus, your data strategy must include an assessment of organizational capacity and filling the gaps accordingly.In order to fill those gaps, an organization is faced with options. The first and most obvious one involves hiring the skilled and experienced individuals you need; however, as we mentioned, you would then be met with such talent in short supply.A second option is a hybrid approach that involves sourcing and attracting skilled professionals as well as identifying potential talent within your organization that can be trained with the skills needed. This approach is appealing because not only does it mitigate the talent supply problem but helps to increase organizational IQ and competency.A final option and one that is growing more and more popular is the outsourcing model, one where you approach an outside vendor to develop, execute, and maintain your data strategy. This option can also be done in tandem with the hybrid approach as there is potential in selecting the right vendor who can not only help you execute your strategy but can help close the skills gap by training your internal teams.Conclusion Technology is now inseparable from business strategy and is a foundational cornerstone of long term success. The need to make better, more informed, actionable and meaningful decisions will not wait; instead, it will continue to grow and dictate just how far organizations can go. The key to that success and what will determine how far your organization can go will be the groundwork you put in now; work that will determine not only how quickly you reach digital maturity, but how digitally mature you can actually become.
The What, Why, and How of Data Management In the Age of Digital

In the previous blog, we covered how to utilize Design Thinking to create your Minimum Viable Product or MVP; however, that is only half of the equation.The reasoning behind creating an MVP is simple but what is exponentially more important is to test and prove your ideas, concepts, and hypothesis before you allocate resources to it. Why? Because it will tell you whether or not you should be following through with your idea in the first place!Here is how resources used to be allocated: “I think that sounds like a great idea for a new feature. Here is your team, budget, and time frame to deliver it.” Sound familiar?And this is how resources should be allocated: “Where’s the proof that this is a good idea to spend time, money, and people on?” Do you see the difference?Building and testing your MVP is a means to make sure you are not wasting valuable resources on a product that doesn’t target a viable market or is not technically feasible. But how do you test and validate your MVP?Here are the best methods for discovering if what you are doing is what you should be doing (even before you do it).Customer Interview customer interview for MVP ValidationThe most common and among the most effective methods to test your MVP is to get feedback and validation from the customers who will use it. This doesn’t need to be an elaborate process, instead, simply hold unscripted interviews with the people for whom the product is intended to bring to light information about the problem they have that your product aims to solve.It’s important to note that these interviews are to be exploratory, not a sales pitch about your product. You want honest answers, so try listing out the problems you believe your product to solve and ask the users what they think of them and rank them in importance.These interviews can provide an abundance of valuable and most of all, actionable information because even if your hypothesis is proven wrong and what you thought mattered to the customer doesn’t, you will have a better insight into your market and can pivot your offering accordingly.A/B Tests A/B test method for MVP validationAnother effective method for validating your MVP is to perform A/B tests. Let’s assume that your new product is a webpage; however, you have two options and find yourself unable to decide which one you like better. First off, you shouldn’t be the one decided; rather, you should enlist the help of those who visit your webpages to determine which one resonates best.The process of running A/B tests is simple, you randomly funnel the visitors to your site to one of two pages (A and B), and then use data gathered through analytics tools to measure the performance of each based on a set of metrics like usage, time on site, bounce rate, conversion and more. When all is said and done, you should know which of the two versions is more desirable and elicits the response you want; or if it is time to go back to the drawing board, except this time, with greater insight, thanks to the A/B tests.Ad Campaigns ad campaigns an effective method for MVP validationAlthough it may seem counterintuitive, running an ad campaign can be an effective method of gaining validation for your MVP. Platforms like Google and Facebook are ideal for these types of tests because they allow you to get ultra-specific about your desired demographic and the particular customers you are trying to reach. As a result, it allows you to run tests to help determine which features or aspects of your product are appealing to the people you want it to be appealing to.It is crucial to keep in mind that at the end of the day, running these campaigns may not give you the optimal exposure you’d hope for a new product, but in terms of testing your hypothesis, it’s priceless.Fundraising (Crowdfunding) crowdfunding and fundraising, KickstarterIf you are familiar with websites like Kickstarter and Indiegogo, then you have already been exposed to this method of MVP validation. Essentially, these websites are just collections of peoples MVPs, whereas the validation and market response comes in the form of peoples interests via contributions to the campaign.One of the greatest appeals of this method is that it combines the advantages of both validated learning and fundraising for product development. So not only are you raising funds (arguably an essential part of new product development) but you also find yourself with a captive audience of highly interested (and invested) early adopters who also have a stake in the success of your product. This a great way to not only receive continuous feedback but can also help spread word-of-mouth.Pre-Order Pages how to validate your MVP with preorder pagesNot unlike Crowdfunding, Pre-Order pages have proven a very effective way to validate your MVP, often, before you even build it.Oculus Rift is a prime example of this method being utilized as they released a pre-order page for their development kit before they even began production of them. This helped them to validate their idea by showing them that demand existed for the product, even before they built it.However, it should be noted that this method is not without its risk. Customers being customers are always, to some degree, wary of the possibility that the product delivered is not the same product that was promised to them. In short – no vaporware.Blogs validate your MVP with blogsA crucial and foundational aspect of MVP validation is an open form of communication between products teams and the market, and few methods of two-way communication have proven as effective in our modern age as the blog.Blogs not only allow you to validate your ideas but will enable you to do so by narrowing down on your target market and gauging their response. This comes with the added benefit of garnering supper from a community of followers; that is, assuming your blog resonates and is received well. But the best part is, even if it doesn’t, you’ll have learned and discovered valuable information that can support your efforts in the next iteration.Although not commonly thought of, a blog itself can serve as an early prototype of a product – and the prime example is a book. Just remember, Eric Ries’ acclaimed and seminal book The Lean Startup started as a blog and built an audience and demand long before a publishing deal was signed.Social-Media & Micro-Surveys utilizing Social-Media and Micro-Surveys for mvp validationOnce you know who you want to target with your MVP, the next step is reaching them. However, if you find yourself at this stage you are already making excellent headway – knowing who your target audience segments are is half the battle, at least, it is when you are utilizing Social-Media and Micro-Surveys.What is the problem with surveys in general? Is it the low response rates, bias, the non-actionable results, or just the overall survey fatigue? In reality, it is all of the above, which makes it so crucial not only what questions you ask but how many.By utilizing Social-Media and Micro-Surveys, you’ll find not only a higher response rate by meeting your audience where they are likely spending their time anyways but by asking only a few, short, poignant questions, you’ll further find your response rate increase. Plus, when you utilize tools like Facebook survey, you can empower your audience to add their own options as answers which can provide some very enlightening feedback.Emailing email communication for MVP validationMost people view email as a means of communication but being that communication is at the core of MVP validation, it only stands to reason that email can serve as a method in its own right.Often referred to as audience building, the premise is simple: Send out an email and track the actions of the recipient using tools and plug-ins. How many users click on the links? How many people respond? While this may seem like basic information, in reality, and as this story demonstrates, it is certainly a fast way to prove that you do, in fact, have an audience.Product Hunt, the popular website that lets its users share and discover the latest products in tech, started as a simple newsletter email. It took the founder, Ryan Hoover, only 20 minutes to prepare and within two weeks had 130 subscribers, many of which turned out to be Silicon Valley influencers. And in case you were wondering Hoover went on to sell his site for an astounding $20 million.Landing Pages landing pages for MVP validationA Landing Page, as I am sure you all know, is the page potential customers go to to find out about your product. However, much more than that, it is a great way to test that product in the real-world market and against actual user expectations.For the most part, landing pages seem to get used as an elaborate email capture page; however, it doesn’t have to be so limited. Rather than using it to build your mailing list, it can be used to measure demand and can even help determine appropriate pricing.By adding an interstitial page between the features and signup form, a page that shows a pricing table (ideal for telecom), you can determine which price is more appealing by analyzing the extra clicks which will help you narrow down on what price is appropriate to the market. This method can be combined with A/B testing to help you further determine which “pitch” works best for conversions.Competitive Products in the Market Validate your MVP using competitive products in the marketWhile I don’t want to be a downer, but the reality is that there is a high likelihood that the product you are looking to launch is already available in the market; or at the very least, a very similar one. Once again, this is not a reason to be discouraged; instead, this is an opportunity to validate your MVP at a substantially lower cost. Why? Because you already have a product to analyze!If your product is similar to another, your first step in validation should be analyzing the already available product to see what they have that your product doesn’t. That is step one, but you shouldn’t stop there. The next logical step is to analyze what your product has that they might be lacking, and then, utilizing some other methods on this list like social-media survey, A/B tests, and more, you can determine how your differentiators resonate with the market. Hopefully, what you’ll discover is that your own products unique features are what the market is looking for; and if not, you have somewhere to pivot towards.Manual-First (aka “Wizard of Oz”) MVP Wizard of Oz,Manual-First approach for MVP validationThe phrase “fake it ’till you make it” is a popular expression amongst startups; however, the same principle can interestingly enough be applied to validating your MVP.The Manual-First approach, also known as Wizard of Oz comes from the idea of giving the users the impression of a fully functioning product or service, but in reality, all the work in the background is being done manually.A prime example of this is the massive e-commerce site Zappos. Nick Swinmurn, the site’s founder, used to put up photos of shoes from local shoe stores on his website to determine the demand for an online store. And when somebody did place an order (keeping in mind this is before any investment or infrastructure was established), he would simply go the store, buy the shoes, and send it to the customer.Concierge MVPs Concierge method for mvps validationIn many ways, the Concierge method is similar to the Manual-first approach, except, rather than faking a working product or service, you’re upfront about the manual work, and even take it one step further by delivering the product as a highly customized service to a select number of customers – thus the name, “Concierge.”A prime example of this method in action was used by a company called Rent the Runway. An online dress rental business, they provided in-person service to their core demographic (female college students) where anyone could try on a dress before renting it. Not only did this successfully spread the word about the business and provide them with valuable feedback, but it validated their most significant uncertainty – would women rent dresses.When you utilize this approach to create Concierge MVPs, instead of pouring time, money, and resources into building a real product, you can find answers to your most important question first – are you creating something that customers will actually pay for.Piecemeal MVPs piecemeal mvps validation methodsA hybrid blend of the Manual-first and Concierge methods of validation, Piecemeal MVPs require building a demo of your product out of the existing tools and platforms at your disposal. This allows you to deliver the experience to your customers without actually having to build anything yourself.One of the best examples of this method in action was with a little site known as Groupon. In its earliest days, Groupon was simply a combination of WordPress, Apple Mail, and an Apple Script that manually generated PDFs as orders came through the website.The distinct advantage to this is the ability to significantly cut down on costs by not investing the time and money required to create your own infrastructure; rather, utilizing existing services and platforms on the market as a foundation – a foundation that will effectively serve to determine whether your product idea is worthy of investment of its own.PaaS & SaaS tools PaaS and SaaS can help build your MVPInvesting in scalable server technology is expensive; especially if there is still uncertainty around whether the product or services that calls for it is worthy of the investment. Knowing this makes reliance on cloud platforms like AWS, Heroku, MongoDB, and Facebook Connect; services like Mixpanel, MailChimp, LiveChat, and Google Forms; and even platforms like WordPress and Drupal that are much more appealing (not to mention economically feasible).Products and services like the ones mentioned can significantly help in your development. To touch on the Groupon example again, when they started as a customized WordPress site where the founders simply posted deals and sent subscribers PDFs manually. As it becomes clear from this example, not only can PaaS and SaaS help to build your MVP, but can, in fact, validate it – much like we see done by Groupon. This method also comes with the added benefit of eliminating many of the issues faced by developers such as compatibility, mobile-friendly design, and code-based issues because these tools have already taken care of these issues.Digital & Paper Prototypes validate your MVP using digital paper prototypeA digital prototype is a great and inexpensive way to validate your MVP. These can be anything from a simple, low-fidelity sketch to screenshot previews; however, it is vital to keep in mind that the objective is to gather feedback, which means that a digital mockup, or “dummy application” should be your end goal to maximize learning.A paper prototype, on the other hand, is similar to its digital counterpart, except these are physical and are usually made out of (you guessed it) paper cutouts that are designed to emulate your product and the experience it gives the user. One of the key advantages of this method over others is that it can be utilized by anyone on the team, from product managers, investors, developers, etc., and require little in ways of explanation as it is a physical representation of the product.Single Feature MVPs single feature mvpHave you ever heard the expression “less is more?” Well, in terms of validating your MVP, this adage may carry more weight than you think.With time and resources coming at a premium, it can often be advantageous to focus on a secular feature of your MVP to save time, money, and effort in development. Not only that but by focusing on a single aspect, you can avoid distracting your users with other elements of the product that are not trying to be validated.By implementing these restrictions on your validation, you can help focus in on your customers and their needs while getting feedback on one feature as opposed to multiple, which can often muddle the process and cause even the most diligent of teams to lose focus.Creating and testing an MVP will invariably take time, resources, and money to do – but it should never be regarded as a waste. After all, what if you end up taking to market a product or service that nobody wants, least of all is willing to pay for?Use several of the testing techniques listed above. Be sure to incorporate different perspectives to elicit your validation, and whatever you do, forget the notion that “if you build it, they will come.” The goal of testing your MVP is not only to minimize the risk but to create something that people want, need, and are willing to pay; in other words, building and testing an MVP is precisely what you want.
16 Techniques to Validate & Improve Your MVP

As the challenges business faces grow in both complexity and impact, so too does the growth in the adoption of Agile to solve those challenges. However, with so much focus on agile’s benefits and value, I’ve noticed that many organizations forget to put the time and effort into a critical first step of this adoption – the formation of an agile team.Today, I will propose a remedy to that and a method to help you get the most out of this critical step towards agile.Challenge Liftoff – A Workshop “Liftoff,” as it is commonly referred to, is among the first steps to transforming to the agile methodology. Essentially, it is a way to ensure that everyone is prepared to work according to agile principles. And depending on the organization and the formation of the team, this step can quickly grow in importance.If team members worked according to the Waterfall methodology, they’d need to adopt the agile mindset. Team members may have been previously working on specific roles like Tech Lead, QA, or so forth, but now entering into an agile team, those titles don’t hold any meaning. The team needs to understand the vision and goal they will be working on to achieve – and, most importantly, how to achieve it.That is where Challenge Liftoff comes in and where I will show you how to design a workshop that achieves the Liftoff Agenda (more on that shortly) through activities that not only give your team purpose but build Alignment and context to achieve business objectives.The Intent Of course, organizations adopt agile to help them meet demand, increase productivity, and reduce time to market, but today, let’s view that desired outcome as the big picture. For Challenge Liftoff, the following is what you’ll want to accomplish:Introduce team members and stakeholders to foster camaraderie Bring the team on the vision, initiative, and planned outcomes to bring Alignment Define roles and responsibilities across the team and communication structure with stakeholders to clarify the organizational hierarchy. Discuss the environment, tools, delivery framework, and feedback loops to understand the supporting structure. Gather assumptions, expectations, and foreseeable risks from the team to consider or mitigate. Now that you understand the intent behind the workshop, it is time to set your agenda.Your Liftoff Agenda Agile methodologyThe purpose of a Liftoff Agenda is to have a common understanding of the reason for the team’s existence, define initial intentions and plans, and begin team building. It doesn’t need to be complicated. Simply use questions that progressively lead the participants closer to reaching the objective at hand.Here’s an example of questions to ask for a relatively common set of participants in this scenario:Participants Product Manager Sponsor Scrum Master Liftoff Facilitator Scrum team Stakeholders Question What will be the best starting point for everyone involved? Have we identified all the right team members? What will the team need to start, and start it well? What skill sets are required, and does the team need upskilling? What support is needed from the stakeholders to be successful? How to bring the team together as one unit? What are the challenges in communication within the team? Will the new information emerge during the Liftoff? How open are the stakeholders to adapt to further information? Achieving the Agenda Now that you’ve got your agenda solidified, you now have to achieve it. To do that, you create Purpose, you build and foster Alignment, and focus in and discuss Context. And in case your next question was, “How do I do that?” Here are some of my favourite activities to choose from.Activities for Purpose Problem-Solving Tree: Brings focus on the specific initiative in hand and define the purpose with collaboration from all based on the initiative.Landscape Diagram: Helps in defining the purpose when solving ambiguous, uncertain, or complex problems.Wicked Questions: Engage everyone in sharper strategic thinking by revealing entangled challenges and possibilities that are not intuitively obvious. Great for outside the box thinking.Activities to Build Alignment Circle of Questions: Engages everyone in the team to build Alignment around the purpose1-2-4-All: Involves every individual is searching for answers, expressing silent conversations and insights before communal expression.Wish Granted:: What is the core of the alignment? Grant it as a wish to the team and collate everyone’s thoughts.Moving Motivators: Determine what motivates the team and learn how it builds alignment.Circle & Soup: Gauges the team’s autonomy to carry out actions based on the Alignment proposed.Activities for Context Systemic Consensus: Sometimes, it is better to know who is not in sync with context rather than agreeing. Encourages people to say “No” and showcase their opinions.Open Item List: Distribute context to different participants and see what thoughts they bring to the table along with action items.Min Specs: This one must ABSOLUTELY be respected while you unleash the group to innovate freely. Respecting the Min Specs will ensure that context will be both purposeful and responsible.You can find more information on these and other activities at Retromat, Liberating Structures, and Management 3.0 respectively.Duration of a Liftoff Challenge agile technologyDetermining the duration of a Liftoff Challenge requires planning, design, and iteration. You’ll need to negotiate a balance of objectives while ensuring participants have a cool-down period after each part.In my experience, I’d estimate one day each for Purpose, Alignment, and Context. I’d also keep 1 day as a buffer and to make any final adjustments to the previous day’s agenda.In short, I’d say you’d be safe with a 4-day duration that would maximize engagement and output while keeping operational interruptions to a minimum.Take away My experience with Liftoff is one of not only results but of education; and a continual one at that. To leave you with some helpful hints on conducting your own workshops, I’d encourage you to consider the following lessons I’ve learned along the way.A Pre-Work Session with respective stakeholders and team members to ensure a smooth liftoff is a must Use a Goodness Checklist to ensure that the team has one common and shared understanding of the outcome, vision, and customer. Prospective Analysis is the time to identify team members’ hidden and overt assumptions and consider the potential threats and hazards, and the opportunities and benefits that may lie ahead. An Outcome-driven Agenda can keep the Liftoff momentum and morale high and teams believing they are investing time and energy into something worthwhile. Lastly, as a practice, I’ve always asked my Scrum Teams for a workshop to define their ground rules. But Liftoff provides a new way of thinking that includes stakeholders in the mix, enabling them to understand the team’s people, the effort they put forward, and their unique, emotional imprint on the project and those around them.I would always suggest a shift to agile. But I would also insist that a Lift Challenge is a part of it.Note: The concept of Liftoff has been widely explained in the book Liftoff: Start and Sustain Successful Agile Teams.
Challenge Liftoff: An Agile Team with Purpose, Alignment & Context

Digital transformation is one of many buzzwords to inundate the marketing world in recent years, and for good reason. The way the world works has changed, and brands who don’t leverage the latest technologies to elevate customer experiences and improve business processes will be left behind.For most organizations undergoing a transformation, their website takes top priority. It’s a critical customer touchpoint and often the preferred way for customers to engage and purchase products and services. Ensuring they’re able to do so seamlessly is essential, or they will go elsewhere – according to PWC, 32% of customers would stop doing business with a brand they loved after one bad experience. Unfortunately, as organizations focus on incorporating the latest technology and trends to amplify their online experience, they often forget one very important thing: accessibility.If you’re transforming your digital properties to improve customer experiences, but are forgetting to factor in accessibility, it’s all for naught, and in the very near future, you’ll likely need to transform again. Why? Without accessibility, you’re severing your brand from millions of users who live with a disability:1.3 billion people with disabilities globally Friends and family represent an additional 2.3 billion consumers with an emotional connection to disability People with disabilities represent a spending power of more than $6 trillion Though not all disabilities directly impact a person’s ability to go online, many do, and as the population ages, more and more people will be affected. With so much of the world reliant on digital services to operate – from banking, to job applications, to ecommerce and everything in between – it’s imperative that organizations prioritize digital accessibility so everyone has the same access and opportunities.According to W3C, people with disabilities represent a spending power of more than $6 trillion.The (Surprising!) Advantages of Accessibility Digital AccessibilityAccessibility can feel like another item in a very long list of things to consider when undergoing a digital transformation, but you can’t ignore it. In fact, it should be a priority. Without accessibility, you’re failing to serve a huge portion of the population, and that’s not just morally wrong, it puts your company in serious legal risk (more on that later). Aside from ensuring equal access, accessible digital properties offer a number of other advantages that can help you deliver on critical KPIs:Increase Customer Engagement. When customers aren’t frustrated by a digital experience, it’s easier for them to do business with you. When they do encounter barriers, they’re more likely to walk away. A study by Click-Away Pound found that 71% of users with disabilities will leave a site immediately if it’s inaccessible. Don’t give your customers a reason to take their business elsewhere. Improve Design and Functionality. There’s a misconception that an accessible website equals a basic or boring website – that couldn’t be further from the truth. Not only does accessibility encourage cleaner code and improve SEO (Google rewards sites that are inclusive), it puts the user first, which improves usability and leads to better experiences for everyone. Think of digital accessibility the same way you think of accessibility measures in physical spaces: everyone takes advantage of curb cuts, automatic doors, etc., – the same will be true of accessibility measures on your online properties. Boost your Brand. Inclusive experiences are better for business – delivering positive, barrier-free interactions to all customers creates loyal customers, and loyal customers share positive experiences with friends and family. It’s also worth noting, a study of Fortune 100 companies found that disability inclusion is common practice among high performing businesses. There’s simply no reason not to embrace accessibility. Limit Legal Risk. In recent years, the volume of ADA Title III lawsuits and demand letters has increased exponentially, with more than 11,000 suits filed in the US in 2019 alone. In Canada, public and private sector organizations will be required to have an accessible website by January 1, 2021 or face severe financial penalties. Having an accessible website means you’re adhering to WCAG standards – the global benchmark for measuring accessibility – which ensures you’re compliant with ADA, AODA, Section 508 and other global requirements, effectively protecting you from risk. Achieving Accessibility Now that you know why an accessible website is important, let’s talk about how you get there. The process is complex, ongoing, and requires regular audits and updates to ensure you’re getting where you need to be – and staying there. Because of this, partnering with an accessibility vendor is ideal. They’ll uncomplicate the process, keep you on track, and help ensure work is completed correctly.The right kind of partnership will begin with both automated and manual audits of your digital properties, which can include everything from websites and wireframes to PDFs and mobile apps. Some common accessibility issues discovered through auditing include:Display: poor color contrast or text size makes content inaccessible to users with vision impairments. Buttons: Critical buttons (e.g. Buy Now, Cancel, Submit) are mislabeled or missing labels, so customers using screen readers are unable to properly engage with content. Navigation: Users are unable to browse your site using keyboard-only navigation. Images: Relevant images are missing alt-text which accurately describes the content of the image to screen reader users. Automated testing provides a bird’s eye view of your accessibility issues, but manual testing is required to dive deeper. Manual tests are performed by experts using the same tools and techniques a user with a disability would employ to engage with your digital properties. This aspect is crucial to determine the full scope of your accessibility issues. Manual testers also weed out false positives (accessibility issues identified by automated tools that don’t actually exist) and perform other critical tasks that require human judgment. For example, when scanning an image for alt text, an automated testing tool would tell you alt text exists and give you a passing grade, but it can’t tell you if it accurately describes the image content. If alt text reads ‘black mouse,” is it describing a rodent or computer accessory?image of a living black mouse and a black computer mouseIs your image alt text descriptive enough for users to understand what’s depicted?This is why it’s essential to include manual testing by accessibility experts. Users shouldn’t have to guess.Once all accessibility bugs are identified, they’ll work with you to create a remediation roadmap to fix issues according to global guidelines, starting with the most critical problems. They’ll also serve as your System of Record, documenting your ongoing accessibility efforts which can be critical to defend against the threat of legal action or accusations of intentional noncompliance.It’s important to remember that, much like your digital transformation, achieving accessibility and compliance is an ongoing process. Auditing and remediation will be required regularly as your digital properties evolve over time. The good news: no matter where you are in your transformation journey, it’s never too late to get serious about accessibility.
Achieving Digital Accessibility while undergoing Digital Transformation

The fact is, you can’t create unique, memorable, or even half the time enjoyable, digital experiences without Usability Testing. However, it seems to me after recently experiencing a few websites and applications that some might be trying to prove this fact wrong.After the frustration subsided (but not forgotten), I started to wonder what might cause a lack of usability testing, even when knowing how vital it is. The first thought that came to mind was money. After all, it’s been difficult times for many, and the appeal of whisking a product to market without adequate testing is understandable. But I didn’t say forgivable.So for the sake of everyone, including budget-conscious businesses and perhaps most importantly, users like myself who are pained by a bad experience, here is the “What, Why, and Who” of usability testing, and most importantly, the “How” to do it on a budget.And because money isn’t the only valuable thing, I’ll stop wasting time and jump right into it.The “What” Before I get into usability testing on a budget, it’s important to first establish what it is, so we are on the same page. It’s essentially a method where users (participants) are asked to go through a typical application or website (interface) journey, or specific tasks and provide feedback on their experience and preferences.The concept is pretty straightforward, and in the event my introduction didn’t convince you, I’ll elaborate a little more on why they are important.The “Why” When a customer uses a product, what matters at the end is how they feel about the experience. And what makes a bad experience? Well, many operate on the rule that if a user cannot get the required info they are looking for within three clicks, there is a high chance that she/he may lose interest and abort the interaction. That doesn’t leave a lot of room for error.This is one of the reasons why usability testing is so important. Not only can it eliminate the fear of going over three clicks, but it also helps:Identify problems in the design in application/products Find opportunities to improve the design To learn the users’ behaviours and preferences The “Who” There are three components to your typical usability testUsability Testing processThe Facilitator.The person responsible for planning and providing guidance to participants.Participants.People who will execute and perform the usability tests.User Journey.Tasks for the participants to complete that relate to the journey you wish to perform user testing on.The Facilitator gives Participants instructions and guidance to go through a user journey to perform specific tasks. The Facilitator also observes and notes the behaviour and feedback of the Participants.Now that we’ve established the What, Why, and Who of usability testing, let’s get into the good stuff of How to do it on a budget.The “How” Even though the digital world is getting more complex, it doesn’t necessarily mean that our approach has to follow. If you are looking to do usability testing on a budget, the simpler your approach, the better.Step 1: Planning Identify the User: To simulate the most users, I’d suggest using the following groups to keep costs low. Don’t be afraid to ask for help from 5-6 people you know and compensate them for spending 1-2 hours with you. You could also try Cloudsourcing, a technique where participants can be hired for usability testing from similar market regions to offset cost. Usability TestingA table showing three age groups and segments of users. Age group 1. 15 to 30 years old. Age group 2. 31 to 50 years old. Age group 3. 50 to 60 years old. Identifying the journey: Selecting the right journey is key to success. They must be real user scenarios on an actual production-like application; otherwise, the results won’t mean much. Let’s take a look at a mobile application for food ordering as an example. The following diagram represents a typical journey. The users are expected to go through this journey and provide their assessment on the applications’ behaviour and their preferences. The various stages of a user journey, from sign-up, login, payment, order, and logoutSet guidelines: Since usability testing is subjective by nature, here is a checklist that you can use to evaluate the user experience when going through the journey. Mobile app usability checklist Description Image Source Step 2: Execution When it comes time to execute, users go through the determined journey or perform specific tasks on devices provided by the facilitator. Is it essential users all have the same devices, including model and operating system. As they go through the journey of ordering food, ask for feedback on their experience, considering the evaluation guidelines. Participants will then rate their experience on a scale of 1-10 and provide comments.Benchmarking with competitors: Another way to gauge the design of your application is through competitive benchmarking. This helps you determine how the thing you are testing stacks up against other similar products. Participants should go through the same journey on competitor applications and rate their experience on a 1-10 scale. The scores of yours and the competitor’s applications should be compared. Step 3: Analyze Throughout testing, the facilitator is to observe and collect feedback from the participants and pass it to design for review. The design team then takes that information to learn more about its users and refine the design accordingly.Usability Testing Usability Testing for Web AppsTake away It wasn’t fancy. It wasn’t particularly hi-tech. But one thing you can’t argue with is that this approach gets the job done – more importantly, on a budget.I feel many people overcomplicate what is required in usability testing. All you need is a few people and appreciation as a way of compensation. And while it may not seem like much, this small effort will significantly impact your digital products and the experience they create for their users. Because while we may think all the complexity and complication is impressive, the user only cares about the experience. Now, hopefully, you can help make sure it’s a good one without breaking the bank.
How Usability Testing Can be Automated Efficiently on a Budget

I think technology, on the whole, can be classified as a paradigm. One of the clearest examples (and conveniently, one that supports my narrative) is this: innovation breeds innovation. And with each step, further expands the adjacent possibility of what has the potential to exist. And while not a betting man, if history is to be believed, I’d wager it occurs to a degree so significant you could assign an exponent to.However, it’s a double-edged sword. Because while the potential and possibilities are growing closer and closer to limitless, it also makes trying to predict “what’s next” with much degree of accuracy very difficult. Google Glass, a hype at one point in time, is nowhere in the vicinity, nor did the Microsoft Surface come into its anticipated, full-fledged existence. However, these innovations were the stepping stone for many others.And while we’ve already established, I’m not a betting man; if I was, this is the innovation and technology that I would be eyeing on now before it becomes too hard to ignore in the future.Cloud Rendering I distinctly remember hearing people tell me to “get my head out of the clouds” when they’d catch me daydreaming. Who knew that we’d live on an edge where people could get things into the cloud fast enough!“Once upon a time, it required enormous amounts of hardware to process our data,” is what you’ll likely tell your grandchildren. That’s because Cloud Rendering is already taking traction with the advent of 5G and it’s only going to increase from here. Our dependency on hardware may be a thing of the past when 5G becomes fully operational by an expected 2025.Cloud rendering is a technology used to offload your expensive processes onto the cloud, eliminating big, heavy, and costly in-house hardware. The most recent example of this (and easily the most visually stunning) is Flight Simulator 2020 by Microsoft. See for yourself and enjoy the breathtaking landscape built in real-time, providing a real-life flying experience. And all the processing? That’s done on the cloud and rendered on the simulator screen in real-time.Flight Simulator 2020 by MicrosoftThanks to 5G, the applications are quite endless. Cloud-connected cameras to track potential threats in stadiums or highly sensitive areas to replace your gaming consoles like Xbox or Playstation – although, Stadia did try. Still, it will take traction in years to come thanks to other innovations that make just such a thing possible.Not convinced yet? How about another use case for good measure!AR/VR mounted devices have been around every nook and corner. Every area – business operations, gaming, and entertainment- has heavily invested in it. And the recent pandemic has only further caused people to turn to technology to fill in where reality can’t safely, especially where that technology has become more affordable, lightweight, and now, can render seamlessly.With cloud rendering entering the picture, it allows AR/VR devices to offload their heavyweight computing and trade it in for a smoother rendering experience. My prediction? All of this translates to practically everyone owning one of these devices to a level that would make their manufacturer grin all the way to the bank.AMP – Accelerated Mobile Pages As we continue “mobile everything” – well, almost everything – we should consult our mobile phones for answers as to what’s to come next!It’s believed It takes 3 seconds for a user to leave a webpage if it doesn’t load. Well, just 3 seconds is what people expect from any website to render a landing page.So how do you make it faster?Use Google’s AMP. To expand, essentially it’s a stripped-down HTML that enables you to load mobile pages faster than ever possible. AMP pages load around four times faster than a regular web page resulting in a drastic increase in hover.google ampYou’re probably wondering how AMP can achieve this – I know I was. These are its three main components:AMP HTML AMP JS AMP Cache Now, the most important question is whether AMP affects the ranking of websites. According to Google, AMP by itself is not a ranking factor. However, loading times do affect ranking. That said, AMP makes your websites faster, which in turn gets ranked higher.But don’t take my word for it – these stats prove it:Impremedia – a digital publisher that caters to the Hispanic audience, has achieved 2x Faster speed and a 160% increase in RPM (Revenue per million).CNBC got on the AMP bandwagon and has seen an average load times of 1.23 seconds, and since implementing AMP, it has seen an increase of 22% in mobile search users who returned to CNBC.com within seven days.Finally, the commits don’t lie. There are 50 repositories under the AMP project on Github, and it is wildly active. The below graph shows just how widespread its usage is.I predict AMP will grow in popularity, eventually becoming the de-facto standard for more and more websites.CNBCAMP can be used to not only build and serve lighting fast ads to pages. There are way more scenarios, like the dreaded, waiting for an ad to load. Ah, the frustration. AMP helps reduce blood pressure while increasing the viewability and click-through rates of your ads. Did I forget to mention this increases monetization, which is a win-win for the users, publishers, and advertisers?AMP Technology13% increase in revenue.Triplift and Cloudfare boost Time Inc.’s revenue with AMP Ads.200% Increase in average clickthrough rate.Teads brings AMP’d mobile video inventory to nearly 100 publishers6x Increase in ad load speedTeads signs on as one of the first advertising partners to join the AMP ProjectAMP’s most recent update was on August 27 – 2020, where they released v2.0 of the official AMP plugin for WordPress.It may not be seen or heard everywhere, but AMP is a dark horse running a very long race. Ignore at your own risk.WebAssembly (WASM) WebAssembly is NOTA programming Language A replacement of JS So what is it, and why even talk about it?It’s an open standard that defines a portable binary-code format for executable programs, and a corresponding textual assembly language, as well as interfaces for facilitating interactions between such programs and their host environment.How it works is you write code in other languages and compile it to WebAssembly, which runs on your browser. Yes, you heard it right – on your browser.Rust / C / C++ / GO – all can be compiled to WebAssembly.Rust,C,C++ & web assemblyIt allows you to compute many things on the browser and not on JS, which has been known to put one in a sticky situation or two over the years.In layman terms, you would think that 0.1 + 0.2 = 0.3, right? Wrong, at least, not in JS. It’s 0.3000000000, and is usually overcome and dealt with by Rust. But with WebAssembly, financial applications can benefit by not only becoming faster but eliminating Rust calls for JS calculations.Image and video editing is another prime use case. Have you ever tried to edit or even rotate an image on the web? No, I’d suggest you try it if you’d like to experience some frustration. That’s because it takes a long time and, sadly, no workaround. That is unless you decide to make your photo and video editing easy with WASM.How is it even possible? Well, WASM has a JS API that allows JS to compile WASM modules and interact with them. What that translates to is you can have your heavy computation done by a WASM module and not JS, resulting in faster results.And don’t worry, I haven’t forgotten about all the gamers out there. Would you believe if I tell you that you can play Doom 3 on your browser? Yes, you read that right – ON YOUR BROWSER! Just type WASM DOOM and enjoy (my little gift to you). If WASM can be used to render and play DOOM well, then the possibilities really might just be endless as far as I am concerned.So, are we getting rid of JS? Heck NO! WebAssembly simply makes JS better. And whether you want to use it (or even like it), I predict that WebAssembly is something that you will hear a lot for a while to come.Takeaway As more technology develops, the potential for greater innovation presents itself. Trends are short-lived, or rather, overshadowed by bigger and better innovations. However, the technology I reference today, Cloud Rendering, AMP, and WebAssembly, are I believe much more than a trend, and time is proving me right. These technologies show promise and aptitude to support the weight of a multitude of other technologies on its shoulders as we push further and further into the adjacent possible.
3 Technologies of the Future: Cloud Rendering, AMP, and WASM

With recent advancements in the IT industry coupled with its growing pace, it’s essential for software companies and professionals alike to up their game. And while there have been many architectural changes with respect to development in an effort to increase productivity and reduce cost, there is certainly a need for similar attention to be paid to the testing of software as well. But where to begin? Fortunately, you begin and end with API automation using BDD.The first thing is to look for a tool that helps you write easy to maintain automated tests, faster. For this article, we’ll focus on automating Rest API testing. I’ve used many tools over the years for this purpose, however, I recently came across one that not only changed my view on automated API testing but on the concept of absolute automation as a whole. It’s called Karate, and if you are involved in automated API testing and don’t have a background in programming, you may want to give it a consideration.What is Karate? Well, for starters, it’s easily my favourite form of martial arts. Secondly, and from a more professional perspective, Karate is an open-source test automation tool for tests written using Behaviour Driven Development (BDD) Gherkin syntax. Unlike other BDD frameworks like Cucumber, Karate defines all the step-definitions by default. This enables even non-developers and people with no programming background to write API tests quicklyThe following is a perfect depiction of what I mean:karate Behaviour Driven DevelopmentNow from the above image, it’s clear how simple it is to write a REST API test using Karate. Though the test’s readability is not as in-depth as the Cucumber test, it does save you all the hassle of defining the steps, business logic, and POJOs. I’d argue that’s worth it. The other coolest thing about Karate is that it is a single stop shop for your API, Web & Native Application tests and that you can easily implement in your CI/CD Pipeline. As for the cherry on top, you can use the same tests for performance testing.BDD Framework & Karate Behaviour-Driven Development (BDD) is a software development and testing approach that bridges the gap between technical and non-technical teams. An offshoot of Test Driven Development, BDD mostly deals with systems user behaviour. In terms of testing and automation, BDD frameworks are especially crucial in small teams where one can’t afford to hire individuals to create and maintain an automation framework. That’s where Karate comes in.TDD Vs BDDGetting Started with Karate Let’s look at some operations you would typically perform in Automated API Testing, assuming you already have your environment setup. If not, please refer to Karate’s official GitHub page, which gives you a complete insight of Karate and how to set-up your project.Definition Karate provides its own DSL (Domain Specific Language), which uses a Gherkin-like language enabling one to write tests without programming knowledge, and write tests in .feature files. Here is an example:Domain Specific Language ExecutionIn the first Background section, we’ll be defining the variables needed to access globally and hence the URL and other variables. Now to make the most out of reusability, Karate lets us easily call and read the other feature files as defined in the background section, so we can access the variables from the called feature.The last thing in the background section is the ‘schema’ variable used for schema validation. From the above example, it’s clear how easy it is to define Karate’s schema instead of using the complex JSON schema.Now let’s understand all the components under the Scenario section of the feature file:Karate follows the “Given When Then And” style for test scripting that helps in understanding and mapping the requirements. The first component is the ‘path’ keyword, which defines your complete path (endpoint) and the base URL specified in the background section. The second is ‘param’, that is simply the query parameter. Thirdly, ‘header’, which is how you define the request headers for your API test. ‘method’ is the HTTP request type. Then starts the assertion block where you’re validating the status code, schema, response time, and finally, printing the console’s response. The things you can do with Karate are not limited to this example. You can use in-line JavaScript functions as JS is native to Karate and on the other hand, there is always an option to write custom Java functions. Karate also supports dynamic data-driven testing through simple implementation of ‘Scenario Outline & Examples,’ similar to what Cucumber has. And finally, you can use the same test feature as your performance test with Gatling.Execution To execute the above feature file, you’ll need a simple Java runner file that will look something like this:karate Behaviour Driven DevelopmentHere we’re using the JUnit 4 Runner. You provide the path to your feature file in @KarateOptions, and that’s pretty much it.Reporting As we’re using the JUnit 4 Runner, Karate can provide very simple yet elegant reports by default for each run, but you can also customize them and attach the failed step’s screenshot. Plus, you can use Cucumber-reporting if you want more detailed reports or if you’re implementing parallel execution.The following is a screenshot of an actual test report:Cucumber reportingIntegration with CI/CD Pipeline Finally, all you need to complete your automation cycle is to integrate your tests with your CI/CD Pipeline. There are a couple of options out there that you can choose from, however, the best in my opinion for web tests are the Jenkins and Saucelabs duo while for API, the Jenkins and docker pair has proven the fittest. You can find ample documentation for docker implementation here.Take away I’ve been using Karate for some time now and it has proven it’s worth in API automation. As far as I’m concerned, it’s simple syntax and ability to support complex code makes it one of the front runners among all the BDD automation frameworks. And in case you weren’t sold, here are a few points i’d like you to consider before we depart ways:Karate can be reused to test any HTTP request. It can be used to test data from Excel or JSON files to execute data-driven tests. The BDD approach and Gherkin style syntax makes it easier for everyone to understand and even design tests without any programming background. “One-click” to execute tests and study the results through reports. Easily integrated with dockers and Jenkins for continuous integration. While I think the benefits of Karate are quite clear at this point, if I had to leave you with one take away, it’d be that if you’re looking for a framework to write easy and fast API tests but lack programming knowledge, Karate might be your best option. Not to mention you could add “Knows Karate” to your resume.The above was written in collaboration with Ragavan Balasubramaniam, Manager, Automation Services at mobileLIVE.
Karate and BDD: Fast, Open-Source API Test Automation Done Right

Why would you utilize Kanban in SAFe? The short answer – to be successful. The longer answer starts with why organizations adopt Agile in the first place.The most successful organizations are the ones that elicit the most value from their efforts and have established best practices and processes to ensure that effort and return is repeatable and scalable. For example, in software development, there have been undeniable advantages and value when clients and end-users are involved in the project. It helps with transparency and visibility on progress and aids in continuous planning and feedback throughout the lifecycle.Software companies appreciate the idea of delivering value, and more specifically, early in the process, and this has been one of the driving factors behind Agile adoption. This methodology not only mitigates some of the development risks, but Agile project management helps produce higher quality products, happier users, and increased project control.Most organizations are adopting Agile methodologies to increase team performance, improve project versatility, and achieve better customer satisfaction. However, those who have already embraced Agile will likely find themselves in a position to better respond to market variability and successfully deliver more projects.Kanban & SAFe: An Agile Approachhow we mentor and remove impediments because we have1. Manageable Team size. 2. Single funnel and decision making. 3. automation and seamless integration. 4. collaboration. 5. self organising team. 6. time bound cycle. 7. tool. 8. quick daily update.Scaling Agile SAFely SAFe, or Scaled Agile Framework, is a means of established practices that allow enterprises to implement and utilize Lean and Agile methodologies in a larger scale and complex scenarios by giving teams the flexibility and autonomy to manage challenges on their own.If it wasn’t obvious, SAFe’s main advantage is it provides a platform to scale up consistent lower-level best practices to deliver large programs; however, it does much more. It also promotes cross-functional teams to collaborate efficiently when prioritizing backlogs, considering the interdependencies among groups, not to mention faster time-to-market, increased velocity and quality, improved employee engagement, and higher transparency.Scaling Agile SAFelyAnd now, Kanban While SAFe is a way of scaling Agile methodologies in an enterprise environment, Kanban is an Agile framework used to organize, record and implement agile software development. Growing in popularity, Kanban’s appeal reflects the real-time status of the project and the full transparency of work being done. Tasks or assignments are represented visually on a Kanban board, allowing project stakeholders to see the progress of any part of a project at any time. Although physical boards are still popular among some teams, our new remote work reality has further pushed their virtual counterparts’ appeal. Electronic virtual boards are crucial in any agile software development tool for task traceability, easier collaboration, and shared accessibility.Kanban BoardIs it Safe to Use Kanban in SAFe? In short – yes. SAFe Kanban teams typically operate in a broader context. Imagine multiple agile teams all working towards a solution by addressing the challenges and bridging the gaps among themselves. To help mitigate challenges and ensure continuous and seamless delivery, it’s best to stick to specific SAFe rules, such as the duration of PI, the Kanban guidelines, and electronic vs physical boards.So how does it work? First, they choose the Program Increment (PI) after considering the dependencies on each other. Next, place tasks in the priority on the board to fulfill each different groups’ needs. Finally, collaborate to make sure that progress is per the set upon agreement. However, it is also important to be flexible where possible and adjust the boards in terms of priority during PI execution to remove blockers.Kanban in SAFe: A Brief Use CaseOrganization XYZ has started multiple dependent projects as a larger, overall program. The organization’s senior leadership wants to have transparency into every project and, so as to gauge the progress of the overall program better. Numerous departments, including Sales, Design, and Marketing, are working together to make the program a success.In this scenario, the virtual Kanban boards would be an ideal solution, providing detailed visibility into the program and smaller projects. Plus, it can prove helpful in removing blockers and impediments through more timely and informed decision making. The image below illustrates how Kanban boards at the project level (tasks/stories) transfer into the program level (epics/theme).Brief Use CaseThe Benefits While we’ve touched on some of the benefits earlier, there are three main benefits an organization can expect from SAFe Kanban teams over other Agile methods.Teams Alignment: SAFe helps align the Program Manager’s strategic roadmap with the Development team’s backlogs. Higher Quality: Quality isn’t something that can’t be added later; instead, it needs to be built in from the beginning. SAFe ensures that every delivery of your software project is a quality one. Transparency: SAFe helps the organization achieve visibility transparency at all levels in the hierarchy; from the C-suite to the junior offices, everyone is authorized to see the backlogs of Sales, Program, and individual teams. Each level in the organization has a clear understanding of the goals aligned to a single objective, eventually building trust. When to Use Kanban with SAFe? Every Agile methodology that has advantages associated with it inevitably also comes with disadvantages. Which is why choosing the right framework is so critical. Here are a few points to consider when selecting the right opportunity to use SAFe and Kanban together:Bigger Projects & Teams: When an organization is inclined to implement an agile approach across larger, multi-team programs and projects. Facing Delays & Failures: Aligns everyone precisely when multiple teams in an organization run their Agile way but regularly face delays and failures. Independent Teams: When teams decide or are instructed to work independently. Scaling Agile: It helps when an organization intends to scale Agile across the organization and in different departments but unsure about creating new roles and changing the existing ones. How do you get the most value out of your organizational efforts? Circling back to my point at the beginning of this article, it should by now be clear that value is often related to the frameworks, methodologies, and best practices we have in place. Few have consistently proven to deliver these like Agile.While Agile continues to evolve, it is essential to continue seeking new ways of utilizing it for organizational benefit and better business outcomes. Its focus on collaboration, self-organization, and the end-user is what makes Agile so appealing to organizations. However, it is how you decide to use it, like combining Kanban and SAFe, that makes Agile not only appealing but valuable.The above was written in collaboration with Ahmar Siddiqui Mohammad, Director of PMO & Head of Solution Delivery at mobileLIVE.
Kanban Boards & SAFe: The Scalable Agile Frameworks

When setting out to make your digital properties accessible, overlays are one potential solution you’ll likely encounter along the way. Marketed as an accessibility ‘quick fix’, vendors promise overlays will instantly make all necessary repairs on your website and help your WCAG non-compliance problems disappear in seconds – all at a fraction of the cost of other accessibility solutions. It almost sounds too good to be true – and that’s because it is. If you’re considering using an overlay to make your website accessible, don’t. These band-aid solutions do not properly solve for accessibility, they often worsen the CX/UX, and they will increase the likelihood of your getting sued. The only way to improve digital accessibility is to actually do the work required to become accessible, and that will not happen overnight.What are Overlays? An accessibility overlay is a plug-in tool that detects accessibility issues directly on a webpage and tries to ‘repair’ them in real time, instead of within the web code as is required. Typically, you’ll get a snippet of JavaScript code to plug into your website, which will then try to automatically fix accessibility issues in the background as the page loads. Some overlays provide additional functionality for the users, usually as a small icon available on the page. Users can click the icon to open a menu of accessibility options that they can engage with as needed. The menu is generally limited to basic accessibility features already addressed in screen readers or operation systems, e.g. text size, color contrast, read text aloud, halt animation, etc. This is a wildly ineffective solution that fails to make any tangible accessibility improvements and forces users with disabilities to learn yet another accessibility tool so they can engage with your content – assuming they’re able to locate and engage with the icon in the first place.Not only does this significantly fail users with disabilities, it poses a number of problems to your organization, including:1. Numerous accessibility gaps will be unaddressed The inadequacies of overlays are common knowledge in the accessibility industry, with most experts agreeing they’re only capable of detecting 20-30% of issues occurring on your website. This means that 70-80% of issues will not even be detected by an overlay, let alone addressed. Applying automatic fixes to the few issues overlays can detect also means risking breaking your website’s user interface, as changing the structure impacts how the page is being rendered.No reputable accessibility company would ever stand behind those numbers or potential performance problems, but of course, that’s never the way overlays are marketed. Overlay vendors will make countless false promises, guarantee your website will be fixed to meet 100% of ADA and WCAG requirements, and let you walk away thinking you’ve done your due diligence, when in actuality, you’ve only installed a superficial solution that fails to make any meaningful accessibility improvements.2. Fixes will not be done in conformance with WCAG Becoming compliant with WCAG is an intensive process that requires expertise and testing by real users with disabilities – overlays simply can’t compare. Because they are just code slapped on top of your website, no remediation work is actually being done to address accessibility issues. If an accessibility scanning tool was used on your site, the results would be the same with and without the overlay – in fact, some overlays will even try to bypass testing tools in order to provide “fixed code” – and that means an ADA demand letter could be knocking at your door. The only true way to achieve WCAG compliance is to do the necessary work; complete an automated and manual audit of your site and address all accessibility issues you uncover at their core. This will almost certainly mean updating both your content and code, and it will not happen overnight, despite what overlay vendors would have you believe.3. Overlays don’t address your mobile properties Becoming accessible doesn’t end with your website – accessibility extends to all of your digital properties. Unless your website, mobile site, and digital app(s) are identical in every way, you must ensure all properties are fully remediated. Plus, with more and more users relying on mobile devices to get things done, it’s a channel you can’t afford to ignore.Mobile traffic now accounts for half of web traffic worldwide 72.6% of internet users worldwide will only use their smartphones to get online by 2025 61% of people won’t return to an inaccessible mobile site Don’t waste time on a futile solution that only addresses part of your problem.4. Privacy and Performance Risks It’s no secret, the more stuff you have on your site, the slower it can perform. Overlays are scripts, and are often hosted on the vendor’s server, meaning you have no control over speed or security. If their server is hacked, your website could be next. If their servers or the overlay script itself are slow, your website will likely be impacted. With customer patience already low (40% of consumers will wait no more than three seconds for a web page to load before abandoning the site[4]), do you really want to give people another reason to walk away? An ineffective accessibility solution is simply not worth all the risk.To put it plainly, overlays are often worse than doing nothing to address your accessibility issues, because they fool you into thinking you’ve done what’s needed to become accessible, when in reality, you’ve barely scratched the surface. Getting your digital properties compliant with ADA, AODA, Section 508, WCAG and other global regulations takes time and requires an ongoing, multifaceted approach that includes both automated and manual tests of your website and digital properties, in addition to testing using popular assistive technology devices.From there, you can start to address your accessibility issues at their root to ensure appropriate fixes are made to achieve full accessibility. This will properly protect your business from potential legal action and allow users with disabilities to engage with your website equally, in a way that works for them. Partnering with a trusted accessibility vendor offering viable solutions will make the process much smoother.
Accessibility Overlays: The “Quick Solution” You Should Not Use

Low-code/No-code (LC/NC) software development is much more than a buzzword; it is something that challenges the definition of what software development is.Intrigued? You should be. And today, we are going to do a crash course covering what low-code/no-code is, where it came from, its value, and why it is getting the attention of some of the biggest players in the game.The Difference Between Low-Code & No-Code Low-code software is essentially software that can be configured and customized with minimal (or “low”) programming efforts. To be clear, it still requires someone with programming knowledge to execute. The result is an ability to develop custom applications in hours or days, not weeks and months, and at a significant cost reduction.On the other hand, no-code takes it one step further and empowers anyone with the ability to create and customize an application, all without any prior experience. While the two are usually clubbed together and referred to as low-code/no-code, it is the latter that is really exciting, in my opinion.Now that we know what they are, it’s time to see where they came from.A Brief History of Low-Code/No-Code You may be surprised to know that early forms of LC/NC tools have been around since the ’80s and ’90s. Rapid Application Development (RADs), Computer Assisted Software Engineering (CASE) tools, and efforts like IBM’s Informix all share lineage with today’s LC/NC, but at the time, they simply couldn’t deliver on their promises.The second wave of tools began appearing in the 2000s, with some even classifying as low, if not, no-code. Jump forward to 2016, and LC/NC is back and trending according to google, as they continue to do today.Why Low-Code/No-Code? Low-Code/No-Code DevelopmentThe enterprise tech stack is getting more and more complex with each passing day. In an ideal world, all applications would easily integrate and come with a perfect shiny frontend. Sadly, anyone living in reality knows this not to be the case. In the real world, IT and engineering teams spend a lot of time fighting fires because of security and internal product bugs. These teams are usually already overburdened and spend 30% of their resources building and maintaining internal tools, further reducing productivity and increasing technical debt.According to Salesforce, seventy-two percent of IT leaders now say project backlogs prevent them from working on strategic projects. This problem is not one that can be solved by hiring either, because as most know, the demand for technical talent far exceeds the supply. This is further compounded by the aforementioned firefighting, as business teams keep adding third-party tools to increase their agility.Standard software development processes are dependent on highly-skilled, costly, and time-intensive technical resources. The communication between the business team and technical teams is often fragmented, resulting in longer user acceptance cycles, increased costs, and time-to-market. And after all that time, effort, and money, your software might still end up with bugs. Low-code/no-code tools can solve all these problems.Low-Code/No-Code App Development Platforms LC/NC application development platforms can vary from tool to tool, but for the most part, you will typically find these components common amongst them:Interface Designer: An interface designer is used to design the app’s entry forms or screens. The interface designer typically adds fields, text, and other layout elements to app screens or forms. Workflow Designer: A workflow designer is used to implement business logic and workflow. For example, if building a submission form, the workflow designer would be used to define where the form should go after submission. Common Database: An integrated database contains the data tables that store the data to be created, retrieved, and updated through the app. Connectors: Connectors (sometimes referred to as spokes, webhooks, or interfaces) allow you to connect your app to other third-party apps or services easily. Connectors allow you to automate workflows and tasks across many apps and services from within the context of your app by exposing app data or services, or by retrieving, consuming, or updating data from other apps and invoking their services. Low Code / No Code Platforms Landscape of Low-code/No-code platforms available in the market Growing & Getting Noticed LC/NC is rapidly growing in popularity, partially thanks to websites such as nocodedev.com and nocode.tech which provide a variety of platforms for creating LC/NC mobile and web applications. It’s also garnered the attention of some big names who are opting to join in rather than sitting on the sidelines.Google announced in Jan 2020 that it is buying AppSheet, an eight-year-old no-code mobile-application-building platform. The company had raised more than $17 million on a $60 million valuation, according to PitchBook data.In late June 2020, Amazon announced its launching the beta version of Honeycode, an LC/NC app building platform. The entry of such large names in the space proves there is room, a need, and desire for an LC/NC platform, and this trend could just shape the future of development.The Future of Low-Code/No-Code The current ongoing pandemic has forced enterprises in every industry, public and private, to re-assess and reconsider low-code/no-code platforms, adopting them at a rapid pace. Since these organizations are looking to spend less and build-out services faster, these platforms have become the obvious answer.Gartner forecasts that low-code application platforms will account for 65 percent of all app development by 2024. This means most apps created in 2024 will be developed using platforms and tools that provide turnkey ways to program. Apps potentially developed by men and women who can’t write a single line of code.The low-code market will top $21 billion in spending by 2022 says,Forrester. That’s a huge number and opportunity. Investors would be wise to support the existing players who can shift rapidly to this newmodel, even when it means giving up short-term services revenue for longer-term competitive advantage. Startups that help build out the industry’s new low and no-code application platforms will also rise, like the design app Canva, valued at $3.2 billion.Take away With the rise of APIs, improved connectivity, growing cloud popularity, and software purchasing and deployment becoming easier, no-code/low-code development platforms have the potential to accelerate enterprise innovation by reducing the need for technical skills and resources. And while LC/NC is already causing a lot of excitement, I think we are still a little while off before we start to see the significant and successful rise of Citizen Developers, but it might not be as long as you think.
How Low Code Development & Platforms Can Accelerate Innovation

Micro Frontends are without question one of the most popular yet controversial topics of web application development today. “Should you split your application?” is that question pursed on everyone’s lips, as they wonder if the hype is real or if it’s just another way for consultants to charge more money by tricking their clients. Today, I hope to provide some clarity on just that.What are Micro Frontends? Before you can understand Micro Frontends, you first need to understand Microservices. Microservices architecture is a well-known framework where we split large backend systems into smaller primitives, i.e. services. Micro Frontends come from the same school of thought and try to bring similar benefits to applications frontend engineering.Different Approaches to Application Architecture There is a stark contrast between where we were and where we are, when it comes to web application development. No longer limited to any one way, today, developers can choose to architect their applications in various manners – with no one-way holding clear dominance over the others. However, with such variety available comes the inherent pros and cons of each, making the right selection often a question of the specific project at hand.Here is a graphical representation of some of the ways to architect web applications, including Micro Frontends.Web Applications ArchitectureWhy you should consider Micro Frontends? Micro Frontends are popular, and like most important things, has some clear advantages associated with it, driving that popularity. That isn’t to suggest that Micro Frontends aren’t without its unique disadvantages. Instead, it is to say that those “cons” are dwarfed by the genuine benefits and advantages associated with them. And in case that glowing endorsement wasn’t enough, here are a few tangible reasons you should consider Micro Frontends for your next application’s architecture.Develop, test, and deploy applications independently: Teams can be broken down into smaller tribes and squads, focusing only on a particular area or piece of functionality. They can easily develop, test, deploy, and reiterate on those small applications without inter-dependency. This advantage is at the heart of Micro Frontends. Simple as it may sound at first, this advantage brings with it a liberating feeling. Develop different pieces of frontend using different technologies: Frontend technologies are evolving daily, and new frameworks are continually knocking on the door. And while some are promising and show potential for your application, you are limited to just one unless you want a giant monolith.Micro Frontends solve this problem by allowing individual teams to choose whatever technology they want to use for their micro-applications and develop complete isolation, yet maintaining more profound synchronicity with the project and teams. Frontend development technologiesUpdate individual pieces without rebuilds: For most, large frontend applications inherent characteristic was the need to rebuild it with each new version release. Although there are ways through which the build system can produce hashed versions of the final bundles, they’re prone to error. Fortunately, webpack 5 is on the horizon with a new deterministic algorithm to handle this problem.Micro Frontends are an ideal solution and one that doesn’t interfere with the bundler itself. As a micro-application is being bundled, the rest of the packages’ bundles remain the same and are cached, resulting in faster bundling and more persistent caching. Server Side CodingDifferent teams can choose different tooling: In a giant frontend monorepo, tooling and infrastructure are primarily centric, and all sub-modules rely on the same set of tooling. However, in Micro Frontends, different applications could potentially use different tooling and bundlers. The value in this stems from facilitating the use of new and improved tools for a single micro-application without a significant overhaul. microfrontend applicationsGovernance can become a lot easier: As mentioned before, large teams can be divided, bringing not only freedom in terms of building software in isolation but also in choosing the tools to do it with, but agility and easier governance as teams are divided, mostly independent, and easier to manage. Take away With their ability to develop, test, and deploy applications independently using different technologies and tools for different components, all while negating the need for version rebuilds, it should be clear to you that yes, Micro Frontends do live up to the hype. However, I mentioned earlier, there isn’t just one way of doing things. You should always account for and let the project dictate and influence your selection. After all, while undoubtedly a game-changer, Micro Frontends still have their time and place.
Micro Frontends: The Power of Microservices Extended to Frontend

How confident are you that the security models and measures in your organization are doing their job as well as you think they are? Or, better still, have you ever considered that the information security you have in place is acting more of a barrier to your development teams than malicious intruders? It is possible that the one thing your security is excelling at is preventing your teams from practicing Agile.When talking about security, by default, most assume that bigger is better. After a breach occurs, the response is usually to upgrade, spend more money, and invest in newer technologies. However, I’d argue (and will) that you don’t need to invest millions of dollars to keep your organization safe. Don’t believe me? Take a look at the below diagram that demonstrates how not only a company with best in class security but an actual security company, was still experiencing spam, phishing, and malware in over 9% of their emails.Saas Application Security Reference Source So what’s the solution? I propose that security problems be treated like any other problem, and most problems can’t be solved by throwing money at them. They can, however, be solved with some intelligence. Today, I will show you our intelligent approach to enterprise-grade security that is designed not only for protection but also for agility.A New Stance on Information Security In a world where everything is connected, cybersecurity must become more comprehensive, adaptive, and collaborative. As complexity grows, companies should create approaches to address threats across the different layers; application and service, software and hardware interfaces, physical network architecture, and edge devices.This will require some companies to take a new stance on security, an adaptive, thorough, and collaborative approach. That’s because security exists in a business context, not only a technical one. Technical experts cannot efficiently solve the problem without understanding the underlying business complications.With every organization at risk, preparation is the key. Here are the first steps:1. Prioritize Assets and Risk by Criticality No matter your size or industry, all companies are exposed to some degree of threat, attack, or malintent. However, given the wide variety of industries and verticals that exist, it stands to reason that generic security solutions won’t suffice. Rather, it is critical to tailor security and control towards the specific industry you’re in and the current threat levels that exist within it.Risk by CriticalityPeople have Threats of Identity theft , Man in the middle, Social engineering, Abuse of authorization and controls on Controlled access, Account monitoring, Security skills and training, Background screening, Awarness and social control. Data has Threats of Data breach, Misuse or manipulation of information, Corruption of data and controls on Data protection (eg, encryption), Data-recovery capability, Boundary defense. Applications have Threats of Manipulation of Software, Unauthorized installation of software, Miseuse of information systems, Denial of service and controls on Email, web-browser protections, Application-software security, Inventory, Secure configuration, Configuration vulnerability assessment. Infrastructure has Threats of Denial of service, Manipulation od hardware, Botnets, Network intrusion, malware and controls on Control of privileged access, Monitoring of audit logs, Malware defenses, Network controls (configuration, ports), Inventory, Secure configuration, Continuous vulnerability assessment. 2. Establish Effective Controls and Processes Every organization should consider establishing the right controls to physical and logical assets. Once assets are identified, define them critically so that proper control can be applied accordingly.Traditional approaches on how controls are implemented and access are granted to assets are not particularly suited for today’s digital world. Companies need to implement GUI and API based access /provisioning while embracing new technology like Artificial intelligence, Automation, and Big Data to cope with the ever-increasing threats, building controls around them.3. Consolidate Organizational Threats and Implement Universal Governance Model The way most organizations’ security is structured is outdated and inefficient. Physical security, information security, business continuity, and crisis management are often their own entities. In truth, they should be consolidated and aligned to serve the organization better. The goal is to achieve “Security by Design,” and that starts with a firm foundation and architecture for data, system, and security.Information Security Transformation Most of the organization, in some way or form, is in the process of digital transformation. It is vital to undergo information security transformation to keep up with new threats. Although the security team’s purpose is safety and protection, I often witness a misalignment between the security team and development teams that delays new features or missed business opportunities. The goal of nearly all organizations is speed and agility, and digitizing your security not only helps you achieve that but will also enhance your security itself.However, before that happens, an organization’s security needs to transform to improve decisioning, bring value to the business, and enable new technologies and methodologies like cloud, Agile, and DevOps.1. Decision Making through Quantitative Risk Analysis Security is essentially deciding which risks to accept and how to mitigate them. Sadly, making those decisions isn’t easy, but that changes when you use quantitative risk analysis. This type of analysis breaks down information and segments it. It provides behavioural analysis to identify signs of internal threats, along with risk-based authentication, which considers metadata – user location, recent access logs, etc. All of these can fit into a comprehensive dashboard that ties business assets, threats, vulnerabilities, and potential mitigation plans together to help organizations make the right decision.2. Security and the Value Chain No matter their size, practically every company, in some shape or form, exchanges sensitive data across networks about their customers, suppliers, or partners. Rather than view this as a problem, take it as an opportunity to build security into your business’s value chain. This step becomes even more critical when you consider the rise of digital transformation and IoT.Product companies should consider security as a core feature when designing products. Service companies should use threat intelligence reports to access supplier/partner technology externally and assess the risk of compromise, allowing security data to be used and leveraged in negotiations.3. DevSecOps and Agile Methodology DevSecOps and Agile MethodologyIT operations in business are transforming to be more dynamic and agile. And on par with this transformation needs to be an agile security model to enable new technology and methodologies.Here are a few steps I would recommend to ensure your information security and keep up with technology:Security access needs to be moved from ticket to API based. This means all interaction/integration should be automated as part of the software development lifecycle. This allows developers to access real-time to IAM service, vulnerability scans, and applications through APIs without the need to raise a ticket and wait for it. Organize the security team into scrum or kanban teams. Transform Team lead or Sr.Dev as the security champions who act as Product Owners (POs) for security best practices in Agile teams, similarly to POs for a product roadmap. Enable cloud-native security model, allowing developers to gain access to instantaneously. Work with architecture and infrastructure teams to bring security service into standard solutions and create large sets of data for analysis. Take away While security and the need for it will only continue to grow alongside our digital evolution, it seems as though it will never be at par. Despite how much organizations spend and no matter what latest and greatest technology they have implemented, it seems it will only be a matter of time until the malicious occurs. Perhaps, that is because the historic security approach is flawed.As I mentioned earlier, and as I am sure you have all heard before, it isn’t often you can solve a problem by throwing money at it, and security is no exception. Instead, I propose we turn to an intelligent approach, one that, as I have outlined, not only keeps your organization safe but complements and brings value to the business.It is possible. You just need to give a little bit of forethought to your approach.
Secure & Agile: An Intelligent Approach to Information Security

One of the hallmarks of digitization's success is the widespread adoption of applications, from mobile to client apps, as the benchmarked standard to serve, interact, and communicate with users.And few things have played such a significant role in this evolution as Microservice Architecture.As one would imagine, the requirements of mobile and desktop applications differ significantly.With technology evolving rapidly and consumers' needs shifting constantly, it becomes increasingly complicated to serve both desktop and mobile-based apps with the same backend microservices.With separate teams working on their respective frontend application interfaces, all it takes is a single bottleneck on the backend to derail the progress if it fails to satisfy the demand of the application.And as any developer knows, this complexity, this opportunity for error and misalignment, will only certainly translate to a diminished experience for the user.But it isn't the only way to move forward, as we discover in a deep dive on microservice architecture and how it impacts frontend as well as backend development.Are Microservices Frontend or Backend?Most of the times, microservices are used for backend development, as each microservice deals with a specific capability in an API.These microservices often have a lot to do with handling business logic, communicating with internal/external services, and interacting with databases — all functions that fall under backend development services.But with that being said, all hope isn't lost for frontend development.While not without its own complexities, the idea of microservices can also be extended to frontend development. This is possible with the microfrontends approach, which enhances the frontend with principles of the microservice model.Is BFF a Microservice?Yes, the Backend For Frontend pattern is one of several types of microservice architecture patterns.Each BFF service is considered a microservice that serves as a connector between frontend and backend development.What is Backend For Frontend Pattern?The Backend For Frontend (BFF) pattern is the key to enhanced and improved user experience.A BFF layer consists of multiple backends developed to address the needs of respective frontend frameworks, like desktop, browser, and native-mobile apps.One of the biggest appeals of BFF is it ensures seamless user interaction regardless of the platform the frontend application is running on. It also enhances the overall efficiency of smart devices’ as the applications developed following BFF architecture optimize resource usage while the application is in use.In BFF, there are APIs for specific uses; significantly reducing the surface area that needs to be secured while greatly enhancing user confidence.In monolithic applications, APIs contain unnecessary data that is sometimes of no use for consumer applications, or at best, a single frontend application instance. Let’s take the example of banking transactions.If the user wants to know their last transaction, a frontend application running on the smartwatch only needs the transaction amount from the API. Developing a generic API in such a case will have unnecessary data in response that’s of no use for a smartwatch but could be used for the client app running on the browser.Such an API will cause overhead on smartwatch applications. Developing a dedicated BFF backend for the smartwatch would help achieve an optimized solution, not only void of overhead cost, but would actually improve the user experience.Filling the Design GapIn BFF application architecture, development teams create a dedicated backend application or service for each frontend application interface.Such a backend service only fulfils one frontend application interface like web, mobile, or any other interface developed in different frontend frameworks. Developers can further fine-tune each backend service to best meet each interface’s needs without worrying about dependency.How does frontend and backend work together?The backend system in BFF architecture is different from traditional APIs.In general, public APIs or monolithic backend applications serve the need for web and mobile-based applications with the same endpoint.The diagram below depicts how an open API serves the different frontend applications developed in a different framework.On the other side, BFF facilitates each frontend application interface to directly fetch the data from the backend system’s respective microservice. The diagram below demonstrates how “Browser BFF” and “Mobile BFF” are two backend interfaces developed to serve a unique requirement.The Benefits of BFFBFF is impacting the development community in many positive ways and here are just a few reasons behind its appeal:Multiple frontend application interfaces can call their respective BFF backends in parallel, and dedicated backend services can respond faster. Following BFF architecture reduces the time to make modifications and enhancements in backend systems with dedicated teams working on the upgrades. The BFF layer in the overall system architecture can benefit from hiding sensitive or unnecessary data before transferring it to the frontend application interface, which helps simplify the system. BFF backend systems can use any protocol like FTP, SOAP, REST or GraphQL to request data from microservices, but still use a single protocol when interacting with the frontend application interface. The Challenges of BFFWhile the appeal of BFF is evident to even the most novice developers, it’s common to encounter challenges and important to consider them before following BFF:Fan Out: In BFF, a breakdown of the single service can bring the entire BFF system down. The below diagram shows how a crash in the backend system can cut off your one frontend application interface from the rest of the system.Fuse: In the BFF layer, any microservice downtime that responds to multiple BFFs can impact the whole system. Below represents how a failure in microservice Sa is changing the three different BFF backends.Duplication & Reuse: There is a high chance of code duplication as multiple development teams take care of different BFFs. In the case of communication gaps, the same implementation can happen across BFFs, making the development cost double.Extra Services & Components: Not following the right DevOps practices can lead to unwanted deployments that could create unnecessary backend components running on your server or cloud, occupy resources, and result in slower response time.Overcoming these ChallengesChallenges are meant to be overcome and those standing in the way of the benefits of BFF easily fall into the category. Here are a few solutions to the challenges mentioned above:Solve Fan Out: To prevent the software system from going down just because of one BFF layer, developers should implement fault isolation mechanisms. For this, ideally, each BFF service would have its own termination point. As the number of deployments increases, the system will have better fault isolation and high software availability to end-users. It's helpful while designing a software system, rethink when and what services to be split.Remediate Fuses: This approach is only possible if there is no dependency among the BFFs running under the system, and there is no shared database involved. If services have to share databases, then chalk this one as technical debt, which will be solved partially by eliminating fan out.Reuse: In case some features will overlap significantly between different BFFs and development teams should identify shared characteristics that can be developed under a single BFF service to be reused. This reduces development costs and decreases time to market.When to use BFF?Just like every software design pattern has its benefits and challenges, it can also be said that they have their own ideal instances of usage. The decision to choose the best fit for your software depends heavily on features and circumstances, but here are a few points worth considering:If your software system is supposed to use a shared or general-purpose backend service that takes significant time to develop and is hard to maintain, consider the backend for frontend pattern. It can significantly help reduce time and cost. If functional requirements across different frontend application interfaces (mobile and web-browser, etc.) are significantly different, having a dedicated BFF service for each of your frontend frameworks will drastically reduce maintenance complexity. In case your software system needs to develop the optimized backend for a specific frontend interface, BFF is a suitable option. How to Build Frontend and Backend for Website?In order to achieve a high-functioning website, frontend development and backend development are both critical components.Once you’ve planned out your website (by defining it’s target audience, it’s main purpose, key features, wireframe, layout, etc.), use the following checklist to keep yourself on track with what you’ll require throughout the frontend and backend development process:Frontend Development ChecklistHTML (HyperText Markup Language) CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) JavaScript Frameworks and Libraries Backend Development ChecklistChoose a Programming Language Database Framework APIs Server Development and Testing Deployment Keep in mind that this is a simplified overview. There are, of course, several factors to be considered when building a website or an API, and the list above is in no way an exhaustive one. The above listed factors can, however, be used as a starting point as well as to differentiate between and organize your frontend and backend efforts.Take AwayBackend For Frontend is a design pattern created with not only the developer but, more importantly, the user and their experience in mind. It is the answer to the ever-growing adoption of applications to meet, interact, and serve customers, ensuring consistency while still meeting their diverse and evolving needs. And while the BFF pattern, like anything, is not without its challenges, I hope that I have not only shown you how to successfully mitigate them, but convinced you that its benefits would undoubtedly outweigh any difficulties along the way.The above was written in collaboration with Uzi Murad, Account Executive, and Imran Salahuddin, Senior Manager, Software Engineering, both of mobileLIVE.
Why “Backend For Frontend” Application Architecture?

By nature, the world of technology and software development is constantly changing. What it is, what it can do, and how it is created are all dynamic, evolving to meet the demands asked of it. However, despite these shifting expectations, there is a constant ask that is unlikely to diminish, instead, only grow in intensity: that it be done FAST!Shortening release cycles, introducing updated features quickly, and responding to the changing trends in the market rapidly are the new demands, and many teams have already heard the call! Take Development, for example; they answered the call for speed with their Agile and DevOps methodologies – and I think we all know that has been working quite well. But where did that leave QA and Testing Teams?Manual Testing & Test Automation Given this new paradigm, it was clear that manual testing couldn’t keep pace with Agile and DevOps to the extent demanded of it. In response, test automation was introduced, reducing or eliminating the mundane, repetitive, time-consuming, and often error-prone task of manual testing. Unfortunately, automating large test suites is not easy or practical, especially when you take into account the majority of test automation tools are code-reliant, and likely, less than a majority of your QA team can write code.Fortunately, much like test automation was a response to the drudgery of manual testing, there is an answer to the prevalent inability of QA teams and testers to execute automation without having to learn code. It is called Codeless Automation Testing, and today, we are going to learn if it really can deliver on the value that QA teams hope it can. After all, isn’t the point of Test Automation to free up resources, not bog them down?What is Codeless Automation? Codeless Automation Testingevolution of test automation.automation with record and playback, automation with reusable functions, automation with frameworks, codeless automation.Much like the name suggestions, Codeless Automation refers to automating test cases without the need to write code. Typically, the codeless test automation approach is a familiar one, based off of Record and Playback. In this instance, a tool would automatically record all the test steps into a script while a tester performs them manually. Once the recording is finished, the script can be replayed and used again and again.However, unlike the legacy approach or tools you might be familiar with that record static test cases, today’s offerings come equipped with artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities that allow you to create and edit the test steps manually, creating structured test flow diagrams.Although the name paints a different picture, it’s important to establish that codeless automation is not 100% codeless. In reality, what happens is that while the tester is recording the test, the codeless automation tool is working in the background, creating a layer of abstraction that translates the user’s interaction to code. This allows for QA and Testers to focus on QA and testing rather than learning how to write code.Advantages of Codeless Automation Advantages of Codeless AutomationChange for the sake of change is rarely beneficial. However, the appeal of Codeless Automation, as I already briefly touched upon earlier, is that it was a response to a genuine need and shortcoming in the QA world, especially those expected to support the life cycle of Agile development. Other benefits that have some flocking to codeless automation include:User-Friendly UI: Unlike code-based automation tools, codeless test automation tools have rich UI that comes with the promise of a quick, easy and codeless experience Keeps Pace with Development: Designed with graphical UI workflows, code is created to make automation easy to learn and implement, matching the pace of agile through continuous integration and testing. Lowers Maintenance Cost & Scalability: Flows can be combined and reused as sub-flows across additional testing use cases. When something is changed in these sub-flows, the changes reflect across all test cases holding that module, making automation flow corrections basically obsolete. Increase Automation Adoption: Codeless automation tools can be used as a holistic automation solution across an organization, unlike code-based frameworks that require a specific skill set to utilize fully. This removes a significant barrier to automation. Greater Process & Change Documentation: Detailed visual descriptions of processes, video recordings, and logs are all effortlessly created and stored to ensure an accurate and easily auditable account of what happened. Disadvantages of Codeless Automation Just as every coin has two sides, so too does almost every business case have two opinions. And while the above benefits surrounding codeless automation are appealing and hard to refute, there are also some limitations and disadvantages associated with it. In fact, once you start using a codeless automation tool, you’ll likely notice a few things and get a greater sense of the picture:Lack of Customization: Automation is processed in the background, leaving little to no opportunity for testers to modify the scripts. Not REALLY Codeless: Although scripts are created and structured automatically, instances can (and likely, will) arise that will require some manual coding. Maintainability is Challenging: If tests weren’t designed to be reusable or modular, issues could arise in maintainability as the number of tests is continuously growing, and the application is continually changing. Interoperability Issues: No codeless test automation solution is universal, with either platform dependency or interoperability issues between multiple browsers and software support, leading to unexpected outcomes. Bugs & Glitches: Although computer-generated, it is not infallible and improper coverage can lead to bugs and glitches in the script. If that script is reusable and modular, that could lead to the recorded script playing back incorrectly or invalid test results. How to Get the Most Out of Codeless Automation Codeless Automation TestingIt is easy to get excited at the prospect of experiencing 100% codeless automation, but it is more important to keep your expectations rooted in reality. The truth is, we are only experiencing the nascent stages and are still a little while off from the authentic, seamless experience that will take codeless test automation from where it is today to widespread adoption. That is because, at present, 100% codeless automation is near impossible to achieve, given the growing complexity of current software systems.However, that isn’t to say codeless automation isn’t without its place and time, and the benefits above are still real, just perhaps not to the degree you’d hope for. Our experience has taught us that at present, codeless automation is best suited for fundamental to intermediate test cases, leading toFaster development and script deployment cycles Removal of skill barriers and enhancing automation adoption What Codeless Automation Needs While admittedly, codeless automation isn’t codeless or able to handle the full breadth of modern complex software systems, it is still at a great jumping-off point towards achieving it. But, before codeless automation will ever really take off, I believe that it needs to add some key capabilities, many of which, are already under development and available:Smart Element Locators: By gathering more than one element during the recording, alternative elements can be used if the original is not found in playback. Conditional Waiting: Instead of waiting “x” number of seconds before continuing to the next step, they wait until the condition is true and then proceed as soon as possible. Reusable Steps: Test authors should be able to record common steps and insert them into any test flow later, promoting reusability and saving time. Cross-Browser Support: Many tools come as browser extensions, meaning they could be tied to a specific browser. Ideally, test authors should be able to record on one browser and play it back on another Ability to Insert Code: No tool is perfect, and letting the author have the ability to insert code for specific cases is helpful. Take Away Codeless automation is cause for excitement, but we are still some time away from reaching its full potential, let alone seeing its mass adoption. That is because the limitations are too great to make a significant impact on the complex reality that is modern software development. But that will change in time as most things in technology inevitably do.As the prevalence of methodologies like agile and DevOps grow, so will the need for QA solutions that can keep pace with this accelerated level. Codeless automation stands to be that solution, enabling a broader range of users to utilize test automation. And while the benefits are certainly appealing, and the barrier of entry diminishing, I would say that the real excitement and value of codeless automation have yet to make themselves known.
Codeless Automation: The Future or Overhyped?

I’ve always prided myself a bit of a futurist, and it’s certainly no coincidence that I work in tech. I love how the more advanced we get, the more connected everything seems to become. And while I am always looking forward to seeing what is new, what’s exciting, and what’s better – I am always reminded that it is only that last point – what’s better – that interested me.Take the below diagram, for example. It accurately shows how Fastify, Kong, and Kuma, three relatively new and exciting names on the development scene are the latest best web development solutions, and how they work together. It depicts how the backend applications developed in Fastify are connected through the Kong API gateway. It displays how the API gateway is monitoring and logging traffic to enhance security as it goes in and out of the application. And finally, it shows how Kuma acts as a service mesh to manage and route traffic between the application, database, and external services. And while the diagram does show the connectivity of the web solutions offered by Fastify, Kong, and Kuma, it doesn’t answer the question – is it better?A technical diagram depicting development architecture built using KongWhile I am a futurist, I am also a realist, and by that, I recognize that we are, and should be rooted in our traditions – and this applies to technology if my comparison wasn’t clear. And one lesson I keep learning in technology is that despite how much we want it to be true, new isn’t always better. That is why today, we are going to look at Fastify, Kong, and Kuma, but we are going to compare them to their traditional or legacy predecessors to let you decide if what’s new is this case, better.What is Fastify? As most of us know, an efficient server-side application responds better under a higher load, has lower infrastructure costs, and eventually satisfies end-users. The question that arises here is how to effectively manage resources without sacrificing security to implement an efficient server-side application to serve the highest number of possible running frontend application instances?Fastify is an ideal solution, specializing in delivering highly advanced developer experiences at low cost and with robust plugin architecture. A framework for Node.js, it was built on the concepts of existing frameworks but optimized to make it much faster than others (just look at its name). However, it isn’t the only solution.The Competition For the Best Web Development Solutions Express.js: Fast, unopinionated, minimalist web frameworkExpress.js is a web server framework of Node.js, released as open-source under MIT and was designed to develop server-side applications. Express.js is a small architectural level layer which provides built-in basic web application features, without overriding the features of Node.js. Many open-source API frameworks such as KeystoneJS, NestJS are based on Express.js.Hapi.js: Simple, secure, and framework developers can trustHapi.js helps the development community create scalable, robust applications, with minimal execution cost. Hapi.js is focused more on application-level security and has built-in methods for end-to-end Code Hygiene, Secure Defaults, Integrated Authorization, and Authentication Architecture, adding to its distinction as a reliable resource.How Fastify Compares? Fastify, in comparison with express.js, is one step ahead in terms of efficiency, but still, hapi.js is rated higher in security features. Fastify, as its name suggests, was built to be a swift Node.js web server framework. It also has friendly and ideal controller syntax despite being built for speed. It offers async functions for use as a control code and automatically adds incoming JSON requests to the queue, resulting in fewer development efforts to code the queue management layer. An experiment conducted by Fastify.io of its latest version (3.0.0) showed it to be two times faster than express.js and can handle 150% more requests than hapi.js. The following image provides a snapshot of how Fastify performed against some other well known Node.js web frameworks:A chart comparing the amount of request per second from Fastify, Koa, Express, Restify, and HapiBenefits & Features of Fastify So what makes Fastify so great? Below are a few features of that help it stand out in comparison to other Node.js frameworks:It’s one of the fastest web frameworks. Depending on the application’s complexity, a Fastify based service-side application can serve up to 77,000 requests per second, as seen above. Hooks, plugins and decorators available in Fastify make it fully extensible and one of the more efficient web development solutions. They use Pino, the best logger framework around, nearly removing the cost of finding critical issues. It’s developer-friendly, without compromising on security and performance, helping developers achieve more with less code. What is Kong? Kong is an open-source API Layer, Gateway or Middleware which has better scalability as a web development solution. It is a platform for developers and enterprise architects to connect, secure, and extend their services. Still, its best use is to facilitate the flow of information between all services within the software system. Kong manages the full open-source API lifecycle, and every request to the backend API will hit Kong first before sending it to the final API when it’s active. The diagram below shows how Kong plays a middleware role between the client application and distributed backend services.A technical diagram showing the relationship between a client, Kong Services, and a APIKong vs Legacy API Management Systems In an earlier era of software development, Legacy API Management web solutions helped address an essential problem: How can developers provide access to externally consumable third-party APIs? Initially, software applications were fundamentally monolithic in design, and intra-function calls were handling the internal communication between different, rather than external open-source APIs. Kong has resolved these communication challenges, being built on a lightweight proxy to deliver unparalleled latency, performance, and scalability for all microservice applications regardless of where they run. It also allows you to control API traffic with Kong’s plugin architecture.Benefits & Features of Kong Scalable: By adding more parallel machines, Kong servers can quickly scale horizontally to make full use of its web development solutions. It’s also possible to upgrade the overall system to handle any load while keeping latency low. Modular: By adding new plugins, Kong can be modularized and easily configured with the RESTful Admin API. Runs Everywhere: It can run on the cloud or virtual machine, independent of what environment is available to execute over. What is Kuma? Kuma is a platform-agnostic, open-source control plane for service mesh and microservices. It can be executed natively environments like Kubernetes and VM, making it very easy to handle and useful. Kuma can use L4/L7 connectivity to secure, monitor, route and improve communication between a backend service and database. It can be used traditionally in Kubernetes with CRDs or with RESTful API in other environments such as VMs and Bare Metal.What Kuma Does? Applications make many requests to communicate with other services in the system like databases, caches, and microservices. However, by default, the network is insecure and unreliable and can introduce notable challenges to any modern environment like routing, tracing, and security. To build L4/L7 connectivity among services and applications, Kuma is the best way. It reduces the code that application teams have to write while improving the reliability, enabling faster delivery of software modules, and upgrading the overall architecture security with minimal effort.A chart of the various features of Kuma, from identity, traffic permissions, traffic logging, Kong Gateway Integration, and moreLet’s take the practical example here: every API in the software system needs to be protected to make it secure. On top, APIs need to be logged, tracked, and monitored to communicate exceptions to the relevant stakeholders. Specially the logs help developers to resolve issues and improve overall system performance. One way is to build a Smart client with extra development work to communicate with the outer world to achieve all of the above. On the other side, service mesh like Kuma comes into the picture to avoid reinventing the wheel and save the development cost. Service mesh setup is an outbox proxy along with backend services. This proxy intercepts every outgoing request that the system makes. The more decoupled the code, the more intra-system requests it will make. And that same proxy will receive the response that outer services are sending back to the system. The service mesh takes care of making outbound and inbound requests. As a result, it maintain logs, tracks and monitors for all API exceptions.Benefits & Features of Kuma Although Kuma is a recent phenomenon trending in the community, it is for a good but simple reason. Essentially, all it does is make sure connectivity issues are fixed and the connections are secure. Below are a few critical features of Kuma that have helped see it grow in popularity:Identify requests loads directed towards specific APIs. Implement traffic permissions and security to enhance the overall system efficiency. Logging network traffic coming to the server, supporting decision making on systems scalability. Kong gateway integration and with the help of Kuma, you can track the request’s complete lifecycle. Take Away Today, we learned that Fastify has emerged as the fastest open-source API framework of Node.js to date (no pun intended). Many renowned IT companies worldwide have endorsed and started using the web development solutions of Fastify for their backend application development. In fact, most would agree it has already made a name for itself in this technologically advanced world on its progression to become a leading framework and one of the top web solutions. We also discussed how Kong and Kuma and their list of features inspire the development community, both having addressed significant connectivity challenges as of late, making sure and working towards better managed and secure system connectivity. But is the new better than what preceded them in these cases?While I stand by my lesson that new is not always better, I have also learned that preference and project can play a big part in selecting tools, technology, and web development solutions, which is why there may not always be “better,” rather, just better-suited options of web solutions and better-informed decisions. And after this article, it is my hope you will be able to do just that – make a better-informed decision.
Fastify, Kuma, and Kong: How they Compare to Traditional Systems

Cloud computing can save you money is perhaps the most touted of the clouds many benefits and it’s easy to see why. It makes better economic sense to lease computer time rather than invest in costly hardware that will depreciate in value and require an ongoing cost to support and maintain. At least, in theory, and it ultimately comes down to how effectively you can manage your cloud.During the process of cloud adoption, most businesses fail to set up a cloud cost-management framework, resulting in the high cost of services. According to one report, organizations spend up to one-third of their cloud investment on services and resources that are less effective for their business. Fortunately, you don’t have to be one of them.Here are 5 steps you can take that will help keep your expenses down, your revenue up, and your cloud costs under control.Step 1. Retire Unused Cloud Resources & Instances Keeping cloud costs low can be difficult for any organization but it can be especially difficult for those who are new to cloud computing.Cloud Cost ManagementFor example, virtual machines on any cloud platform remain an expense even if they are idle or unused. On average, 15% of the cloud cost is associated with unattended and inactive services because such services are still leasing compute power. Businesses need to be careful about their cloud resource usage and consider cloud storage pricing accordingly. If you are not using particular resources or services – terminate it. These idle services or instances can be stopped manually through the cloud portals or by scheduling automated processes using scripts.Automated scheduling is the most cost-effective method because it’s a one-time job and does not require ongoing human involvement to monitor all cloud services or instances. One can set up cloud instances to run during designated time windows (e.g. from Monday to Friday only) and can group worker nodes to stay alive, so they are not terminated after scheduled hours. In case you do not need the Virtual Machines and services, make a point to retire and eliminate the cost.Step 2. Always Autoscale Cloud Resources To Save on Cloud Storage Cost If you aren’t utilizing an auto-scaling mechanism then you are missing out on a key benefit of cloud computing. What auto-scaling does is, it buys capacity as needed; scaling up or down when required. The most common mistake in cloud engagements is buying more capacity than necessary. The more cost-effective method is to simply automatically resize your capacity as requirements dictate, without spending a lot on cloud storage pricing.Autoscale Cloud ResourcesThe figure above shows an implementation of an auto-scaling feature. As you can see, when a system reaches a threshold, another cloud instance is added to relieve the pressure. One use case is when a cloud instance serves all the user’s requests and fulfills their demand; however, the traffic only increases exponentially at peak hours. In such a case, a more appropriate approach will be to use an auto-scaling feature rather than using a more significant capacity cloud instance, which would be costly. This feature can automatically add up the same specification, additional instance, and balance the traffic load. When the user traffic falls to a reasonable threshold, the scaled instance will automatically shut down to save cost.Step 3. Automation Techniques & Strategies One can, and more importantly, should use cloud automation tools to setup and configure cloud computing services whenever needed. Automating tasks like the backup of virtual machines and storage units, source code deployments and unit tests execution, security, and compliance can minimize human involvement. This way, you can shift your focus from these “maintenance” tasks to higher-level design and strategic business processes. Dynamic asset provisioning can help setup strategies to avoid over-usage of resources.automation testingThere are some third-party tools such as Terraform that can even automate infrastructure level deployment. Its structure setup relies on source code and can be used to provision or modify on-demand. The code can be used to set up a single to multi-cloud configuration with just the help of scripts, significantly speeding up the provisioning process.Step 4. Serverless Computing & Function as a Service Serverless computing refers to using (and paying for) services for a particular time, and after that usage, the computing resources are returned to the cloud provider. This approach is also known as Function as a Service or FaaS. With FaaS, organizations only incur cloud costs when and if they are used. When the need arises to perform a business process or task, the service triggers the start of the instance and shuts down automatically after completion. It uses precise cloud resources to reduce the cost and maximize efficiency by avoiding unnecessary modules running all the time.automation testingStep 5. Utilize Reserved & Spot Cloud Instances Just like no two organizations are the same, the same could be said for their usage of the cloud. For example, taking a Reserved Instance Approach, or committing to a fixed amount of resources over a period of time, would be a cost-effective strategy if demand is steady, as it requires a long-term commitment. Taking such an approach for a year can yield savings of up to 40% while a three-year commitment could bet you 60% in savings.Another cost-saving approach to consider is using Spot Cloud Instances. This is where unused instances from a service provider are purchased at steep discounts. Typically, a spot instance is 70% to 90% cheaper than the price of an equivalent-sized regular cloud instance. It is not without risk though, as that they can be shut down or closed at any point without notice. However, there are many different ways to mitigate that, and it’s impact like only using spot instances for low priority tasks or running stateless services that are not business-critical. An alternative approach to deal with this risk is to use auto-scaling, which can maintain a particular count of instances even if the spot instance is closed.Take away If managed and executed correctly, migrating to the cloud can undoubtedly save your business money. But it can also do much more than that. It can make your business more competitive, flexible, and able to adapt to rapid changes in customer demands. But to succeed, it requires planning, development, and investment to create the seamless experience you are after. Laying out a sequential strategy will help you build out your cloud capabilities and help you achieve a cost-effective and future-forward solution that provides value to both the user and your business.The above was written in collaboration with Uzi Murad, Account Executive at mobileLIVE.
5 Steps to Better Cloud Cost Management

The benefits of test automation are apparent – faster feedback to your development team, more frequent test executions, increased code coverage, and faster, more frequent releases. And it’s these reasons and many others that shed light on why companies worldwide invest millions of dollars in test automation – to ensure that they are developing exceptional software!However, the number of devices and platforms running that same business software isn’t static, rather, ever-increasing. Your software might depend on other platforms that your customers use to interact with your services and products. All the in-app software services are transitioning to “inter-app,” and because of this transition, your automation must account for the following paradigms when testing more complex software:Increased number of interfaces (inputs & outputs) Increased IoT (more devices = more testing) Increased inter connectivity With the exponentially increasing number of interdependent and connected devices causing the software ecosystem to grow, it becomes more critical than ever to consider End-to-End (E2E) Test Automation for your operations.The What & Why of E2E Testing E2E testing is a technique used to test the whole software product from the start to the end, ensuring that it behaves as expected. While testing, it’s typically done it from the end user’s perspective by simulating the software in a real environment. E2E testing validates various dependencies and also checks data integrity and integration components.Aside from better products, there are a number of growing drivers for adopting E2E testing:Reduces costs Reduces time to market Achieve higher code quality Shorter cycle times Frequent product releases Seamless integration with DevOps Software systems today are complex and often span multiple platforms, and those go on to contain various software subsystems. And the entire software can crash if even just one of those subsystems were to fail. From the perspective of business-ready software, this alone should underline the importance of E2E testing – but it is far from the only factor.Most modern software today allows various interactions between their subsystems. This added multiplatform complexity brings an elevated risk of failure; risks that can be avoided by adopting the following strategies:A regular check for any issues in the subsystems Expanding test coverage Verify the software product system flow There are ample use cases to apply E2E testing techniques that utilize the above strategies from a software development perspective. For instance, the very first step to develop an application begins with laying down the UI features and various UI interactions. E2E testing can simulate the entire data flow in these features to find out any bugs or dependencies early on. But we’ll get more into examples and use cases later. First, let’s tackle the most significant challenge at hand.where do we focus our time, from E2E, integration, and unitThe Biggest E2E Challenge How do you automate the E2E testing scenarios across various platforms and layers in a seamless manner? That is the biggest challenge in E2E testing.With increasing complexity and focus on interconnected software, the entire application ecosystem is composed of various independent subsystems. Such subsystems may be third-party or self-owned. While we all want to implement E2E test automation in our workflows, orchestrating the test automation across various platforms isn’t a job for an amateur.It requires merging together capabilities and technologies like Artificial Intelligence and Robotic Process Automation. And when you combine these you get HyperAutomation, the answer to the biggest question in E2E testing.What’s HyperAutomation? According to Gartner, “HyperAutomation is an unavoidable market state in which organizations must rapidly identify and automate all possible business processes.”Think of it as a bike versus a car. Sure, they can both take you to where you want to go, but the car will get you there much faster and more comfortably. Add in a little AI into the car, and suddenly you have a car that can take you to your destination with minimal input from you, safely and securely. That’s HyperAutomation.You should already be aware of the complex behaviour that modern software systems can have. E2E testing such systems demand not only a variety of tools, but multiplatform E2E test automation requires orchestrating these tools in such a way to achieve the desired level of testing.Multiplatform HyperAutomation is not an easy-to-implement methodology. It requires a unique approach, one that utilizes and balances the use of RPA, RTA (Robotic Test Automation), and AI to test any platform, ensuring maximum coverage. Not just that, in the end, a single report enables the agent to monitor the overall testing of the product. The entire process starts with making a wise selection of orchestrators to handle the multiple interfaces (self-built or 3rd party interfaces) within the product.RPA Process ExecutionHow to Combine RPA & RTA Concepts in 3 steps Select a multiplatform tool as the orchestrator. The orchestrator helps perform automation tasks on each interface and check the result before moving on to the next. Program the orchestrator as per your requirements using RPA. It enables Robotic Test Automation (RTA) among the various interfaces in the software. These interfaces might spread across multiple platforms. Our approach and recommendation to ensure they are tested is to do so independently using custom-built bots. Observe the entire flow in a single report using a central control once the test is complete. HyperAutomation In Action Now that you have a better understanding of what HyperAuromation is, let’s take a look at how it looks in application with a couple of real world use cases.Use Case #1 – Enterprise Banking One of our clients, a large Canadian bank, required testing their E2E procedure of opening a chequing account. For example, let’s assume a customer goes to a bank to open a chequing account. The teller would open the account using their banking software (desktop). Once the transaction gets completed, the form is pushed automatically to an iPad, where the customer can eSign it. When the eSignature completes, the teller downloads the eForms. For the E2E testing purpose, the bot validates the forms against a golden eForm.E2E Automation We then utilized an automation platform, in this instance, chose UXPLORE, to orchestrate interfaces across multiple platforms, quickly simplifying the requirement. Custom designed and developed client requirement oriented bots for downloading and comparing forms for complex scenarios like Form Download and Validation.These bots were then integrated with our automation platform for E2E orchestration. For instance, the transaction bot marked the start of the process for opening a chequing account. Finally, after all, bots complete their tasks, we provide a consolidated report as opposed to multiple reports for each platform and tool.Use Case #2 – IoT Infotainment System Recently, we received a requirement from one of Canada’s leading IoT firms to test their infotainment application. The application incorporated a test for temperature control using a circular knob. The user turned a knob on the application, and as a response, the temperature changes. E2E testing was needed to analyze the behaviour of the IoT system for the correct response.IoT Infotainment SystemAfter assimilating and analyzing the requirements, the use case suited HyperAutomation using the Eggplant Functional tool as the chief orchestrator and Python libraries for OBD Interface and Control Knob.We simulated the user turning the temperature control knob on the screen, setting the temperature to a particular value, say ‘x’ degrees. We were able to accomplish this by deploying a Python library-based simulation.To test a successful execution of the operation, we established a VNC connection using which we compared the actual output on the screen with the expected output as the visible test result.For posterity and thoroughness, we validated the information through the OBD interface to report on the screen for real-world testing. The final attestation was performed for the end-to-end process by simulating the condition in real life.Take away It is often said that necessity is the mother of all inventions, and overcoming the bottleneck E2E testing creates in the process of software deployment is definitely of pressing concern. That is because the world (and the systems that power it) is growing more complex, and we must abandon traditional methods of testing that no longer serve us. As should be clear from the information above, HyperAutomation is the solution to the most significant challenge facing E2E testing. And as this type of testing is no longer optional to handle the growing complexity of our environments, we anticipate that HyperAutomation is going to grow in not just popularity, but necessity.
Testing Interdependent & Connected Devices with HyperAutomation

The smartphone in your pocket or that is sitting on your desk are impressive pieces of hardware in their own right, and keep you connected to your life and the people within it. But what is really impressive is the operating system running on them because that is what makes the real magic happen.These operating systems are all different and as such, require different frameworks, tools, and languages for application development. However, today, I am going to focus on just one, Kotlin. That’s is because it isn’t very often a programming language that gets adopted as a specialized framework for the Android platform, only to evolve to now support iOS. Needless to say, Kotlin is well on the road to being a widely-used, multiplatform programming language.But, I think I am getting ahead of myself. Let’s take a step back and start at the beginning.Kotlin and Kotlin/Native: A Brief Overview Kotlin came into existence in July 2011, a product of JetBrains. However, it wasn’t until May 2017 that Google announced its support of Kotlin, over a year after its first official stable version (Feb 2016). Since then, Kotlin has become the preferred language for Android application development. Slowly, but steadily, it’s also growing popular for other platforms, including iOS application development. Kotlin/native is used for this purpose, which compiles the Kotlin code to native binaries that run without any virtual machine. Kotlin/native is an LLVM (Low-Level Virtual Machine) based backend for Kotlin compiler that converts the Kotlin code to LLVM Intermediate Representation (IR). The LLVM compiler understands that Intermediate Representation and creates binaries for multiple platforms.Kotlin code to LLVM Intermediate RepresentationBoth iOS and Android platforms have different approaches when it comes to native application development. But now Kotlin has made it comparatively easy by supporting both. This saves the additional effort of developers in learning two different programming languages [Java & Swift]. Developers can now develop the business, network, and repository layer in Kotlin as a dependency module for native applications. iOS and Android apps can use the same libraries, saving them time and effort in creating two. The below diagram shows the separated layers of the application architecture while following the Kotlin based custom developed multiplatform library.iOS and Android apps developmentandroid app view fragment and iOS app view UIViewController have common presenter, interactor: business logic, repository: persistence (sqlite, shared Pref), repository: networking (HTTP, serialization). Benefits of Kotlin in Multiplatform App Development The ability to share code between mobile platforms is undoubtedly one of the most important and appealing use cases of Kotlin, however, they extend beyond that. Here are a few of the more commonly experienced benefits of developers cite from using Kotlin:It’s a timely and cost-effective solution to develop common layers in your mobile application development architecture Two-thirds of the source code resides inside the shared Kotlin library, making management easy Provides bi-directional interoperability along with modules and libraries that can all be used with Objective-C, Swift, and Java Significantly improve time to market for new products by developing the multiplatform supported core modules of your application Compiles the iOS and Android native platform SDKs/binaries, with limitations in comparison to other multiplatform frameworks available in the market Developers only have to write one unit test and reuse it to validate the application’s business logic on both iOS and Android platforms No lagging behind native platforms: Software developers don’t have to wait until vendors or the mobile community add support for new features Key Challenges With Kotlin Initially, every programming language starts with its own set of challenges, and the one reason this will keep happening as it takes a community to help refine. As a new programming languages’ ecosystem builds up, so to will increase its adaptability, reliability, and function. However, this can take months, if not years. Considering this, developers might encounter some challenges while using Kotlin for iOS and Android app development and here are a few to be wary of:As a comparatively new platform for iOS app development, it’s not without challenges and issues. It lacks a mature ecosystem for iOS app development which can create obstacles for developers looking for outside the box solutions. Developers need to understand both the iOS and Android platforms to utilize for multiplatform development effectively. It is a daunting task to understand better both the architectured required to make effective use of Kotlin and reduce the time and effort costs. Both iOS and Android have their own set of recognized design patterns that are being followed globally as a standard practice, like VIPER in iOS and MVVM in Android app development. Application developers might encounter the hurdle of figuring out the best suitable app development pattern while developing the core modules with Kotlin for the usage in multiple platforms. Does Kotlin Makes App Maintenance Easier? kotlin app developmentIt’s a common understanding that an application is easier to maintain if there is a higher portion of shared code. For example, if an application has core modules developed in Kotlin that are shared across the platform and cover 80% of the business logic. Now, let’s say there is a change in the requirement to upgrade the repository layer and add a new collection in the database schema. The developers in such a case only have to manage this change from the centralized Kotlin based shared library. It results in reflecting the difference in both iOS and Android platforms, which eventually saves time and cost effort for the business. So in short – yesTake away The critical point to focus on here is how rapidly technology is changing and how it benefits mobile app development. We can confidently predict that, soon, Kotlin/native will be one of the key contributors in multiplatform mobile app development. The main advantage Kotlin/native has over other frameworks is its operability with Java and Swift. It also allows developers to develop the native iOS and Android applications using shared code. Sharing a significant part of the codebase between iOS and Android gives an experience of enhanced maintainability. This results in cost savings and enhanced value that all stakeholders, from developer to end-user, can feel.The above was written in collaboration with Imran Mian, Vice President of Digital Transformation and Abrar Ahmed Sair, Senior Android Developer, both of mobileLIVE.
Is Kotlin Becoming A Multiplatform Language For App Development

A decade ago software developers typically found themselves limited to coding and writing unit tests, a fact that inevitably led to problems during deployment. Keeping this issue in the forefront, software developers started experimenting with virtual environments, such as Virtual Box and Vagrant to compensate and, as is often the case, with time, came change and improvements.For instance, new roles emerged, such as DevOps Engineer, which didn’t exist a decade ago. On top of that, developers now had access to advanced tools that eliminated the difficulties or challenges during application code deployments. Docker, OpenShift, and Jenkins are a few of the popular options for establishing the fundamental processes of DevOps Engineering. Such tools are user-friendly and provide plug and play functionality to quickly and effectively set up DevOps processes.However, before we go any further, let’s take a step back and first briefly define the term DevOps.traditional development approach is write code, write test. Advanced development approach is build, run, deploy. Traditional development approach vs Advanced development approach What is DevOps? DevOps is (much like the name suggests) a combination of “development” and “operation” that defines the coordination of both software engineers and data innovation (IT) experts who automate the processes that transfer the executable application to end-users. DevOps’ goal is to set up a culture and process where building, testing, and deployment can happen quickly and as often as possible.DevOps engineers are considered an integral part of this technical team. For example, in the event the application has issues that were missed in earlier phases of development, DevOps can catch them with the help of automated tests execution and ensure the seamless delivery of the app to end-users.Where do Software Developers Fit In? Keeping in view the role of DevOps engineering, software developers today have to not only work closely with DevOps to understand their processes but collaborate accordingly to achieve maximum efficiency. This change brought a new set of expectations and challenges to the traditional developer role – but that isn’t always bad. Here are a few considerations for developers to keep in mind when working with specialized DevOps engineers that might make their life easier:Properly structure the application code considering all the issues that a DevOps engineer could potentially run into when setting up the CI/CD process. Ensure the security of every module being developed and deployed in the software system so that it aligns with the code of ethics of DevOps philosophy. Script and automate the deployment processes. (Third-party tools can help with this) In some smaller teams, take the critical responsibility of deploying the software application with the help of CI/CD processes to ensure the faster, better, and high-quality applications eliminating the dependency on the DevOps engineering teams. Aside from coding, software engineers should be familiar with concepts such as Ops, security, and deployment architectures.How to make the Process Effective As is often the case, communication across the department is paramount to success. However, this can be easier said than done due to a lack of common language and knowledge between parties. Here are a few considerations to help you communicate effectively:Developers should work in tandem with the DevOps engineering team for timely project delivery without issues during deployment. Software developers should be able to convey a finalized code structure that can facilitate the CI/CD process effectively. In cloud configurations, DevOps gives full rights to a software developer for setting up processes on a cloud platform and can oversee all configurations skillfully. Once the developers and DevOps are on the same page, they mutually will provide better outcomes and adaptable frameworks. Developers and DevOps should work together on the cloud; offering great productivity and effectiveness in the overall delivery process keeping in mind that without DevOps, developers have limited customization and no hold on center control. Software Developers deal with five significant procedures: Correspondence, CI/CD, Configuration Management, Security and Monitoring, and Alert management. Having a good command in these reduces communication gaps between developers and DevOps for easier deployment. Developer Challenges in DevOps Now that you have a better understanding of how developers and DevOps can effectively work together, it seems only fair to be upfront that you can expect some challenges. Here are few that I’ve encountered and to be aware of:The latest DevOps tools, such as Jenkins and Docker, have advanced features that can prove difficult to get a command over. Software developers also face challenges in the maintenance of systems configured with such advanced tools. Keeping yourself updated with multiple areas of expertise is challenging. Developers may find it difficult to stay aligned with the latest trends and technologies in both their field and DevOps. Security is an important factor and is treated as a separate subdomain in DevOps named DevSecOps. Software developers usually don’t have much experience with DevSecOps which leads to challenges when implementing security-related features. Benefits of Developers Being DevOps While there are always challenges associated with anything worth doing, there are, of course, proportional benefits. And in this case, once developers get a firm grip of DevOps concepts, they can expect:To be able to observe code structures and development strategies from the initial stages of development and determine if it would benefit from an effective deployment to the cloud. The ability to deliver higher quality software to end-users much faster. More effective communication and collaboration across departments, reducing the gaps and planning the project delivery from initial stages of software development to achieve high-quality delivery to end-users. Take Away A fact about our modern age is that the gap between developers and business operations isn’t shrinking – it’s being purposefully minimized. The need to deliver high-quality software quickly isn’t going to slow down, rather, it will only intensify. That is why it is so critical to not only understand the relationships that come from DevOps, but their intricacies, challenges, benefits, and how they can be approached for the maximum benefit of not only the user but the business.A special thank you to Athar Aslam for his contributions to the above article.
How a Developer Fits Into a DevOps Culture

I remember a few years ago, I was in a meeting, and the agenda turned out to be website analytics. Typically, anything data and analytics related is of interest to me, so my ears perked instantly up. However, I was shocked and disappointed that the duration of that “website analytics agenda” consisted of announcing that they had over 10,000 visitors the previous month. That’s it! Now, tell me, what good is that piece of information to anyone?What are Effective Web Analytics? Web analytics are powerful, and if you are beginning and ending your endeavour with them at how many people visit your website, you are doing yourself a grave injustice. That is because web analytics enables you to collect and analyze what is happening on the site, not just how many visitors are coming, but who they are, how long they stay, what they do, and much more. Effective web analytics isn’t just about collecting and analyzing data. Instead, it is an opportunity to be leveraged to help understand what your business needs, what is working, what isn’t, and using that information to make better, more data-driven decisions.While ensuring the success of any website can be difficult, it always starts with a defined analytics strategy that aligns with key business goals. Then, you would utilize tools to measure your website’s performance against those set goals. Below is what I’d recommend as a practical approach to web analytics.adobe tag managerIdentity Key Stakeolders, Define Goals, Build KPIs, Setup Tools/Framework, Collect Data, Analyze/Visualize Data, Gap Analysis and last Refine and Improve. While the appeal of web analytics should be evident, it isn’t without its difficulties. Tool selection is one critical area to consider, which we often overlook. Undoubtedly, the most useful analytics will almost always leverage all the features of the best analytics tool available. Some widely used analytics tools include Google Analytics, Clicktale, CrazyEgg, IBM Digital Analytics, and many more. However, today I will focus on effective ways of using Adobe Analytics, which is one of the best web analytics tools for large enterprises.Our Tool of Choice: Adobe Analytics Adobe Analytics, formerly known as Omniture SiteCatalyst, is a leading solution for real-time web analytics and segmentation across multiple channels. It is part of a more massive Adobe Analytics Cloud offering along with the Adobe Experience Cloud, which provides tools for more end-to-end analytics needs.Adobe Analytics, along with Launch, allows you to capture data from various sources, analyze and integrate with other systems, to provide end-to-end web analytics requirements. Adobe Launch is Adobe’s latest offering for tag management, which replaces Adobe Dynamic Tag Manager (DTM). Launch has extensions, including Data Elements, Rule Builder, Modular Container Tag and Enterprise Publishing, to name a few. The Analytics Cloud is also very well connected with other Adobe offerings like Adobe Marketing Cloud, and Adobe Advertising Cloud for more digital marketing focused needs. However, we will look solely on the Analytics solution for today, and we’ll start with some of the most common mistakes people make when using this powerful tool.Most Common Adobe Analytics Mistakes Much like a carpenter requires tools to build a house; by the same measure, they also need to know how to use the tools correctly to create anything worthwhile.DTMThat is why we will dive into some of the most common mistakes I see when people utilize Adobe Analytics to avoid a similar fate.Not Upgrading and Missing Useful Features: Many times, people do not upgrade to the latest version of their tools until it becomes mandatory, or they start losing functionality and support. If you keep using Adobe DTM instead of Adobe Launch, you might miss some critical upgrades which can benefit your analytics journey.Incorrect Implementation of Features: Often, an incorrect implementation leads to inflated page views and duplicate server calls. Also, we take eVars for granted and apply it everywhere instead of using the correct type of variables like Props.A Lack of Documentation: We know documentation is not much fun, but it is critical for the success of any analytics initiative. What happens when a new analyst joins the team? Adobe provides hundreds of eVars, Props, and Events. Do you remember exactly how they are used and what data is populated into Adobe Analytics? It would be impressive if you did!Restrict use of Adobe Analytics for Specific Channels Only: Sometimes people do not realize the full potential of Adobe Analytics and can support multi-channel data collection. Not only that, but it can also consolidate data from other sources and visualize it for better comprehension.Complex Adobe Solutions and Integrations: Adobe has a lot of products with tons of features. However, while they may be appealing, these advanced features can come with complex integrations that can set you back unless planned and implemented correctly.Adobe Analytics Best Practices Now that you’ve learned a few common mistakes while using Adobe Analytics, I hope you will be able to avoid them. Moreover, the following best practices will ensure that you are always getting the most of your Adobe Analytics (and data) as possible.Use Adobe Launch instead of DTM: If you have not upgraded to Adobe Launch and are still using DTM, you might miss some essential features. Consider upgrading to the latest tools to get most of what they have to offer. You can use an automated migration tool to upgrade from DTM to Adobe Launch. I’d also suggest creating as many development environments with Launch as needed so that different development teams can work independently. You can use the Chrome Launch Switch extension to use multiple environments and debug. Use _satellite.logger instead of console.log in Launch so that you can only output logs in debug mode and make it invisible in production.Making Proper use of the Technical Capabilities Offered: To get the most out of any tool, you need to learn how to use it properly. Understand the use of eVars vs Props vs Events in Adobe Analytics. Focus on other types of variables as well and use eVar or Props or Events as needed. Furthermore:Make sure you do not use s.t() click tracking for page count along with s.tl() to avoid the duplication of page views counts. Ensure the Internal Url Filter is set in s.linkInternalFilters before enabling external link tracking in s.trackExternalLinks. It will provide accurate numbers for external visits and prevent unwanted calls from clicking on every internal link. Limit the length of image request URLs to Adobe Analytics and make sure it does not exceed what the browser can handle. Prevent inflated page views and duplicate server calls by naming beacons correctly. Leverage the mathematical and statistical calculated metrics readily available in Adobe Analytics to increase efficiency. Use Marketing Cloud ID to implement tag management and keep in mind that Launch tag management javascript should not be deferred. Unlock your Adobe Data: Adobe Analytics provides excellent visualization tools to generate dashboards and ad-hoc reports – but do not forget its data export capabilities.adobe abalytics workspacesIf you are using external data lakes or data warehouses, then Adobe Analytics provides enough capabilities to utilize it in many ways:Use Adobe ClickStream to get Adobe Data Feed at regular intervals and build Data Lake for a bigger picture. Use Adobe Data Warehouse exports to export analytics data into a specific format needed by your Data Warehouse or analytics tool like Tableau. Governance and Documentation: Governance is a vital part of any analytics implementation. Document the business requirements and create Adobe Analytics Solution Design Documents. Implement a process to get it reviewed, approved, and maintained. Make sure that you include KPIs for measurements, eVars, Props and Events definition and rules are captured, including data elements used. Document any custom configurations like pathing, expiration, allocation, list support etc.QA for Adobe Analytics Projects: You can set up a separate Workspace for QA projects. Use Context Data Layer variables along with the time range in the Freeform table to generate a dashboard. The key point to remember is to apply the Segment to the workspace, and the Segment should be hit-scoped or visit-container-based so that only relevant test data can be shown in the workspace for validation. Use the DTM Switch tool or console commands to force DTM to use staging libraries on the production website.Intelligent Analytics with Adobe Sensei: Adobe Sensei is Adobe’s AI and machine learning technology designed to shrink the time between marketing ideation and execution. Use Adobe Sensei’s AI capabilities for anomaly detection and get intelligent alerts automatically generated based on AI and machine learning.Skills Upgrade and Experts Engagement: To ensure that you are getting the most out of your data, you need to utilize your tools fully and have implemented them correctly. Often, the best way is to consult with an expert to ensure that your setup is optimized. It means that you are utilizing all the features you need (and none that you don’t). The right approach, coupled with proper guidance goes a long way in implementing Adobe Analytics and ensuring you get the type of data insights you’re looking for.Take Away By now, I hope it’s clear that web analytics is much more than just reporting visitor numbers. With the use of tools like Adobe Analytics and following some of the best practices mentioned above, your organization can achieve useful data-driven insights and decisions. Adobe Analytics is costly compared to many other tools in the market, but it is worth using for large enterprises as they move into the future. So if you find yourself an avid user of Adobe Analytics, make sure that you are leveraging its features fully and have implemented it correctly to get the most out of your data.
How to Effectively Use Adobe Analytics for Data-Driven Decisions

In many enterprises and across departments, the introduction of digital tools and practices are being instituted with a clear goal in mind – to make things easier, more efficient, and create greater value within the organization. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems enabled organizations to develop standardized data definitions and effective governance to streamline processes, ensuring a single source of truth. Moving these systems to the cloud has taken this a step further by integrating them across the value chain through APIs. Increasing adoption of Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) systems has provided the essential “missing link” between strategy planning and execution, while data analytics and visualization tools have empowered users to generate new insights to improve efficiencies across the board.Things are indeed transforming in the accounting and finance departments of organizations, and today, I’d like to dive a little deeper and share the digital tools and technologies that are making this transformation possible.Book Closures & Reporting Typically, accounting and finance teams have used spreadsheets to make manual entries while tracking approvals via email. But that is no longer the case. Account reconciliations can be automated and centralized, enabling organizations to adopt a continuous accounting approach. In fact, accounting and finance teams no longer need to carry out quarterly or semi-annual book closures; instead, these systems do all the work in near real-time to ensure reporting is available as and when needed.Journey Entries & Policy Compliance Ask anyone who has ever manually managed accounts payable and receivable and they will likely tell you that not only does it take talent and skill; it is also incredibly draining – but it doesn’t have to be. Through automation, the entire process becomes not only sped up but more accurate with less human input. With the help of technology like Optical Character Recognition (OCR), intelligent bots can scan through receipts, expense claims, and other documents to ensure data and policy compliance. AI-powered process automation goes further and ensures correct accounting codes are identified and journal entries are automatically validated, certified, and posted. This not only improves accuracy but saves considerable time freeing up valuable resources to concentrate on real value creation.Procurement With the adoption of cloud-based platforms, APIs are being increasingly used across the procurement functions to integrate along the value chain by connecting downstream as well as upstream. With the help of AI and process automation, bots can be trained to process unstructured data and track price changes amongst a pool of suppliers to identify the best-suited supplier at a given time.Integrity & Traceability of Records Since accounting became a profession, mechanisms and techniques like double-entry bookkeeping have been developed to prevent, or at least make forgery difficult. However, technology is at it again with Blockchain, a truly transparent, low-cost-to-use, and openly available distributed ledger offering that is already proving promising. Blockchain not only simplifies regulatory compliance by ensuring immutability and accessibility but can also eliminate the need for reconciling partner ledgers.Risk Mitigation Integration with third party systems is now being used to carry out tasks like supplier or customer vetting. This can be done, for example, by looking up credit scores or accessing tax information to create risk profiles in real-time and make decisions that traditionally used to take days or weeks in just minutes.Improved Customer Experience Customer ExperienceIt isn’t only internally that accounting and finance functions get to benefit – for this value can and will be passed directly to the customers. With advancements in technology like Natural Language Processing (NLP), chatbots are now commonplace for dealing with basic customer queries, including account balance information, upcoming bills, account status and more, all at a fraction of the cost when compared with traditional models.Planning & Forecasting The power and sophistication of technologies like AI and Machine Learning are growing daily, allowing more and more enterprises to utilize predictive analytics to improve the accuracy of key initiatives like sales forecasts. Not only a tool for prediction this use of data can help to significantly reduce operational costs through optimizing working capital management.Strategy Execution The availability of EPM platforms and their integration with deployed ERP systems has empowered finance teams to utilize them to strategize, plan, analyze, optimize, and close financial results. These platforms extend the capabilities of traditional ERP systems, driving digital transformation, including increased agility and accelerated planning cycles, improved decision support, reduced time and user errors associated with manual planning processes.Take Away The transformation of accounting and finance functions is well underway and is already creating real value for enterprises. Research has shown us that with the help of RPA and AI, 80% of the key accounting and finance processes can be standardized and automated. And while nobody would ever argue the value that this critical department holds in an organization, the time has come to make their jobs and lives a little easier and the value they create a little greater and more widely felt.
Overcoming Hurdles in Accounting & Finance with Cloud Technology

In the form of a global pandemic, the world found itself faced with a crisis, unlike anything any of us have experienced in our lifetimes. And as countries around the globe looked to mitigate and contain the outbreak, the world was put on lockdown.While confining people to their homes proved effective for slowing and containing the spread of the virus, it also came with the unwanted byproduct of hindering local and global economies with employees finding themselves unable to be physically present at work. This has caused a surge in organizations to find new ways to enable their employees to effectively function remotely, and not surprisingly, these businesses are looking to technology as their solution to enable access, communication, and collaboration – no matter the physical distance. This is promising to make “COVID-19 to be the most compelling subject to impact the technology sector by 2020”.Although the internet and many of its ensuing technologies have laid the foundation for businesses to operate remotely, it still remains a challenging proposition be it culturally, technologically, or otherwise.Cloud computing has been slowly alleviating many of these challenges, however, recent events have seemingly forced a hand in expediting the processes. After all, cloud computing stands to benefit from this abrupt and seemingly forced transition to a remote work paradigm at a global scale. In fact, research indicates that the cloud computing market is set to expand at ~20% CAGR between 2019-24 to $661B; a figure that will undoubtedly be much higher as a result of recent events.A Unique Crisis of Business Continuity Looking through antiquity, global pandemics of this nature aren’t a question of “if,” but rather, “when.” What makes this instance unique, however, is that given our place and time in human history, an epidemic of such nature has been able to transcend organizational boundaries. Businesses, schools, and governments – rarely, or perhaps never, has a crisis cast such a wide net and left all of humanity so humbled, exasperated, and in search of a solution.Undoubtedly, the biggest barrier to business continuity in this new reality is physical distance. While the order of the hour seems to be “physical distancing,” it seems many are locked in an outdated paradigm that in order to be effective or rather effectively managed, people must work from traditional offices or business locations. In fact, the evolution of technology in recent years has made remote work more than possible but antiquated notions of “traditional work” persist, seemingly baked into our culture and management styles and slowing down what should be a natural progression of work.Rise of Cloud Computing Rise of Cloud Computing IT seemed to escape this paradigm to some degree, however, even when remote and distributed work became more accepted in some industries, the overall proportion of employees remotely working remained virtually the same over nearly a twenty years period since. Nevertheless, a few of the faithful pushed towards remote and flexible work; with study after study showing not only its merit but its inevitability.It wasn’t only cultural and structural issues but also real technical challenges that prevented organizations from devoting the required resources to enable a remote workforce. Cloud computing has emerged as a real enabler in the past few years by tearing many technology barriers down. The pandemic is now forcing the hands of most businesses to adapt both culturally and technologically. And technology vendors and IT service to providers to put together innovative solutions that painlessly solve business continuity issues.The Rise of Cloud Computing The trend of cloud computing has been steadily increasing over the years as reservations around the technology began to subside and its benefits became more apparent. Interestingly enough, among the many and heavily documented benefits of cloud computing, neither remote work nor business continuity are listed, although benefits highlighted ultimately provide both.Among the ever-diminishing hurdles of cloud adoptions were trust and security issues, including data privacy, as well as a fear of losing control or vendor lock-in. In addition to these real concerns, geographic and regulatory hurdles posed challenges along with a lack of skill and knowhow for successful implementation which remains a big challenge for organizations of all sizes even today.Over time, security and data privacy concerns proved to be unfounded with even large enterprises beginning to adopt, confident in their ability to keep their information safe. Regulatory and geographical constraints have also diminished with hyper-scale platforms like AWS, Azure and others as their data centers have mushroomed around the globe. And if vendor-lock in made some enterprises re-evaluate their adoption plans, multi-cloud options have given them a reason to move forward. Ultimately, the business and technology landscape in the past several years has made cloud computing a necessity rather than a desirable alternative.Cloud Computing – Path to Business Continuity & Remote Work Nirvana Technological challenges faced by companies in their journey to remote work and business continuity are usually dependent on their individual circumstances. To broadly discuss these hurdles, company size is a great starting off point and we will go further to discuss these unique challenges as they pertain to the SMB, Mid, and Enterprise market.Business Continuity in SMB SMBs Cloud ComputingSmall and Medium-sized Businesses (SMB) are an important segment of the economy that generates about 50% of employment in the private sector. Sadly, it is also the most vulnerable sector of the economy in terms of the ability to weather the crisis as well as the proportion of vulnerable jobs. Business Continuity, in terms of remote and distributed work, is particularly challenging for SMBs as it is an entirely new experience for many of them. Some of the more common obstacles they face include:Lack of organized IT, i.e. SMBs are likely to have no formal IT departments or resources to support the workforce transition. Legacy IT infrastructure was not built to reliably provide remote access to an increasing number of users. Network access required for users to work effectively. Security (as VPN) to provide needed peace of mind. User devices required software applications and infrastructure to manage and support. Adequate communications and collaboration tools. User training and handholding while they get acquainted and acclimatized to a new reality of work. A multi-vendor environment. These are significant hurdles to climb, especially for SMBs. Given the urgency that recent events have had on this group, many have been turning to readily available communication and collaboration tools, and VPN licenses to ensure work, but these are short term solutions. Strategy, planning, and expertise are required to create a reliable, cloud-based setup that benefits the business in the long term by enabling not only remote work but creating agility and flexibility within the business; positioning it for innovation and growth.The two most significant concerns for SMBs regarding digital and technological initiatives are cost, and know-how, which is no surprise, as technology selection, implementation, and management are daunting tasks for even large enterprises. The tech landscape is so dynamic, so complex, and changes so rapidly that keeping up with all that is required for a successful IT presence is simply unfeasible for smaller businesses.But this shouldn’t be a point of discouragement for the SMB market. On the contrary, shifting in this direction is no longer a prudent or proactive choice but rather a necessity of our new reality. And it is at this moment that small businesses should act and set the foundation for the future of their business. Emerging tech like AI and Machine Learning will be pivotal in the future, and establishing a foundation in the cloud now, will position these businesses to capitalize on it.Although implementation can come with its challenges, cloud computing itself isn’t without its ups and downs. SMB cloud computing adoption has revolved mainly around utilizing cloud-based applications in various business activities, for instance, deploying finance and accounting solutions. A large portion of these applications are still on-premise and dependent on IT infrastructure managed by the company and unsuitable for supporting workforce mobility. SMBs are also likely to have a multi-vendor environment, further complicating the situation, with ~40% reporting having ten vendors.Despite these challenges, most report that it is the upfront cost of migration that is the biggest hurdle of cloud adoption for SMB. However, the global pandemic has made this and many other objections and obstacles seem quite small and manageable when compared with the alternatives.Business Continuity in Mid-Market Unlike SMBs, businesses in the mid-market typically have remote work capabilities and IT business continuity plans. However, unlike an enterprise, they usually lack IT resources, knowledge, and financial resources. The IT maturity in the mid-market is historically low, with a typical 15-20 hours of unplanned downtime each year. The truth about this segment is they lack the resilience and organizational capabilities required to withstand disruption at such a scale that many have had to. There are three key challenges that mid-market businesses are likely to face in terms of business continuity:Infrastructure to enable total worker mobility. Management of IT infrastructure given on-prem IT. Data and application protection from disasters. Employing a robust IT infrastructure means more IT resources, more expenditure, complex planning and management. The alternative is cloud adoption across the board to cover not only workforce mobility but other aspects of business continuity.Ensure that labels have the proper weighting, that the title should be the most prominent, that the axis labels should be legible and balanced, and that bolding should be used sparingly for emphasis.In addition, a legend or annotation can go a long way in improving the usability of your data visualization.Business Continuity in Enterprises Business Continuity in EnterprisesA typical enterprise already supports workforce mobility and is largely prepared for a crisis in terms of business continuity. However, there are areas where enterprises are likely to struggle or develop cracks in their ability to fully support a remote workforce. Tools to effectively communicate, collaborate, along with workforce literacy and the capability to train them in effectively using these tools might not be fully ready.The primary value proposition for enterprises to adopt the cloud is cost savings and might not be crisis management. However, the adoption of cloud computing can ultimately strengthen not only the ability to address the crisis but bring the enterprise to a higher level of resilience, regardless of what tomorrow brings.Cloud Computing & Permanence of Remote Work – A Trend in the Making? Although the rush to adopt remote work technologies and tools has risen from an unprecedented crisis, it is not just conceivable, but likely, that the trend of remote work and working from home will continue and find wider acceptance.Given that the world was seemingly forced into an unexpected experiment in remote working, we can take this as an opportunity to make some foundational changes and prepare for what lays ahead. Cost, agility, flexibility, and resilience moving forward are perhaps some of the greatest catalysts that will hasten a much needed cultural shift.Take Away Digital has and continues to become an indispensable part of modern business. HR, finance, marketing, and operations are more dependent on digital than ever before. The rise of the cloud has taken the proliferation of technology to a whole new level, and the global pandemic has further compounded this.As a result, I think it is safe to say that organizations and businesses of all sizes are at crossroads. Many were already on their way to cloud computing in varying degrees. However, this forced adoption has not only sped up the process but has seemingly set the foundation moving forward. It isn’t easy to imagine going back to the way things used to be, and with cloud computing where it is today, we don’t have to. Instead, we should focus on what we can build from here, not how we can rebuild what we had.
The Impact of Cloud Computing on Business Continuity
Get thought-provoking insights, events, and news - first
By submitting this information, I agree to receive updates from mobileLIVE as applicable. Your privacy is important, and we will never send you unwanted emails or distribute your information to anyone else. You can manage your email preferences and read our privacy policy at any time.
Thank You!
We have sent you a confirmation email.
Please check your inbox.


